Abstract
Upon their initial discovery, hydrothermal vents and methane seeps were considered to be related but distinct ecosystems, with different distributions, geomorphology, temperatures, geochemical properties and mostly different species. However, subsequently discovered vents and seep systems have blurred this distinction. Here, we report on a composite, hydrothermal seep ecosystem at a subducting seamount on the convergent Costa Rica margin that represents an intermediate between vent and seep ecosystems. Diffuse flow of shimmering, warm fluids with high methane concentrations supports a mixture of microbes, animal species, assemblages and trophic pathways with vent and seep affinities. Their coexistence reinforces the continuity of reducing environments and exemplifies a setting conducive to interactive evolution of vent and seep biota.
Keywords: Costa Rica margin, chemosynthetic ecosystem, deep sea, hydrothermal vent, methane seep
1. Introduction
Since discovery of the first deep-sea hydrothermal vent over three decades ago [1], scientists have worked to understand how these chemosynthesis-based ecosystems are formed and function. The discovery of methane-fuelled, cold seep ecosystems in the 1980s led to an early belief that there are at least two types of deep-sea chemosynthetic environment fuelled by reduced compounds from the Earth's interior [2]. Hydrothermal vent and methane seep ecosystems were initially found in geographically separate and tectonically distinct portions of the deep sea [3], but are now known to occur in close proximity in some areas such as the Japan Sea and Guaymas Basin [4–6]. Vents and seeps share many major taxa, notably siboglinid tubeworms, vesicomyid clams, bathymodiolin mussels, provannid gastropods, alvinocarid shrimp, galatheid and Kiwa crabs. However, they typically share no more than 20 per cent of their species, even when vent and seep sites are in geographical proximity [4,5]. A subset of modern species appears to be successful at both methane-rich cold seeps and at sedimented hot vents including the siboglinid tubeworms Lamellibrachia barhami and Escarpia spicata, Paraescarpia echinospica, the vesicomyid clams Archivesica gigas, Phreagena okutanii and Calyptogena solidissima and the bathymodiolin mussels Bathymodiolus japonicus and Bathymodiolus platifrons [4,6–8], suggesting that environment along with water depth, rather than geological setting, dictates species composition [4,9,10]. Once large foundation species such as those mentioned above are present, associated species follow to create characteristic assemblages [11].
Key abiotic features characterizing vent ecosystems include the occurrence of elevated temperature, the presence of heavy metals and sulphides in fluid emissions and sulphide, basalt, iron oxide or serpentenite carbonate substrates. Seep sediments typically have higher methane and sulphide concentrations and seep carbonates are precipitated by anaerobic methane oxidation [3]. Microbial and metazoan composition distinctions and different metabolic, C fixation and trophic pathways are also recognized (See electronic supplemental material, table S1), yet both vent and seep fluids may contain methane [3], elevated temperatures [12] and similar geochemistry [9]. Vents and seeps exhibit a continuum of abiotic and biotic characteristics, however, biological observations along this continuum are often restricted to the large, symbiont-bearing megafauna.
Below, we report on a reducing system that we refer to as a hydrothermal seep, which represents an intermediate setting in the continuum described above. We present observations made during exploratory dives near the base of Jaco Scar, formed from a subducting seamount on the convergent Costa Rica margin. This region hosts over 40 cold seeps with diverse morphologies [13], but hydrothermal activity has not been reported previously. Here, we use geochemical observations and subsequent analyses of microbes, macro- and megafaunal biota at this site to conduct in-depth exploration of the co-occurrence of hot vent and cold seep organisms from the perspective of ecological assemblage, phylogenetic affinities and trophic structure. We place these observations in a broader context by drawing comparisons with other vent and seep systems exhibiting end-member or intermediate attributes, and predict where similar intermediate habitats are likely to occur.
2. Material and methods
Photography, sampling and observations were carried out with the submersible Alvin during RV Atlantis Legs AT 15_44 (Dive no. 4513; 7 March 2009) and 15_59 (Dive no. 4590, 4591—11 and 12 January 2010) at depths of 1752–1805 m (9o 7.05′ N, 84o 50.38′ W). Seafloor water temperature was measured with a low-temperature probe. Water over Jaco Scar and Jaco Summit was sampled with a SBE9+ CTD and rosette, with 2-L Niskin bottles mounted on the submersible, and with a Major Pair titanium water sampler. Methane in water was analysed according to Ussler & Paull [14]; chloride and sulphate were analysed according to Ussler & Paull [15] in pore water samples obtained from push core sediment (15 cm in length divided into 3 cm sections) using a Reeburgh-style pore water squeezer. Faunal density calculations were made from 49 still photographs taken from Alvin with an externally mounted Insite Scorpio digital camera with 10 cm laser scale. Areal cover estimates for the vestimentiferan meadows were made from video frame grabs using x–y coordinates. Animal tissues for stable isotope analyses (δ13C, δ15N) were sorted, processed and analysed according to methods in Levin & Mendoza [16]. For phylogenetic affinity, animal tissues were extracted and the mitochondrial gene Cytochrome oxidase subunit 1 was amplified according to Folmer et al. [17]. Purification of bacterial DNA from mussel gill tissue was based on Goffredi et al. [18]. An approximately 1500 bp fragment of 16S rRNA gene was generated by bacteria-specific 16S rRNA primers [19]. PCR products were sequenced directly, compared with those available from GenBank via Blastn and parsimony analyses were executed in PAUP* v. 4.0b10 [20]. For microbial analysis, total genomic DNA was extracted from filtered water samples (0.2 µm Durapore) as in Tavormina et al. [21] and used to construct 16S rRNA clone libraries for bacteria (35 insert containing clones for the major titanium sampler and 43 for Niskin water) using standard Domain-specific PCR primers (27F-1492R) [19]. OTUs from both libraries were grouped by RFLP with the restriction enzymes HaeIII and RsaI, and a neighbour-joining phylogeny was constructed in ARB [22]. Methanotroph diversity and abundance were determined using the monooxygenase interspacer analysis (MISA) method and quantitative PCR assays designed to target the cosmopolitan planktonic pmoA phylotypes, OPU1 and OPU3 [23].
