Abstract
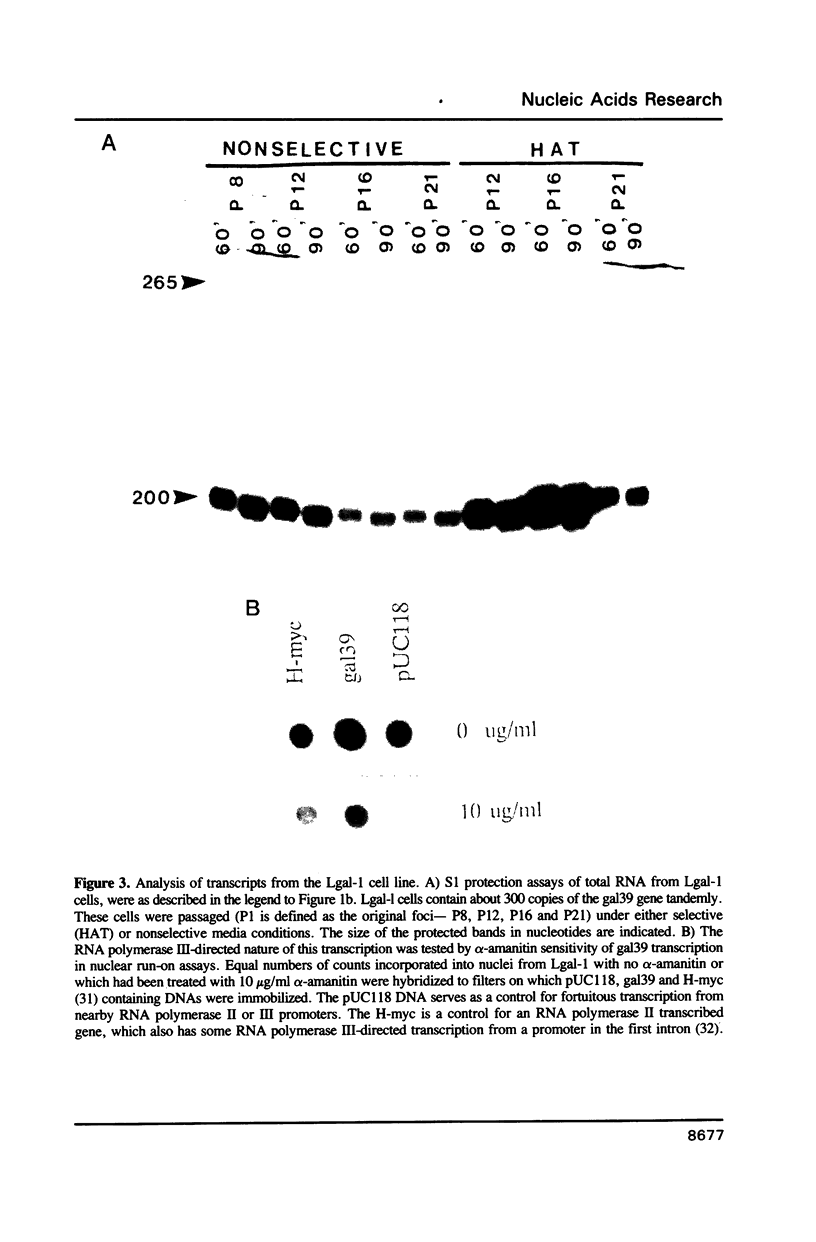
SINE transcription was studied by introducing a galago Monomer family member (gal39), into the mouse Ltk- cell line. Cells transiently transfected with gal39 produce gal39-specific RNA polymerase III-directed transcripts. In permanent cell lines gal39 expression was largely shut off. Genomic environment, copy number and tandem repetition of integrated SINE sequences influenced whether or not RNA polymerase III-directed gal39 transcripts were detectable. These transcripts differ in length from the observed endogenous transcript in cultured galago cells which hybridizes to this repetitive DNA family.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allan M., Paul J. Transcription in vivo of an Alu family member upstream from the human epsilon-globin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):1193–1200. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.1193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradshaw H. D., Jr, Parson W. W., Sheffer M., Lioubin P. J., Mulvihill E. R., Gordon M. P. Design, construction, and use of an electroporator for plant protoplasts and animal cells. Anal Biochem. 1987 Nov 1;166(2):342–348. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90583-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey M. F., Singh K., Botchan M., Cozzarelli N. R. Induction of specific transcription by RNA polymerase III in transformed cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;6(9):3068–3076. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.9.3068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung J., Sussman D. J., Zeller R., Leder P. The c-myc gene encodes superimposed RNA polymerase II and III promoters. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1001–1008. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90586-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciliberto G., Raugei G., Costanzo F., Dente L., Cortese R. Common and interchangeable elements in the promoters of genes transcribed by RNA polymerase iii. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):725–733. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90058-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels G. R., Deininger P. L. A second major class of Alu family repeated DNA sequences in a primate genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 11;11(21):7595–7610. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.21.7595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels G. R., Deininger P. L. Repeat sequence families derived from mammalian tRNA genes. 1985 Oct 31-Nov 6Nature. 317(6040):819–822. doi: 10.1038/317819a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeChiara T. M., Brosius J. Neural BC1 RNA: cDNA clones reveal nonrepetitive sequence content. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2624–2628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan C., Biro P. A., Choudary P. V., Elder J. T., Wang R. R., Forget B. G., de Riel J. K., Weissman S. M. RNA polymerase III transcriptional units are interspersed among human non-alpha-globin genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5095–5099. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder J. T., Pan J., Duncan C. H., Weissman S. M. Transcriptional analysis of interspersed repetitive polymerase III transcription units in human DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Mar 11;9(5):1171–1189. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.5.1171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhrman S. A., Deininger P. L., LaPorte P., Friedmann T., Geiduschek E. P. Analysis of transcription of the human Alu family ubiquitous repeating element by eukaryotic RNA polymerase III. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6439–6456. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutierrez-Hartmann A., Baxter J. D. Stable accumulation of a rat truncated repeat transcript in Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3106–3110. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutierrez-Hartmann A., Lieberburg I., Gardner D., Baxter J. D., Cathala G. G. Transcription of two classes of rat growth hormone gene-associated repetitive DNA: differences in activity and effects of tandem repeat structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7153–7173. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keshet I., Lieman-Hurwitz J., Cedar H. DNA methylation affects the formation of active chromatin. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):535–543. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90263-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon S. H., Baxter J. D., Gutierrez-Hartmann A. Cell-specific expression of transfected brain identifier repetitive DNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 May 11;16(9):3963–3976. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.9.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens G. P., Chaudhari N., Hahn W. E. Brain "identifier sequence" is not restricted to brain: similar abundance in nuclear RNA of other organs. Science. 1985 Sep 20;229(4719):1263–1265. doi: 10.1126/science.2412293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulson K. E., Schmid C. W. Transcriptional inactivity of Alu repeats in HeLa cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 11;14(15):6145–6158. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.15.6145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sapienza C., St-Jacques B. 'Brain-specific' transcription and evolution of the identifier sequence. 1986 Jan 30-Feb 5Nature. 319(6052):418–420. doi: 10.1038/319418a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer R. H., Penman S. Stability of HeLa cell mRNA in actinomycin. Nature. 1972 Nov 10;240(5376):100–102. doi: 10.1038/240100a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh K., Carey M., Saragosti S., Botchan M. Expression of enhanced levels of small RNA polymerase III transcripts encoded by the B2 repeats in simian virus 40-transformed mouse cells. Nature. 1985 Apr 11;314(6011):553–556. doi: 10.1038/314553a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanton L. W., Watt R., Marcu K. B. Translocation, breakage and truncated transcripts of c-myc oncogene in murine plasmacytomas. Nature. 1983 Jun 2;303(5916):401–406. doi: 10.1038/303401a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G., Milner R. J., Bloom F. E., Lerner R. A. Common 82-nucleotide sequence unique to brain RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):4942–4946. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.4942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G., Milner R. J., Gottesfeld J. M., Lerner R. A. Identifier sequences are transcribed specifically in brain. Nature. 1984 Mar 15;308(5956):237–241. doi: 10.1038/308237a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullu E., Weiner A. M. Upstream sequences modulate the internal promoter of the human 7SL RNA gene. 1985 Nov 28-Dec 4Nature. 318(6044):371–374. doi: 10.1038/318371a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner M. J., Sharp J. A., Summers W. C. Nucleotide sequence of the thymidine kinase gene of herpes simplex virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1441–1445. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson J. B., Sutcliffe J. G. Primate brain-specific cytoplasmic transcript of the Alu repeat family. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3324–3327. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner A. M., Deininger P. L., Efstratiadis A. Nonviral retroposons: genes, pseudogenes, and transposable elements generated by the reverse flow of genetic information. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:631–661. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Silverstein S., Lee L. S., Pellicer A., Cheng Y. c., Axel R. Transfer of purified herpes virus thymidine kinase gene to cultured mouse cells. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):223–232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90333-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]