Abstract
We describe the structure (3840 bp) of a novel Euglena gracilis chloroplast ribosomal protein operon that encodes the five genes rpl16-rpl14-rpl5-rps8-rpl36. The gene organization resembles the spc and the 3'-end of the S10 ribosomal protein operons of E. coli. The rpl5 is a new chloroplast gene not previously reported for any chloroplast genome to date and also not described as a nuclear-encoded, chloroplast protein gene. The operon contains at least 7 introns. We present evidence from primer extension analysis of chloroplast RNA for the correct in vivo splicing of five of the introns. Two of the introns within the rps8 gene flank an 8 bp exon, the smallest exon yet characterized in a chloroplast gene. Three introns resemble the classical group II introns of organelle genomes. The remaining 4 introns appear to be unique to the Euglena chloroplast DNA. They are uniform in size (95-109 nt), share common features with each other and are distinct from both group I and group II introns. We designate this new intron category as 'group III'.
Full text
PDF






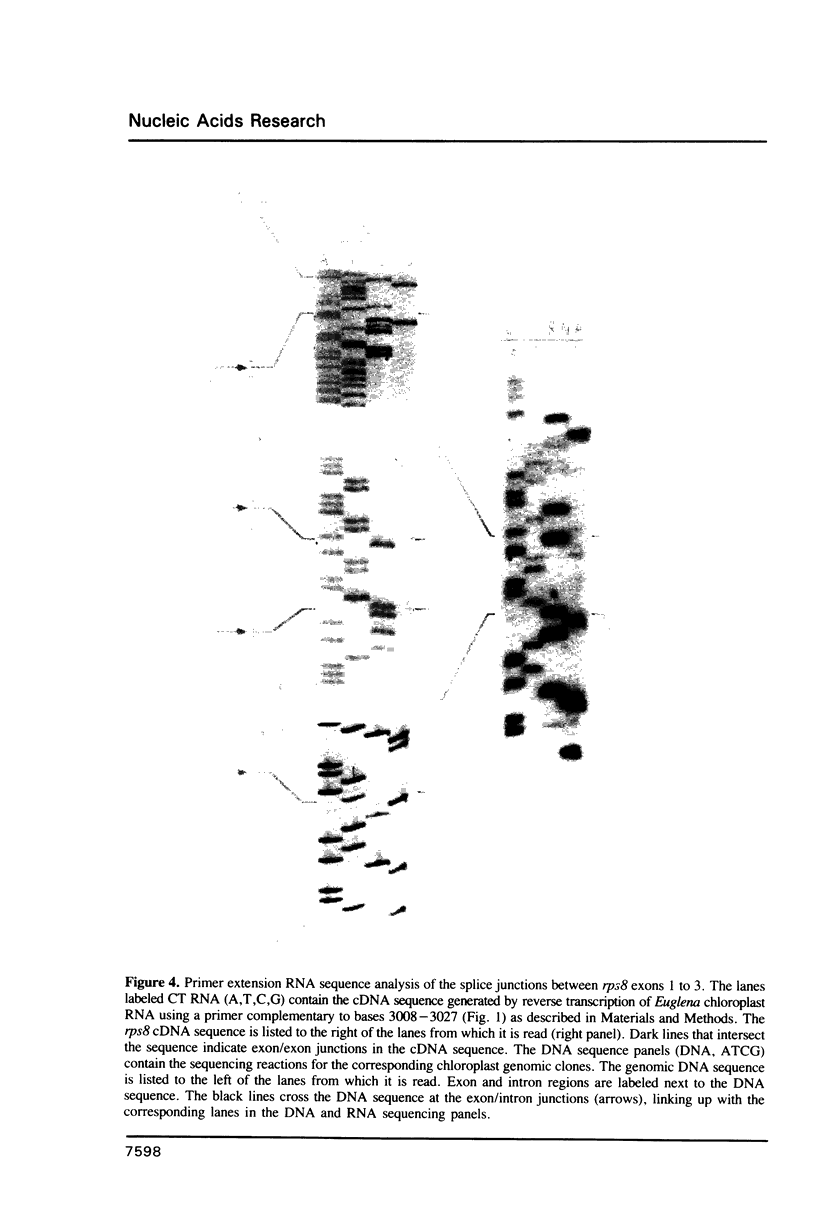










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cerretti D. P., Dean D., Davis G. R., Bedwell D. M., Nomura M. The spc ribosomal protein operon of Escherichia coli: sequence and cotranscription of the ribosomal protein genes and a protein export gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 May 11;11(9):2599–2616. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.9.2599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christopher D. A., Cushman J. C., Price C. A., Hallick R. B. Organization of ribosomal protein genes rpl23, rpl2, rps19, rpl22 and rps3 on the Euglena gracilis chloroplast genome. Curr Genet. 1988 Sep;14(3):275–285. doi: 10.1007/BF00376748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushman J. C., Hallick R. B., Price C. A. The two genes for the P700 chlorophyll a apoproteins on the Euglena gracilis chloroplast genome contain multiple introns. Curr Genet. 1988 Feb;13(2):159–171. doi: 10.1007/BF00365651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng X. W., Gruissem W. Control of plastid gene expression during development: the limited role of transcriptional regulation. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):379–387. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90290-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng D. F., Doolittle R. F. Progressive sequence alignment as a prerequisite to correct phylogenetic trees. J Mol Evol. 1987;25(4):351–360. doi: 10.1007/BF02603120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gantt J. S., Key J. L. Isolation of nuclear encoded plastid ribosomal protein cDNAs. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Feb;202(2):186–193. doi: 10.1007/BF00331635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gingrich J. C., Hallick R. B. The Euglena gracilis chloroplast ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase gene. I. Complete DNA sequence and analysis of the nine intervening sequences. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 25;260(30):16156–16161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruissem W., Zurawski G. Analysis of promoter regions for the spinach chloroplast rbcL, atpB and psbA genes. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3375–3383. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04093.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildebrand M., Hallick R. B., Passavant C. W., Bourque D. P. Trans-splicing in chloroplasts: the rps 12 loci of Nicotiana tabacum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):372–376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacquier A., Michel F. Multiple exon-binding sites in class II self-splicing introns. Cell. 1987 Jul 3;50(1):17–29. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90658-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrell K. A., Dietrich R. C., Perlman P. S. Group II intron domain 5 facilitates a trans-splicing reaction. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2361–2366. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohchi T., Umesono K., Ogura Y., Komine Y., Nakahigashi K., Komano T., Yamada Y., Ozeki H., Ohyama K. A nicked group II intron and trans-splicing in liverwort, Marchantia polymorpha, chloroplasts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 11;16(21):10025–10036. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.21.10025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koller B., Delius H. Intervening sequences in chloroplast genomes. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):613–622. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90341-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koller B., Fromm H., Galun E., Edelman M. Evidence for in vivo trans splicing of pre-mRNAs in tobacco chloroplasts. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):111–119. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90361-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koller B., Gingrich J. C., Stiegler G. L., Farley M. A., Delius H., Hallick R. B. Nine introns with conserved boundary sequences in the Euglena gracilis chloroplast ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase gene. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):545–553. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90247-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl L., Zengel J. M. Ribosomal genes in Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:297–326. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.001501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman D. J., Pearson W. R. Rapid and sensitive protein similarity searches. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1435–1441. doi: 10.1126/science.2983426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lou J. K., Wu M., Chang C. H., Cuticchia A. J. Localization of a r-protein gene within the chloroplast DNA replication origin of Chlamydomonas. Curr Genet. 1987;11(6-7):537–541. doi: 10.1007/BF00384617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manzara T., Hallick R. B. Nucleotide sequence of the Euglena gracilis chloroplast gene for ribosomal protein L20. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 May 11;15(9):3927–3927. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.9.3927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markmann-Mulisch U., Subramanian A. R. Nucleotide sequence and linkage map position of the genes for ribosomal proteins L14 and S8 in the maize chloroplast genome. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jan 4;170(3):507–514. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13728.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markmann-Mulisch U., von Knoblauch K., Lehmann A., Subramanian A. R. Nucleotide sequence and linkage map position of the secX gene in maize chloroplast and evidence that it encodes a protein belonging to the 50S ribosomal subunit. Biochem Int. 1987 Nov;15(5):1057–1067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattheakis L. C., Nomura M. Feedback regulation of the spc operon in Escherichia coli: translational coupling and mRNA processing. J Bacteriol. 1988 Oct;170(10):4484–4492. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.10.4484-4492.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel F., Dujon B. Conservation of RNA secondary structures in two intron families including mitochondrial-, chloroplast- and nuclear-encoded members. EMBO J. 1983;2(1):33–38. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01376.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montandon P. E., Knuchel-Aegerter C., Stutz E. Euglena gracilis chloroplast DNA: the untranslated leader of tufA-ORF206 gene contains an intron. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 12;15(19):7809–7822. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.19.7809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montandon P. E., Stutz E. The genes for the ribosomal proteins S12 and S7 are clustered with the gene for the EF-Tu protein on the chloroplast genome of Euglena gracilis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Mar 26;12(6):2851–2859. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.6.2851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount D. W., Conrad B. Improved programs for DNA and protein sequence analysis on the IBM personal computer and other standard computer systems. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 10;14(1):443–454. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.1.443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkubo S., Muto A., Kawauchi Y., Yamao F., Osawa S. The ribosomal protein gene cluster of Mycoplasma capricolum. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Dec;210(2):314–322. doi: 10.1007/BF00325700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posno M., van Vliet A., Groot G. S. The gene for Spirodela oligorhiza chloroplast ribosomal protein homologous to E. coli ribosomal protein L16 is split by a large intron near its 5' end: structure and expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Apr 25;14(8):3181–3195. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.8.3181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmelzer C., Müller M. W. Self-splicing of group II introns in vitro: lariat formation and 3' splice site selection in mutant RNAs. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):753–762. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90098-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt R. J., Myers A. M., Gillham N. W., Boynton J. E. Chloroplast ribosomal proteins of Chlamydomonas synthesized in the cytoplasm are made as precursors. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;98(6):2011–2018. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.6.2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinozaki K., Ohme M., Tanaka M., Wakasugi T., Hayashida N., Matsubayashi T., Zaita N., Chunwongse J., Obokata J., Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K. The complete nucleotide sequence of the tobacco chloroplast genome: its gene organization and expression. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2043–2049. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04464.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sijben-Müller G., Hallick R. B., Alt J., Westhoff P., Herrmann R. G. Spinach plastid genes coding for initiation factor IF-1, ribosomal protein S11 and RNA polymerase alpha-subunit. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 24;14(2):1029–1044. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.2.1029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugita M., Manzara T., Pichersky E., Cashmore A., Gruissem W. Genomic organization, sequence analysis and expression of all five genes encoding the small subunit of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase from tomato. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Sep;209(2):247–256. doi: 10.1007/BF00329650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka M., Wakasugi T., Sugita M., Shinozaki K., Sugiura M. Genes for the eight ribosomal proteins are clustered on the chloroplast genome of tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum): similarity to the S10 and spc operons of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):6030–6034. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.6030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas F., Massenet O., Dorne A. M., Briat J. F., Mache R. Expression of the rpl23, rpl2 and rps19 genes in spinach chloroplasts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 25;16(6):2461–2472. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.6.2461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. Production of single-stranded plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:3–11. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson J. C., Surzycki S. J. Extensive sequence homology in the DNA coding for elongation factor Tu from Escherichia coli and the Chlamydomonas reinhardtii chloroplast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2264–2267. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou D. X., Quigley F., Massenet O., Mache R. Cotranscription of the S10- and spc-like operons in spinach chloroplasts and identification of three of their gene products. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Apr;216(2-3):439–445. doi: 10.1007/BF00334388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






