Abstract
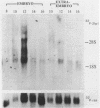
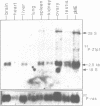
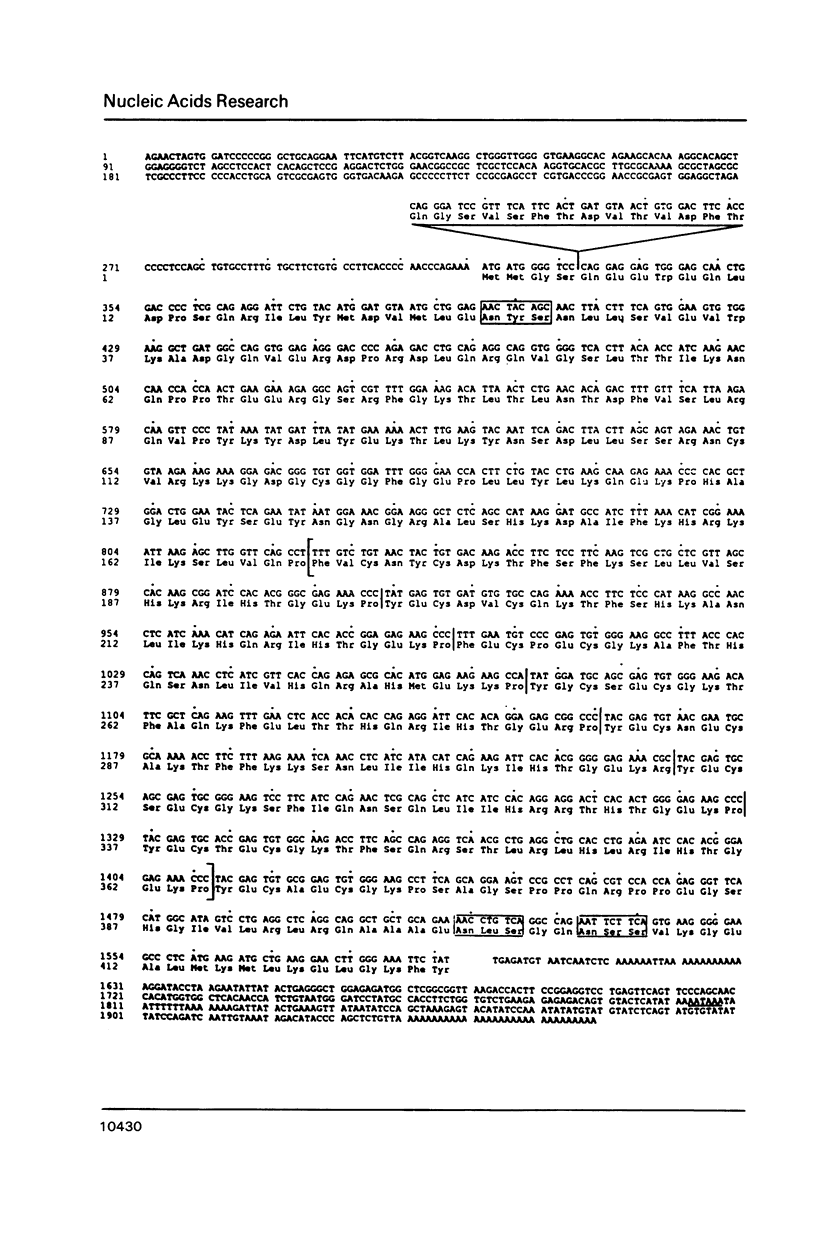
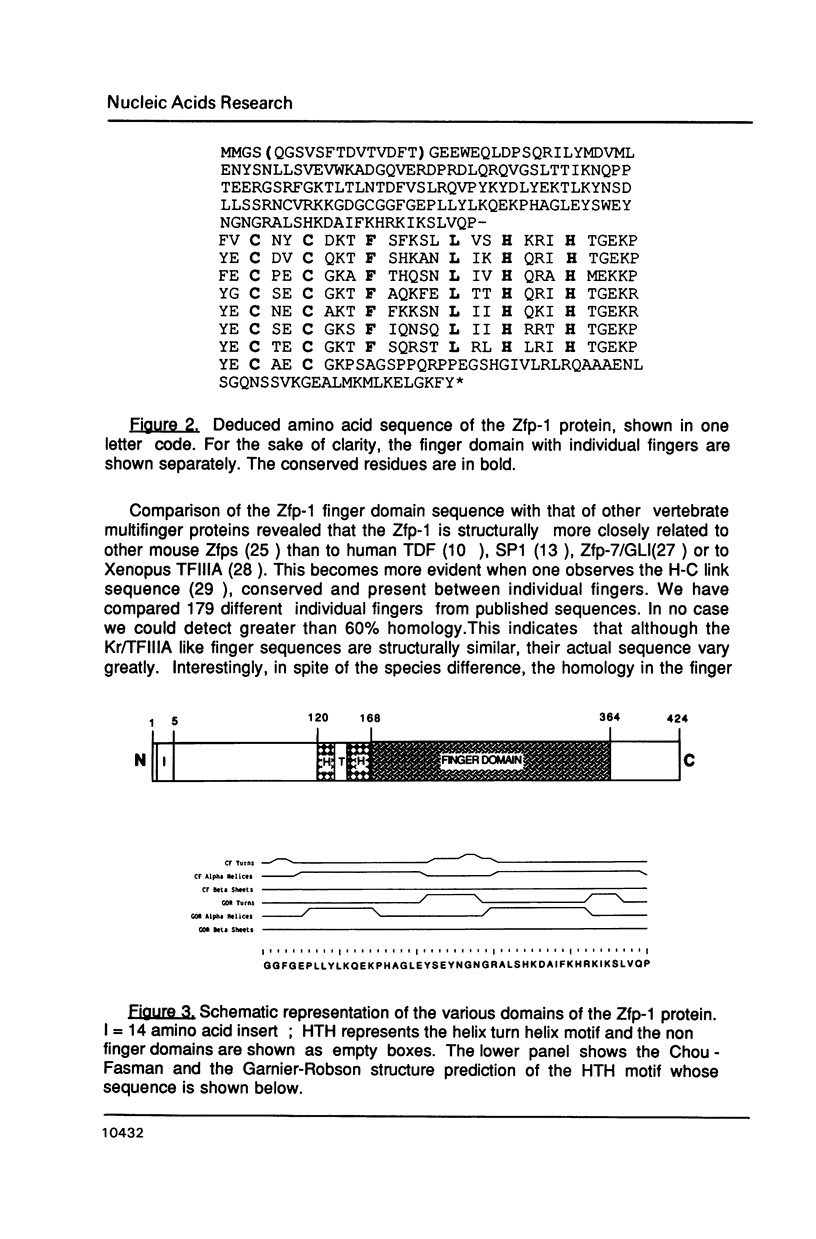
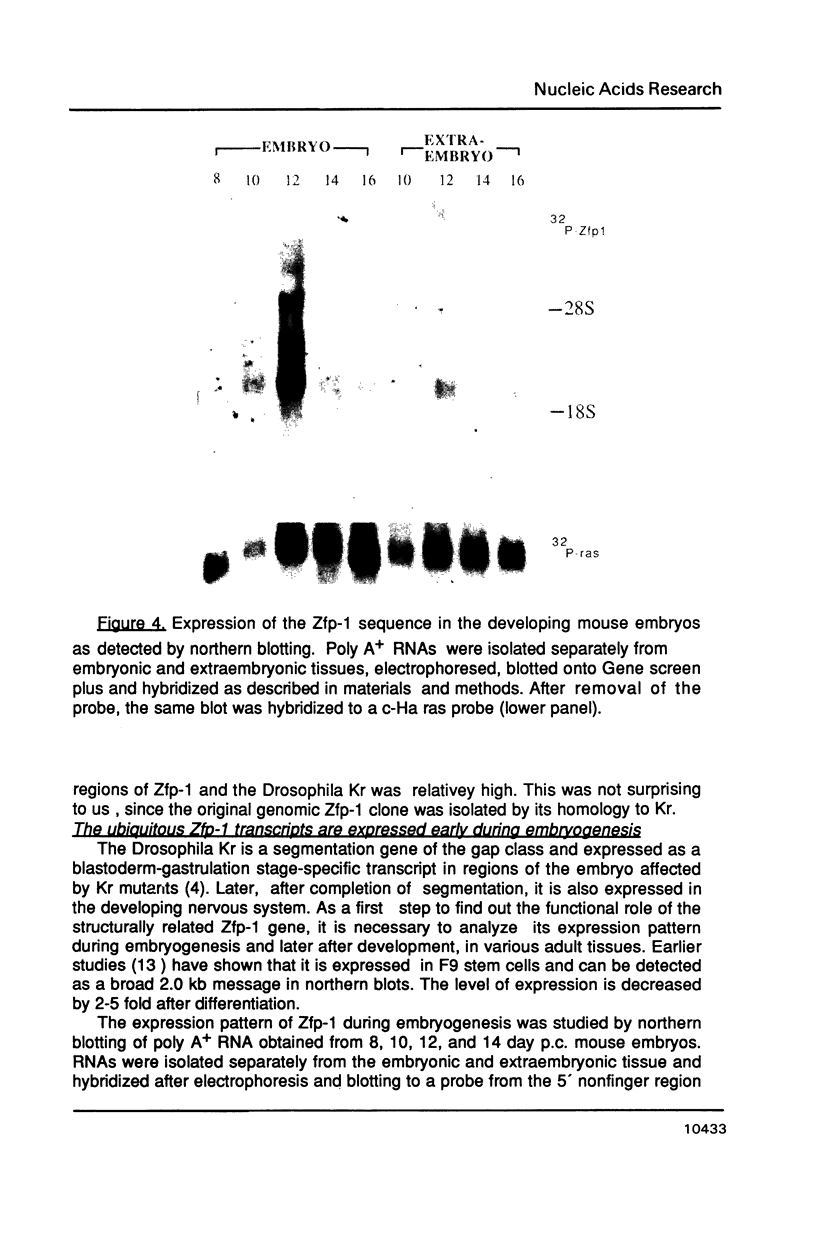
Zinc finger proteins (Zfp) are encoded by a large family of genes present in many organisms including yeast and human. Some of them are transcriptional activators and bind specifically to DNA by zinc mediated folded structures commonly known as zinc fingers. The Drosophila Krüppel (Kr) is a segmentation gene and encodes a zinc finger protein. Using a probe from the finger domain of Kr, we have isolated a structurally related gene Zfp-1 from the mouse. In this paper, we report the complete nucleotide sequence of two cDNA clones and the amino acid sequence deduced from them. The putative Zfp-1 protein contains in addition to 7 zinc fingers, two helix-turn-helix motifs. During murine embryogenesis, the Zfp-1 was found to express at a peak level in day 12 embryos. The ubiquitously expressed Zfp-1 gene is located in the 16q region on mouse chromosome 8, between the uvomorulin and the tyrosine amino transferase genes.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beato M. Gene regulation by steroid hormones. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):335–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90237-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellefroid E. J., Lecocq P. J., Benhida A., Poncelet D. A., Belayew A., Martial J. A. The human genome contains hundreds of genes coding for finger proteins of the Krüppel type. DNA. 1989 Jul-Aug;8(6):377–387. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1989.8.377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg J. M. DNA binding specificity of steroid receptors. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1065–1068. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90042-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. S., Argos P. Fingers and helices. Nature. 1986 Nov 20;324(6094):215–215. doi: 10.1038/324215a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. S., Sander C., Argos P. The primary structure of transcription factor TFIIIA has 12 consecutive repeats. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jul 8;186(2):271–274. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80723-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavrier P., Lemaire P., Revelant O., Bravo R., Charnay P. Characterization of a mouse multigene family that encodes zinc finger structures. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1319–1326. