Abstract
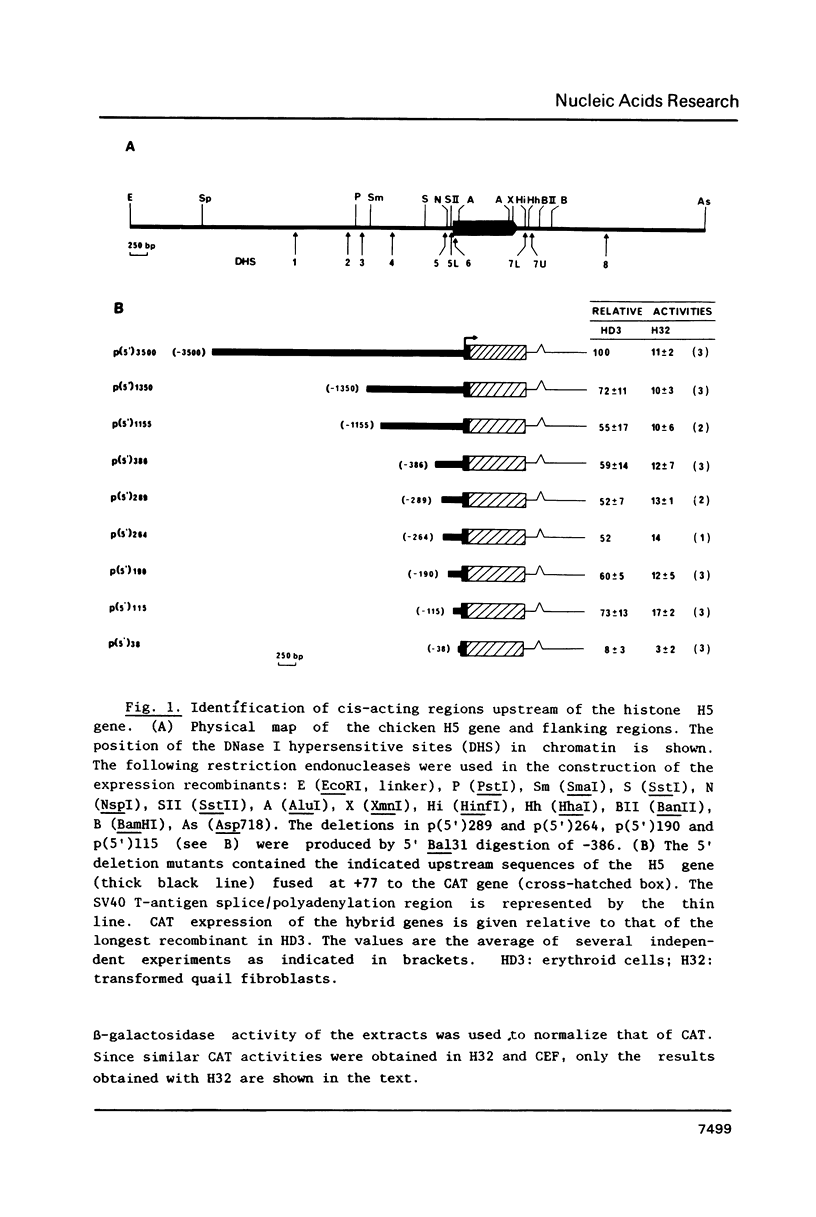
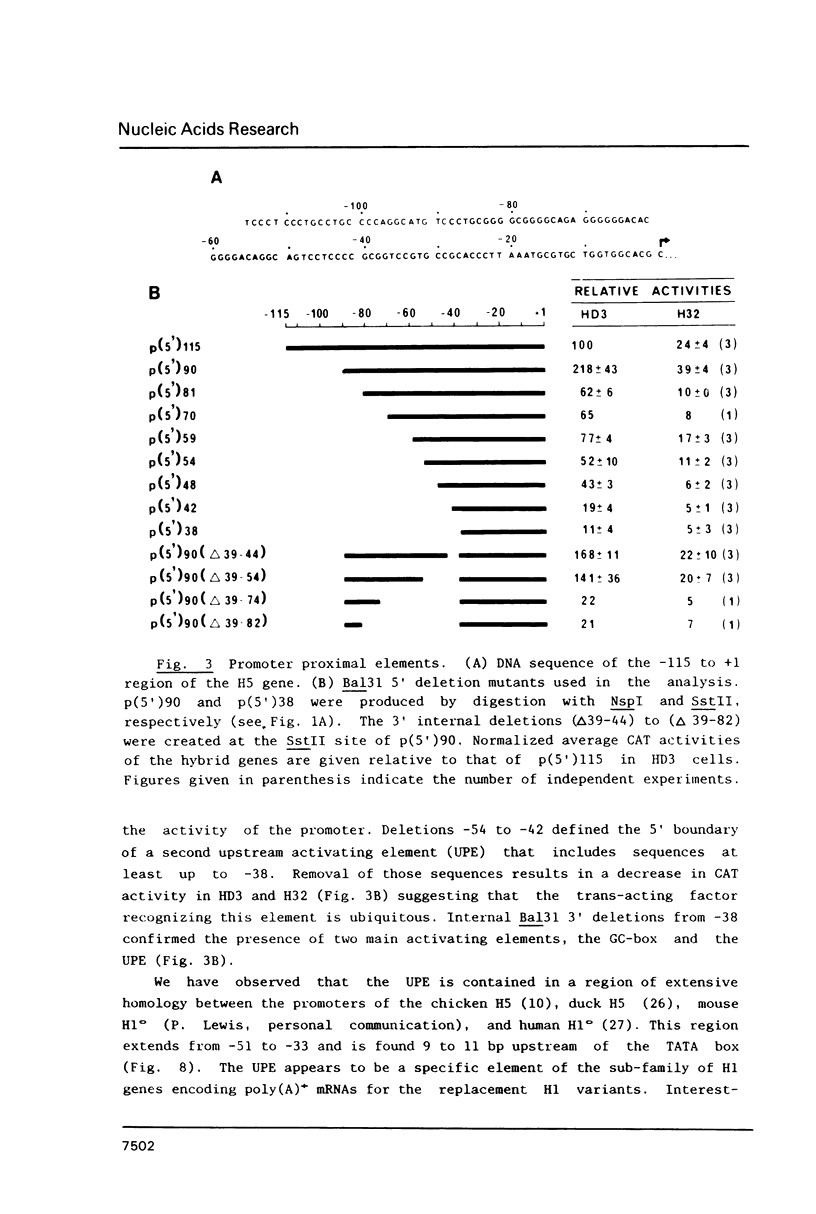
Sequences from -3500 to +1365 of the chicken histone H5 gene have been analyzed for the presence of cis-acting elements in H5 expressing (transformed CFU-E) and non-expressing cells (fibroblasts). The region from -3500 to -115 had little effect on transcription. Proximal upstream sequences contain a negative element (UNE, -115 to -95), capable to also repress the activity of the heterologous HSV tk promoter, and two positive elements, a consensus GC-box (-83 to -74) and a proximal element (UPE, -54 to -38). The sequence of the UPE is highly related to the histone H4 subtype-specific element and it has been conserved in the duck H5 and the human and mouse H1(0) genes at equivalent positions. Although the effect of the UNE, GC-box and UPE was not tissue-specific, sequences from -38 to +77 appear to confer a degree of tissue specificity to the promoter. An activating erythroid-specific element (DE) was found downstream of the H5 gene (+1042 to +1185). The activity of the DE was modest but independent of position and orientation and required the presence of the promoter proximal elements. The DE harbors the sequence AGATAA that is recognized by a protein factor, presumably the same that binds to other erythrocyte-specific enhancers. The low activity of DE in the CFU-E may be related to the low concentration of the AGATAA-binding factor in the differentiation-blocked cells.
