Abstract
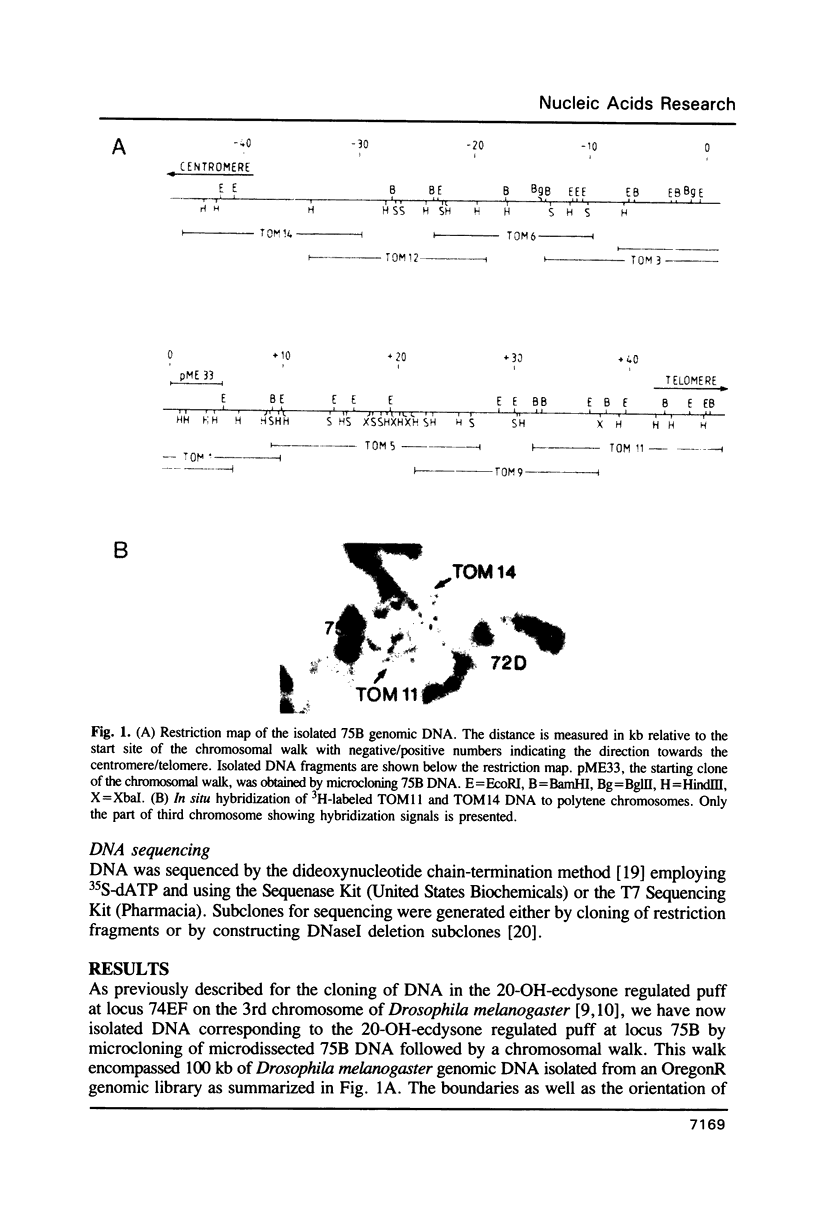
Drosophila melanogaster DNA has been cloned which encompasses a major part of the 20-OH-ecdysone inducible puff 75B. One 20-OH-ecdysone responsive transcription unit was detected which is expressed into two transcripts which accumulate upon the incubation of salivary glands of 3rd instar larvae with 20-OH-ecdysone. This accumulation is correlated with the 20-OH-ecdysone induced activity of puff 75B. 75B cDNA analysis indicates that the activity of puff 75B leads to the synthesis of a protein which belongs to the steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. The highest similarity of the derived 75B protein sequence was found to the DNA and ligand binding domains of human retinoic acid receptor. A study of the tissue distribution in larvae revealed that 75B mRNA is present in most, if not all 20-OH-ecdysone target tissues. It is proposed that 75B protein is a DNA-binding protein playing a key role in mediating the regulation of the larval molt by 20-OH-ecdysone.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arriza J. L., Weinberger C., Cerelli G., Glaser T. M., Handelin B. L., Housman D. E., Evans R. M. Cloning of human mineralocorticoid receptor complementary DNA: structural and functional kinship with the glucocorticoid receptor. Science. 1987 Jul 17;237(4812):268–275. doi: 10.1126/science.3037703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner M. Patterns of puffing activity in the salivary gland chromosomes of Drosophila. VI. Induction by ecdysone in salivary glands of D. melanogaster cultured in vitro. Chromosoma. 1972;38(3):255–281. doi: 10.1007/BF00290925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner M. Sequential gene activation by ecdysone in polytene chromosomes of Drosophila melanogaster. I. Dependence upon ecdysone concentration. Dev Biol. 1973 Nov;35(1):47–61. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(73)90006-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner M. Sequential gene activation by ecdysone in polytene chromosomes of Drosophila melanogaster. II. The effects of inhibitors of protein synthesis. Dev Biol. 1974 Jul;39(1):141–157. doi: 10.1016/s0012-1606(74)80016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BECKER H. J. [The puffs of salivary gland chromosomes of Drosophilia melanogaster. Part 1. Observations on the behavior of a typical puff in the normal strain and in two mutants, giant and lethal giant larvae]. Chromosoma. 1959;10:654–678. doi: 10.1007/BF00396591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker A. R., McDonnell D. P., Hughes M., Crisp T. M., Mangelsdorf D. J., Haussler M. R., Pike J. W., Shine J., O'Malley B. W. Cloning and expression of full-length cDNA encoding human vitamin D receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3294–3298. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann A., Krah-Jentgens I., Müller R., Müller-Holtkamp F., Seidel R., Kecskemethy N., Casal J., Ferrus A., Pongs O. Molecular organization of the maternal effect region of the Shaker complex of Drosophila: characterization of an I(A) channel transcript with homology to vertebrate Na channel. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3419–3429. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02665.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beato M. Gene regulation by steroid hormones. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):335–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90237-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bialojan S., Falkenburg D., Renkawitz-Pohl R. Characterization and developmental expression of beta tubulin genes in Drosophila melanogaster. EMBO J. 1984 Nov;3(11):2543–2548. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02170.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. S., Kokontis J., Liao S. T. Structural analysis of complementary DNA and amino acid sequences of human and rat androgen receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7211–7215. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debuire B., Henry C., Bernissa M., Biserte G., Claverie J. M., Saule S., Martin P., Stehelin D. Sequencing the erbA gene of avian erythroblastosis virus reveals a new type of oncogene. Science. 1984 Jun 29;224(4656):1456–1459. doi: 10.1126/science.6328658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M., Arriza J. L. A molecular framework for the actions of glucocorticoid hormones in the nervous system. Neuron. 1989 Feb;2(2):1105–1112. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90177-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. The steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):889–895. doi: 10.1126/science.3283939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S., Chambon P. Nuclear receptors enhance our understanding of transcription regulation. Trends Genet. 