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavrier P., Zerial M., Lemaire P., Almendral J., Bravo R., Charnay P. A gene encoding a protein with zinc fingers is activated during G0/G1 transition in cultured cells. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):29–35. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02780.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury K., Deutsch U., Gruss P. A multigene family encoding several "finger" structures is present and differentially active in mammalian genomes. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):771–778. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90074-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury K., Dressler G., Breier G., Deutsch U., Gruss P. The primary structure of the murine multifinger gene mKr2 and its specific expression in developing and adult neurons. EMBO J. 1988 May;7(5):1345–1353. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02950.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury K., Rohdewohld H., Gruss P. Specific and ubiquitous expression of different Zn finger protein genes in the mouse. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 11;16(21):9995–10011. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.21.9995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielsen M., Hinck L., Ringold G. M. Two amino acids within the knuckle of the first zinc finger specify DNA response element activation by the glucocorticoid receptor. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1131–1138. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90050-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dressler G. R., Gruss P. Do multigene families regulate vertebrate development? Trends Genet. 1988 Aug;4(8):214–219. doi: 10.1016/s0168-9525(88)80003-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emini E. A., Hughes J. V., Perlow D. S., Boger J. Induction of hepatitis A virus-neutralizing antibody by a virus-specific synthetic peptide. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):836–839. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.836-839.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M., Hollenberg S. M. Zinc fingers: gilt by association. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90522-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. The steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):889–895. doi: 10.1126/science.3283939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahrner K., Hogan B. L., Flavell R. A. Transcription of H-2 and Qa genes in embryonic and adult mice. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1265–1271. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02363.