Abstract
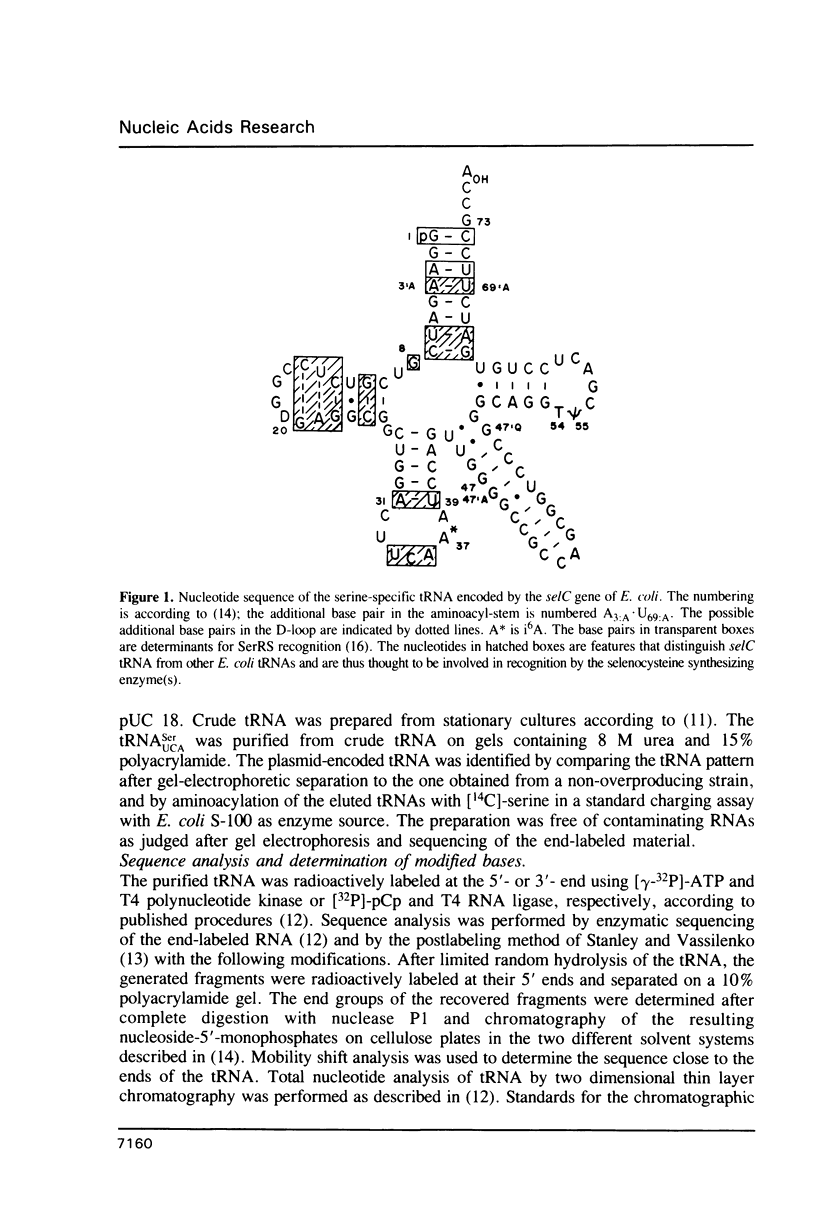
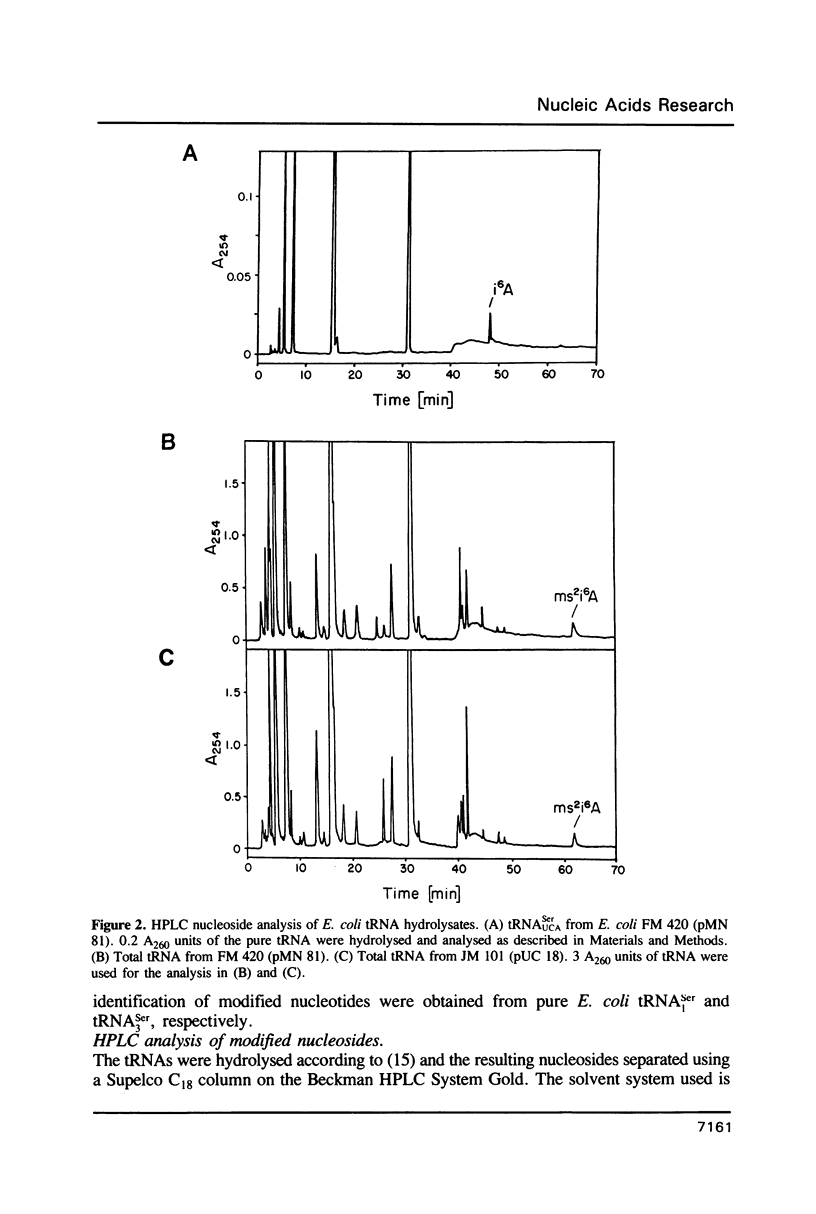
Selenocysteine is cotranslationally incorporated into selenoproteins in a unique pathway involving tRNA mediated suppression of a UGA nonsense codon (1-3). The DNA sequence of the gene for this suppressor tRNA from Escherichia coli predicts unusual features of the gene product (4). We determined the sequence of this serine tRNA (tRNA(UCASer]. It is the longest tRNA (95 nt) known to date with an acceptor stem of 8 base pairs and lacks some of the 'invariant' nucleotides found in other tRNAs. It is the first E. coli tRNA that contains the hypermodified nucleotide i6A, adjacent to the UGA-recognizing anticodon UCA. The implications of the unusual structure and modification of this tRNA on recognition by seryl-tRNA synthetase, by tRNA modifying enzymes, and on codon recognition are discussed.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burkard U., Söll D. The unusually long amino acid acceptor stem of Escherichia coli selenocysteine tRNA results from abnormal cleavage by RNase P. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Dec 23;16(24):11617–11624. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.24.11617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers I., Frampton J., Goldfarb P., Affara N., McBain W., Harrison P. R. The structure of the mouse glutathione peroxidase gene: the selenocysteine in the active site is encoded by the 'termination' codon, TGA. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1221–1227. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04350.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox J. C., Edwards E. S., DeMoss J. A. Resolution of distinct selenium-containing formate dehydrogenases from Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1317–1324. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1317-1324.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gefter M. L., Russell R. L. Role modifications in tyrosine transfer RNA: a modified base affecting ribosome binding. J Mol Biol. 1969 Jan 14;39(1):145–157. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90339-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehrke C. W., Kuo K. C., McCune R. A., Gerhardt K. O., Agris P. F. Quantitative enzymatic hydrolysis of tRNAs: reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography of tRNA nucleosides. J Chromatogr. 1982 Jul 9;230(2):297–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosjean H., Nicoghosian K., Haumont E., Söll D., Cedergren R. Nucleotide sequences of two serine tRNAs with a GGA anticodon: the structure-function relationships in the serine family of E. coli tRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Aug 12;13(15):5697–5706. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.15.5697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatfield D., Diamond A., Dudock B. Opal suppressor serine tRNAs from bovine liver form phosphoseryl-tRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6215–6219. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houssier C., Grosjean H. Temperature jump relaxation studies on the interactions between transfer RNAs with complementary anticodons. The effect of modified bases adjacent to the anticodon triplet. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1985 Oct;3(2):387–408. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1985.10508425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leinfelder W., Forchhammer K., Zinoni F., Sawers G., Mandrand-Berthelot M. A., Böck A. Escherichia coli genes whose products are involved in selenium metabolism. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):540–546. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.540-546.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leinfelder W., Zehelein E., Mandrand-Berthelot M. A., Böck A. Gene for a novel tRNA species that accepts L-serine and cotranslationally inserts selenocysteine. Nature. 1988 Feb 25;331(6158):723–725. doi: 10.1038/331723a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARCKER K., SANGER F. N-FORMYL-METHIONYL-S-RNA. J Mol Biol. 1964 Jun;8:835–840. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80164-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClain W. H., Wilson J. H., Seidman J. G. Genetic analysis of structure and function in phage T4 tRNASer. J Mol Biol. 1988 Oct 5;203(3):549–553. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90191-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normanly J., Ogden R. C., Horvath S. J., Abelson J. Changing the identity of a transfer RNA. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):213–219. doi: 10.1038/321213a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PINSENT J. The need for selenite and molybdate in the formation of formic dehydrogenase by members of the coli-aerogenes group of bacteria. Biochem J. 1954 May;57(1):10–16. doi: 10.1042/bj0570010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pecher A., Zinoni F., Böck A. The seleno-polypeptide of formic dehydrogenase (formate hydrogen-lyase linked) from Escherichia coli: genetic analysis. Arch Microbiol. 1985 May;141(4):359–363. doi: 10.1007/BF00428850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. J. Staphylococcal transfer ribonucleic acids. II. Sequence analysis of isoaccepting glycine transfer ribonucleic acids IA and IB from Staphylococcus epidermidis Texas 26. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 10;249(15):4787–4796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roe B. A. Studies on human tRNA. I. The rapid, large scale isolation and partial fractionation of placenta and liver tRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1975 Jan;2(1):21–42. doi: 10.1093/nar/2.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers M. J., Söll D. Discrimination between glutaminyl-tRNA synthetase and seryl-tRNA synthetase involves nucleotides in the acceptor helix of tRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6627–6631. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schön A., Kannangara C. G., Gough S., Söll D. Protein biosynthesis in organelles requires misaminoacylation of tRNA. Nature. 