3. Results and discussion
(a). Physical and chemical attributes
Scientists in the submersible Alvin during dives AD 4590 and AD 4591 observed diffuse fluid flow beneath seep-affiliated tubeworms located at 1790 m water depth. Close examination revealed shimmering, warm water emerging from a hole at the base of one massive tubeworm (siboglinid) bush and from rocks surrounded by bathymodiolin mussels and vesicomyid clams (electronic supplementary material, figure S1a and movie S1). Water temperature measured near the base of a large Lamellibrachia barhami bush ranged from 3.6°C to 5.2°C over two consecutive days; maximum temperatures were elevated nearly 3°C above ambient values of 2.4–2.6°C (electronic supplementary material, table S2). A second site located approximately 118 m to the west at a similar depth exhibited slightly cooler flow through rock-covered sea floor (3.6–3.9°C; electronic supplementary material, table S2). Flow rates were not measured, but the fluid flow beneath the giant tubeworm bush was sufficient to cause fluttering of white bacterial floc attached to biotic substrates and the temperature differential was sufficient to cause obvious shimmering (electronic supplementary material, movies S1–S2).
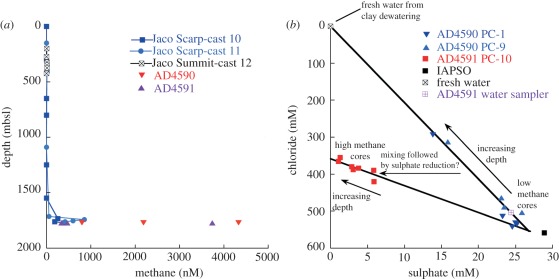
A sediment push core (AD 4590 PC-1) taken within several metres of the vent site revealed the presence of low salinity pore fluids in the near subsurface (12–15 cmbsf; Cl− = 294 mM; SO4= = 13.8 mM; electronic supplementary material, table S3) suggesting upward migration and mixing of fresh water are occurring at Jaco Scar. Nearby push cores show even more dramatic evidence for fresh water addition (figure 1b); the elevated fluid temperatures and mixing trends suggest that fresh water is being released from subducted sediments. There are a number of geochemical processes that may produce fresh water from subducted sediments along convergent margins. These include clay mineral dehydration reactions, particularly the smectite-to-illite transition that occurs at approximately 1.5 km depth [24], differential-stress-induced smectite dehydration [25], and the opal-A to opal-CT transformation [26]. Evidence for migration of low salinity water is found along the Peruvian margin [27], along the décollement at the Costa Rica margin [28,29], and the Barbados margin [30].
Figure 1.
(a) Methane concentrations in water sampled by CTD casts over Jaco Scar and Summit sites and by Niskin bottles tripped within and adjacent to sites of shimmering flow. (b) Pore water chloride and sulphate concentrations in three push cores (PC 1, PC 9 and PC 10), all 15 cm in length, collected close to fluid discharge show effects of fresh water addition. IAPSO seawater is plotted for reference purposes.
Methane measurements made by previous investigators in the region [31] and in this study (figure 1) indicate that Jaco Scar bottom waters are highly methane-enriched, a cold seep-like attribute. Methane concentrations were 4300 nM and 3700 nM in water collected immediately adjacent to the Lamellibrachia bush with visible fluid flow during Alvin dives 4590 and 4591 on consecutive days (electronic supplementary material, table S2), more than three orders of magnitude higher than background seawater distant from seafloor methane sources (approx. 1 nM). Pore fluids contained in sediments approximately 2–3 m from the source of venting had methane concentrations up to 3500 nM (electronic supplementary material, table S3). Further from the Lamellibrachia bush (approx. 110 m to the east), near-seafloor methane concentrations above flowing fluid vents ranged from 340 to 470 nM (electronic supplementary material, table S2). Methane concentrations were elevated above the bottom at 1764–1734 m (190–860 nM; figure 1a; electronic supplementary material, table S2) possibly owing to rising methane bubbles, whereas water collected at the summit of Jaco seamount (approx. 745 m) had methane concentrations less than 15 nM. Despite elevated HS− values in a low sulphate core (AD 4591 PC-10), which imply active near-seafloor anaerobic oxidation of methane, surprisingly little authigenic carbonate was present at Jaco Scar, consistent with high fluid flow rates and limited activity of anaerobic methane oxidizers.
The Jaco Scar site was first investigated by others with a CTD and TV (video) sled deployed from the surface [13,31]. Geologists, geophysicists and microbiologists had visited this site, along with numerous other mounds and subducting seamounts, but hydrothermal fluid emission has not been reported previously. Füri et al. [32] previously sampled water at Jaco Scar locations near the vent site and recorded 3He/4He of 1.31 and 1.23, indicating a small component of mantle-derived fluid. 4He/20Ne ratios of 0.74–0.75 were elevated relative to ambient seawater. They suggested that He enrichment could reflect mantle derivation, while Ne depletion could possibly result from interaction of noble gasses with methane bubbles [32]. However, close-up visual observations made by scientists diving in Alvin were required to detect the shimmering water, the site of water emission, and to make the precise temperature measurements that documented potential hydrothermal activity and diffusive fluid flow at the site originally reported to be a methane seep [13].
(b). The biological community
The physical attributes of the Jaco Scar system reflect a composite of hydrothermal vent and methane seep characteristics, but it sits on a convergent margin characterized by subduction erosion, an environment that normally gives rise to methane seeps [13]. Based on setting, and the fact that the dominant megafaunal taxon, Lamellibrachia barhami also serves as a foundation species at many nearby Costa Rica margin seeps [13], we suggest the Jaco system may be described as an intermediate between cold seep and hot vent, a ‘hydrothermal seep’, with characters from both. Based on the physical attributes, we hypothesized that resident species and their trophic characteristics should exhibit some vent and seep affinities, and these may provide clues about factors that shape the continuum of vent and seep assemblages.
