Abstract
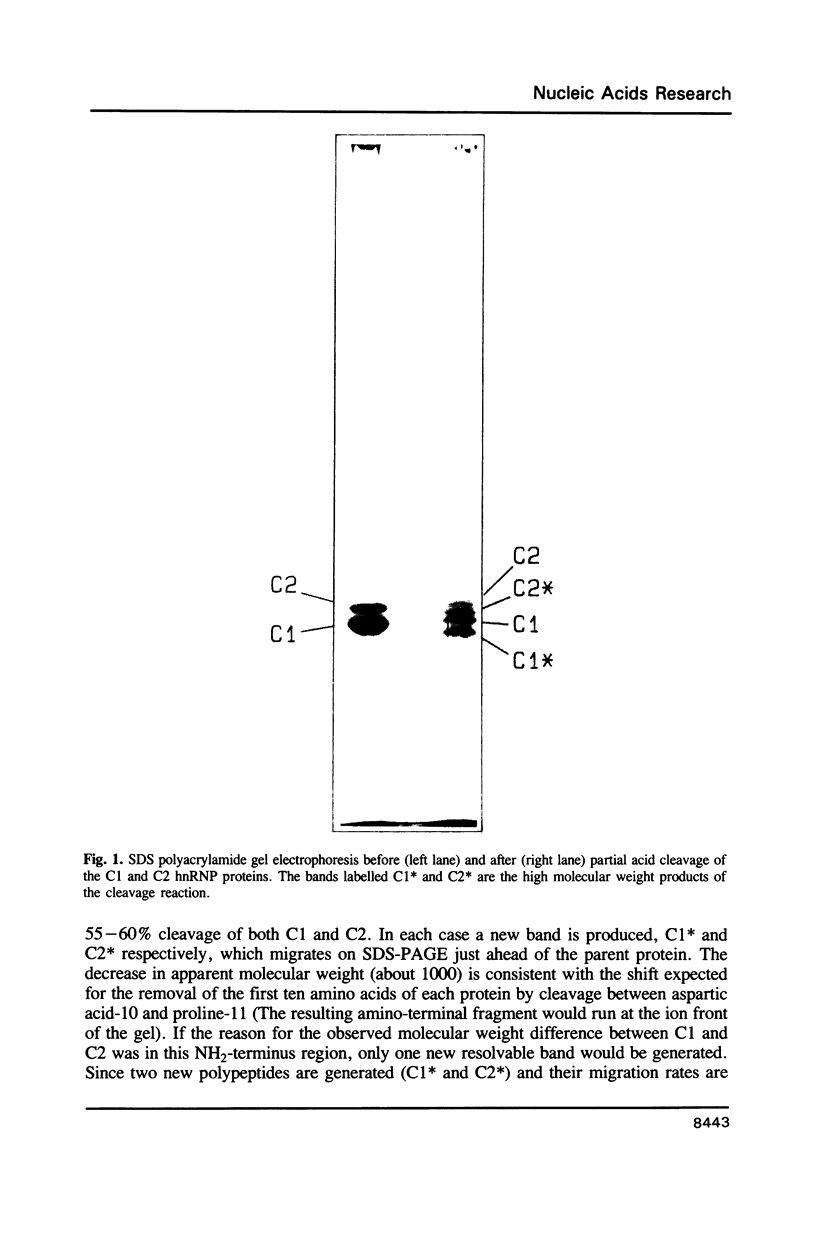
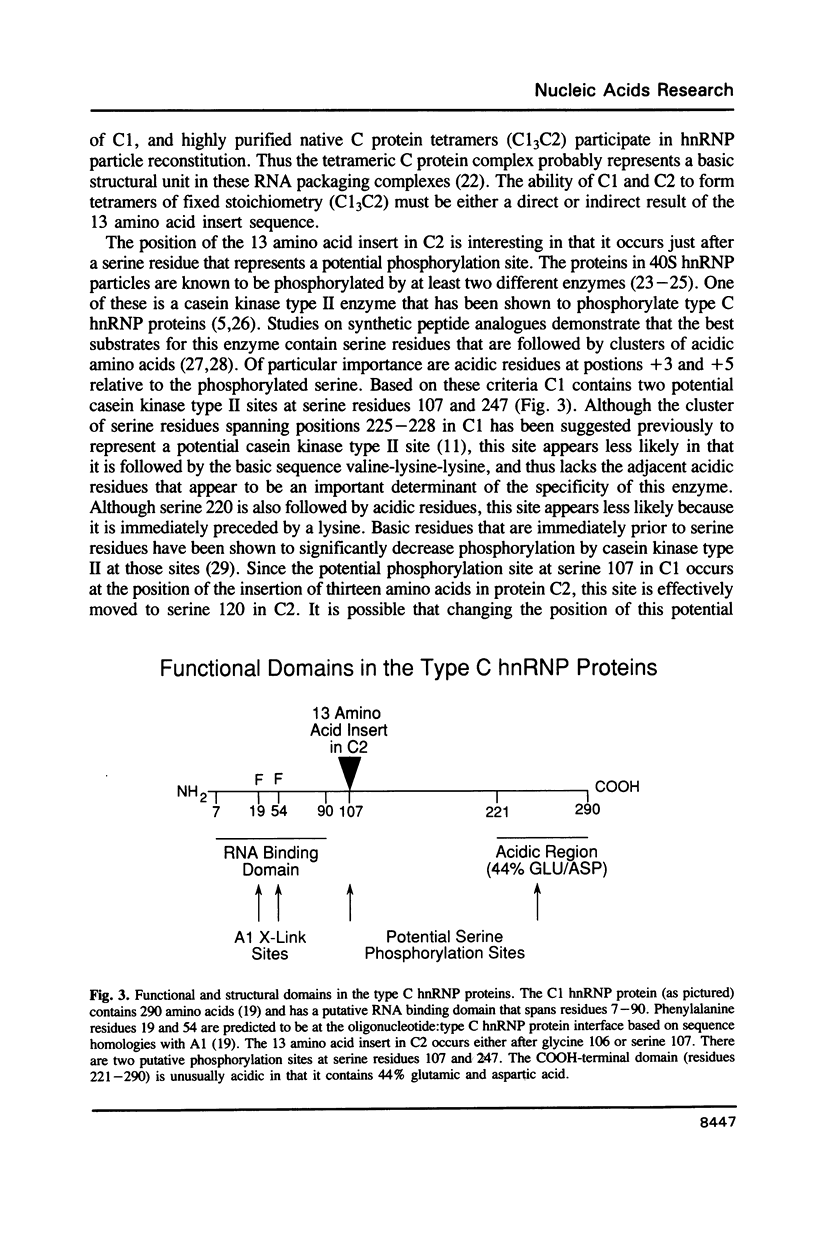
Partial acid cleavage, comparative HPLC tryptic peptide mapping and amino acid sequencing of the C1 and C2 proteins of HeLa heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein (hnRNP) particles demonstrate that proteins C1 and C2 differ in primary structure by the presence of a 13 amino acid insert sequence in C2. This C2 insert sequence occurs after either glycine 106 or serine 107 in C1. The additional 13 amino acids that are present in C2 account for the observed molecular weight difference between the C1 and C2 hnRNP proteins on SDS polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Because C1 and C2 appear identical except for the 13 residue insert and because the 3' and 5' untranslated regions of the corresponding mRNAs also appear to be the same (Swanson et al., Mol. Cell. Biol. 7: 1731-1739), it is possible that both polypeptides are produced from a single transcription unit through an alternative splicing mechanism.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnett S. F., Friedman D. L., LeStourgeon W. M. The C proteins of HeLa 40S nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles exist as anisotropic tetramers of (C1)3 C2. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):492–498. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnett S. F., LeStourgeon W. M., Friedman D. L. Rapid purification of native C protein from nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1988 May;16(1):87–97. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(88)90106-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beyer A. L., Christensen M. E., Walker B. W., LeStourgeon W. M. Identification and characterization of the packaging proteins of core 40S hnRNP particles. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):127–138. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90323-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biamonti G., Buvoli M., Bassi M. T., Morandi C., Cobianchi F., Riva S. Isolation of an active gene encoding human hnRNP protein A1. Evidence for alternative splicing. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jun 5;207(3):491–503. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90459-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitbart R. E., Andreadis A., Nadal-Ginard B. Alternative splicing: a ubiquitous mechanism for the generation of multiple protein isoforms from single genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:467–495. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.002343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi Y. D., Grabowski P. J., Sharp P. A., Dreyfuss G. Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins: role in RNA splicing. Science. 