Abstract
We describe the construction of a new generation of vectors (pRE) for the hyperexpression of lethal gene products such as adenylate cyclase in Escherichia coli. The pRE vectors are based on the lambda PL promoter and lambda cII ribosome binding site described by Shimatake and Rosenberg (Nature, 292, 128-132, 1981). They have a unique NdeI restriction endonuclease site 3' of the lambda cII ribosome binding site that includes the ATG initiation codon, multilinker cloning sites 3' to the NdeI site, and two lambda transcription terminators 5' and 3' of the lambda PL promoter to eliminate nonspecific transcription and reduce leaky PL transcription, respectively. For hyperexpression of adenylate cyclase, tight control of transcription was necessary since elevation of cAMP levels above the physiological range is lethal to E. coli. Lethality associated with the overproduction of adenylate cyclase was shown to be mediated through the cAMP receptor protein. We used this expression system to overproduce adenylate cyclase 7500 fold, corresponding to 30% of the total cellular protein. Under these conditions the enzyme precipitated with significant loss of activity. Reducing the rate and amount of adenylate cyclase expression to 16% of the total cell protein produced one fourth of the enzyme in a soluble form with high specific activity. The soluble adenylate cyclase was purified to near homogeneity.
Full text
PDF



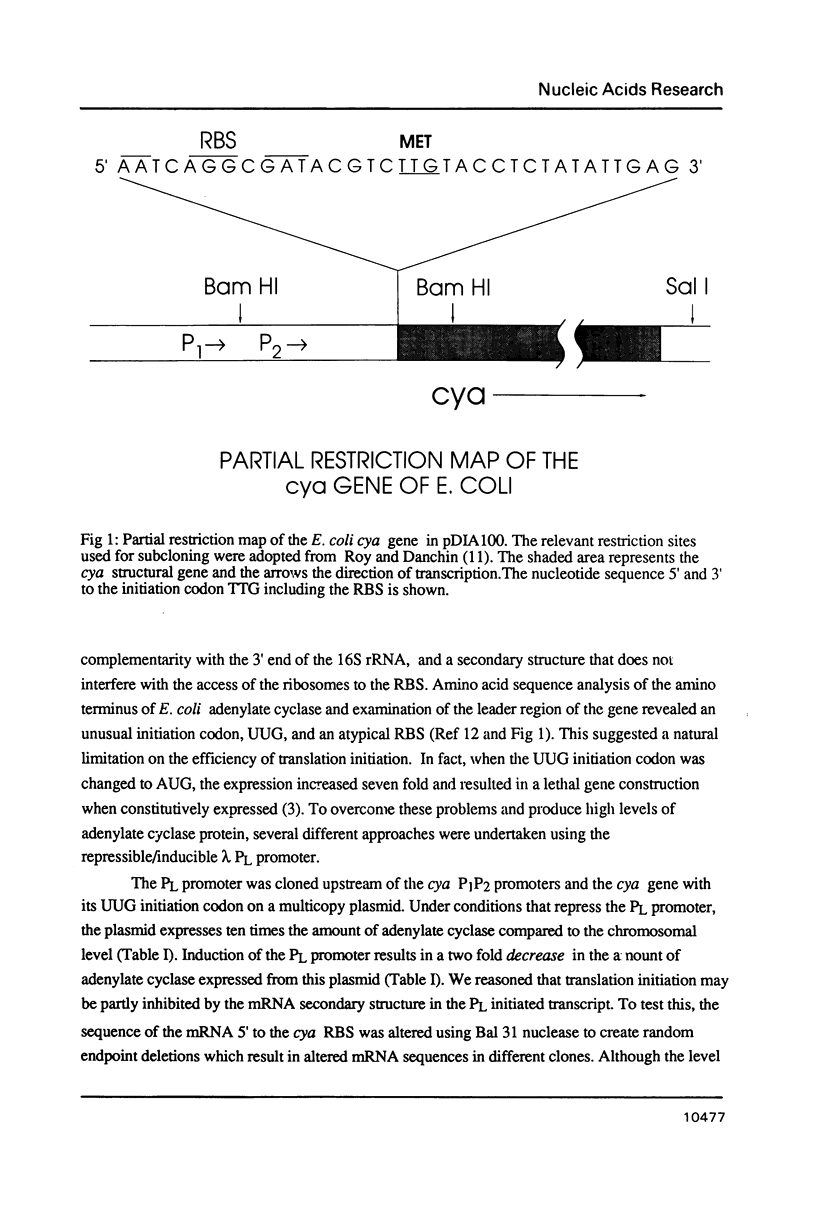
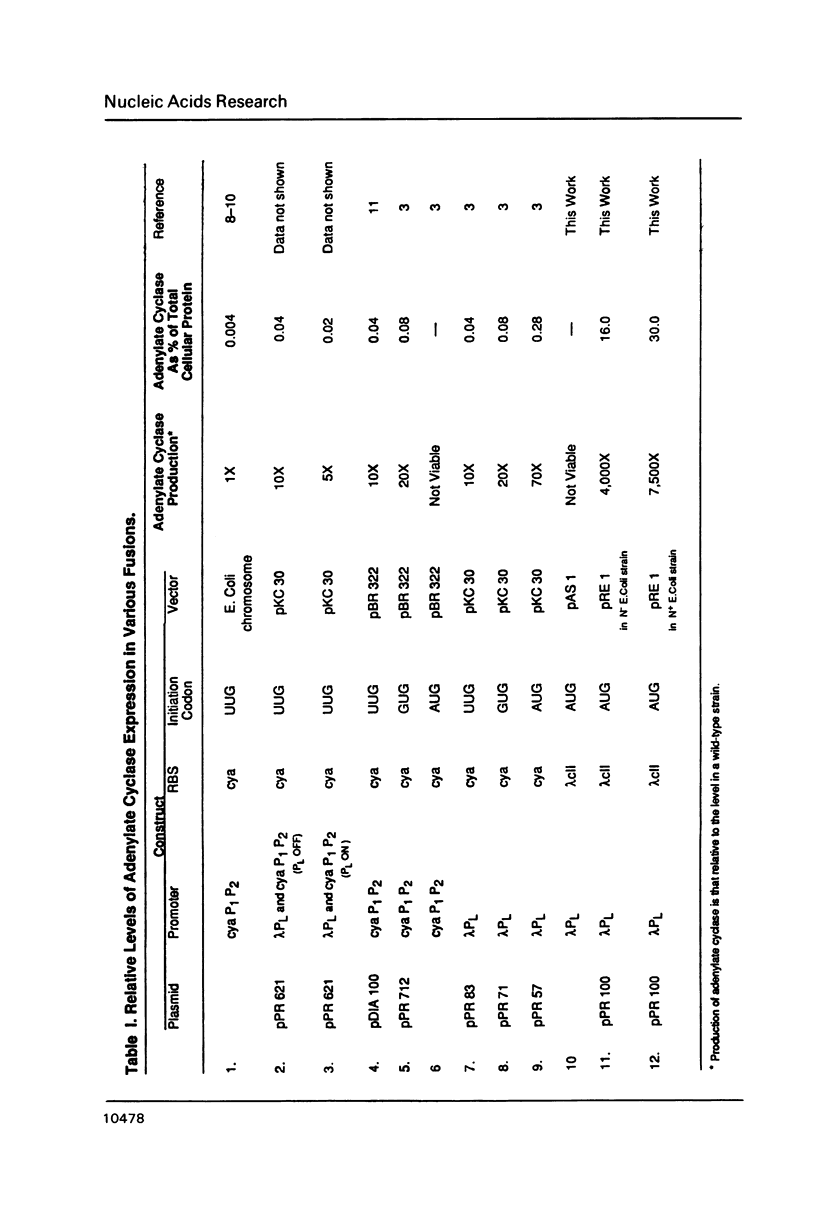

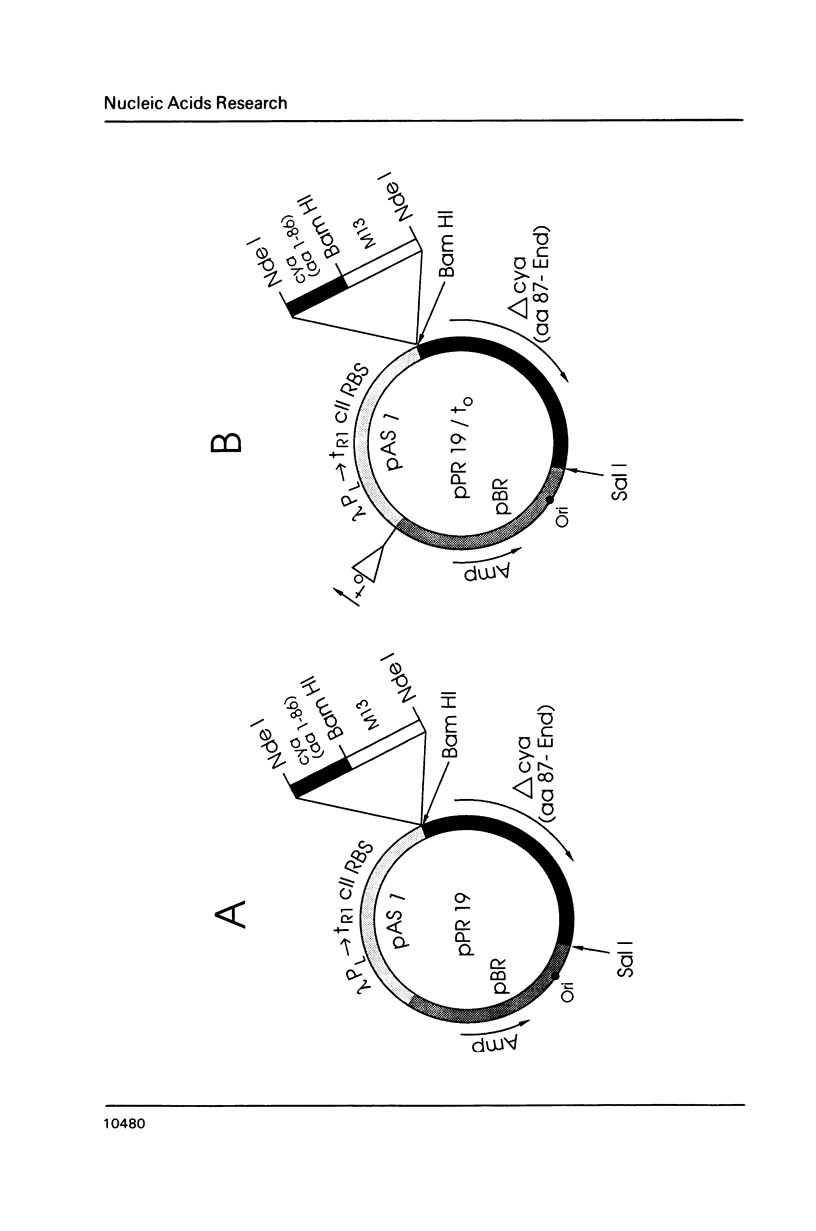


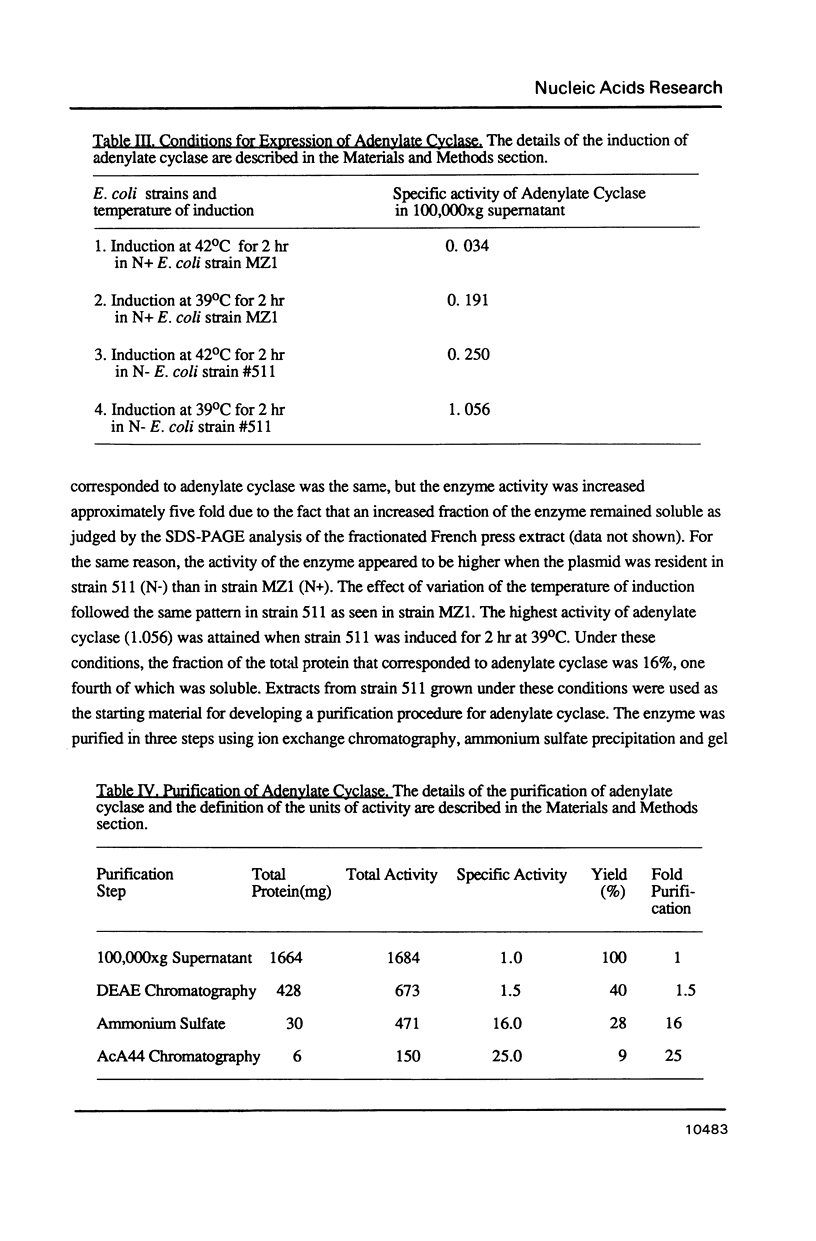