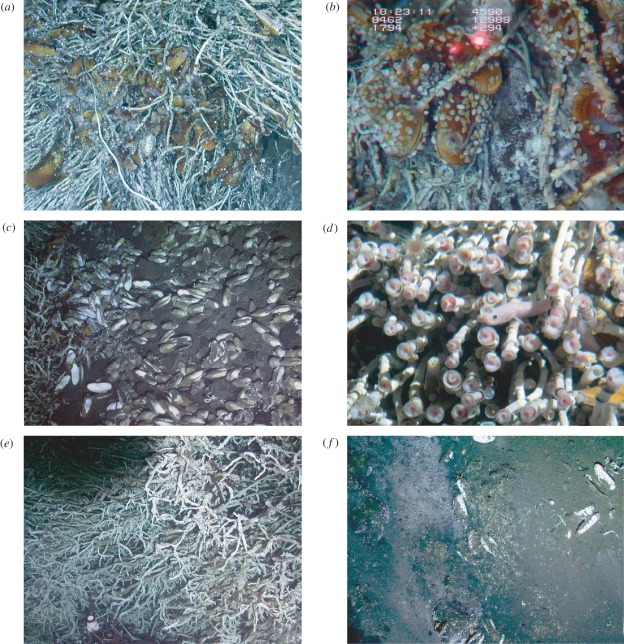
Structurally dominant taxa at this site were the siboglinid polychaetes Lamellibrachia barhami and Escarpia spicata, species that occupy both seeps and vents [7]. Lamellibrachia barhami either formed large spherical bushes 1–2 m in diameter (electronic supplementary material, figure S1a) or coalesced into continuous meadows from 30 to 70 m2 in area (electronic supplementary material, figure S1b). The largest Lamellibrachia bush (approx. 2.4 m diameter), with hydrothermal fluids venting from its base, was estimated to contain 14 770 individual tubeworms. Nicknamed The Volkswagen because of its size, the bush-supported bathymodiolin mussels living in and on the tubes (196 ind. m−2; figure 2a). Mussels and tubeworms bathed in shimmering fluids were heavily covered by lepetodrilid limpets (Lepetodrilus aff. elevatus and Lepetodrilus aff. shannonae), at densities of nearly 1280 ind m−2 (figure 2b; electronic supplementary material, table S4 and movies S1, S2). Lepetodrilids occur mainly at vents, although they have been reported from two additional seep sites [33]. Vesicomyid clams (Archivesica gigas) were also present, but were most dense in sediments surrounding the bush base (figure 2c). This species occurs at sedimented vents and seeps in Guaymas Basin [34], and as a group, the vesicomyids often occur at sites that have attributes of both methane seeps and hot vents [10]. Zoarcid fishes (Pachycara sp.) hovered over and nestled within the worm tubes (figure 2d) at densities up to 28 ind. m−2. Zoarcids are the dominant fishes at hydrothermal vents, but they also occur at seeps on the Florida Escarpment and in the Mediterranean [35]. DNA sequence data suggest that the Jaco Scar Pachycara species is most closely related to Pachycara thermophilum from Mid-Atlantic Ridge hydrothermal vents (electronic supplementary material, table S5).
Figure 2.
Representative assemblages and habitats in the vicinity of hydrothermal flow at the Jaco Scar methane seep. (a) Bathymodiolus n. sp. (nr. thermophilus) in a Lamellibrachia barhami bush, (b) Lepetodrilus spp. on mussel and tubeworm surfaces, (c) Vesicomyid clam bed (Archivesica gigas) adjacent to the vent site. Note high densities of galatheid crabs (Munidopsis sp.) and gastropods, (d) The zoarcid Pachycara sp. on a L. barhami bush (e) Serpulid polychaetes (Neovermilia n. sp.) covering L. barhami tubes, (f) Ophiuroid aggregation adjacent to venting fluids and a vesicomyid clam bed.
A dense bed of Archivesica gigas (130 ind. m−2; figure 2c) was present within 2–3 m of The Volkswagen bush Lamellibrachia site. These were covered with gastropods (5 ind m−2) and galatheid crabs (Munidopsis sp., 40 ind. m−2; electronic supplementary material, table S4). Frenulate siboglinids (Siboglinum sp.) formed a distinctive field nearby. The clams and frenulates are typically associated with a sulphidic sediment matrix and are highly characteristic of methane seep ecosystems [5,16].
Several additional features of the assemblage are vent-like in nature. Space competition between bathymodiolin mussels and tubeworms within the same ‘bush’ is evident (figure 2a). DNA sequence data show that the mussels, most of which represented two undescribed species, are most closely related to Bathymodiolus thermophilus (C. Feehery & G.W.R., 2012, unpublished data). A single specimen of B. thermophilus, which is a hydrothermal vent species, was also recovered. The thiotrophic bacterial symbionts of the two new Bathymodiolus species are 99 per cent similar (based on 16S rRNA) to B. thermophilus from vents of the East Pacific Rise and to those in mussels from the seeps of the Gulf of Mexico ([36]; electronic supplementary material, table S5). The multiple morphologies of L. barhami at Jaco Scar (spherical bushes and continuous meadows; figure 1) resemble Ridgeia piscesae at Juan de Fuca vents [37]. Aggregations of serpulids (Neovermilia new sp.) are present (E. Kupriyanova & G.W.R., 2012, personal communication), in this case attached to Lamellibrachia tubes outside the warm vent area or on sediments (figure 2e). Serpulid aggregations are common at hydrothermal vents [38] and have been reported from only a single seep site deep on the Peru margin in the vicinity of temperature anomalies [39]. High densities of ophiuroids (Ophiuridae) occur on sediments near clam aggregations adjacent to the site of fluid emission (figure 2f). Ophiuroid aggregations are commonly reported at vents on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge and East Pacific Rise [40], but are known from seeps at Blake Ridge in the Atlantic [41], and as an early stage in organic fall succession [42]. Many of the gastropod genera present such as Lepetodrilus, Bathyacmaea, Fucaria and Neomphalidae new genus (electronic supplementary material, table S6) are most often found at vents [43] but others, including Margarites, Neolepetopsis and Provanna also occur at seeps [44]. Also we have found that two of the annelid species (Amphisamytha fauchaldi and Archinome new sp.) are otherwise known only from hydrothermal vent systems in Guaymas Basin [45].
Species diversity at seeps is typically higher than at vents, while habitat endemism is typically lower [44,46]. We hypothesize that a hydrothermal seep should provide a broad range of physiologically and nutritionally prescribed ecological niches. The diversity of taxa that attain localized high densities at Jaco Scar (electronic supplementary material, table S4), and the speciose gastropod fauna documented to date (i.e. 15 of 23 gastropod species are new to science; electronic supplementary material, table S6), suggest the Jaco Scar hydrothermal seep exhibits diversities that surpass those of typical vent and seep sites.