1986 Mar 28;231(4745):1534–1539. doi: 10.1126/science.3952495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung S. Y., Wooley J. Set of novel, conserved proteins fold pre-messenger RNA into ribonucleosomes. Proteins. 1986 Nov;1(3):195–210. doi: 10.1002/prot.340010302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conway G., Wooley J., Bibring T., LeStourgeon W. M. Ribonucleoproteins package 700 nucleotides of pre-mRNA into a repeating array of regular particles. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;8(7):2884–2895. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.7.2884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman D. L., Kleiman N. J., Campbell F. E., Jr Nuclear protein phosphorylation in isolated nuclei from HeLa cells. Evidence that 32P incorporation from [gamma-32P]GTP is catalyzed by nuclear kinase II. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Nov 20;847(2):165–176. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(85)90017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hathaway G. M., Traugh J. A. Casein kinases--multipotential protein kinases. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1982;21:101–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holcomb E. R., Friedman D. L. Phosphorylation of the C-proteins of HeLa cell hnRNP particles. Involvement of a casein kinase II-type enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):31–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jauregui-Adell J., Marti J. Acidic cleavage of the aspartyl-proline band and the limitations of the reaction. Anal Biochem. 1975 Dec;69(2):468–473. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90148-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landon Cleavage at aspartyl-prolyl bonds. Methods Enzymol. 1977;47:145–149. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(77)47017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marin O., Meggio F., Marchiori F., Borin G., Pinna L. A. Site specificity of casein kinase-2 (TS) from rat liver cytosol. A study with model peptide substrates. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Oct 15;160(2):239–244. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09962.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayrand S., Setyono B., Greenberg J. R., Pederson T. Structure of nuclear ribonucleoprotein: identification of proteins in contact with poly(A)+ heterogeneous nuclear RNA in living HeLa cells. J Cell Biol. 1981 Aug;90(2):380–384. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.2.380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGregor C. W., Knowler J. T. Two endogenous protein kinase activities in heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles (hnRNP). Mol Biol Rep. 1987;12(2):85–92. doi: 10.1007/BF00368875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meggio F., Marchiori F., Borin G., Chessa G., Pinna L. A. Synthetic peptides including acidic clusters as