Abstract
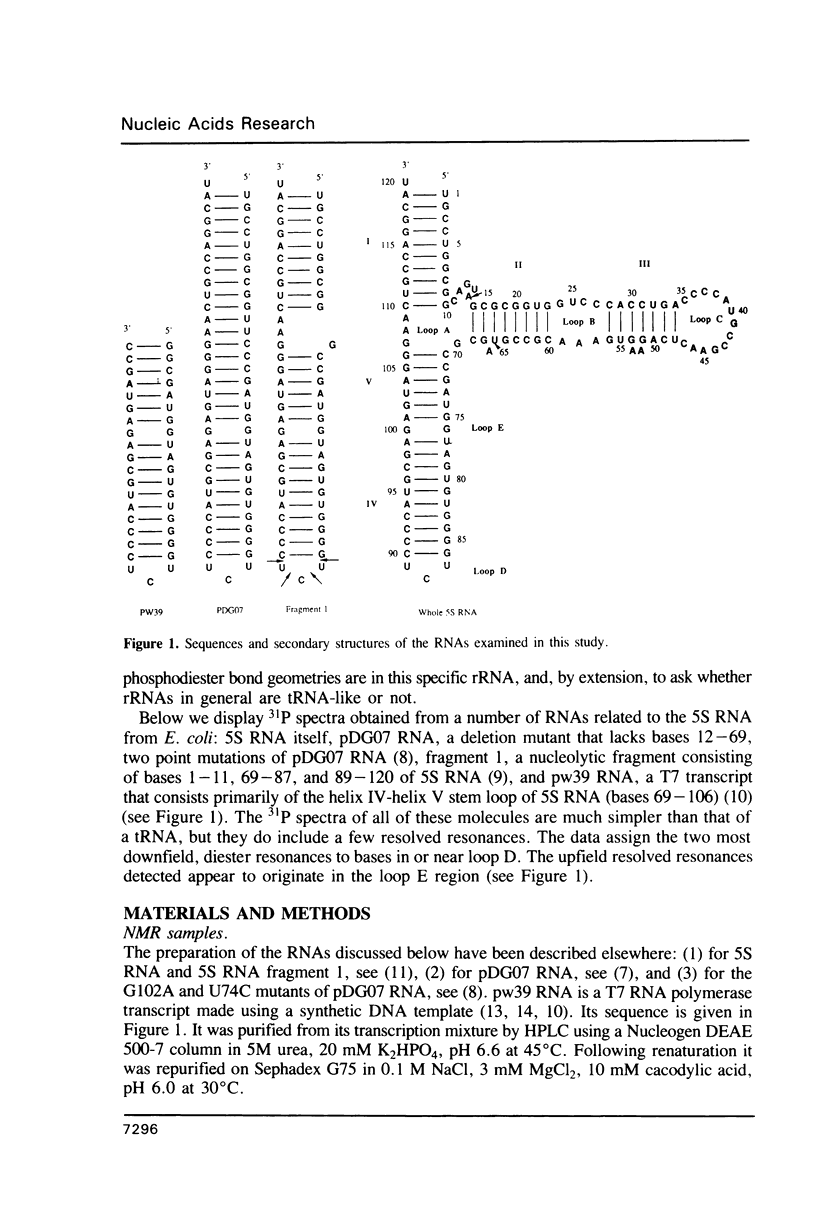
Only a small number of resolved, single phosphorous, phosphodiester resonances are observed in the 31P spectrum of the 5S rRNA from E. coli. Its spectrum is much simpler than that of a tRNA (Gueron, M. and Shulman, R.G. (1975) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 72, 3482-3484), which suggests that 5S RNA does not have a tightly folded, tRNA-like, tertiary structure. The resolved resonances in the 5S spectrum originate in loops D and E, near bases 88 and 76, respectively.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gewirth D. T., Abo S. R., Leontis N. B., Moore P. B. Secondary structure of 5S RNA: NMR experiments on RNA molecules partially labeled with nitrogen-15. Biochemistry. 1987 Aug 11;26(16):5213–5220. doi: 10.1021/bi00390a047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gewirth D. T., Moore P. B. Effects of mutation on the downfield proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum of the 5S RNA of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1987 Sep 8;26(18):5657–5665. doi: 10.1021/bi00392a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gewirth D. T., Moore P. B. Exploration of the L18 binding site on 5S RNA by deletion mutagenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 25;16(22):10717–10732. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.22.10717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorenstein D. G., Luxon B. A. High-resolution phosphorus nuclear magnetic resonance spectra of yeast phenylalanine transfer ribonucleic acid. Melting curves and relaxation effects. Biochemistry. 1979 Aug 21;18(17):3796–3804. doi: 10.1021/bi00584a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guéron M., Shulman R. G. 31P magnetic resonance of tRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3482–3485. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kime M. J., Gewirth D. T., Moore P. B. Assignment of resonances in the downfield proton spectrum of Escherichia coli 5S RNA and its nucleoprotein complexes using components of a ribonuclease-resistant fragment. Biochemistry. 1984 Jul 17;23(15):3559–3568. doi: 10.1021/bi00310a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kime M. J., Moore P. B. Physical evidence for a domain structure in Escherichia coli 5 S RNA. FEBS Lett. 1983 Mar 7;153(1):199–203. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80147-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan J. F., Groebe D. R., Witherell G. W., Uhlenbeck O. C. Oligoribonucleotide synthesis using T7 RNA polymerase and synthetic DNA templates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 11;15(21):8783–8798. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.21.8783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P. B., Abo S., Freeborn B., Gewirth D. T., Leontis N. B., Sun G. Preparation of 5S RNA-related materials for nuclear magnetic resonance and crystallography studies. Methods Enzymol. 1988;164:158–174. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(88)64041-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salemink P. J., Swarthof T., Hilbers C. W. Studies of yeast phenylalanine-accepting transfer ribonucleic acid backbone structure in solution by phosphorus-31 nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1979 Aug 7;18(16):3477–3485. doi: 10.1021/bi00583a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tritton T. R., Armitage I. M. Phosphorus-31 NMR studies of E. coli ribosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Oct;5(10):3855–3869. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.10.3855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