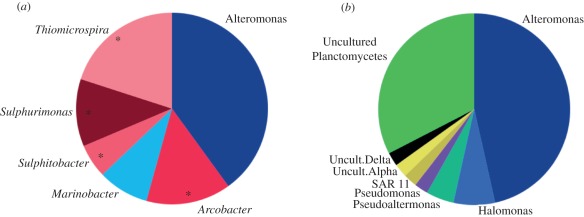
Nutritional sources remain a key feature that set vent and seep communities apart from most of the deep sea [3,5]. Both vent and seep assemblages are fuelled by chemoautolithotrophic bacteria and archaea. However, the carbon fixation pathways and sources can differ at vents and seeps, and often yield distinct isotopic signatures [47]. Carbon fixation fuelled by sulphide oxidation is the most widespread metabolic pathway in both ecosystems, and usually generates intermediate δ13C signatures from −22 to −35 ‰. Indeed, 16S rRNA microbial community analysis of the shimmering fluids and white flocculent material within The Volkswagen bush recovered a significant proportion of bacterial phylotypes (25%) affiliated with sulphide-oxidizing gamma, alpha and epsilonproteobacteria (figure 3). These included members of the genera Thiomicrospira, Sulphitobacter, Sulphurimonas and Arcobacter, previously reported from hydrothermal vent plumes, seep sediments and euxinic basins (electronic supplementary material, figure S2) [48,49]. The loose white floc associated with The Volkswagen bush is reminiscent of the biogenic sulphur-rich precipitate pervasive at ‘snow blower’ diffuse flow vents, believed to be produced by sulphide-oxidizing epsilonproteobacteria that are phylogenetically affiliated with the sulphur-respiring organisms recovered from Jaco Scar [50]. Sulphur-oxidizing phylotypes were not recovered from the water column immediately above the tubeworm bush (approx. 10 cm distance), suggesting that these putative chemolithoautotrophs may be directly associated with the flocculent material sampled within the tubeworm bush. Additionally, metabolic genes indicative of aerobic methanotrophs (particulate methane monooxygenase, pMMO; [51]) were also detected in the shimmering fluids surrounding the tubeworm bush. Despite the high CH4 concentrations within the shimmering fluids, the pMMO abundance and diversity were not found to be significantly different from seawater samples collected by CTD within approximately 8 m of the bush. In contrast to the apparent localized distribution of sulphide-oxidizing micro-organisms, aerobic methanotrophs may be more widely distributed throughout the bathypelagic zone surrounding Jaco Scar.
Figure 3.
Bacterial 16S rRNA gene diversity from water column samples collected (a) within The volkswagen tubeworm bush using a titanium water sampler (n = 35 clones) and (b) approximately 10 cm above the tubeworms within or adjacent to the shimmering fluids (n = 43). Asterisks in panel a designate bacterial genera associated with the chemolithotrophic gamma, epsilon and alphaproteobacteria capable of sulphur-oxidation.
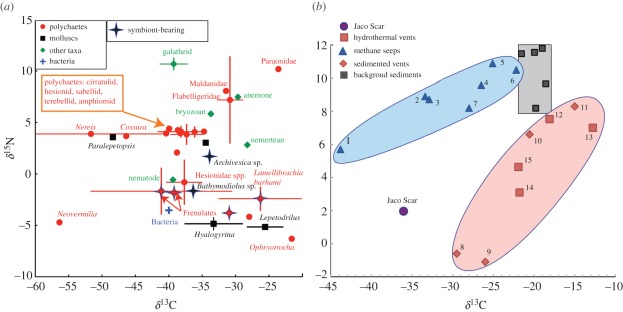
The incorporation of methane-derived carbon is prevalent among more taxa at seeps than vents, although bathymodiolin mussels are an important exception. Syntrophic clusters of archaea and bacteria carry out anaerobic oxidation of methane at seeps, yielding isotopically light microbial biomass that can be consumed by seep heterotrophs [52]. Heavy δ13C signatures (≥−15‰) in vent animals may result from alternative rubisco pathways in CO2 fixation via the Calvin Benson Bassham (CBB) cycle and/or from consumption of bacteria carrying out the rTCA cycle [53]. An isotopic survey of species at Jaco Scar (figure 4a) reveals that, despite the occurrence of planktonic epsilonproteobacteria at this site, the fauna lack the heavy δ13C signatures characteristic of other hydrothermal vents in the East Pacific [58]. The symbiont-bearing mussels, clams, frenulates and vestimentiferans at Jaco Scar have isotopic signatures consistent with reliance on sulphide oxidation coupled with CBB (average δ13C = −39 to −26‰) for nutrition, as do the majority of deposit-feeding annelids, grazers and predatory taxa (figure 4a). Among the animals, only a serpulid (Neovermilia sp.), nereidid and cossurid polychaetes, and a limpet (Paralepetopsis sp.) exhibit the isotopically light δ13C indicating methane-derived carbon (δ13C −56‰ to −46‰; figure 4a); these species may consume the aerobic methanotrophs detected in venting fluids. Notably, the attached filamentous bacteria bathed by hydrothermal fluids are also light (δ13C = −40‰), potentially reflecting a light DIC pool and methane influence, or an association with methylotrophs [59]. Similar trophic pathways have been reported from seeps in the Gulf of Mexico [60] and Anya's Garden, a sedimented vent on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge [61].
Figure 4.
(a) Stable isotope signatures of invertebrate species present at Jaco Scar. Major taxa are colour-coded. Each point represents the average δ13C and δ15N signature for a single species. Error bars are s.e. (b) Average invertebrate isotope signatures from Pacific hydrothermal vents and seeps. Seeps: Hydrate Ridge, OR microbial mat (1), clam bed (2) [52]; Kodiak, AK (3), Unimak, AK (4) [16]; Eel River CA clam bed (5) and microbial mat (6) [52]; New Zealand seeps (7) [54]; Sedimented Vents: Middle Valley clam microbial mat (8), and clam bed (9) [55]; Chile margin (10) (Thurber et al., unpublished data); South Su, Papua New Guinea (11) [55]; hydrothermal vents: Marianas Back Arc (12) [56]; Hanging Gardens, East Pacific Rise (13) [56]; Juan de Fuca—Endeavour Segment (14) (L. Levin et al., unpublished data); Guaymas Basin Vents (15) [57]; background sediments: (black squares), from Costa Rica, CA margin, OR margin, Gulf of Alaska, Aleutian Islands.
