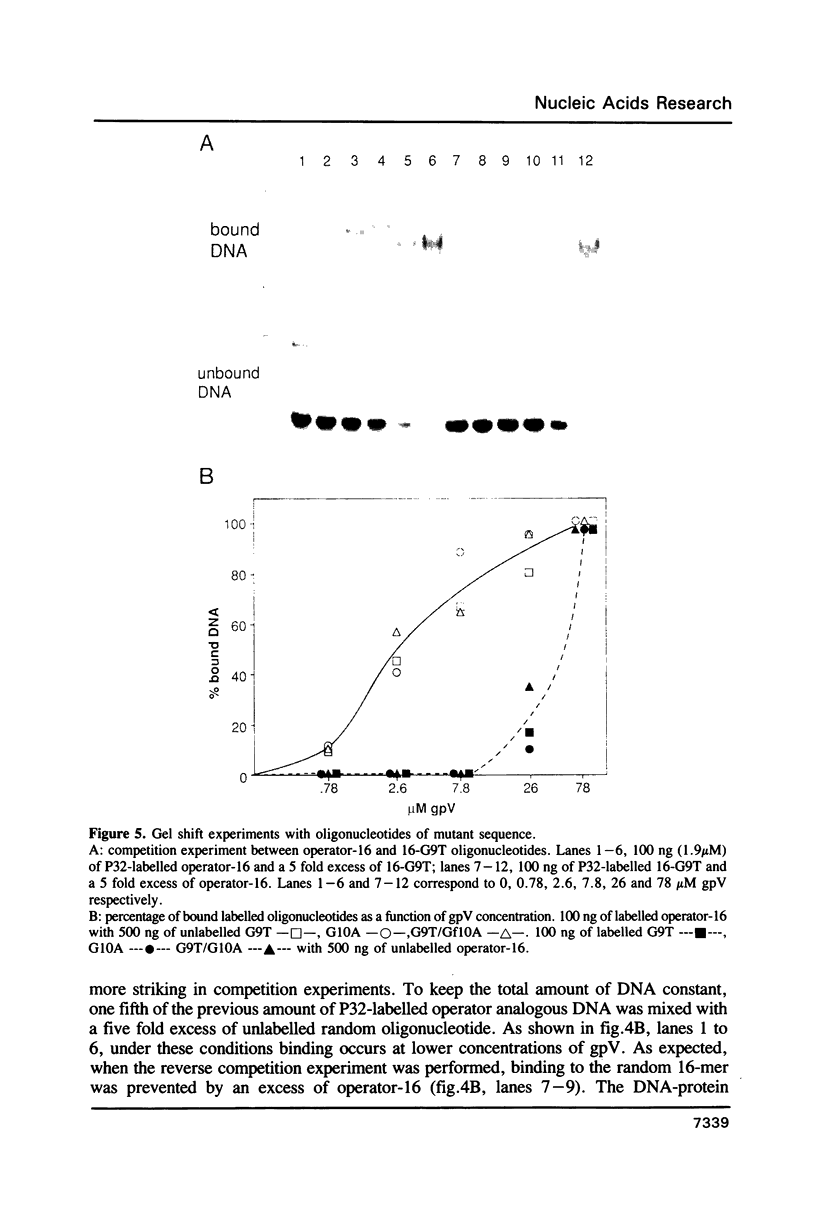
Abstract
We have investigated the binding of the f1 single-stranded DNA-binding protein (gene V protein) to DNA oligonucleotides and RNA synthesized in vitro. The first 16 nucleotides of the f1 gene II mRNA leader sequence were previously identified as the gene II RNA-operator; the target to which the gene V protein binds to repress gene II translation. Using a gel retardation assay, we find that the preferential binding of gene V protein to an RNA carrying the gene II RNA-operator sequence is affected by mutations which abolish gene II translational repression in vivo. In vitro, gene V protein also binds preferentially to a DNA oligonucleotide whose sequence is the DNA analog of the wild-type gene II RNA-operator. Therefore, the gene V protein recognizes the gene II mRNA operator sequence when present in either an RNA or DNA context.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberts B., Frey L., Delius H. Isolation and characterization of gene 5 protein of filamentous bacterial viruses. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jul 14;68(1):139–152. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90269-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alma N. C., Harmsen B. J., de Jong E. A., Ven J., Hilbers C. W. Fluorescence studies of the complex formation between the gene 5 protein of bacteriophage M13 and polynucleotides. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jan 5;163(1):47–62. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90029-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alma N. C., Harmsen B. J., van Boom J. H., van der Marel G., Hilbers C. W. 1H NMR studies of the binding of bacteriophage-M13-encoded gene-5 protein to oligo(deoxyadenylic acid)s of varying length. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Feb;122(2):319–326. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb05883.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson R. A., Nakashima Y., Coleman J. E. Chemical modifications of functional residues of fd gene 5 DNA-binding protein. Biochemistry. 1975 Mar 11;14(5):907–917. doi: 10.1021/bi00676a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brayer G. D., McPherson A. Refined structure of the gene 5 DNA binding protein from bacteriophage fd. J Mol Biol. 1983 Sep 15;169(2):565–596. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80065-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulsink H., Harmsen B. J., Hilbers C. W. DNA-binding properties of gene-5 protein encoded by bacteriophage M13. 2. Further characterization of the different binding modes for poly- and oligodeoxynucleic acids. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Oct 1;176(3):597–608. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14319.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulsink H., Harmsen B. J., Hilbers C. W. Specificity of the binding of bacteriophage M13 encoded gene-5 protein to DNA and RNA studied by means of fluorescence titrations. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1985 Oct;3(2):227–247. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1985.10508413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulsink H., Wijnaendts van Resandt R. W., Harmsen B. J., Hilbers C. W. Different DNA-binding modes and cooperativities for bacteriophage M13 gene-5 protein revealed by means of fluorescence depolarisation studies. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Jun 2;157(2):329–334. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09672.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman J. E., Williams K. R., King G. C., Prigodich R. V., Shamoo Y., Konigsberg W. H. Protein chemistry-nuclear magnetic resonance approach to mapping functional domains in single-stranded DNA binding proteins. J Cell Biochem. 