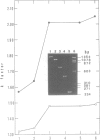
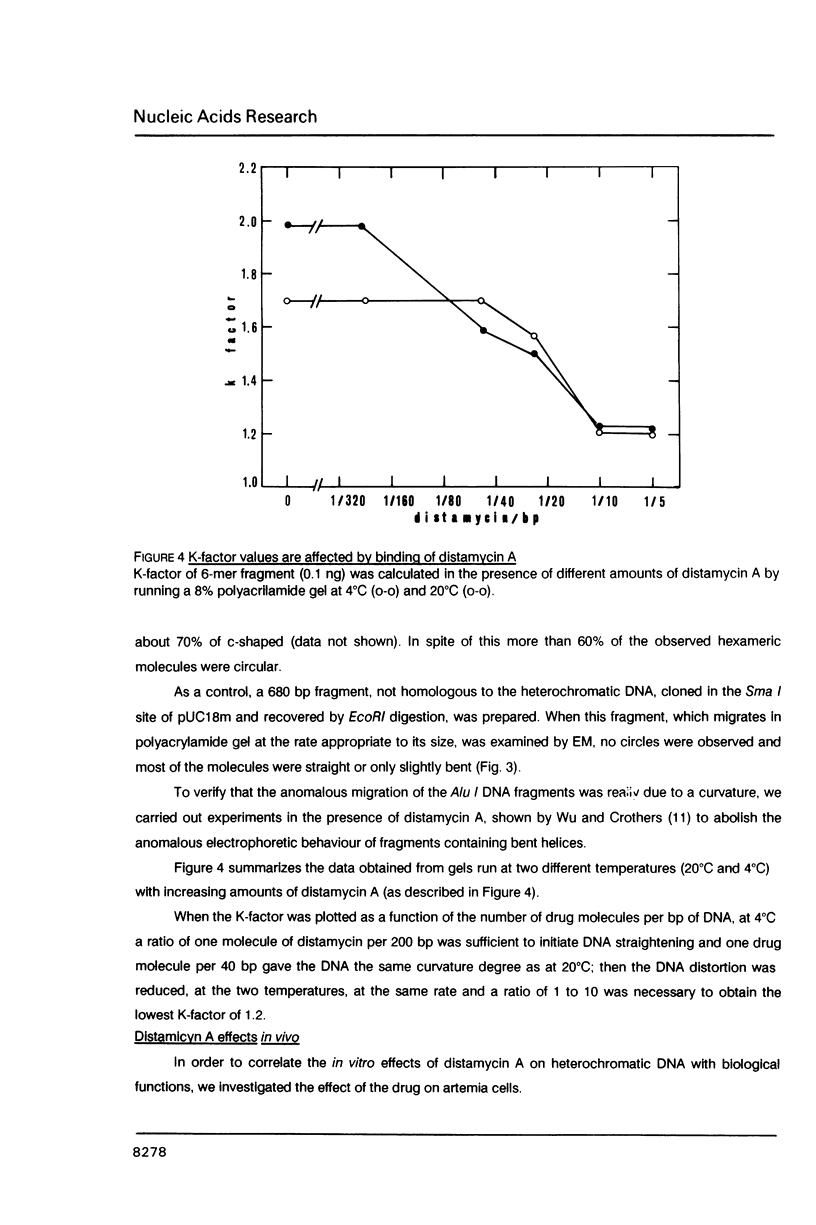
Abstract
An Alu I family of repeated DNA sequence 113 bp in length was found to be the major component of the heterochromatin in Artemia franciscana. On the basis of the analysis of cloned oligomeric (monomer to examer) heterchromatic fragments we predicted that the sequence could produce a stable curvature in chromosomal DNA. This prediction was confirmed by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis analysis and by electron microscope observations. The anomalous mobility of these fragments is reversed when the DNA samples are electrophoresed in the presence of distamycin A. Moreover treatment of living Artemia with this drug produces visible decondensation of heterochromatic masses in the interphase nuclei.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avila J., Montejo de Garcini E., Wandosell F., Villasante A., Sogo J. M., Villanueva N. Microtubule-associated protein MAP2 preferentially binds to a dA/dT sequence present in mouse satellite DNA. EMBO J. 1983;2(8):1229–1234. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01574.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brutlag D. L. Molecular arrangement and evolution of heterochromatic DNA. Annu Rev Genet. 1980;14:121–144. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.14.120180.001005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calladine C. R., Drew H. R., McCall M. J. The intrinsic curvature of DNA in solution. J Mol Biol. 1988 May 5;201(1):127–137. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90444-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruces J., Wonenburger M. L., Díaz-Guerra M., Sebastián J., Renart J. Satellite DNA in the crustacean Artemia. Gene. 1986;44(2-3):341–345. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90200-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diekmann S., Wang J. C. On the sequence determinants and flexibility of the kinetoplast DNA fragment with abnormal gel electrophoretic mobilities. J Mol Biol. 1985 Nov 5;186(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90251-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faccio Dolfini S., Bonifazio Razzini A. High resolution of heterochromatin of Drosophila melanogaster by distamycin A. Experientia. 1983 Dec 15;39(12):1402–1404. doi: 10.1007/BF01990127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatti M., Smith D. A., Baker B. S. A gene controlling condensation of heterochromatin in Drosophila melanogaster. Science. 1983 Jul 1;221(4605):83–85. doi: 10.1126/science.6407113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith J., Bleyman M., Rauch C. A., Kitchin P. A., Englund P. T. Visualization of the bent helix in kinetoplast DNA by electron microscopy. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):717–724. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90347-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagerman P. J. Evidence for the existence of stable curvature of DNA in solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4632–4636. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harshman K. D., Dervan P. B. Molecular recognition of B-DNA by Hoechst 33258. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jul 11;13(13):4825–4835. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.13.4825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Sakaki Y. Dideoxy sequencing method using denatured plasmid templates. Anal Biochem. 1986 Feb 1;152(2):232–238. