Abstract
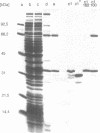
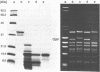
The c1 repressor gene of bacteriophage P1 and the temperature-sensitive mutants P1c1.100 and P1c1.162 was cloned into an expression vector and the repressor proteins were overproduced. A rapid purification procedure was required for the isolation of the thermolabile repressor proteins. Identification of the highly purified protein of an apparent molecular weight of 33,000 as the product of the c1 gene was verified by (i) the coincidence of partial amino acid sequences determined experimentally to that deduced from the c1 DNA sequence, and (ii) the temperature-sensitive binding to the operator DNA of the thermolabile repressor proteins. Analysis of the products of c1-c1.100 recombinant DNAs relates the thermolability to an unknown alteration in the C-terminal half of the c1.100 repressor. Binding to the operator DNA of c1 repressor is sensitive to N-ethylmaleimide. Since the only three cysteine residues are located in the C-terminal half of the repressor it is suggested that this part of the molecule is important for the binding to the operator DNA. This assumption is supported by the findings that a 14-kDa C-terminal repressor fragment obtained by cyanogen bromide cleavage retains DNA binding properties.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baumstark B. R., Scott J. R. The c1 repressor of bacteriophage P1. I. Isolation of the c1 protein and determination of the P1 DNA region to which it binds. J Mol Biol. 1980 Jul 15;140(4):471–480. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90266-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumstark B. R., Stovall S. R., Ashkar S. Interaction of the P1c1 repressor with P1 DNA: localization of repressor binding sites near the c1 gene. Virology. 1987 Feb;156(2):404–413. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90420-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattoraj D. K., Snyder K. M., Abeles A. L. P1 plasmid replication: multiple functions of RepA protein at the origin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2588–2592. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Citron M., Velleman M., Schuster H. Three additional operators, Op21, Op68, and Op88, of bacteriophage P1. Evidence for control of the P1 dam methylase by Op68. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3611–3617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreiseikelmann B., Velleman M., Schuster H. The c1 repressor of bacteriophage P1. Isolation and characterization of the repressor protein. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 25;263(3):1391–1397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliason J. L., Sternberg N. Characterization of the binding sites of c1 repressor of bacteriophage P1. Evidence for multiple asymmetric sites. J Mol Biol. 1987 Nov 20;198(2):281–293. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90313-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fürste J. P., Pansegrau W., Frank R., Blöcker H., Scholz P., Bagdasarian M., Lanka E. Molecular cloning of the plasmid RP4 primase region in a multi-host-range tacP expression vector. Gene. 1986;48(1):119–131. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90358-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinzel T., Velleman M., Schuster H. ban operon of bacteriophage P1. Mutational analysis of the c1 repressor-controlled operator. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jan 5;205(1):127–135. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90370-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heisig A., Severin I., Seefluth A. K., Schuster H. Regulation of the ban gene containing operon of prophage P1. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Mar;206(3):368–376. doi: 10.1007/BF00428873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho Y. S., Wulff D. L., Rosenberg M. Bacteriophage lambda protein cII binds promoters on the opposite face of the DNA helix from RNA polymerase. Nature. 1983 Aug 25;304(5928):703–708. doi: 10.1038/304703a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Sauer R. T. Protein-DNA recognition. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:293–321. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Sauer R. T., Sturtevant J. M., Ptashne M. The lambda repressor contains two domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1608–1612. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosner J. L. Formation, induction, and curing of bacteriophage P1 lysogens. Virology. 1972 Jun;48(3):679–689. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90152-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. R. Genetic studies on bacteriophage P1. Virology. 1968 Dec;36(4):564–574. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90188-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Kaer L., Van Montagu M., Dhaese P. Transcriptional control in the EcoRI-F immunity region of Bacillus subtilis phage phi 105. Identification and unusual structure of the operator. J Mol Biol. 1987 Sep 5;197(1):55–67. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90609-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velleman M., Dreiseikelmann B., Schuster H. Multiple repressor binding sites in the genome of bacteriophage P1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5570–5574. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]