Abstract
An in vitro system has been developed that allows the formation of translation initiation complexes with Euglena chloroplast 30S ribosomal subunits and natural mRNAs. For these experiments two regions of the Euglena chloroplast genome have been cloned behind the T7 transcriptional promoter and the corresponding RNAs synthesized in vitro. These mRNAs are capable of forming initiation complexes with chloroplast 30S subunits in the presence of fMet-tRNA and E. coli initiation factors. Deletion of the normal translation start site results in a message that is no longer recognized by the chloroplast subunits suggesting that the correct AUG initiation codon on the mRNA is being selected by the small ribosomal subunit. Initiation complex formation with the chloroplast 30S subunits is specific for chloroplast mRNAs and mRNA from the phage MS2 is not active in this system.
Full text
PDF



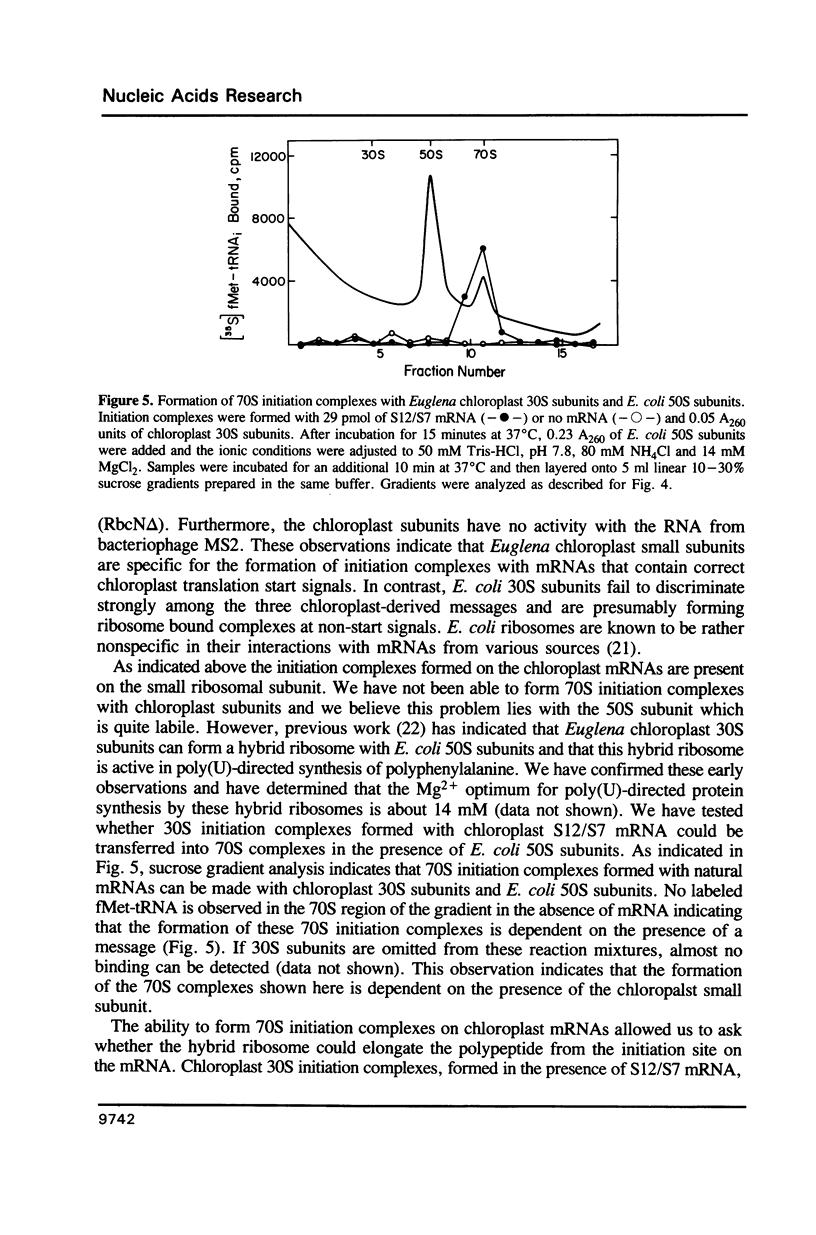


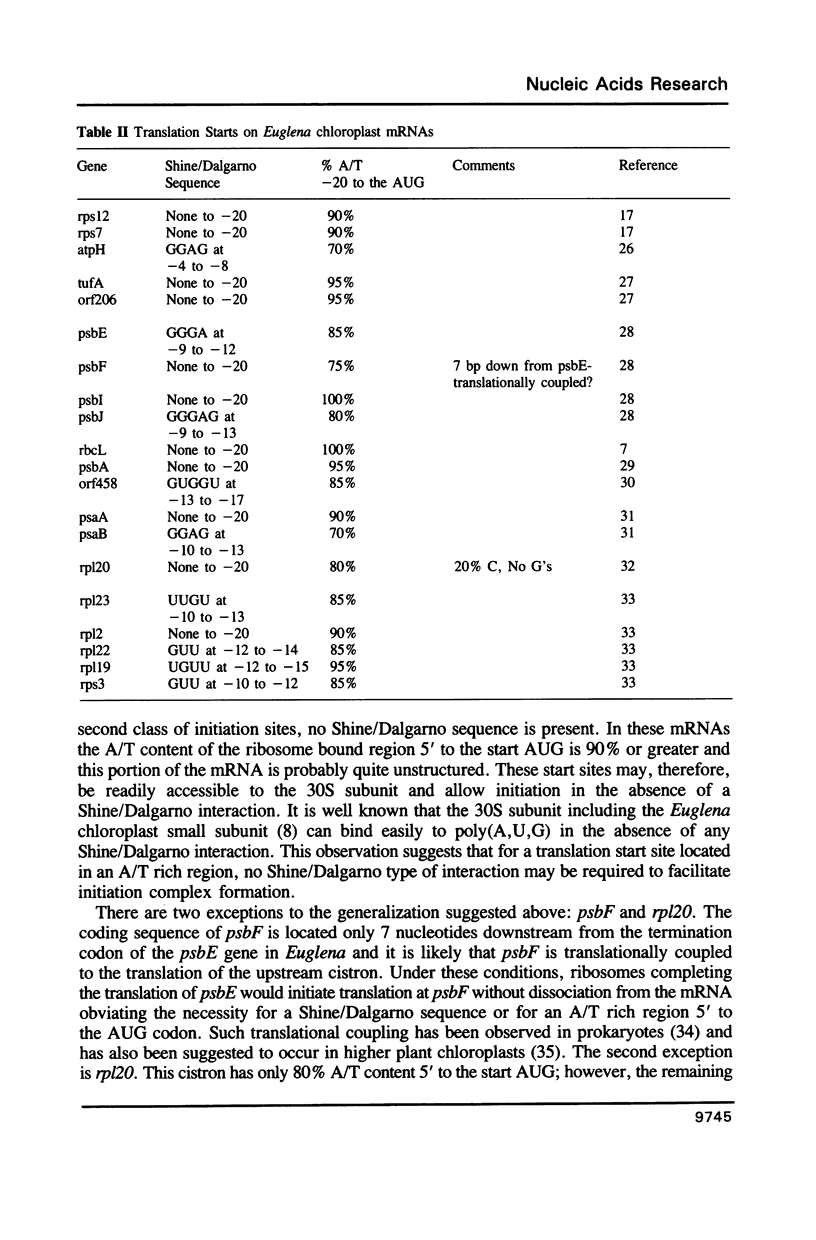


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonham-Smith P. C., Bourque D. P. Translation of chloroplast-encoded mRNA: potential initiation and termination signals. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 11;17(5):2057–2080. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.5.2057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitenberger C. A., Spremulli L. L. Purification of Euglena gracilis chloroplast elongation factor G and comparison with other prokaryotic and eukaryotic translocases. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 25;255(20):9814–9820. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan V. L., Smith M. In vitro generation of specific deletions in DNA cloned in M13 vectors using synthetic oligodeoxyribonucleotides: mutants in the 5'-flanking region of the yeast alcohol dehydrogenase II gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Mar 12;12(5):2407–2419. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.5.2407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christopher D. A., Cushman J. C., Price C. A., Hallick R. B. Organization of ribosomal protein genes rpl23, rpl2, rps19, rpl22 and rps3 on the Euglena gracilis chloroplast genome. Curr Genet. 1988 Sep;14(3):275–285. doi: 10.1007/BF00376748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushman J. C., Christopher D. A., Little M. C., Hallick R. B., Price C. A. Organization of the psbE, psbF, orf38, and orf42 gene loci on the Euglena gracilis chloroplast genome. Curr Genet. 1988 Feb;13(2):173–180. doi: 10.1007/BF00365652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushman J. C., Hallick R. B., Price C. A. The two genes for the P700 chlorophyll a apoproteins on the Euglena gracilis chloroplast genome contain multiple introns. Curr Genet. 1988 Feb;13(2):159–171. doi: 10.1007/BF00365651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox L., Erion J., Tarnowski J., Spremulli L., Brot N., Weissbach H. Euglena gracilis chloroplast EF-Ts. Evidence that it is a nuclear-coded gene product. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 10;255(13):6018–6019. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatenby A. A., Rothstein S. J., Nomura M. Translational coupling of the maize chloroplast atpB and atpE genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4066–4070. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gingrich J. C., Hallick R. B. The Euglena gracilis chloroplast ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase gene. II. The spliced mRNA and its product. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 25;260(30):16162–16168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold J. C., Spremulli L. L. Euglena gracilis chloroplast initiation factor 2. Identification and initial characterization. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):14897–14900. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold L. Posttranscriptional regulatory mechanisms in Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:199–233. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.001215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves M. C., Breitenberger C. A., Spremulli L. L. Euglena gracilis chloroplast ribosomes: improved isolation procedure and comparison of elongation factor specificity with prokaryotic and eukaryotic ribosomes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1980 Oct 15;204(2):444–454. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(80)90055-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves M. C., Spremulli L. L. Activity of Euglena gracilis chloroplast ribosomes with procaryotic and eucaryotic initiation factors. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Apr 1;222(1):192–199. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90516-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haralson M. A., Spremulli L. L., Shive W., Ravel J. M. Occurrence of initiation factor 2 in the postribosomal fraction and identification of an initiation inhibitor as elongation factor G. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Nov;165(1):247–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90161-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraus B. L., Spremulli L. L. Chloroplast initiation factor 3 from Euglena gracilis. Identification and initial characterization. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 15;261(11):4781–4784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. G., Evans W. R. Hybrid ribosome formation from Escherichia coli and chloroplast ribosome subunits. Science. 1971 Jul 16;173(3993):241–242. doi: 10.1126/science.173.3993.241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodish H. F. Specificity in bacterial protein synthesis: role of initiation factors and ribosomal subunits. Nature. 1970 May 23;226(5247):705–707. doi: 10.1038/226705a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manzara T., Hallick R. B. Nucleotide sequence of the Euglena gracilis chloroplast gene for ribosomal protein L20. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 May 11;15(9):3927–3927. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.9.3927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattheakis L. C., Nomura M. Feedback regulation of the spc operon in Escherichia coli: translational coupling and mRNA processing. J Bacteriol. 1988 Oct;170(10):4484–4492. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.10.4484-4492.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montandon P. E., Knuchel-Aegerter C., Stutz E. Euglena gracilis chloroplast DNA: the untranslated leader of tufA-ORF206 gene contains an intron. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 12;15(19):7809–7822. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.19.7809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montandon P. E., Stutz E. The genes for the ribosomal proteins S12 and S7 are clustered with the gene for the EF-Tu protein on the chloroplast genome of Euglena gracilis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Mar 26;12(6):2851–2859. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.6.2851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montandon P. E., Vasserot A., Stutz E. Euglena gracilis chloroplast DNA: analysis of a 1.6 kb intron of the psb C gene containing an open reading frame of 458 codons. Curr Genet. 1986;11(1):35–39. doi: 10.1007/BF00389423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raué H. A., Klootwijk J., Musters W. Evolutionary conservation of structure and function of high molecular weight ribosomal RNA. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1988;51(2):77–129. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(88)90011-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remold-O'Donnell E., Thach R. E. A new method for the purification of initiation factor F2 in high yield, and an estimation of stoichiometry in the binding reaction. J Biol Chem. 1970 Nov 10;245(21):5737–5742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner M. K., Griswold M. D. Fluorographic detection of radioactivity in polyacrylamide gels with 2,5-diphenyloxazole in acetic acid and its comparison with existing procedures. Biochem J. 1983 Jan 1;209(1):281–284. doi: 10.1042/bj2090281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sreedharan S. P., Beck C. M., Spremulli L. L. Euglena gracilis chloroplast elongation factor Tu. Purification and initial characterization. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):3126–3131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stallcup M. R., Sharrock W. J., Rabinowitz J. C. Specificity of bacterial ribosomes and messenger ribonucleic acids in protein synthesis reactions in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1976 Apr 25;251(8):2499–2510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steege D. A., Graves M. C., Spremulli L. L. Euglena gracilis chloroplast small subunit rRNA. Sequence and base pairing potential of the 3' terminus, cleavage by colicin E3. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10430–10439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttle D. P., Haralson M. A., Ravel J. M. Initiation factor 3 requirement for the formation of initiation complexes with synthetic oligonucleotides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Mar 17;51(2):376–382. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91268-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttle D. P., Ravel J. M. The effects of initiation factor 3 on the formation of 30S initiation complexes with synthetic and natural messengers. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Mar 25;57(2):386–393. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90942-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster R. E., Engelhardt D. L., Zinder N. D., Konigsberg W. Amber mutants and chain termination in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1967 Oct 14;29(1):27–43. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90179-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamir A., Miskin R., Vogel Z., Elson D. The inactivation and reactivation of Escherichia coli ribosomes. Methods Enzymol. 1974;30:406–426. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)30042-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]