While vents and seep organisms share carbon fixation pathways, vent and seep invertebrate assemblages exhibit distinct average δ13C and δ15N isotope signatures in the Pacific Ocean (figure 4b). The average isotopic signature of taxa sampled at Jaco Scar is intermediate to those surveyed at other Pacific vent and seep communities and is distinct from typical background organisms (figure 4b). It appears equidistant from that of Hydrate Ridge (a methane seep) and Middle Valley (a sedimented vent; figure 4b).
Elevated temperatures associated with methane seepage have been reported previously (electronic supplemental material, table S7). Fluids in brine pools and mud volcanoes in the Gulf of Mexico [62], the SW Barents Sea [63] and the eastern Mediterranean Sea [64] all exhibit temperatures elevated above ambient, but the sediments are typically hypersaline, anoxic and/or physically disrupted, and are marked by an absence of metazoan fauna. Fluids advected at Extrovert Cliff (950 m) in Monterey Bay have temperatures up to 9°C in contrast with an ambient 4.1°C temperature, and elevated He concentrations and 3He/4He ratios associated with a deep aquifer and several fault zones [12,65]. However, the fauna does not appear vent-like; the sole presence of bacterial mats, vesicomyid clams and associated heterotrophic fauna may reflect low oxygen concentrations in overlying waters. At these depths in Monterey Bay, dissolved oxygen concentrations are approximately 0.3 ml l−1, whereas the Jaco Scar site has bottom water oxygen concentrations six times greater (1.6–1.9 ml l−1). Tubeworms, mussels and other taxa found at Jaco Scar may require a well-oxygenated water column. Much smaller temperature anomalies (+0.44oC over 40 cm depth in the sediment) have been reported from another erosive margin off Peru [39], where clams, galatheid crabs and serpulid aggregations are similar to those described for Jaco Scar. Additional regions where we might expect to find intermediate ecosystems include recently discovered sites of off-axis magmatic intrusions in the Guaymas Basin, where biological communities are potentially supported by methane released from magma-driven thermogenic alterations of sediments [66], the Chile Triple Junction, where subduction of a spreading centre occurs beneath a margin rife with methane seeps [67], a subduction seep off Hatsushima Island, Sagami Bay exhibiting elevated temperatures [4], other fore-arc seamounts where extensional spreading induces hydrothermal circulation, and thermogenic methane is released [68], and possibly at serpentinite-hosted hydrothermal systems such as Lost City and Ghost City on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge [69].
4. Conclusions
The Jaco Scar site is a geologically and geochemically heterogeneous landscape that supports animals that have either seep or vent affinities, or foundation species that occur in both settings. Composite, reducing habitats on subducting seamounts, such as the one reported here, provide a setting in which these groups can evolve together. The Jaco Scar observations further support environmental influence on availability of energy and carbon sources as a key determinant of assemblage composition in chemosynthetic ecosystems. These findings enrich our understanding of the spectrum of chemosynthetic ecosystems that exist along a reducing continuum of vents, seeps and organic falls. Given our limited knowledge of the deep sea floor, it is likely that additional intermediate or mosaic ecosystems, with different combinations of reducing system attributes, and possibly even hydrothermal seep habitat endemics, remain undiscovered.
Acknowledgements
We thank the Captain and crew of the RV Atlantis, the Alvin Pilots, as well as scientific participants of AT 15_59, especially A. Thurber, G. Mendoza and A. Dekas for their assistance at sea. We also thank H. Sahling and M. Tryon for their assistance in providing maps and other location information, H. Carson and R. Vargas for their observations during AD 4513, and P. Tavormina, S. Connon and M. Muscovova for their assistance and contributions to the molecular community analysis. Two anonymous reviewers provided constructive comments on an earlier version of the manuscript. The research was supported by the US National Science Foundation grants OCE 0826254, 0825436, 0825791, 0939559 and 0939557.
References
- 1.Lonsdale P. 1977. Clustering of suspension-feeding macrobenthos near abyssal hydrothermal vents at oceanic spreading centers. Deep-Sea Res. 24, 857–863 10.1016/0146-6291(77)90478-7 (doi:10.1016/0146-6291(77)90478-7) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Paull C. K., et al. 1984. Biological communities at the Florida Escarpment resemble hydrothermal vent taxa. Science 226, 965–967 10.1126/science.226.4677.965 (doi:10.1126/science.226.4677.965) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Tunnicliffe V., Juniper S. K., Sibuet M. 2003. Reducing environments of the deep-sea floor. In Ecosystems of the deep oceans (ed. Tyler P.), pp. 81–110 Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Elsevier Science B; V. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Watanabe H., Fujikura K., Kojima S., Miyazaki J. I., Fujiwara Y. 2010. Japan: vents and seeps in close proximity. In The vent and seep biota: aspects from microbes to ecosystems (ed. Kiel S.), pp. 379–401 Netherlands: Springer; 10.1007/978-90-481-9572-5_12 (doi:10.1007/978-90-481-9572-5_12) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Sibuet M., Olu K. 1998. Biogeography, biodiversity and fluid dependence of deep-sea cold-seep communities at active and passive margins. Deep-Sea Res. 45, 517–556 10.1016/S0967-0645(97)00074-X (doi:10.1016/S0967-0645(97)00074-X) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Fujikura K., Hashimoto J., Okutani T. 2002. Estimated population densities of megafauna in two chemosynthesis-based communities: a cold seep in Sagami Bay and a hydrothermal vent in the Okinawa Trough. Benthos. Res. 57, 21–30 [Google Scholar]
