Abstract
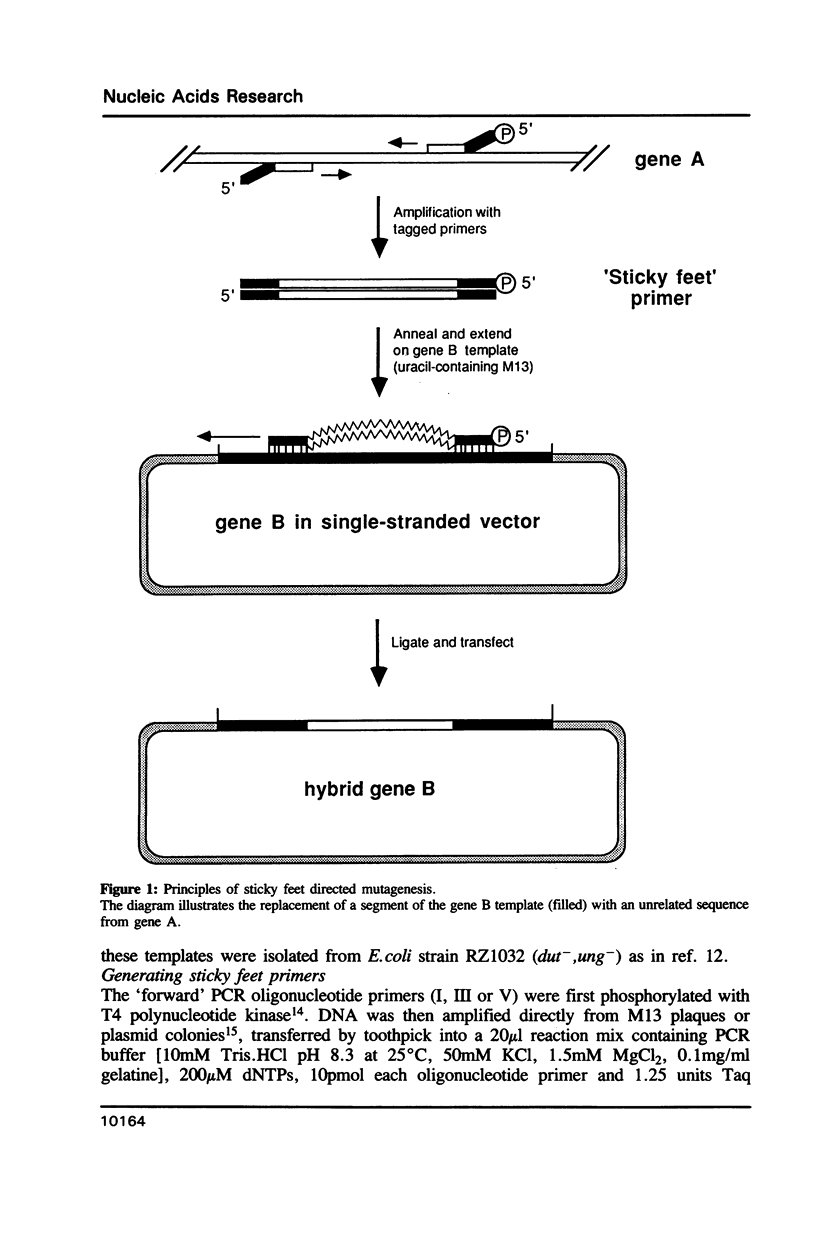
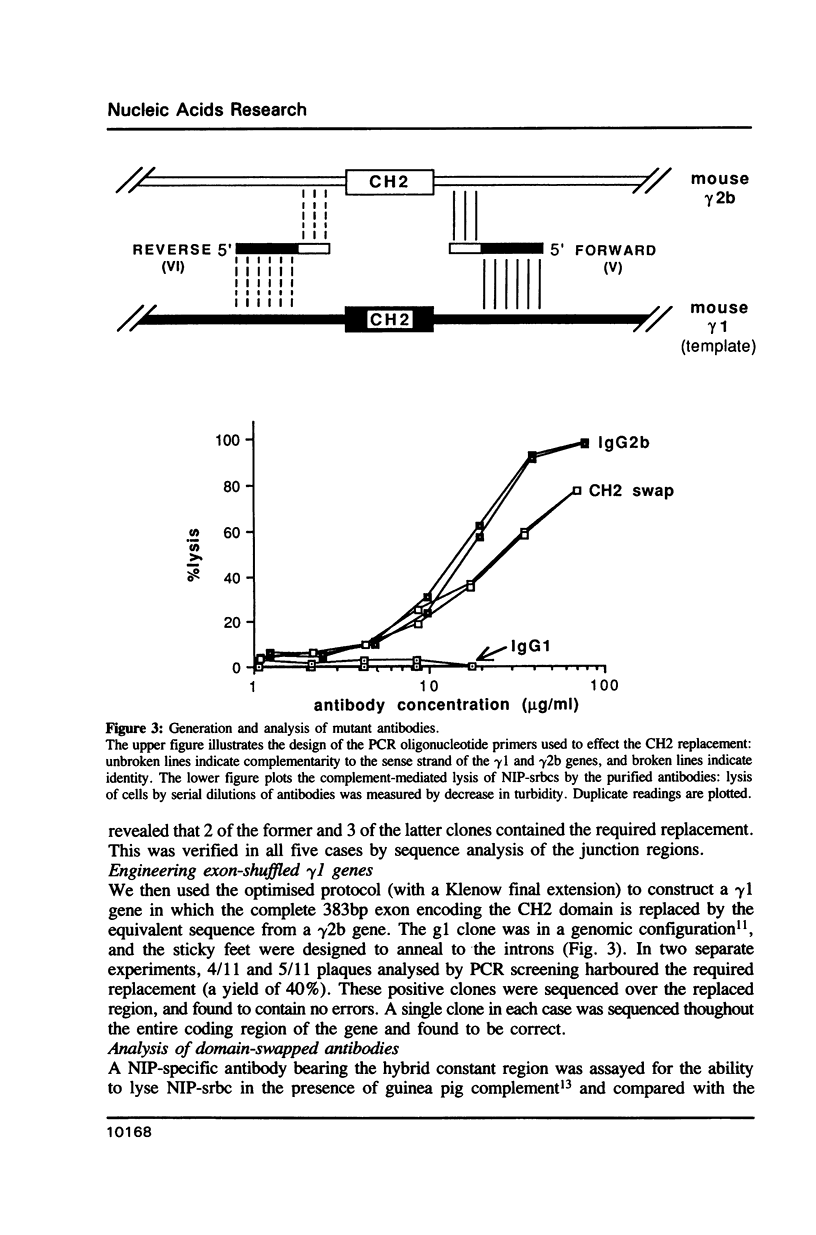
We describe a novel technique for precisely cutting and pasting two DNA sequences without using restriction sites. The method is based on site-directed mutagenesis and uses a long primer, generated by the polymerase chain reaction (PCR), to transfer large segments of DNA into a single-stranded template. The primer anneals to the template by virtue of 'sticky feet' sequences (complementary to the template) which are introduced at the ends of the primer by the PCR. Yields of desired recombinants were high (approximately 36%) and the transplanted sequences (approximately 400bp) free of errors. We have used this technique to swap CH2 domains between two mouse antibodies, and find that this domain can carry features critical for triggering complement lysis, in addition to the C1q binding motif.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brüggemann M., Teale C., Clark M., Bindon C., Waldmann H. A matched set of rat/mouse chimeric antibodies. Identification and biological properties of rat H chain constant regions mu, gamma 1, gamma 2a, gamma 2b, gamma 2c, epsilon, and alpha. J Immunol. 1989 May 1;142(9):3145–3150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton D. R., Boyd J., Brampton A. D., Easterbrook-Smith S. B., Emanuel E. J., Novotny J., Rademacher T. W., van Schravendijk M. R., Sternberg M. J., Dwek R. A. The Clq receptor site on immunoglobulin G. Nature. 1980 Nov 27;288(5789):338–344. doi: 10.1038/288338a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter P., Bedouelle H., Winter G. Improved oligonucleotide site-directed mutagenesis using M13 vectors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 25;13(12):4431–4443. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.12.4431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter P. Improved oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis using M13 vectors. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:382–403. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54086-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dangl J. L., Wensel T. G., Morrison S. L., Stryer L., Herzenberg L. A., Oi V. T. Segmental flexibility and complement fixation of genetically engineered chimeric human, rabbit and mouse antibodies. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):1989–1994. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03037.