substrates and inhibitors of rat liver casein kinase TS (type-2). J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14576–14579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrill B. M., Stone K. L., Cobianchi F., Wilson S. H., Williams K. R. Phenylalanines that are conserved among several RNA-binding proteins form part of a nucleic acid-binding pocket in the A1 heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 5;263(7):3307–3313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Periasamy M., Brunel C., Jeanteur P. Protein kinase associated with hnRNP from Hela cell nuclei. Partial purification and properties. Biochimie. 1979;61(7):823–826. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(79)80276-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preugschat F., Wold B. Isolation and characterization of a Xenopus laevis C protein cDNA: structure and expression of a heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein core protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9669–9673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweiger A., Kostka G. Phosphoproteins crosslinked to poly(A) + heterogeneous nuclear RNA after irradiation with ultraviolet light. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Nov 13;826(2-3):87–94. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(85)90112-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A. Splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Science. 1987 Feb 13;235(4790):766–771. doi: 10.1126/science.3544217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson M. S., Nakagawa T. Y., LeVan K., Dreyfuss G. Primary structure of human nuclear ribonucleoprotein particle C proteins: conservation of sequence and domain structures in heterogeneous nuclear RNA, mRNA, and pre-rRNA-binding proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1731–1739. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilk H. E., Werr H., Friedrich D., Kiltz H. H., Schäfer K. P. The core proteins of 35S hnRNP complexes. Characterization of nine different species. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Jan 2;146(1):71–81. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08621.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilks A. F., Knowler J. T. The phosphorylation of the proteins of rat liver heterogeneous ribonucleoprotein particles by an endogenous kinase activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jan 29;652(1):228–233. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(81)90226-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Eekelen C. A., Riemen T., van Venrooij W. J. Specificity in the interaction of hnRNA and mRNA with proteins as revealed by in vivo cross linking. FEBS Lett. 1981 Aug 3;130(2):223–226. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)81125-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