- 7.Black M. B., Halanych K. M., Maas P. A. Y., Hoeh W. R., Hashimoto J., Desbruyéres D., Lutz R. A., Vrijenhoek R. C. 1997. Molecular systematics of vestimentiferan tubeworms from hydrothermal vents and cold-water seeps. Mar. Biol. 130, 141–149 10.1007/s002270050233 (doi:10.1007/s002270050233) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Craddock C., Hoeh W. R., Gustafson R. G., Lutz R. A., Hashimoto J., Vrijenhoek R. J. 1995. Evolutionary relationships among deep-sea mytilids (Bivalvia, Mytilidae) from hydrothermal vents and cold-water methane sulfide seeps. Mar. Biol. 121, 477–485 10.1007/BF00349456 (doi:10.1007/BF00349456) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Sahling H., Wallman K., Dahlmann A., Schmaljohann R., Petersen S. 2005. The physicochemical habitat of Sclerolinum sp. at Hook Ridge hydrothermal vent, Bransfield Strait, Antarctica. Limnol. Oceanogr. 50, 598–606 10.4319/lo.2005.50.2.0598 (doi:10.4319/lo.2005.50.2.0598) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Krylova E., Sahling H. 2006. Recent bivalve mollusks of the genus Calyptogena (Vesicomyidae). J. Mollus Stud. 72, 359–395 (doi:10.1093/mollus/eyl022) [Google Scholar]
- 11.Govenar B. 2010. Shaping vent and seep communities: habitat provision and modification by foundation species. In The vent and seep biota: aspects from microbes to ecosystems (ed. Kiel S.), pp. 403–432 Netherlands: Springer; 10.1007/978-90-481-9572-5_13 (doi:10.1007/978-90-481-9572-5_13) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 12.LaBonte A. L., Brown K. M., Tryon M. D. 2007. Monitoring periodic and episodic flow events at Monterey Bay seeps using a new optical flow meter. J. Geophys. Res. Sol Ea 112, B02105. 10.1029/2006jb004410 (doi:10.1029/2006jb004410) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Sahling H., Masson D. G., Ranero C. R., Huhnerbach V., Weinrebe W., Klaucke I., Burk D., Bruckmann W., Suess E. 2008. Fluid seepage at the continental margin offshore Costa Rica and southern Nicaragua. Geochem. Geophy. Geosyst. 9, Q05S05. 10.1029/2008gc001978 (doi:10.1029/2008gc001978) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ussler W., III, Paull C. K. 2008. Detection of methane sources along the California continental margin using water column anomalies. In Proc. 6th Int. Conf. on Gas Hydrates (ICGH), Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, 6–10 July 2008, 12 pp See http://circle.ubc.ca/handle/2429/1089; accessed February 17, 2012. Vancouver, Canada: University of British Columbia. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Ussler W., III, Paull C. K. 2008. Rates and consequences of anaerobic oxidation of methane and authigenic carbonate precipitation in deep-sea sediments inferred from porewater chemical profiles. Earth Planet Sci. Lett. 266, 271–287 10.1016/j.epsl.2007.10.056 (doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2007.10.056) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Levin L. A., Mendoza G. 2007. Community structure and nutrition of deep methane seep macroinfauna from the Aleutian Margin and Florida Escarpment, Gulf of Mexico. Mar. Ecol. 28, 131–151 10.1111/j.1439-0485.2006.00131.x (doi:10.1111/j.1439-0485.2006.00131.x) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Folmer O., Black M., Hoeh W., Lutz R., Vrijenhoek R. 1994. DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Mol. Mar. Biol. Biotech. 3, 294–299 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Goffredi S. K., Orphan V. J., Rouse G. W., Jahnke L., Embaye T., Turk K., Lee R., Vrijenhoek R. C. 2005. Evolutionary innovation: a bone-eating marine symbiosis. Environ. Microbiol. 7, 1369–1378 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2005.00824.x (doi:10.1111/j.1462-2920.2005.00824.x) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Lane D. J. 1991. 16S/23S rRNA sequencing. In Nucleic acid techniques in bacterial systematics (eds Stackebrandt E., Goodfellow M.), pp. 115–175 New York, NY: John Wiley & Sons, Inc [Google Scholar]
- 20.Swofford, D. L. 2002. PAUP*: Phylogenetic analysis using parsimony (*and other methods) v. 4. Sunderland, MA: Sinauer Associates [Google Scholar]
- 21.Tavormina P. L., Ussler W., III, Orphan V. J. 2008. Planktonic and sediment-associated aerobic methanotrophs in two seep systems along the North American margin. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 74, 3985–3995 10.1128/aem.00069-08 (doi:10.1128/aem.00069-08) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ludwig W., et al. 2004. ARB: a software environment for sequence data. Nucleic Acids Res. 32, 1363–1371 (doi:10.1093/nar/gkh293) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Tavormina P. L., Ussler W., III, Joye S. B., Harrison B. K., Orphan V. J. 2010. Distributions of putative aerobic methanotrophs in diverse pelagic marine environments. ISME J. 4, 700–710 10.1038/ismej.2009.155 (doi:10.1038/ismej.2009.155) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Perry E. A., Hower J. 1972. Late-stage dehydration in deeply buried pelitic sediments. Am. Assoc. Petr. Geol. B 56, 2013–2021 [Google Scholar]
- 25.Fitts T. G., Brown K. M. 1999. Stress-induced smectite dehydration; ramifications for patterns of freshening and fluid expulsion in the North Barbados accretionary wedge. Earth Planet Sci. Lett. 172, 179–197 10.1016/S0012-821X(99)00168-5 (doi:10.1016/S0012-821X(99)00168-5) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kastner M., Keene J. B., Gieskes J. M. 1977. Diagenesis of siliceous oozes–I. Chemical controls on the rate of opal-A to opal-CT transformation—an experimental study. Geochim. Cosmochim. Ac 41, 1041–1059 10.1016/0016-7037(77)90099-0 (doi:10.1016/0016-7037(77)90099-0) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kastner M., Elderfield H., Martin J. B., Suess E., Kvenvolden K. A., Garrison R. E. 1990. Diagenesis and interstitial-water chemistry at the Peruvian continental margin–major constituents and strontium isotopes. In Proc. Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results, vol. 112 (eds Suess E., et al.), pp. 413–440 College Station, TX: Ocean Drilling Program [Google Scholar]