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan A. R., Winter G. The binding site for C1q on IgG. Nature. 1988 Apr 21;332(6166):738–740. doi: 10.1038/332738a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emanuel E. J., Brampton A. D., Gagnon J., Dwek R. A. Chemical verification of the C1q receptor site on IgG. FEBS Lett. 1982 Jan 25;137(2):298–302. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80371-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Güssow D., Clackson T. Direct clone characterization from plaques and colonies by the polymerase chain reaction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 25;17(10):4000–4000. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.10.4000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemsley A., Arnheim N., Toney M. D., Cortopassi G., Galas D. J. A simple method for site-directed mutagenesis using the polymerase chain reaction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 25;17(16):6545–6551. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.16.6545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi R., Krummel B., Saiki R. K. A general method of in vitro preparation and specific mutagenesis of DNA fragments: study of protein and DNA interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7351–7367. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honjo T., Obata M., Yamawaki-Katoaka Y., Kataoka T., Kawakami T., Takahashi N., Mano Y. Cloning and complete nucleotide sequence of mouse immunoglobulin gamma 1 chain gene. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):559–568. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90072-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton R. M., Hunt H. D., Ho S. N., Pullen J. K., Pease L. R. Engineering hybrid genes without the use of restriction enzymes: gene splicing by overlap extension. Gene. 1989 Apr 15;77(1):61–68. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90359-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Innis M. A., Myambo K. B., Gelfand D. H., Brow M. A. DNA sequencing with Thermus aquaticus DNA polymerase and direct sequencing of polymerase chain reaction-amplified DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9436–9440. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenman D. E., Dorrington K. J., Painter R. H. The structure and function of immunoglobulin domains. II. The importance of interchain disulfide bonds and the possible role of molecular flexibility in the interaction between immunoglobulin G and complement. J Immunol. 