Full text
PDF














Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Affolter M., Côté J., Renaud J., Ruiz-Carrillo A. Regulation of histone and beta A-globin gene expression during differentiation of chicken erythroid cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3663–3672. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Affolter M., Ruiz-Carrillo A. Transcription unit of the chicken histone H5 gene and mapping of H5 pre-mRNA sequences. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 5;261(25):11496–11502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baniahmad A., Muller M., Steiner C., Renkawitz R. Activity of two different silencer elements of the chicken lysozyme gene can be compensated by enhancer elements. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2297–2303. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02504.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beug H., von Kirchbach A., Döderlein G., Conscience J. F., Graf T. Chicken hematopoietic cells transformed by seven strains of defective avian leukemia viruses display three distinct phenotypes of differentiation. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):375–390. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90057-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briggs M. R., Kadonaga J. T., Bell S. P., Tjian R. Purification and biochemical characterization of the promoter-specific transcription factor, Sp1. Science. 1986 Oct 3;234(4772):47–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3529394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerc R. G., Bucher P., Strub K., Birnstiel M. L. Transcription of a cloned Xenopus laevis H4 histone gene in the homologous frog oocyte system depends on an evolutionary conserved sequence motif in the -50 region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Dec 20;11(24):8641–8657. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.24.8641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coen D. M., Weinheimer S. P., McKnight S. L. A genetic approach to promoter recognition during trans induction of viral gene expression. Science. 1986 Oct 3;234(4772):53–59. doi: 10.1126/science.3018926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowie A., Myers R. M. DNA sequences involved in transcriptional regulation of the mouse beta-globin promoter in murine erythroleukemia cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3122–3128. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dailey L., Roberts S. B., Heintz N. Purification of the human histone H4 gene-specific transcription factors H4TF-1 and H4TF-2. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12B):1700–1712. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12b.1700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalton S., Coleman J. R., Wells J. R. Transcription of the histone H5 gene is not S-phase regulated. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):601–606. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doenecke D., Tönjes R. Conserved dyad symmetry structures at the 3' end of H5 histone genes. Analysis of the duck H5 gene. J Mol Biol. 1984 Sep 15;178(2):121–135. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90135-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doenecke D., Tönjes R. Differential distribution of lysine and arginine residues in the closely related histones H1 and H5. Analysis of a human H1 gene. J Mol Biol. 1986 Feb 5;187(3):461–464. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90446-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Reitman M., Felsenfeld G. An erythrocyte-specific DNA-binding factor recognizes a regulatory sequence common to all chicken globin genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5976–5980. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galson D. L., Housman D. E. Detection of two tissue-specific DNA-binding proteins with affinity for sites in the mouse beta-globin intervening sequence 2. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):381–392. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodbourn S., Burstein H., Maniatis T. The human beta-interferon gene enhancer is under negative control. Cell. 1986 May 23;45(4):601–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90292-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heintz N., Zernik M., Roeder R. G. The structure of the human histone genes: clustered but not tandemly repeated. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):661–668. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90092-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbomel P., Bourachot B., Yaniv M. Two distinct enhancers with different cell specificities coexist in the regulatory region of polyoma. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):653–662. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90472-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W. Diethyl pyrocarbonate: a chemical probe for secondary structure in negatively supercoiled DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8009–8013. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaaden O. R., Lange S., Stiburek B. Establishment and characterization of chicken embryo fibroblast clone LSCC-H32. In Vitro. 1982 Oct;18(10):827–834. doi: 10.1007/BF02796323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg P. A., Robins A. J., D'Andrea R., Wells J. R. The chicken H5 gene is unlinked to core and H1 histone genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Feb 11;11(3):619–627. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.3.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai Z. C., Maxson R., Childs G. Both basal and ontogenic promoter elements affect the timing and level of expression of a sea urchin H1 gene during early embryogenesis. Genes Dev. 1988 Feb;2(2):173–183. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.2.