- 28.Tobin H., Vannucchi P., Meschede M. 2001. Structure, inferred mechanical properties and implications for fluid transport in the decollement zone, Costa Rica convergent margin. Geology 29, 907–910 (doi:10.1130/0091-7613(2001)029<0907:SIMPAI>2.0.CO;2) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Hensen C., Wallmann K., Schmidt M., Ranero C. R., Suess E. 2004. Fluid expulsion related to mud extrusions off Costa Rica–A window to the subducting slab. Geology 32, 201–204 10.1130/G20119.1 (doi:10.1130/G20119.1) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Martin J. B., Kastner M., Henry P., LePichon X., Lallement S. 1996. Chemical and isotopic evidence for sources of fluids in a mud volcano field seaward of the Barbados accretionary wedge. J. Geophys. Res. 101, 20 325–20 345 10.1029/96JB00140 (doi:10.1029/96JB00140) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Bohrmann G., et al. 2002. Widespread fluid expulsion along the seafloor of the Costa Rica convergent margin. Terra Nova 14, 69–79 10.1046/j.1365-3121.2002.00400.x (doi:10.1046/j.1365-3121.2002.00400.x) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Füri E., Hilton D. R., Tryon M. D., Brown K. M., McMurtry G. M., Bruckmann W., Wheat C. G. 2010. Carbon release from submarine seeps at the Costa Rica fore arc: implications for the volatile cycle at the Central America convergent margin. Geochem. Geophy. Geosyst. 11, Q04S21. 10.1029/2009gc002810 (doi:10.1029/2009gc002810) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Johnson S. B., Waren A., Vrijenhoek R. C. 2008. DNA barcoding of Lepetodrilus limpets reveals cryptic species. J. Shellfish Res. 27, 43–51 10.2983/0730-8000(2008)27[43:DBOLLR]2.0.CO;2 (doi:10.2983/0730-8000(2008)27[43:DBOLLR]2.0.CO;2) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Desbruyéres D., Segonzac M., Bright M. 2006. Handbook of deep-sea hydrothermal vent fauna, 2nd edn Linz, Austria: Biologiezentrum; 10.1111/j.1439-0485.2006.00107.x (doi:10.1111/j.1439-0485.2006.00107.x) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Biscoito M., Segonzac M., Almeida A. J., Desbruyéres D., Geistdoerfer P., Turnipseed M., Van Dover C. L. 2002. Fishes from the hydrothermal vents and cold seeps—an update. Cah. Biol. Mar. 43, 359–362 [Google Scholar]
- 36.Won Y.-J., Jones W. J., Vrijenhoek R. C. 2008. Absence of cospeciation between deep-sea mytilids and their thiotrophic endosymbionts. J. Shellfish Res. 27, 129–138 10.2983/0730-8000(2008)27[129:AOCBDM]2.0.CO;2 (doi:10.2983/0730-8000(2008)27[129:AOCBDM]2.0.CO;2) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Urcuyo I. A., Massoth G. J., Julian D., Fisher C. R. 2003. Habitat, growth and physiological ecology of a basaltic community of Ridgeia piscesae from the Juan de Fuca Ridge. Deep-Sea Res. 50, 763–780 10.1016/s0967-0637(03)00061-x (doi:10.1016/s0967-0637(03)00061-x) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Ten Hove H. A., Zibrowius H. 1986. Laminatubus alvini gen. et sp.n. and Protis hydrothermica sp.n. (Polychaeta, Serpulidae) from the bathyal hydrothermal vent communities in the eastern Pacific. Zool. Scr. 15, 21–31 10.1111/j.1463-6409.1986.tb00205.x (doi:10.1111/j.1463-6409.1986.tb00205.x) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Olu K., Duperret A., Sibuet M., Foucher J. P., Fiala-Médioni A. 1996. Structure and distribution of cold seep communities along the Peruvian active margin: relationship to geological and fluid patterns. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 132, 109–125 10.3354/meps132109 (doi:10.3354/meps132109) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Stohr S., Segonzac M. 2005. Deep-sea ophiuroids (Echinodermata) from reducing and non-reducing environments in the North Atlantic Ocean. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 85, 383–402 10.1017/S0025315405011318h (doi:10.1017/S0025315405011318h) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Van Dover C. L., et al. 2003. Blake Ridge methane seeps: characterization of a soft-sediment, chemosynthetically based ecosystem. Deep-Sea Res. 50, 281–300 10.1016/s0967-0637(02)00162-0 (doi:10.1016/s0967-0637(02)00162-0) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Smith C. R. 1985. Food for the deep sea—utilization, dispersal, and flux of nekton falls at the Santa-Catalina basin floor. Deep-Sea Res. 32, 417–442 10.1016/0198-0149(85)90089-5 (doi:10.1016/0198-0149(85)90089-5) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Waren A., Bouchet P. 1993. New records, species, genera, and a new family of gastropods from hydrothermal vents and hydrocarbon seeps. Zool. Scr. 22, 1–90 10.1111/j.1463-6409.1993.tb00342.x (doi:10.1111/j.1463-6409.1993.tb00342.x) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Sasaki T., Waren A., Kano Y., Okutani T., Fujikura K. 2010. Gastropods from recent hot vents and cold seeps: systematics, diversity and life strategies. In The vent and seep biota: aspects from microbes to ecosystems (ed. Kiel S.), pp. 169–254 Netherlands: Springer; 10.1007/978-90-481-9572-5_7 (doi:10.1007/978-90-481-9572-5_7) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Borda E., Kudenov J. D., Blake J. A., Chevaldonné P., Desbruyéres D., Shank T. M., Pleijel F., Rouse G. W. Cryptic species of Archinome (Annelida: Amphinomidae) from hydrothermal vents and cold seeps. In Society for Integrative and Comparative Biology 2012 Charleston, SC: Oxford University Press [Google Scholar]
