Abstract
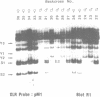
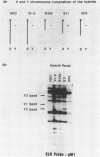
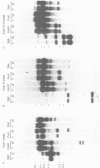
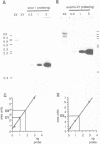
The XLR sequence family encodes RNA transcripts specific to late-stage T and B cells and their neoplasms. Only one apparently functional mRNA has been identified thus far and this encodes a novel 25 kDa nuclear protein. In this report, we find that the XLR gene family is composed of 50-75 copies per haploid genome which localize to at least two different portions of the mouse X chromosome. Neither of these locations are near the xid mutation that earlier work had correlated with XLR. In addition, some members of this family are also on the Y chromosome. Another surprising finding is that while the fourteen genomic clones examined to date have the same exon-intron structure and are closely related with respect to sequence conservation (90%), all appear (in most cases by multiple criteria) to be non-functional, raising the possibility that all but one of the members of this large semi-dispersed family are pseudogenes.
Full text
PDF













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amar L. C., Arnaud D., Cambrou J., Guenet J. L., Avner P. R. Mapping of the mouse X chromosome using random genomic probes and an interspecific mouse cross. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 30;4(13B):3695–3700. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04137.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avner P., Amar L., Dandolo L., Guénet J. L. Genetic analysis of the mouse using interspecific crosses. Trends Genet. 1988 Jan;4(1):18–23. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90123-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avner P., Arnaud D., Amar L., Cambrou J., Winking H., Russell L. B. Characterization of a panel of somatic cell hybrids for regional mapping of the mouse X chromosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5330–5334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avner P., Bishop C., Amar L., Cambrou J., Hatat D., Arnaud D., Mattei M. G. Mapping the mouse X chromosome: possible symmetry in the location of a family of sequences on the mouse X and Y chromosomes. Development. 1987;101 (Suppl):107–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bates P. F., Swift R. A. Double cos site vectors: simplified cosmid cloning. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(2-3):137–146. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90183-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berning A. K., Eicher E. M., Paul W. E., Scher I. Mapping of the X-linked immune deficiency mutation (xid) of CBA/N mice. J Immunol. 1980 Apr;124(4):1875–1877. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockdorff N., Fisher E. M., Cavanna J. S., Lyon M. F., Brown S. D. Construction of a detailed molecular map of the mouse X chromosome by microcloning and interspecific crosses. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3291–3297. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02648.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. D., Brockdorff N., Cavanna J. S., Fisher E. M., Greenfield A. J., Lyon M. F., Nasir J. The long-range mapping of mammalian chromosomes. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1988;137:3–12. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-50059-6_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chien Y., Becker D. M., Lindsten T., Okamura M., Cohen D. I., Davis M. M. A third type of murine T-cell receptor gene. Nature. 1984 Nov 1;312(5989):31–35. doi: 10.1038/312031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen D. I., Hedrick S. M., Nielsen E. A., D'Eustachio P., Ruddle F., Steinberg A. D., Paul W. E., Davis M. M. Isolation of a cDNA clone corresponding to an X-linked gene family (XLR) closely linked to the murine immunodeficiency disorder xid. 1985 Mar 28-Apr 3Nature. 314(6009):369–372. doi: 10.1038/314369a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen D. I., Steinberg A. D., Paul W. E., Davis M. M. Expression of an X-linked gene family (XLR) in late-stage B cells and its alteration by the xid mutation. 1985 Mar 28-Apr 3Nature. 314(6009):372–374. doi: 10.1038/314372a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freytag S. O., Bock H. G., Beaudet A. L., O'Brien W. E. Molecular structures of human argininosuccinate synthetase pseudogenes. Evolutionary and mechanistic implications. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 10;259(5):3160–3166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garchon H. J., Davis M. M. The XLR gene product defines a novel set of proteins stabilized in the nucleus by zinc ions. J Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;108(3):779–787. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.3.779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy R. R., Hayakawa K., Parks D. R., Herzenberg L. A., Herzenberg L. A. Murine B cell differentiation lineages. J Exp Med. 1984 Apr 1;159(4):1169–1188. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.4.1169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoopes B. C., McClure W. R. Studies on the selectivity of DNA precipitation by spermine. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 24;9(20):5493–5504. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.20.5493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kung J. T., Sharrow S. O., Ahmed A., Habbersett R., Scher I., Paul W. E. B lymphocyte subpopulation defined by a rat monoclonal antibody, 14G8. J Immunol. 1982 May;128(5):2049–2056. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. R., Cartwright E. M., Brownlee G. G., Fedoroff N. V., Brown D. D. The nucleotide sequence of oocyte 5S DNA in Xenopus laevis. II. The GC-rich region. Cell. 1978 Apr;13(4):717–725. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90221-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M. A catalogue of splice junction sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):459–472. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy E. D., Roths J. B. A Y chromosome associated factor in strain BXSB producing accelerated autoimmunity and lymphoproliferation. Arthritis Rheum. 1979 Nov;22(11):1188–1194. doi: 10.1002/art.1780221105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagamine C. M., Michot J. L., Roberts C., Guénet J. L., Bishop C. E. Linkage of the murine steroid sulfatase locus, Sts, to sex reversed, Sxr: a genetic and molecular analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 25;15(22):9227–9238. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.22.9227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng S. Y., Gunning P., Eddy R., Ponte P., Leavitt J., Shows T., Kedes L. Evolution of the functional human beta-actin gene and its multi-pseudogene family: conservation of noncoding regions and chromosomal dispersion of pseudogenes. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2720–2732. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page D. C., Mosher R., Simpson E. M., Fisher E. M., Mardon G., Pollack J., McGillivray B., de la Chapelle A., Brown L. G. The sex-determining region of the human Y chromosome encodes a finger protein. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1091–1104. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90595-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roiha H., Miller J. R., Woods L. C., Glover D. M. Arrangements and rearrangements of sequences flanking the two types of rDNA insertion in D. melanogaster. Nature. 1981 Apr 30;290(5809):749–753. doi: 10.1038/290749a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scher I. The CBA/N mouse strain: an experimental model illustrating the influence of the X-chromosome on immunity. Adv Immunol. 1982;33:1–71. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60834-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel J. N., Turner C. A., Klinman D. M., Wilkinson M., Steinberg A. D., MacLeod C. L., Paul W. E., Davis M. M., Cohen D. I. Sequence analysis and expression of an X-linked, lymphocyte-regulated gene family (XLR). J Exp Med. 1987 Dec 1;166(6):1702–1715. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.6.1702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soares M. B., Schon E., Henderson A., Karathanasis S. K., Cate R., Zeitlin S., Chirgwin J., Efstratiadis A. RNA-mediated gene duplication: the rat preproinsulin I gene is a functional retroposon. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):2090–2103. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.2090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. DNA sequence analysis with a modified bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tso J. Y., Sun X. H., Kao T. H., Reece K. S., Wu R. Isolation and characterization of rat and human glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase cDNAs: genomic complexity and molecular evolution of the gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 11;13(7):2485–2502. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.7.2485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner A. M., Deininger P. L., Efstratiadis A. Nonviral retroposons: genes, pseudogenes, and transposable elements generated by the reverse flow of genetic information. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:631–661. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E. H. Molecular biology of the mouse Q region. Immunol Res. 1987;6(3):179–191. doi: 10.1007/BF02918090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]