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman L. P., Luisi B. F., Korszun Z. R., Basavappa R., Sigler P. B., Yamamoto K. R. The function and structure of the metal coordination sites within the glucocorticoid receptor DNA binding domain. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):543–546. doi: 10.1038/334543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier J., Osguthorpe D. J., Robson B. Analysis of the accuracy and implications of simple methods for predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guénet J. L. The contribution of wild derived mouse inbred strains to gene mapping methodology. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1986;127:109–113. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-71304-0_13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T., Carner K. R., Masiarz F. R., Tjian R. Isolation of cDNA encoding transcription factor Sp1 and functional analysis of the DNA binding domain. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1079–1090. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90594-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinzler K. W., Ruppert J. M., Bigner S. H., Vogelstein B. The GLI gene is a member of the Kruppel family of zinc finger proteins. Nature. 1988 Mar 24;332(6162):371–374. doi: 10.1038/332371a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knipple D. C., Seifert E., Rosenberg U. B., Preiss A., Jäckle H. Spatial and temporal patterns of Krüppel gene expression in early Drosophila embryos. Nature. 1985 Sep 5;317(6032):40–44. doi: 10.1038/317040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Comparison of initiation of protein synthesis in procaryotes, eucaryotes, and organelles. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Mar;47(1):1–45. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.1.1-45.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mader S., Kumar V., de Verneuil H., Chambon P. Three amino acids of the oestrogen receptor are essential to its ability to distinguish an oestrogen from a glucocorticoid-responsive element. Nature. 1989 Mar 16;338(6212):271–274. doi: 10.1038/338271a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milbrandt J. A nerve growth factor-induced gene encodes a possible transcriptional regulatory factor. Science. 1987 Nov 6;238(4828):797–799. doi: 10.1126/science.3672127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J., McLachlan A. D., Klug A. Repetitive zinc-binding domains in the protein transcription factor IIIA from Xenopus oocytes. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1609–1614. