Abstract
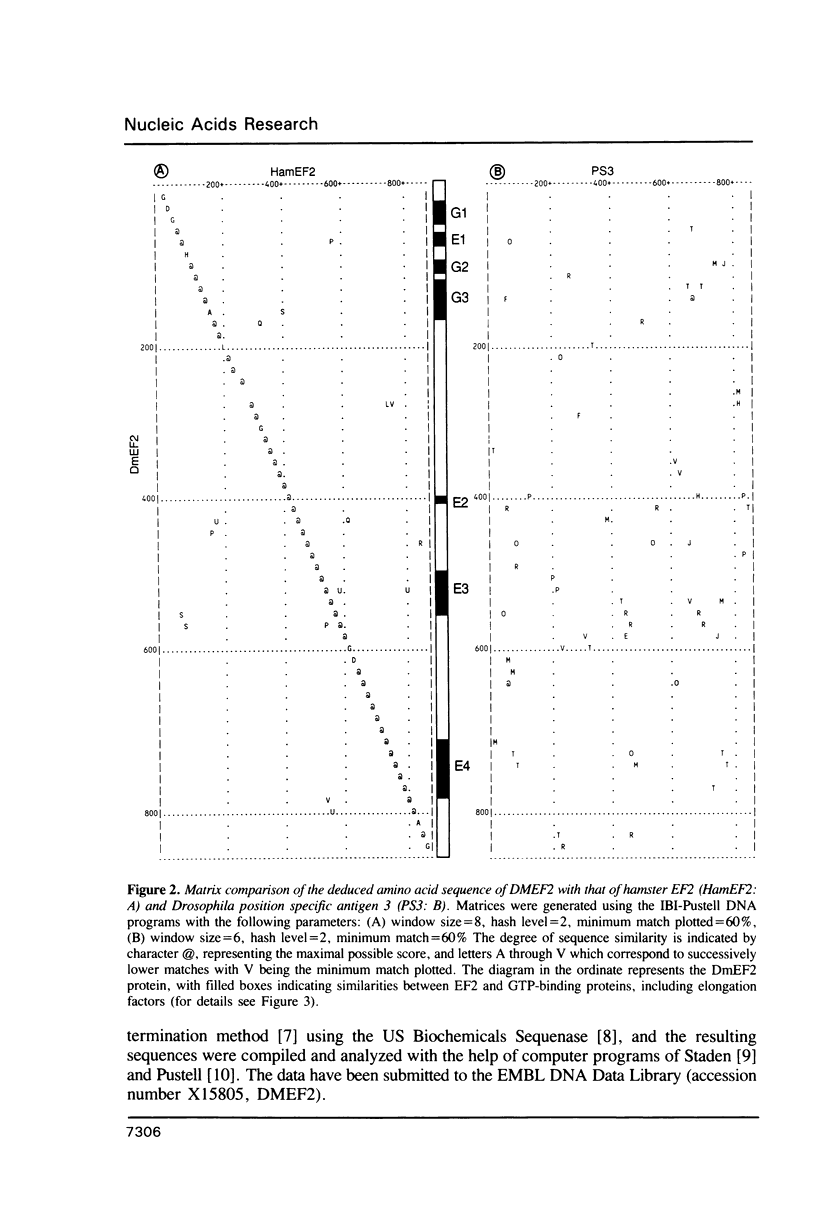
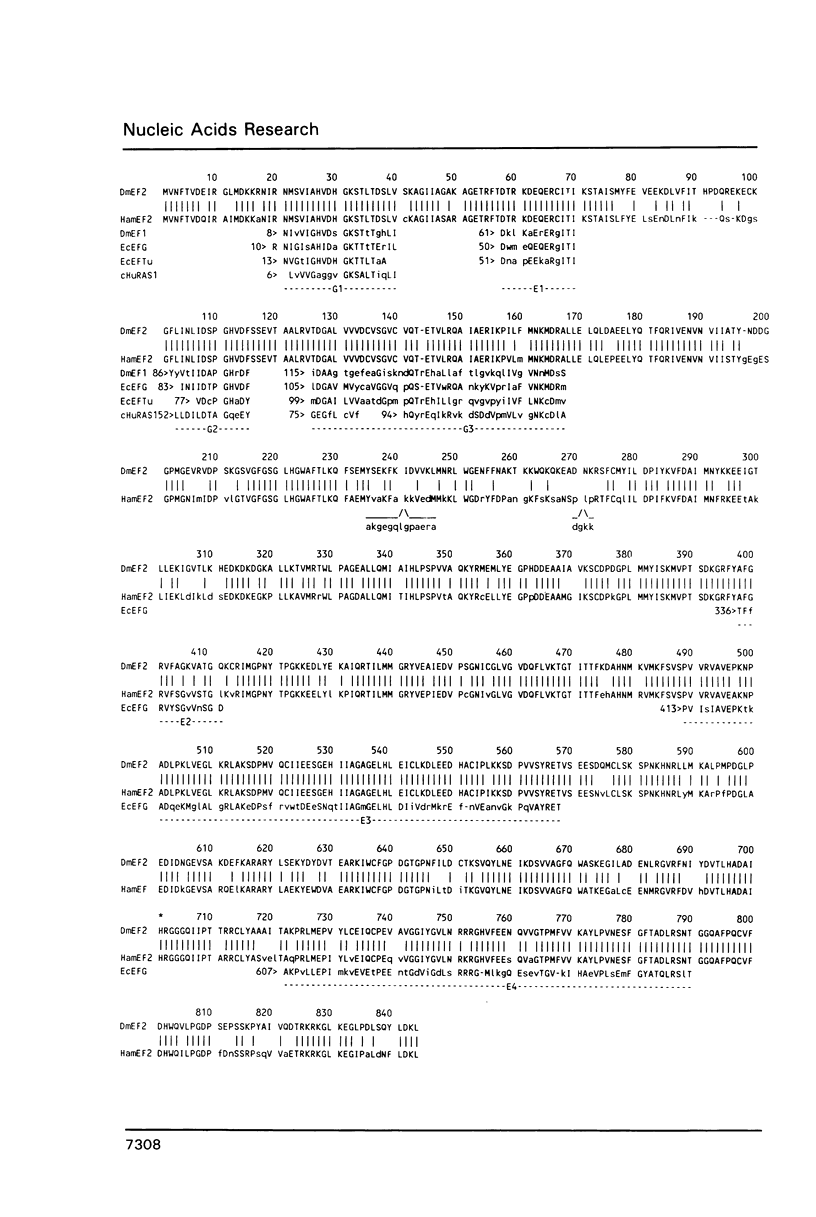
We have isolated a cDNA clone that encodes the Drosophila melanogaster elongation factor 2 (EF2), a protein involved in the elongation step of protein synthesis. This identification was based on the high degree of its amino acid sequence identity (greater than 80%) to that of hamster EF2. The gene encoding Drosophila EF2 is found at position 39E-F of the 2L chromosomal arm and maybe identical to the M(2)H locus, which produces a Minute phenotype when mutated. The genomic organization of the locus includes four exons. Conserved sequence segments shared with a variety of GTP binding proteins are found in the amino terminal third of the protein, and segments unique to EF2 and its prokaryotic functional homolog, EF-G, are in the carboxy terminal half; these two regions are segregated in two respective exons.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bogaert T., Brown N., Wilcox M. The Drosophila PS2 antigen is an invertebrate integrin that, like the fibronectin receptor, becomes localized to muscle attachments. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):929–940. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90580-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown N. H., Kafatos F. C. Functional cDNA libraries from Drosophila embryos. J Mol Biol. 1988 Sep 20;203(2):425–437. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capon D. J., Chen E. Y., Levinson A. D., Seeburg P. H., Goeddel D. V. Complete nucleotide sequences of the T24 human bladder carcinoma oncogene and its normal homologue. Nature. 1983 Mar 3;302(5903):33–37. doi: 10.1038/302033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Digan M. E., Haynes S. R., Mozer B. A., Dawid I. B., Forquignon F., Gans M. Genetic and molecular analysis of fs(1)h, a maternal effect homeotic gene in Drosophila. Dev Biol. 1986 Mar;114(1):161–169. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90392-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geysen H. M., Mason T. J., Rodda S. J. Cognitive features of continuous antigenic determinants. J Mol Recognit. 1988 Feb;1(1):32–41. doi: 10.1002/jmr.300010107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovemann B., Richter S., Walldorf U., Cziepluch C. Two genes encode related cytoplasmic elongation factors 1 alpha (EF-1 alpha) in Drosophila melanogaster with continuous and stage specific expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Apr 25;16(8):3175–3194. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.8.3175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohno K., Uchida T., Ohkubo H., Nakanishi S., Nakanishi T., Fukui T., Ohtsuka E., Ikehara M., Okada Y. Amino acid sequence of mammalian elongation factor 2 deduced from the cDNA sequence: homology with GTP-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):4978–4982. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.4978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kongsuwan K., Yu Q., Vincent A., Frisardi M. C., Rosbash M., Lengyel J. A., Merriam J. A Drosophila Minute gene encodes a ribosomal protein. Nature. 1985 Oct 10;317(6037):555–558. doi: 10.1038/317555a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasko P. F., Ashburner M. The product of the Drosophila gene vasa is very similar to eukaryotic initiation factor-4A. Nature. 1988 Oct 13;335(6191):611–617. doi: 10.1038/335611a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leptin M., Bogaert T., Lehmann R., Wilcox M. The function of PS integrins during Drosophila embryogenesis. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):401–408. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90243-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKrell A. J., Blumberg B., Haynes S. R., Fessler J. H. The lethal myospheroid gene of Drosophila encodes a membrane protein homologous to vertebrate integrin beta subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2633–2637. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montandon P. E., Stutz E. Nucleotide sequence of a Euglena gracilis chloroplast genome region coding for the elongation factor Tu; evidence for a spliced mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 10;11(17):5877–5892. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.17.5877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson L., Nygård O. Localization of the sites of ADP-ribosylation and GTP binding in the eukaryotic elongation factor EF-2. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Apr 15;148(2):299–304. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08839.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson L., Nygård O. The mechanism of the protein-synthesis elongation cycle in eukaryotes. Effect of ricin on the ribosomal interaction with elongation factors. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Nov 17;161(1):111–117. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb10130.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nygård O., Nilsson L. Nucleotide-mediated interactions of eukaryotic elongation factor EF-2 with ribosomes. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Apr 2;140(1):93–96. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08070.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pustell J., Kafatos F. C. A convenient and adaptable package of computer programs for DNA and protein sequence management, analysis and homology determination. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 2):643–655. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part2.643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryazanov A. G., Shestakova E. A., Natapov P. G. Phosphorylation of elongation factor 2 by EF-2 kinase affects rate of translation. Nature. 1988 Jul 14;334(6178):170–173. doi: 10.1038/334170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel J. G. Genetic characterization of the region of the Drosophila genome known to include the histone structural gene sequences. Genetics. 1981 Jul;98(3):505–527. doi: 10.1093/genetics/98.3.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. A computer program to enter DNA gel reading data into a computer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 2):499–503. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part2.499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. DNA sequence analysis with a modified bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walldorf U., Hovemann B., Bautz E. K. F1 and F2: Two similar genes regulated differently during development of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5795–5799. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox M., Brown N., Piovant M., Smith R. J., White R. A. The Drosophila position-specific antigens are a family of cell surface glycoprotein complexes. EMBO J. 1984 Oct;3(10):2307–2313. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02131.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zengel J. M., Archer R. H., Lindahl L. The nucleotide sequence of the Escherichia coli fus gene, coding for elongation factor G. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Feb 24;12(4):2181–2192. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.4.2181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