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laimins L. A., Khoury G., Gorman C., Howard B., Gruss P. Host-specific activation of transcription by tandem repeats from simian virus 40 and Moloney murine sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6453–6457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieber T., Angerer L. M., Angerer R. C., Childs G. A histone H1 protein in sea urchins is encoded by a poly(A)+ mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4123–4127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopata M. A., Cleveland D. W., Sollner-Webb B. High level transient expression of a chloramphenicol acetyl transferase gene by DEAE-dextran mediated DNA transfection coupled with a dimethyl sulfoxide or glycerol shock treatment. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5707–5717. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin D. I., Tsai S. F., Orkin S. H. Increased gamma-globin expression in a nondeletion HPFH mediated by an erythroid-specific DNA-binding factor. Nature. 1989 Mar 30;338(6214):435–438. doi: 10.1038/338435a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mignotte V., Wall L., deBoer E., Grosveld F., Romeo P. H. Two tissue-specific factors bind the erythroid promoter of the human porphobilinogen deaminase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jan 11;17(1):37–54. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauli U., Chrysogelos S., Stein G., Stein J., Nick H. Protein-DNA interactions in vivo upstream of a cell cycle-regulated human H4 histone gene. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1308–1311. doi: 10.1126/science.3035717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins N. D., Nicolas R. H., Plumb M. A., Goodwin G. H. The purification of an erythroid protein which binds to enhancer and promoter elements of haemoglobin genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 25;17(4):1299–1314. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.4.1299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renaud J., Ruiz-Carrillo A. Fine analysis of the active H5 gene chromatin of chicken erythroid cells at different stages of differentiation. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):217–226. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90392-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reue K., Leff T., Breslow J. L. Human apolipoprotein CIII gene expression is regulated by positive and negative cis-acting elements and tissue-specific protein factors. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6857–6864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Carrillo A., Affolter M., Renaud J. Genomic organization of the genes coding for the six main histones of the chicken: complete sequence of the H5 gene. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 15;170(4):843–859. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80191-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Carrillo A., Renaud J. Endonuclease G: a (dG)n X (dC)n-specific DNase from higher eukaryotes. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):401–407. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04769.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Carrillo A. The histone H5 gene is flanked by S1 hypersensitive structures. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Aug 24;12(16):6473–6492. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.16.6473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Vazquez R., Ruiz-Carillo A. Construction of chimeric plasmids containing histone H5 cDNA from hen erythrocyte. DNA sequence of a fragment derived from the 5' region of H5 mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Mar 25;10(6):2093–2108. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.6.2093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutherford T., Nienhuis A. W. Human globin gene promoter sequences are sufficient for specific expression of a hybrid gene transfected into tissue culture cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):398–402. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiler-Tuyns A., Birnstiel M. L. Structure and expression in L-cells of a cloned H4 histone gene of the mouse. J Mol Biol. 1981 Oct 5;151(4):607–625. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90426-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun J. M., Wiaderkiewicz R., Ruiz-Carrillo A. Histone H5 in the control of DNA synthesis and cell proliferation. Science. 1989 Jul 7;245(4913):68–71. doi: 10.1126/science.2740916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Südhof T. C., Russell D. W., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. 42 bp element from LDL receptor gene confers end-product repression by sterols when inserted into viral TK promoter. Cell. 1987 Mar 27;48(6):1061–1069. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90713-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trainor C. D., Stamler S. J., Engel J. D. Erythroid-specific transcription of the chicken histone H5 gene is directed by a 3' enhancer. 1987 Aug 27-Sep 2Nature. 328(6133):827–830. doi: 10.1038/328827a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twigg A. J., Sherratt D. Trans-complementable copy-number mutants of plasmid ColE1. Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):216–218. doi: 10.1038/283216a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. W., Robins A. J., d'Andrea R., Wells J. R. Inverted duplication of histone genes in chicken and disposition of regulatory sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 25;13(4):1369–1387. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.4.1369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigley P. L., Wells J. R. H5 gene specific trans-activation by nuclear extracts from avian erythroid cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3853–3856. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- deBoer E., Antoniou M., Mignotte V., Wall L., Grosveld F. The human beta-globin promoter; nuclear protein factors and erythroid specific induction of transcription. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4203–4212. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03317.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






