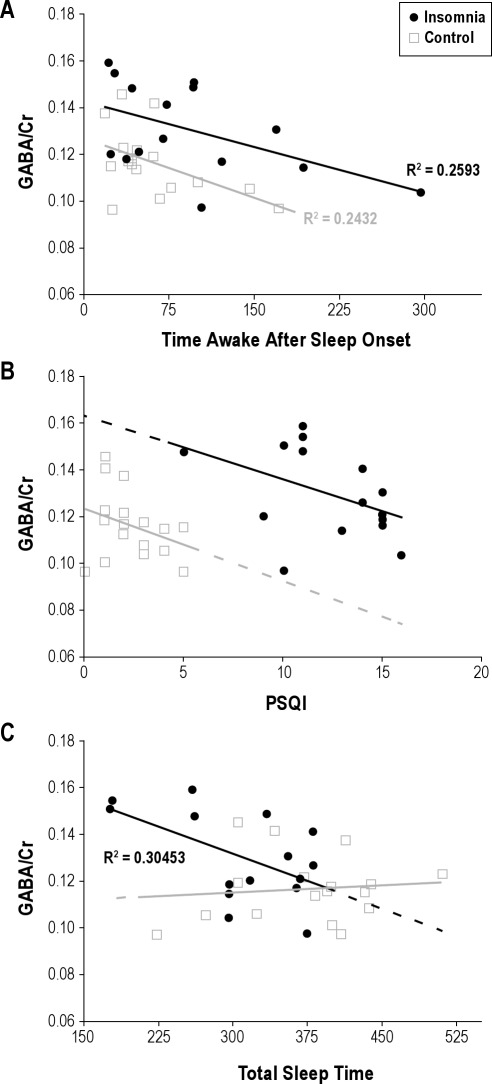
Figure 2.
(A) GABA/Cr is negatively correlated to time awake after sleep onset in persons with primary insomnia (linear correlation, P < 0.05) and in controls (P < 0.05). There is no difference in R between groups (Rdiff = 0.021 ± 0.561 [90% confidence interval]). Mean GABA/Cr is higher in persons with insomnia (P < 0.05). (B) Relationship between GABA/Cr and PSQI in the insomnia and control groups. A trend toward a significant correlation was observed in the insomnia group (R = 0.19, P < 0.1). The projected y-intercepts are non-overlapping at confidence intervals of ∼90% (0.163 ± 0.03 [90% CI] in the insomnia group and 0.123 ± 0.01 [90% CI] in the control group). (C) Shorter total sleep time is correlated with higher GABA/Cr in persons with primary insomnia (P < 0.05) but not in controls.