1988 Nov;4(11):309–314. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90108-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene G. L., Gilna P., Waterfield M., Baker A., Hort Y., Shine J. Sequence and expression of human estrogen receptor complementary DNA. Science. 1986 Mar 7;231(4742):1150–1154. doi: 10.1126/science.3753802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hafen E., Levine M., Garber R. L., Gehring W. J. An improved in situ hybridization method for the detection of cellular RNAs in Drosophila tissue sections and its application for localizing transcripts of the homeotic Antennapedia gene complex. EMBO J. 1983;2(4):617–623. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01472.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenberg S. M., Weinberger C., Ong E. S., Cerelli G., Oro A., Lebo R., Thompson E. B., Rosenfeld M. G., Evans R. M. Primary structure and expression of a functional human glucocorticoid receptor cDNA. Nature. 1985 Dec 19;318(6047):635–641. doi: 10.1038/318635a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janknecht R., Taube W., Lüdecke H. J., Pongs O. Characterization of a putative transcription factor gene expressed in the 20-OH-ecdysone inducible puff 74EF in Drosophila melanogaster. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 26;17(12):4455–4464. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.12.4455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlson P. Ecdyson, das Häutungshormon der Insekten. Naturwissenschaften. 1966 Sep;53(18):445–453. doi: 10.1007/BF00601742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin H. C., Lei S. P., Wilcox G. An improved DNA sequencing strategy. Anal Biochem. 1985 May 15;147(1):114–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90016-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J., McLachlan A. D., Klug A. Repetitive zinc-binding domains in the protein transcription factor IIIA from Xenopus oocytes. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1609–1614. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03825.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misrahi M., Atger M., d'Auriol L., Loosfelt H., Meriel C., Fridlansky F., Guiochon-Mantel A., Galibert F., Milgrom E. Complete amino acid sequence of the human progesterone receptor deduced from cloned cDNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Mar 13;143(2):740–748. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91416-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möritz T., Edström J. E., Pongs O. Cloning of a gene localized and expressed at the ecdysteroid regulated puff 74EF in salivary glands of Drosophila larvae. EMBO J. 1984 Feb;3(2):289–295. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01798.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nauber U., Pankratz M. J., Kienlin A., Seifert E., Klemm U., Jäckle H. Abdominal segmentation of the Drosophila embryo requires a hormone receptor-like protein encoded by the gap gene knirps. Nature. 1988 Dec 1;336(6198):489–492. doi: 10.1038/336489a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petkovich M., Brand N. J., Krust A., Chambon P. A human retinoic acid receptor which belongs to the family of nuclear receptors. Nature. 1987 Dec 3;330(6147):444–450. doi: 10.1038/330444a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pongs O. Ecdysteroid-regulated gene expression in Drosophila melanogaster. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Aug 1;175(2):199–204. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14184.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüle R., Muller M., Kaltschmidt C., Renkawitz R. Many transcription factors interact synergistically with steroid receptors. Science. 1988 Dec 9;242(4884):1418–1420. doi: 10.1126/science.3201230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serfling E. Autoregulation--a common property of eukaryotic transcription factors? Trends Genet. 1989 May;5(5):131–133. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker V. K., Ashburner M. The control of ecdysterone-regulated puffs in Drosophila salivary glands. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(2 Pt 2):269–277. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90309-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger C., Thompson C. C., Ong E. S., Lebo R., Gruol D. J., Evans R. M. The c-erb-A gene encodes a thyroid hormone receptor. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):641–646. doi: 10.1038/324641a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]