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03825.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nüsslein-Volhard C., Wieschaus E. Mutations affecting segment number and polarity in Drosophila. Nature. 1980 Oct 30;287(5785):795–801. doi: 10.1038/287795a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlendorf D. H., Matthews B. W. Structural studies of protein-nucleic acid interactions. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1983;12:259–284. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.12.060183.001355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page D. C., Mosher R., Simpson E. M., Fisher E. M., Mardon G., Pollack J., McGillivray B., de la Chapelle A., Brown L. G. The sex-determining region of the human Y chromosome encodes a finger protein. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1091–1104. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90595-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Brownlee G. G. 3' non-coding region sequences in eukaryotic messenger RNA. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):211–214. doi: 10.1038/263211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuh R., Aicher W., Gaul U., Côté S., Preiss A., Maier D., Seifert E., Nauber U., Schröder C., Kemler R. A conserved family of nuclear proteins containing structural elements of the finger protein encoded by Krüppel, a Drosophila segmentation gene. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):1025–1032. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90817-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. P., Tamkun J. W., Hartzell G. W., 3rd The structure and function of the homeodomain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jul 28;989(1):25–48. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(89)90033-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih C., Shilo B. Z., Goldfarb M. P., Dannenberg A., Weinberg R. A. Passage of phenotypes of chemically transformed cells via transfection of DNA and chromatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5714–5718. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka I., Appelt K., Dijk J., White S. W., Wilson K. S. 3-A resolution structure of a protein with histone-like properties in prokaryotes. Nature. 1984 Aug 2;310(5976):376–381. doi: 10.1038/310376a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umesono K., Evans R. M. Determinants of target gene specificity for steroid/thyroid hormone receptors. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1139–1146. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90051-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]