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aiba H., Mori K., Tanaka M., Ooi T., Roy A., Danchin A. The complete nucleotide sequence of the adenylate cyclase gene of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 21;12(24):9427–9440. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.24.9427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aiba H. Transcription of the Escherichia coli adenylate cyclase gene is negatively regulated by cAMP-cAMP receptor protein. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):3063–3070. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard H. U., Helinski D. R. Use of the lambda phage promoter PL to promote gene expression in hybrid plasmid cloning vehicles. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:482–492. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68037-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C. A rapid alkaline extraction method for the isolation of plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:243–255. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00059-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brickman E., Soll L., Beckwith J. Genetic characterization of mutations which affect catabolite-sensitive operons in Escherichia coli, including deletions of the gene for adenyl cyclase. J Bacteriol. 1973 Nov;116(2):582–587. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.2.582-587.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter P., Bedouelle H., Winter G. Improved oligonucleotide site-directed mutagenesis using M13 vectors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 25;13(12):4431–4443. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.12.4431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danchin A., Guiso N., Roy A., Ullmann A. Identification of the Escherichia coli cya gene product as authentic adenylate cyclase. J Mol Biol. 1984 May 25;175(3):403–408. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90356-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Robertis E. M., Jr, Judewicz R. D., Torres H. N. On the control mechanism of bacterial growth by cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Dec 10;55(3):758–764. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91209-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland M. M., Leib T. K., Gerlt J. A. Isolation and characterization of a small catalytic domain released from the adenylate cyclase from Escherichia coli by digestion with trypsin. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 15;263(29):14661–14668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liberman E., Reddy P., Gazdar C., Peterkofsky A. The Escherichia coli adenylate cyclase complex. Stimulation by potassium and phosphate. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 10;260(7):4075–4081. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenney K., Shimatake H., Court D., Schmeissner U., Brady C., Rosenberg M. A system to study promoter and terminator signals recognized by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Gene Amplif Anal. 1981;2:383–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai K., Thøgersen H. C. Generation of beta-globin by sequence-specific proteolysis of a hybrid protein produced in Escherichia coli. 1984 Jun 28-Jul 4Nature. 309(5971):810–812. doi: 10.1038/309810a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy P., Meadow N., Roseman S., Peterkofsky A. Reconstitution of regulatory properties of adenylate cyclase in Escherichia coli extracts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8300–8304. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy P., Miller D., Peterkofsky A. Stimulation of Escherichia coli adenylate cyclase activity by elongation factor Tu, a GTP-binding protein essential for protein synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 5;261(25):11448–11451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy P., Peterkofsky A., McKenney K. Translational efficiency of the Escherichia coli adenylate cyclase gene: mutating the UUG initiation codon to GUG or AUG results in increased gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5656–5660. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reizer J., Sutrina S. L., Saier M. H., Stewart G. C., Peterkofsky A., Reddy P. Mechanistic and physiological consequences of HPr(ser) phosphorylation on the activities of the phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase system in gram-positive bacteria: studies with site-specific mutants of HPr. EMBO J. 1989 Jul;8(7):2111–2120. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03620.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Ho Y. S., Shatzman A. The use of pKc30 and its derivatives for controlled expression of genes. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:123–138. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01009-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy A., Danchin A. The cya locus of Escherichia coli K12: organization and gene products. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;188(3):465–471. doi: 10.1007/BF00330050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy A., Haziza C., Danchin A. Regulation of adenylate cyclase synthesis in Escherichia coli: nucleotide sequence of the control region. EMBO J. 1983;2(5):791–797. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01502.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabourin D., Beckwith J. Deletion of the Escherichia coli crp gene. J Bacteriol. 1975 Apr;122(1):338–340. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.1.338-340.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Hong G. F., Hill D. F., Petersen G. B. Nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage lambda DNA. J Mol Biol. 1982 Dec 25;162(4):729–773. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90546-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seth A., Lapis P., Vande Woude G. F., Papas T. High-level expression vectors to synthesize unfused proteins in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1986;42(1):49–57. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90149-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simatake H., Rosenberg M. Purified lambda regulatory protein cII positively activates promoters for lysogenic development. Nature. 1981 Jul 9;292(5819):128–132. doi: 10.1038/292128a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGEL H. J., BONNER D. M. Acetylornithinase of Escherichia coli: partial purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jan;218(1):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter G., Fersht A. R., Wilkinson A. J., Zoller M., Smith M. Redesigning enzyme structure by site-directed mutagenesis: tyrosyl tRNA synthetase and ATP binding. Nature. 1982 Oct 21;299(5885):756–758. doi: 10.1038/299756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J. K., Epstein W. Purification and characterization of adenylate cyclase from Escherichia coli K12. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):3750–3758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuber M., Patterson T. A., Court D. L. Analysis of nutR, a site required for transcription antitermination in phage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(13):4514–4518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.13.4514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




