Abstract
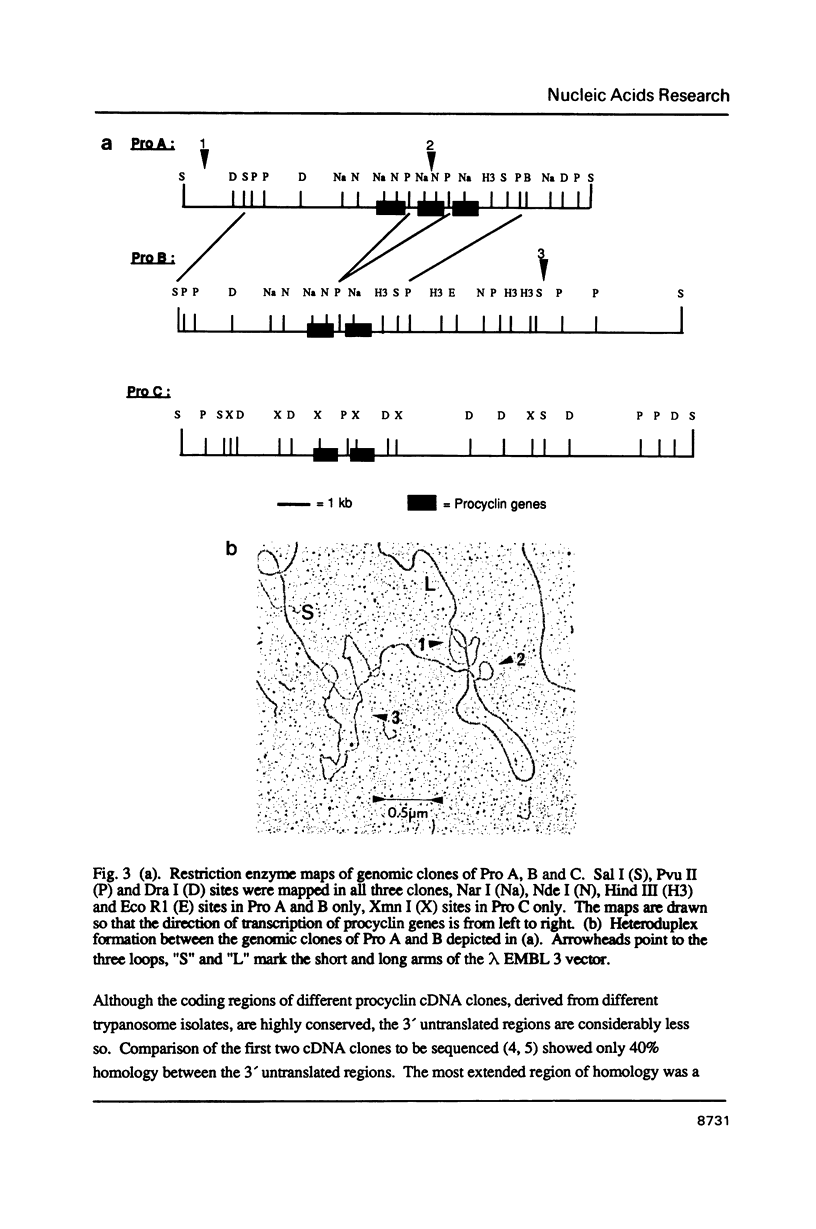
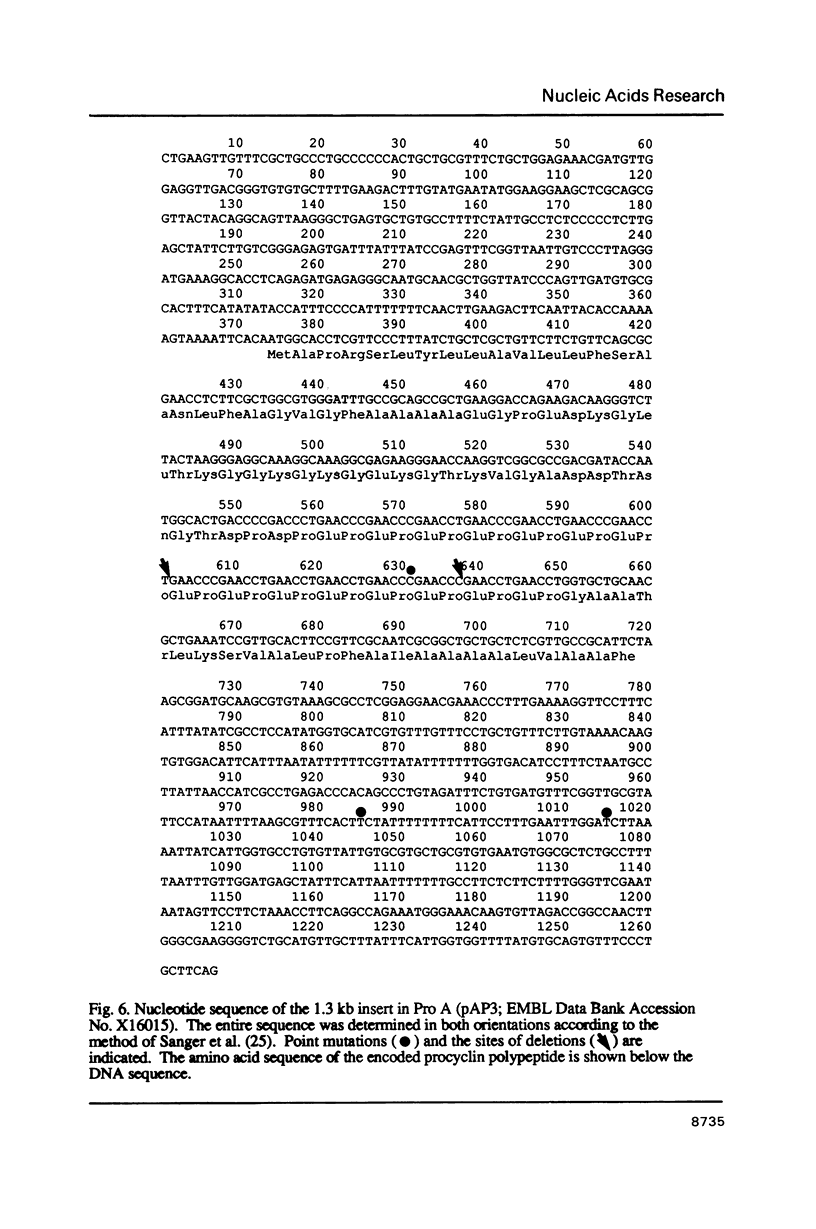
The genes encoding procyclin, the major glycoprotein expressed on the surface of procyclic forms of Trypanosoma brucei, comprise a multigene family. It has previously been demonstrated that procyclin genes in cloned trypanosome strains from Kenya and Uganda show restriction fragment polymorphisms. A detailed study of the Kenyan strain 227 has revealed that procyclin genes are arranged in tandem at 3 distinct loci (Pro A, B and C) and that the polymorphism is due to the duplication of 1.3 kb in the Pro A locus, which has generated an additional procyclin gene. Northern blot analysis has shown that at least 2 loci are transcribed and that a minimum of 3 procyclin genes are expressed within a cloned line. The transcription of procyclin genes is resistant to 1 mg ml-1 alpha-amanitin, whereas that of the 5' flanking gene in the Pro A locus is sensitive. This observation suggests that the two genes form part of separate transcription units with a promoter between them.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bertrand G., Brunet P., Brun G., Pierre F., Thébault G. La prescription des anti-inflammatoires au cabinet. Rev Odontostomatol (Paris) 1979 Sep-Oct;8(5):289–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boothroyd J. C., Paynter C. A., Cross G. A., Bernards A., Borst P. Variant surface glycoproteins of Trypanosoma brucei are synthesised with cleavable hydrophobic sequences at the carboxy and amino termini. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Sep 25;9(18):4735–4743. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.18.4735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brack C. DNA electron microscopy. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1981;10(2):113–169. doi: 10.3109/10409238109114551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer G., Ross J. Poly(A) shortening and degradation of the 3' A+U-rich sequences of human c-myc mRNA in a cell-free system. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1697–1708. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrington M., Roditi I., Williams R. O. The structure and transcription of an element interspersed between tandem arrays of mini-exon donor RNA genes in Trypanosoma brucei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 23;15(24):10179–10198. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.24.10179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross G. A., Manning J. C. Cultivation of Trypanosoma brucei sspp. in semi-defined and defined media. Parasitology. 1973 Dec;67(3):315–331. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000046540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Lange T., Borst P. Genomic environment of the expression-linked extra copies of genes for surface antigens of Trypanosoma brucei resembles the end of a chromosome. Nature. 