1975 Jun;114(6):1726–1729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClary J. A., Witney F., Geisselsoder J. Efficient site-directed in vitro mutagenesis using phagemid vectors. Biotechniques. 1989 Mar;7(3):282–289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison S. L., Canfield S., Porter S., Tan L. K., Tao M. H., Wims L. A. Production and characterization of genetically engineered antibody molecules. Clin Chem. 1988 Sep;34(9):1668–1675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuberger M. S., Rajewsky K. Activation of mouse complement by monoclonal mouse antibodies. Eur J Immunol. 1981 Dec;11(12):1012–1016. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830111212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuberger M. S., Williams G. T., Fox R. O. Recombinant antibodies possessing novel effector functions. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):604–608. doi: 10.1038/312604a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newton C. R., Graham A., Heptinstall L. E., Powell S. J., Summers C., Kalsheker N., Smith J. C., Markham A. F. Analysis of any point mutation in DNA. The amplification refractory mutation system (ARMS). Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 11;17(7):2503–2516. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.7.2503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell L. M., Wallis S. C., Pease R. J., Edwards Y. H., Knott T. J., Scott J. A novel form of tissue-specific RNA processing produces apolipoprotein-B48 in intestine. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):831–840. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90510-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhoeyen M., Milstein C., Winter G. Reshaping human antibodies: grafting an antilysozyme activity. Science. 1988 Mar 25;239(4847):1534–1536. doi: 10.1126/science.2451287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Smith M. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis using M13-derived vectors: an efficient and general procedure for the production of point mutations in any fragment of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 25;10(20):6487–6500. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.20.6487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]