- 46.Turnipseed M., Knick K. E., Lipcius R. N., Dreyer J., Van Dover C. L. 2003. Diversity in mussel beds at deep-sea hydrothermal vents and cold seeps. Ecol. Lett. 6, 518–523 10.1046/j.1461-0248.2003.00465.x (doi:10.1046/j.1461-0248.2003.00465.x) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Van Dover C. L. 2008. Stable isotope studies in marine chemoautotrophically-based ecosystems: an update. In Stable isotopes in ecology and environmental science (eds Michener W., Lajtha K.), 2nd edn Oxford, UK: Blackwell Publishing; 10.1002/9780470691854.ch8 (doi:10.1002/9780470691854.ch8) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Huber J. A., Butterfield D. A., Baross J. A. 2003. Bacterial diversity in a subseafloor habitat following a deep-sea volcanic eruption. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 43, 393–409 10.1111/j.1574-6941.2003.tb01080.x (doi:10.1111/j.1574-6941.2003.tb01080.x) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Lavik G., et al. 2009. Detoxification of sulphidic African shelf waters by blooming chemolithotrophs. Nature 457, 581–586 10.1038/nature07588 (doi:10.1038/nature07588) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Taylor C. D., Wirsen C. O., Gaill F. 1999. Rapid microbial production of filamentous sulfur mats at hydrothermal vents. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 65, 2253–2255 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Tavormina P., Orphan V. J., Kalyuzhnaya M., Jetten M., Klotz M. 2011. A novel family of functional operons encoding methane/ammonia monooxygenase-related proteins in gammaproteobacterial methanotrophs. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 3, 91–100 10.1111/j.1758-2229.2010.00192.x (doi:10.1111/j.1758-2229.2010.00192.x) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Levin L. A., Michener R. H. 2002. Isotopic evidence for chemosynthesis-based nutrition of macrobenthos: the lightness of being at Pacific methane seeps. Limnol. Oceanogr. 47, 1336–1345 10.4319/lo.2002.47.5.1336 (doi:10.4319/lo.2002.47.5.1336) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Hugler M., Sievert S. M. 2011. Autotrophic carbon fixation in the ocean. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 3, 261–289 10.1146/annurev-marine-120709-142712 (doi:10.1146/annurev-marine-120709-142712) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Thurber A. R., Kröger K., Neira C., Wiklund H., Levin L. A. 2010. Stable isotope signatures and methane use by New Zealand cold seep benthos. Mar. Geol. 272, 260–269 10.1016/j.margeo.2009.06.001 (doi:10.1016/j.margeo.2009.06.001) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Levin L. A., Mendoza G. F., Konotchick T., Lee R. 2009. Macrobenthos community structure and trophic relationships within active and inactive Pacific hydrothermal sediments. Deep-Sea Res. 56, 1632–1648 10.1016/j.dsr2.2009.05.010 (doi:10.1016/j.dsr2.2009.05.010) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Van Dover C. L., Fry B. 1989. Stable isotopic compositions of hydrothermal vent organisms. Mar. Biol. 102, 257–263 10.1007/bf00428287 (doi:10.1007/bf00428287) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Soto L. A. 2009. Stable carbon and nitrogen isotopic signatures of fauna associated with the deep-sea hydrothermal vent system of Guaymas Basin, Gulf of California. Deep-Sea Res. 56, 1675–1682 10.1016/j.dsr2.2009.05.013 (doi:10.1016/j.dsr2.2009.05.013) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Bergquist D. C., Eckner J. T., Urcuyo I. A., Cordes E. E., Hourdez S., Macko S. A., Fisher C. R. 2007. Using stable isotopes and quantitative community characteristics to determine a local hydrothermal vent food web. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 330, 49–65 10.3354/meps330049 (doi:10.3354/meps330049) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Ding H., Valentine D. L. 2008. Methanotrophic bacteria occupy benthic microbial mats in shallow marine hydrocarbon seeps, Coal Oil Point, California. J. Geophys. Res. 113, G01015. 10.1029/2007jg000537 (doi:10.1029/2007jg000537) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 60.MacAvoy S. E., Fisher C. R., Carney R. S., Macko S. A. 2005. Nutritional associations among fauna at hydrocarbon seep communities in the Gulf of Mexico. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 292, 51–60 10.3354/meps292051 (doi:10.3354/meps292051) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Southward E. C., Gebruk A., Kennedy H., Southward A. J., Chevaldonee P. 2001. Different energy sources for symbiotic bacteria of three bivalve molluscs at the Logatchev hydrothermal site (Mid-Atlantic Ridge). J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 81, 655–661 10.1017/S0025315401004337 (doi:10.1017/S0025315401004337) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Joye S. B., MacDonald I. R., Montoya J. P., Peccini M. 2005. Geophysical and geochemical signatures of Gulf of Mexico seafloor brines. Biogeosciences 2, 295–309 10.5194/bg-2-295-2005 (doi:10.5194/bg-2-295-2005) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Feseker T., Foucher J. P., Harmegnies F. 2008. Fluid flow or mud eruptions? Sediment temperature distributions on Håkon Mosby mud volcano, SW Barents Sea slope. Mar. Geol. 247, 194–207 10.1016/j.margeo.2007.09.005 (doi:10.1016/j.margeo.2007.09.005) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Feseker T., Brown K. R., Blanchet C., Scholz F., Nuzzo M., Reitz A., Schmidt M., Hensen C. 2010. Active mud volcanoes on the upper slope of the western Nile deep-sea fan—first results from the P362/2 cruise of R/V Poseidon. Geo-Mar. Lett. 30, 169–186 10.1007/s00367-010-0192-0 (doi:10.1007/s00367-010-0192-0) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Füri E., Hilton D. R., Brown K. M., Tryon M. D. 2009. Helium systematics of cold seep fluids at Monterey Bay, California, USA: temporal variations and mantle contributions. Geochem. Geophy. Geosyst. 10, Q08013. 10.1029/2009gc002557 (doi:10.1029/2009gc002557) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Lizarralde D., Soule S. A., Seewald J. S., Proskurowski G. 2011. Carbon release by off-axis magmatism in a young sedimented spreading centre. Nat. Geosci. 4, 50–54 10.1038/ngeo1006 (doi:10.1038/ngeo1006) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 67.German C. R., et al. 2010. Hydrothermal exploration at the Chile Triple Junction—ABE's last adventure? In American Geophysical Union 2010 San Francisco, CA [Google Scholar]
- 68.Stecher J., Tunnicliffe V., Turkay M. 2003. Population characteristics of abundant bivalves (Mollusca, Vesicomyidae) at a sulphide-rich seafloor site near Lihir Island, Papua New Guinea. Can. J. Zool. 81, 1815–1824 10.1139/z03-180 (doi:10.1139/z03-180) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Lartaud F., et al. 2011. Fossil evidence for serpentinization fluids fueling chemosynthetic assemblages. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 108, 7698–7703 10.1073/pnas.1009383108 (doi:10.1073/pnas.1009383108) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]