1982 Sep 30;299(5882):451–453. doi: 10.1038/299451a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imboden M. A., Laird P. W., Affolter M., Seebeck T. Transcription of the intergenic regions of the tubulin gene cluster of Trypanosoma brucei: evidence for a polycistronic transcription unit in a eukaryote. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 25;15(18):7357–7368. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.18.7357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenni L., Marti S., Schweizer J., Betschart B., Le Page R. W., Wells J. M., Tait A., Paindavoine P., Pays E., Steinert M. Hybrid formation between African trypanosomes during cyclical transmission. Nature. 1986 Jul 10;322(6075):173–175. doi: 10.1038/322173a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenardo M. J., Rice-Ficht A. C., Kelly G., Esser K. M., Donelson J. E. Characterization of the genes specifying two metacyclic variable antigen types in Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6642–6646. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine B. J., Chodchoy N., Marzluff W. F., Skoultchi A. I. Coupling of replication type histone mRNA levels to DNA synthesis requires the stem-loop sequence at the 3' end of the mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6189–6193. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthyssens G., Michiels F., Hamers R., Pays E., Steinert M. Two variant surface glycoproteins of Trypanosoma brucei have a conserved C-terminus. Nature. 1981 Sep 17;293(5829):230–233. doi: 10.1038/293230a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melefors O., von Gabain A. Site-specific endonucleolytic cleavages and the regulation of stability of E. coli ompA mRNA. Cell. 1988 Mar 25;52(6):893–901. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90431-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. N., Turner M. J. Analysis of antigenic types appearing in first relapse populations of clones of Trypanosoma brucei. Parasitology. 1981 Feb;82(1):63–80. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000041871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mowatt M. R., Clayton C. E. Developmental regulation of a novel repetitive protein of Trypanosoma brucei. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2838–2844. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mowatt M. R., Clayton C. E. Polymorphism in the procyclic acidic repetitive protein gene family of Trypanosoma brucei. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4055–4062. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mowatt M. R., Wisdom G. S., Clayton C. E. Variation of tandem repeats in the developmentally regulated procyclic acidic repetitive proteins of Trypanosoma brucei. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):1332–1335. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.1332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muhich M. L., Boothroyd J. C. Polycistronic transcripts in trypanosomes and their accumulation during heat shock: evidence for a precursor role in mRNA synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3837–3846. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müllner E. W., Kühn L. C. A stem-loop in the 3' untranslated region mediates iron-dependent regulation of transferrin receptor mRNA stability in the cytoplasm. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):815–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90098-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pays E., Steinert M. Control of antigen gene expression in African trypanosomes. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:107–126. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.000543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pays E., Tebabi P., Pays A., Coquelet H., Revelard P., Salmon D., Steinert M. The genes and transcripts of an antigen gene expression site from T. brucei. Cell. 1989 Jun 2;57(5):835–845. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90798-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portier C., Dondon L., Grunberg-Manago M., Régnier P. The first step in the functional inactivation of the Escherichia coli polynucleotide phosphorylase messenger is a ribonuclease III processing at the 5' end. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):2165–2170. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02484.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rackwitz H. R., Zehetner G., Frischauf A. M., Lehrach H. Rapid restriction mapping of DNA cloned in lambda phage vectors. Gene. 1984 Oct;30(1-3):195–200. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90120-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. P., Beecroft R. P., Tolson D. L., Liu M. K., Pearson T. W. Procyclin: an unusual immunodominant glycoprotein surface antigen from the procyclic stage of African trypanosomes. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1988 Dec;31(3):203–216. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(88)90150-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. P., Jenni L., Beecroft R. P., Pearson T. W. Procyclic tsetse fly midgut forms and culture forms of African trypanosomes share stage- and species-specific surface antigens identified by monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1986 Mar 15;136(6):2259–2264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roditi I., Carrington M., Turner M. Expression of a polypeptide containing a dipeptide repeat is confined to the insect stage of Trypanosoma brucei. Nature. 1987 Jan 15;325(6101):272–274. doi: 10.1038/325272a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roditi I., Dobbelaere D., Williams R. O., Masterson W., Beecroft R. P., Richardson J. P., Pearson T. W. Expression of Trypanosoma brucei procyclin as a fusion protein in Escherichia coli. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1989 Apr;34(1):35–43. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(89)90017-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roditi I., Schwarz H., Pearson T. W., Beecroft R. P., Liu M. K., Richardson J. P., Bühring H. J., Pleiss J., Bülow R., Williams R. O. Procyclin gene expression and loss of the variant surface glycoprotein during differentiation of Trypanosoma brucei. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):737–746. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider A., Hemphill A., Wyler T., Seebeck T. Large microtubule-associated protein of T. brucei has tandemly repeated, near-identical sequences. Science. 1988 Jul 22;241(4864):459–462. doi: 10.1126/science.3393912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sgaramella V., Khorana H. G. CXII. Total synthesis of the structural gene for an alanine transfer RNA from yeast. Enzymic joining of the chemically synthesized polydeoxynucleotides to form the DNA duplex representing nucleotide sequence 1 to 20. J Mol Biol. 1972 Dec 28;72(2):427–444. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90155-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg J., Tait A., Haley S., Wells J. M., Le Page R. W., Schweizer J., Jenni L. Gene exchange in African trypanosomes: characterisation of a new hybrid genotype. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1988 Jan 15;27(2-3):191–200. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(88)90038-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tait A. Evidence for diploidy and mating in trypanosomes. Nature. 1980 Oct 9;287(5782):536–538. doi: 10.1038/287536a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vickerman K. Developmental cycles and biology of pathogenic trypanosomes. Br Med Bull. 1985 Apr;41(2):105–114. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a072036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vickerman K., Tetley L., Hendry K. A., Turner C. M. Biology of African trypanosomes in the tsetse fly. Biol Cell. 1988;64(2):109–119. doi: 10.1016/0248-4900(88)90070-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells J. M., Prospero T. D., Jenni L., Le Page R. W. DNA contents and molecular karyotypes of hybrid Trypanosoma brucei. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1987 May;24(1):103–116. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(87)90121-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. O., Young J. R., Majiwa P. A. Genomic environment of T. brucei VSG genes: presence of a minichromosome. Nature. 1982 Sep 30;299(5882):417–421. doi: 10.1038/299417a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson T., Treisman R. Removal of poly(A) and consequent degradation of c-fos mRNA facilitated by 3' AU-rich sequences. Nature. 1988 Nov 24;336(6197):396–399. doi: 10.1038/336396a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. R., Donelson J. E., Majiwa P. A., Shapiro S. Z., Williams R. O. analysis of genomic rearrangements associated with two variable antigen genes of Trypanosoma brucei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Feb 11;10(3):803–819. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.3.803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]