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90403-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo H. S., Crothers D. M. Calibration of DNA curvature and a unified description of sequence-directed bending. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1763–1767. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopka M. L., Yoon C., Goodsell D., Pjura P., Dickerson R. E. The molecular origin of DNA-drug specificity in netropsin and distamycin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(5):1376–1380. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.5.1376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laundon C. H., Griffith J. D. Curved helix segments can uniquely orient the topology of supertwisted DNA. Cell. 1988 Feb 26;52(4):545–549. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90467-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lica L. M., Narayanswami S., Hamkalo B. A. Mouse satellite DNA, centromere structure, and sister chromatid pairing. J Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;103(4):1145–1151. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.4.1145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marini J. C., Effron P. N., Goodman T. C., Singleton C. K., Wells R. D., Wartell R. M., Englund P. T. Physical characterization of a kinetoplast DNA fragment with unusual properties. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 25;259(14):8974–8979. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marini J. C., Levene S. D., Crothers D. M., Englund P. T. Bent helical structure in kinetoplast DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7664–7668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pimpinelli S., Gatti M., De Marco A. Evidence for heterogeneity in heterochromatin of Drosophila melanogaster. Nature. 1975 Jul 24;256(5515):335–337. doi: 10.1038/256335a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radic M. Z., Lundgren K., Hamkalo B. A. Curvature of mouse satellite DNA and condensation of heterochromatin. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1101–1108. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90176-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder K., Silver S., DeLucia A. L., Fanning E., Tegtmeyer P. An altered DNA conformation in origin region I is a determinant for the binding of SV40 large T antigen. Cell. 1986 Mar 14;44(5):719–725. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90838-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer M. F. Highly repeated sequences in mammalian genomes. Int Rev Cytol. 1982;76:67–112. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61789-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder M., Buchman A. R., Davis R. W. Bent DNA at a yeast autonomously replicating sequence. Nature. 1986 Nov 6;324(6092):87–89. doi: 10.1038/324087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venditti S., Caserta M., Di Mauro E., Camilloni G. DNA conformational variations in the in vitro torsionally strained Ig kappa light chain gene localize on consensus sequences. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Nov 10;951(1):139–148. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(88)90034-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. M., Crothers D. M. The locus of sequence-directed and protein-induced DNA bending. Nature. 1984 Apr 5;308(5959):509–513. doi: 10.1038/308509a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahn K., Blattner F. R. Sequence-induced DNA curvature at the bacteriophage lambda origin of replication. Nature. 1985 Oct 3;317(6036):451–453. doi: 10.1038/317451a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]