Abstract
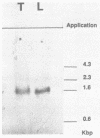
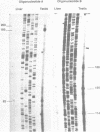
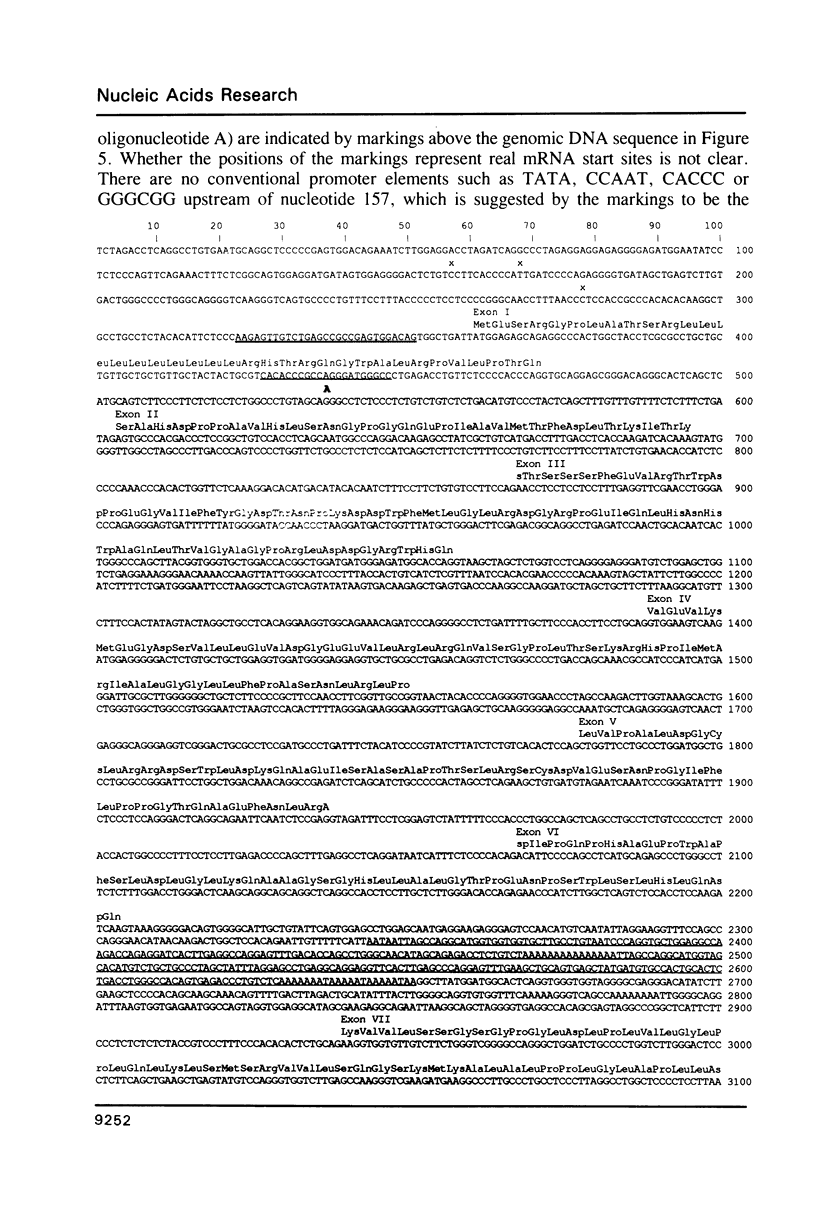
A genomic cosmid clone for human sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG), a liver-secreted plasma glycoprotein that binds sex steroids, was isolated with a previously characterized liver cDNA as probe. Southern blot analysis of genomic DNA indicated that only one SHBG gene is present in the human haploid genome. A 3.8 Kb Xba I-fragment of the clone containing the entire coding region of SHBG was sequenced. The SHBG gene has 8 exons. The 5'-end preceding the translation start site had no TATA box or CAAT box promoter elements. Screening of a human testis cDNA library resulted in the isolation of two distinct cDNA forms. One cDNA was identical with the previously characterized liver SHBG cDNA, thus suggesting that human SHBG and the androgen binding protein (ABP) produced by Sertoli cells are coded for by the same gene. The second cDNA differed from the first by having exon I exchanged with a completely different sequence and exon VII deleted. An exon coding for the 5'-end of this cDNA was found in the cosmid clone 1.5 kb upstream of the first SHBG exon. Primer extension experiments showed the alternatively spliced transcript corresponding to the second cDNA to be present in both liver and testis. From the primary structure of this putative SHBG-gene-related protein, it may be deduced that it is a protein very different from SHBG and probably without steroid binding activity.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng C. Y., Musto N. A., Gunsalus G. L., Bardin C. W. Demonstration of heavy and light protomers of human testosterone-estradiol-binding globulin. J Steroid Biochem. 1983 Oct;19(4):1379–1389. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(83)91111-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng C. Y., Musto N. A., Gunsalus G. L., Frick J., Bardin C. W. There are two forms of androgen binding protein in human testes. Comparison of their protomeric variants with serum testosterone-estradiol binding globulin. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 10;260(9):5631–5640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng S. L., Kotite N., Musto N. A. Comparison of rabbit androgen binding protein with testosterone estradiol binding globulin--I. Physical and chemical properties. J Steroid Biochem. 1984 Dec;21(6):669–676. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(84)90029-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danzo B. J., Bell B. W. The microheterogeneity of androgen-binding protein in rat serum and epididymis is due to differences in glycosylation of their subunits. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 15;263(5):2402–2408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershagen S., Fernlund P., Lundwall A. A cDNA coding for human sex hormone binding globulin. Homology to vitamin K-dependent protein S. FEBS Lett. 1987 Aug 10;220(1):129–135. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80890-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershagen S., Henningsson K., Fernlund P. Subunits of human sex hormone binding globulin. Interindividual variation in size. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 15;262(17):8430–8437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond G. L., Robinson P. A., Sugino H., Ward D. N., Finne J. Physicochemical characteristics of human sex hormone binding globulin: evidence for two identical subunits. J Steroid Biochem. 1986 Apr;24(4):815–824. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(86)90442-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond G. L., Underhill D. A., Smith C. L., Goping I. S., Harley M. J., Musto N. A., Cheng C. Y., Bardin C. W. The cDNA-deduced primary structure of human sex hormone-binding globulin and location of its steroid-binding domain. FEBS Lett. 1987 May 4;215(1):100–104. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80121-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson V. Heterogeneity in end-terminal sugars of rabbit and rat androgen binding protein (ABP). Int J Androl. 1981 Apr;4(2):220–226. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2605.1981.tb00705.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek W. R., Schmid C. W. Repetitive sequences in eukaryotic DNA and their expression. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:813–844. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.004121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph D. R., Hall S. H., Conti M., French F. S. The gene structure of rat androgen-binding protein: identification of potential regulatory deoxyribonucleic acid elements of a follicle-stimulating hormone-regulated protein. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 Jan;2(1):3–13. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-1-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura H., Yoshioka H., Sogawa K., Sakai Y., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Complementary DNA cloning of cytochrome P-450s related to P-450(M-1) from the complementary DNA library of female rat livers. Predicted primary structures for P-450f, PB-1, and PB-1-related protein with a bizarre replacement block and their mode of transcriptional expression. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 15;263(2):701–707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs W. J., Bell B. W., Turney M. K., Danzo B. J. Monoclonal antibodies to rat androgen-binding protein recognize both of its subunits and cross-react with rabbit and human testosterone-binding globulin. Endocrinology. 1988 Jun;122(6):2639–2647. doi: 10.1210/endo-122-6-2639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little P. F., Cross S. H. A cosmid vector that facilitates restriction enzyme mapping. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3159–3163. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercier-Bodard C., Radanyi C., Roux C., Groyer M. T., Robel P., Dadoune J. P., Petra P. H., Jolly D. J., Baulieu E. E. Cellular distribution and hormonal regulation of h-SBP in human hepatoma cells. J Steroid Biochem. 1987;27(1-3):297–307. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(87)90321-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mischke W., Weise H. C., Graesslin D., Rüsch R., Tamm J. Isolation of highly purified sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG): evidence for microheterogeneity. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1979 Apr;90(4):737–742. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0900737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musto N. A. The extracellular sex steroid-binding proteins of testis and liver. Structure-function studies. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;538:37–44. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb48847.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petra P. H., Que B. G., Namkung P. C., Ross J. B., Charbonneau H., Walsh K. A., Griffin P. R., Shabanowitz J., Hunt D. F. Affinity labeling, molecular cloning, and comparative amino acid sequence analyses of sex steroid-binding protein of plasma. A multidisciplinary approach for understanding steroid-protein interaction and its physiological role. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;538:10–24. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb48844.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petra P. H., Stanczyk F. Z., Senear D. F., Namkung P. C., Novy M. J., Ross J. B., Turner E., Brown J. A. Current status of the molecular structure and function of the plasma sex steroid-binding protein (SBP). J Steroid Biochem. 1983 Jul;19(1B):699–706. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(83)90238-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Que B. G., Petra P. H. Characterization of a cDNA coding for sex steroid-binding protein of human plasma. FEBS Lett. 1987 Jul 27;219(2):405–409. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80261-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reventos J., Hammond G. L., Crozat A., Brooks D. E., Gunsalus G. L., Bardin C. W., Musto N. A. Hormonal regulation of rat androgen-binding protein (ABP) messenger ribonucleic acid and homology of human testosterone-estradiol-binding globulin and ABP complementary deoxyribonucleic acids. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 Feb;2(2):125–132. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-2-125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosner W., Aden D. P., Khan M. S. Hormonal influences on the secretion of steroid-binding proteins by a human hepatoma-derived cell line. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1984 Oct;59(4):806–808. doi: 10.1210/jcem-59-4-806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. An interactive graphics program for comparing and aligning nucleic acid and amino acid sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 11;10(9):2951–2961. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.9.2951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. Automation of the computer handling of gel reading data produced by the shotgun method of DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Aug 11;10(15):4731–4751. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.15.4731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner E. E., Ross J. B., Namkung P. C., Petra P. H. Purification and characterization of the sex steroid binding protein from macaque serum. Comparison with the human protein. Biochemistry. 1984 Jan 31;23(3):492–497. doi: 10.1021/bi00298a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Baelen H., Heyns W., De Moor P. Microheterogeneity of the testosterone binding globulin of human pregnancy serum demonstrated by isoelectric focusing. Ann Endocrinol (Paris) 1969;30(Suppl):199–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigersky R. A., Loriaux D. L., Howards S. S., Hodgen G. B., Lipsett M. B., Chrambach A. Androgen binding proteins of testis, epididymis, and plasma in man and monkey. J Clin Invest. 1976 Nov;58(5):1061–1068. doi: 10.1172/JCI108557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh K. A., Titani K., Takio K., Kumar S., Hayes R., Petra P. H. Amino acid sequence of the sex steroid binding protein of human blood plasma. Biochemistry. 1986 Nov 18;25(23):7584–7590. doi: 10.1021/bi00371a048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]