1988 Jan 14;331(6152):187–190. doi: 10.1038/331187a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schön A., Krupp G., Gough S., Berry-Lowe S., Kannangara C. G., Söll D. The RNA required in the first step of chlorophyll biosynthesis is a chloroplast glutamate tRNA. Nature. 1986 Jul 17;322(6076):281–284. doi: 10.1038/322281a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprinzl M., Hartmann T., Meissner F., Moll J., Vorderwülbecke T. Compilation of tRNA sequences and sequences of tRNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987;15 (Suppl):r53–188. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.suppl.r53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadtman T. C. Selenium-dependent enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:93–110. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.000521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley J., Vassilenko S. A different approach to RNA sequencing. Nature. 1978 Jul 6;274(5666):87–89. doi: 10.1038/274087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starzyk R., Schoemaker H., Schimmel P. Covalent enzyme-RNA complex: a tRNA modification that prevents a covalent enzyme interaction also prevents aminoacylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):339–342. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söll D. Genetic code: enter a new amino acid. Nature. 1988 Feb 25;331(6158):662–663. doi: 10.1038/331662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vacher J., Grosjean H., Houssier C., Buckingham R. H. The effect of point mutations affecting Escherichia coli tryptophan tRNA on anticodon-anticodon interactions and on UGA suppression. J Mol Biol. 1984 Aug 5;177(2):329–342. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90460-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox M., Nirenberg M. Transfer RNA as a cofactor coupling amino acid synthesis with that of protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Sep;61(1):229–236. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.1.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R. K., Roe B. A. Presence of the hypermodified nucleotide N6-(delta 2-isopentenyl)-2-methylthioadenosine prevents codon misreading by Escherichia coli phenylalanyl-transfer RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):409–413. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarus M. Translational efficiency of transfer RNA's: uses of an extended anticodon. Science. 1982 Nov 12;218(4573):646–652. doi: 10.1126/science.6753149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinoni F., Birkmann A., Leinfelder W., Böck A. Cotranslational insertion of selenocysteine into formate dehydrogenase from Escherichia coli directed by a UGA codon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3156–3160. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinoni F., Birkmann A., Stadtman T. C., Böck A. Nucleotide sequence and expression of the selenocysteine-containing polypeptide of formate dehydrogenase (formate-hydrogen-lyase-linked) from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4650–4654. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



