Abstract
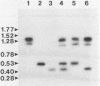
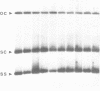
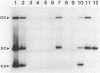
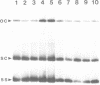
Tomato golden mosaic geminivirus has a genome of two single-stranded (ss) DNA components, A and B. An almost identical 'common' region in DNA A and DNA B is thought to contain sequence elements controlling replication and transcription. Hence investigation of sequences important for DNA replication by in vitro mutagenesis is complicated by possible effects on the transcription of genes for replication proteins. To overcome this problem, transgenic plants expressing open reading frames (ORFs) of DNA A from an enhanced cauliflower mosaic virus 35S RNA promoter were constructed and tested for their ability to support the replication of DNA B and DNA B mutants. The results show that plants transgenic for ORF AL1 are able to support the replication of the double-stranded (ds) forms of DNA B, but that ORF AL2 is required in addition to produce ssDNA B. ORFs AL3, BL1 or BR1 were not required for replication of ds or ssDNA B. To the best of our knowledge this is the first time that essential replication proteins of a geminivirus have been expressed constitutively from a plant genome without giving rise to replicating DNA A molecules, thereby allowing DNA B to replicate alone. Such transgenic plants should enable not only the mutational analysis of sequence elements within the replication origin region, but also the construction of a new generation of vectors for gene amplification in plants, based on a minimal virus replicon.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bevan M. Binary Agrobacterium vectors for plant transformation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 26;12(22):8711–8721. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.22.8711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elmer J. S., Brand L., Sunter G., Gardiner W. E., Bisaro D. M., Rogers S. G. Genetic analysis of the tomato golden mosaic virus. II. The product of the AL1 coding sequence is required for replication. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 25;16(14B):7043–7060. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.14.7043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner W. E., Sunter G., Brand L., Elmer J. S., Rogers S. G., Bisaro D. M. Genetic analysis of tomato golden mosaic virus: the coat protein is not required for systemic spread or symptom development. EMBO J. 1988 Apr;7(4):899–904. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02894.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton W. D., Bisaro D. M., Coutts R. H., Buck K. W. Demonstration of the bipartite nature of the genome of a single-stranded DNA plant virus by infection with the cloned DNA components. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 11;11(21):7387–7396. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.21.7387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton W. D., Stein V. E., Coutts R. H., Buck K. W. Complete nucleotide sequence of the infectious cloned DNA components of tomato golden mosaic virus: potential coding regions and regulatory sequences. EMBO J. 1984 Sep;3(9):2197–2205. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02114.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanley-Bowdoin L., Elmer J. S., Rogers S. G. Transient expression of heterologous RNAs using tomato golden mosaic virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 25;16(22):10511–10528. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.22.10511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes R. J., Coutts R. H., Buck K. W. Stability and expression of bacterial genes in replicating geminivirus vectors in plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 11;17(7):2391–2403. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.7.2391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferson R. A., Kavanagh T. A., Bevan M. W. GUS fusions: beta-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):3901–3907. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02730.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay R., Chan A., Daly M., McPherson J. Duplication of CaMV 35S Promoter Sequences Creates a Strong Enhancer for Plant Genes. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1299–1302. doi: 10.1126/science.236.4806.1299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathe R., Kieny M. P., Skory S., Lecocq J. P. Linker tailing: unphosphorylated linker oligonucleotides for joining DNA termini. DNA. 1984;3(2):173–182. doi: 10.1089/dna.1984.3.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odell J. T., Nagy F., Chua N. H. Identification of DNA sequences required for activity of the cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):810–812. doi: 10.1038/313810a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt D., Laws P., Griffith J. Complex of bacteriophage M13 single-stranded DNA and gene 5 protein. J Mol Biol. 1974 Feb 5;82(4):425–439. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90239-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers S. G., Bisaro D. M., Horsch R. B., Fraley R. T., Hoffmann N. L., Brand L., Elmer J. S., Lloyd A. M. Tomato golden mosaic virus A component DNA replicates autonomously in transgenic plants. Cell. 1986 May 23;45(4):593–600. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90291-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sunter G., Gardiner W. E., Bisaro D. M. Identification of tomato golden mosaic virus-specific RNAs in infected plants. Virology. 1989 May;170(1):243–250. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90372-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]