Abstract
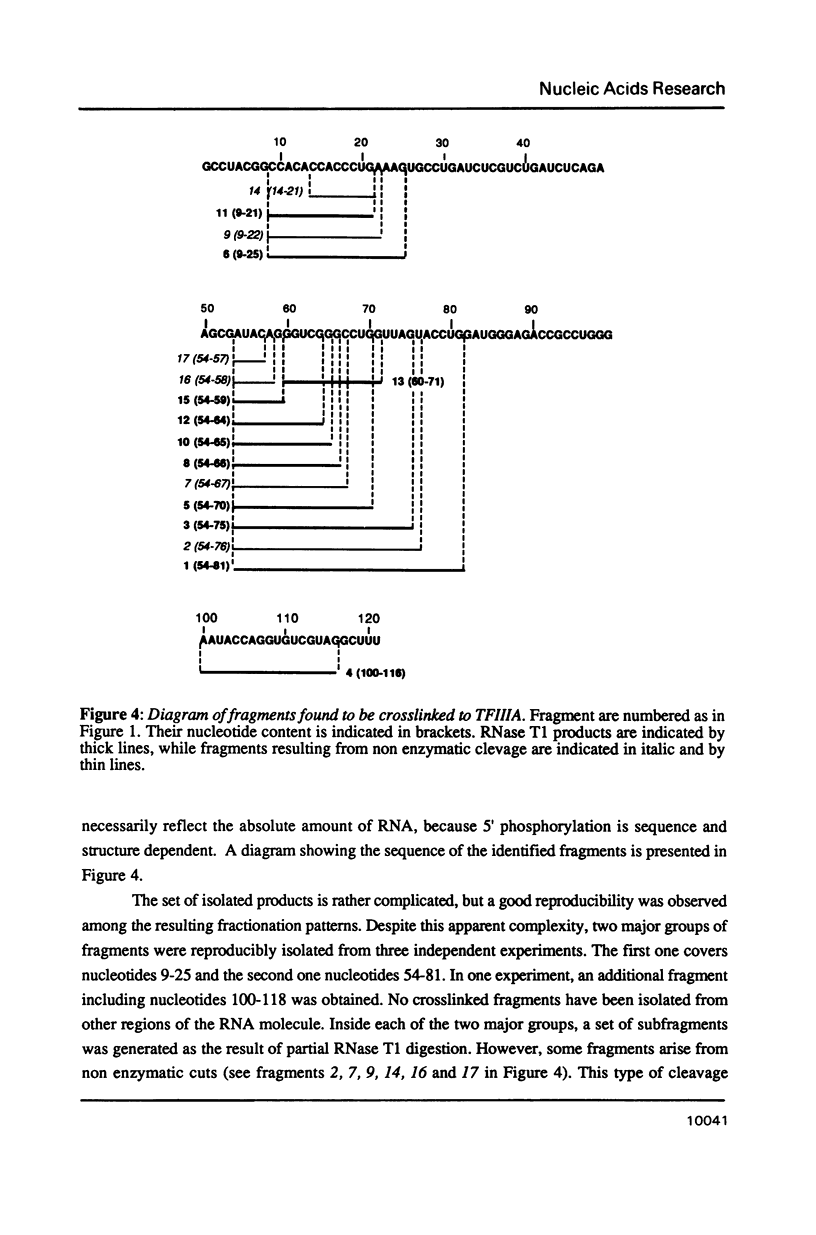
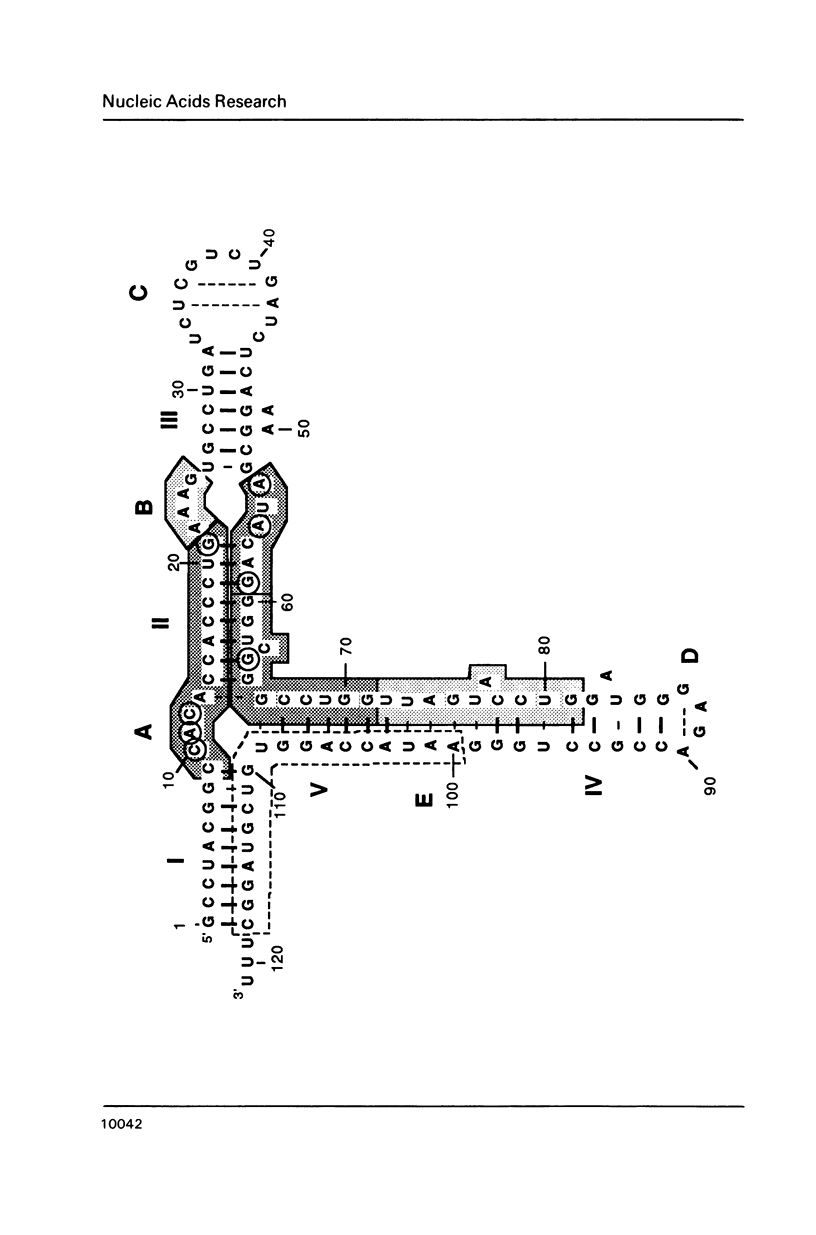
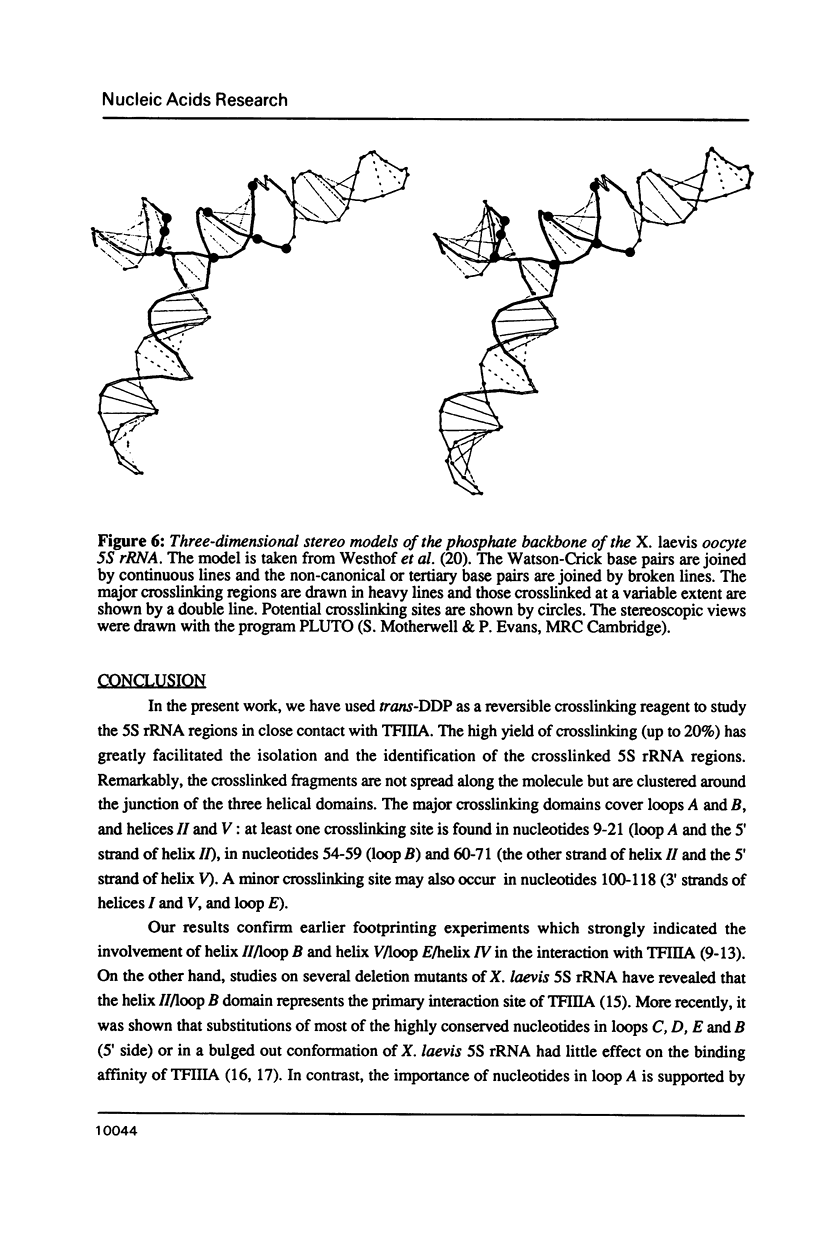
Trans-diamminnedichloroplatinum (II) was used to induce reversible crosslinks between 5S rRNA and TFIIIA within the 7S RNP particle from X. laevis immature oocyte. The crosslinked fragments have been unambiguously identified. These fragments exclusively arise from three RNA regions centered around the hinge region at the junction of the three helical domains. Major crosslinking sites are located in region 9-21 (comprising loops A and helix II) and region 54-71 (comprising loop B, helices II and V). A minor site is also found in the 3' part of helix I and helix V (region 100-120). Our results point to the crucial role of the junction region and of the three-dimensional folding of the RNA in the recognition of the 5S rRNA by TFIIIA.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen J., Delihas N. Characterization of RNA-protein interactions in 7 S ribonucleoprotein particles from Xenopus laevis oocytes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 25;261(6):2912–2917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen J., Delihas N., Hanas J. S., Wu C. W. 5S RNA structure and interaction with transcription factor A. 2. Ribonuclease probe of the 7S particle from Xenopus laevis immature oocytes and RNA exchange properties of the 7S particle. Biochemistry. 1984 Nov 20;23(24):5759–5766. doi: 10.1021/bi00319a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baudin F., Romaniuk P. J. A difference in the importance of bulged nucleotides and their parent base pairs in the binding of transcription factor IIIA to Xenopus 5S RNA and 5S RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 11;17(5):2043–2056. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.5.2043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. S., Sander C., Argos P. The primary structure of transcription factor TFIIIA has 12 consecutive repeats. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jul 8;186(2):271–274. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80723-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiansen J., Brown R. S., Sproat B. S., Garrett R. A. Xenopus transcription factor IIIA binds primarily at junctions between double helical stems and internal loops in oocyte 5S RNA. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):453–460. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04775.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donis-Keller H., Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Mapping adenines, guanines, and pyrimidines in RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Aug;4(8):2527–2538. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.8.2527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehresmann C., Moine H., Mougel M., Dondon J., Grunberg-Manago M., Ebel J. P., Ehresmann B. Cross-linking of initiation factor IF3 to Escherichia coli 30S ribosomal subunit by trans-diamminedichloroplatinum(II): characterization of two cross-linking sites in 16S rRNA; a possible way of functioning for IF3. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 25;14(12):4803–4821. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.12.4803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelke D. R., Ng S. Y., Shastry B. S., Roeder R. G. Specific interaction of a purified transcription factor with an internal control region of 5S RNA genes. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):717–728. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80048-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairall L., Rhodes D., Klug A. Mapping of the sites of protection on a 5 S RNA gene by the Xenopus transcription factor IIIA. A model for the interaction. J Mol Biol. 1986 Dec 5;192(3):577–591. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90278-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg A. M., King B. O., Roeder R. G. Xenopus 5S gene transcription factor, TFIIIA: characterization of a cDNA clone and measurement of RNA levels throughout development. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):479–489. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90455-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanas J. S., Bogenhagen D. F., Wu C. W. Cooperative model for the binding of Xenopus transcription factor A to the 5S RNA gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2142–2145. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber P. W., Wool I. G. Identification of the binding site on 5S rRNA for the transcription factor IIIA: proposed structure of a common binding site on 5S rRNA and on the gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1593–1597. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J., McLachlan A. D., Klug A. Repetitive zinc-binding domains in the protein transcription factor IIIA from Xenopus oocytes. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1609–1614. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03825.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Brown D. D. A specific transcription factor that can bind either the 5S RNA gene or 5S RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4170–4174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard B., Wegnez M. Isolation of a 7S particle from Xenopus laevis oocytes: a 5S RNA-protein complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):241–245. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieler T., Erdmann V. A. Isolation and characterization of a 7 S RNP particle from mature Xenopus laevis oocytes. FEBS Lett. 1983 Jul 4;157(2):283–287. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80562-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romaniuk P. J. Characterization of the RNA binding properties of transcription factor IIIA of Xenopus laevis oocytes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jul 25;13(14):5369–5387. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.14.5369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romaniuk P. J. The role of highly conserved single-stranded nucleotides of Xenopus 5S RNA in the binding of transcription factor IIIA. Biochemistry. 1989 Feb 7;28(3):1388–1395. doi: 10.1021/bi00429a067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romaniuk P. J., de Stevenson I. L., Ehresmann C., Romby P., Ehresmann B. A comparison of the solution structures and conformational properties of the somatic and oocyte 5S rRNAs of Xenopus laevis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 25;16(5):2295–2312. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.5.2295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romaniuk P. J., de Stevenson I. L., Wong H. H. Defining the binding site of Xenopus transcription factor IIIA on 5S RNA using truncated and chimeric 5S RNA molecules. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 25;15(6):2737–2755. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.6.2737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakonju S., Brown D. D., Engelke D., Ng S. Y., Shastry B. S., Roeder R. G. The binding of a transcription factor to deletion mutants of a 5S ribosomal RNA gene. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):665–669. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90429-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tukalo M. A., Kubler M. D., Kern D., Mougel M., Ehresmann C., Ebel J. P., Ehresmann B., Giegé R. trans-Diamminedichloroplatinum(II), a reversible RNA-protein cross-linking agent. Application to the ribosome and to an aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase/tRNA complex. Biochemistry. 1987 Aug 11;26(16):5200–5208. doi: 10.1021/bi00390a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westhof E., Romby P., Romaniuk P. J., Ebel J. P., Ehresmann C., Ehresmann B. Computer modeling from solution data of spinach chloroplast and of Xenopus laevis somatic and oocyte 5 S rRNAs. J Mol Biol. 1989 May 20;207(2):417–431. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90264-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikman F. P., Romby P., Metz M. H., Reinbolt J., Clark B. F., Ebel J. P., Ehresmann C., Ehresmann B. Crosslinking of elongation factor Tu to tRNA(Phe) by trans-diamminedichloroplatinum (II). Characterization of two crosslinking sites in the tRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 24;15(14):5787–5801. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.14.5787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]