1986;32(4):305–326. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240320407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dotto G. P., Zinder N. D. Reduction of the minimal sequence for initiation of DNA synthesis by qualitative or quantitative changes of an initiator protein. Nature. 1984 Sep 20;311(5983):279–280. doi: 10.1038/311279a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunker A. K., Anderson E. A. The binding of fd gene-5 protein to single-stranded nucleic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Aug 6;402(1):31–34. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(75)90366-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulford W., Model P. Specificity of translational regulation by two DNA-binding proteins. J Mol Biol. 1984 Feb 25;173(2):211–226. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90190-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. F., Petersen G. B. Nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage f1 DNA. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):32–46. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.32-46.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kansy J. W., Clack B. A., Gray D. M. The binding of fd gene 5 protein to polydeoxynucleotides: evidence from CD measurements for two binding modes. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1986 Jun;3(6):1079–1110. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1986.10508487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King G. C., Coleman J. E. Two-dimensional 1H NMR of gene 5 protein indicates that only two aromatic rings interact significantly with oligodeoxynucleotide bases. Biochemistry. 1987 May 19;26(10):2929–2937. doi: 10.1021/bi00384a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazur B. J., Zinder N. D. The role of gene V protein in f1 single-strand synthesis. Virology. 1975 Dec;68(2):490–502. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90289-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPheeters D. S., Stormo G. D., Gold L. Autogenous regulatory site on the bacteriophage T4 gene 32 messenger RNA. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jun 5;201(3):517–535. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90634-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan J. F., Groebe D. R., Witherell G. W., Uhlenbeck O. C. Oligoribonucleotide synthesis using T7 RNA polymerase and synthetic DNA templates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 11;15(21):8783–8798. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.21.8783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Model P., McGill C., Mazur B., Fulford W. D. The replication of bacteriophage f1: gene V protein regulates the synthesis of gene II protein. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):329–335. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90149-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Sauer R. T. Protein-DNA recognition. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:293–321. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen T. S., Webster R. E. Translational control of bacteriophage f1 gene II and gene X proteins by gene V protein. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):337–345. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90150-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinder N. D., Boeke J. D. The filamentous phage (Ff) as vectors for recombinant DNA--a review. Gene. 1982 Jul-Aug;19(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90183-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]