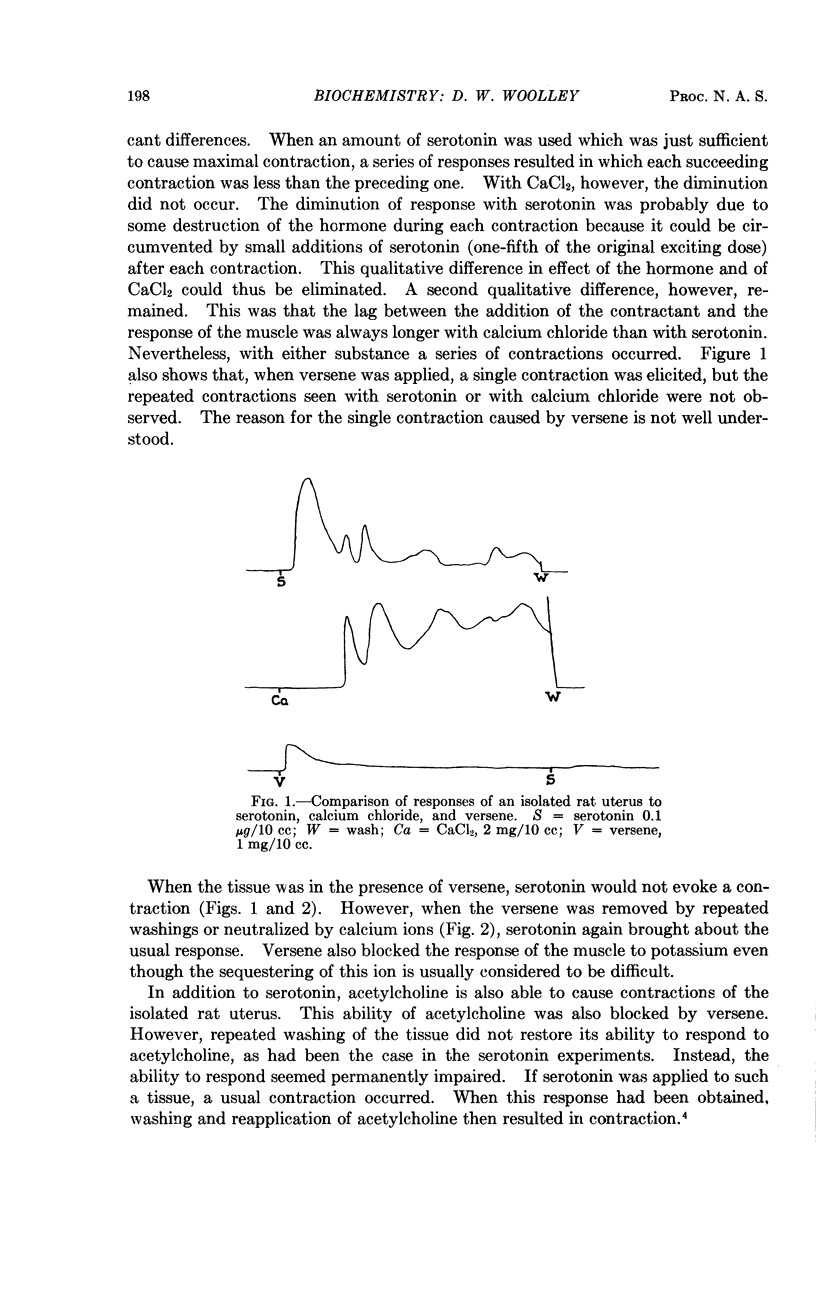
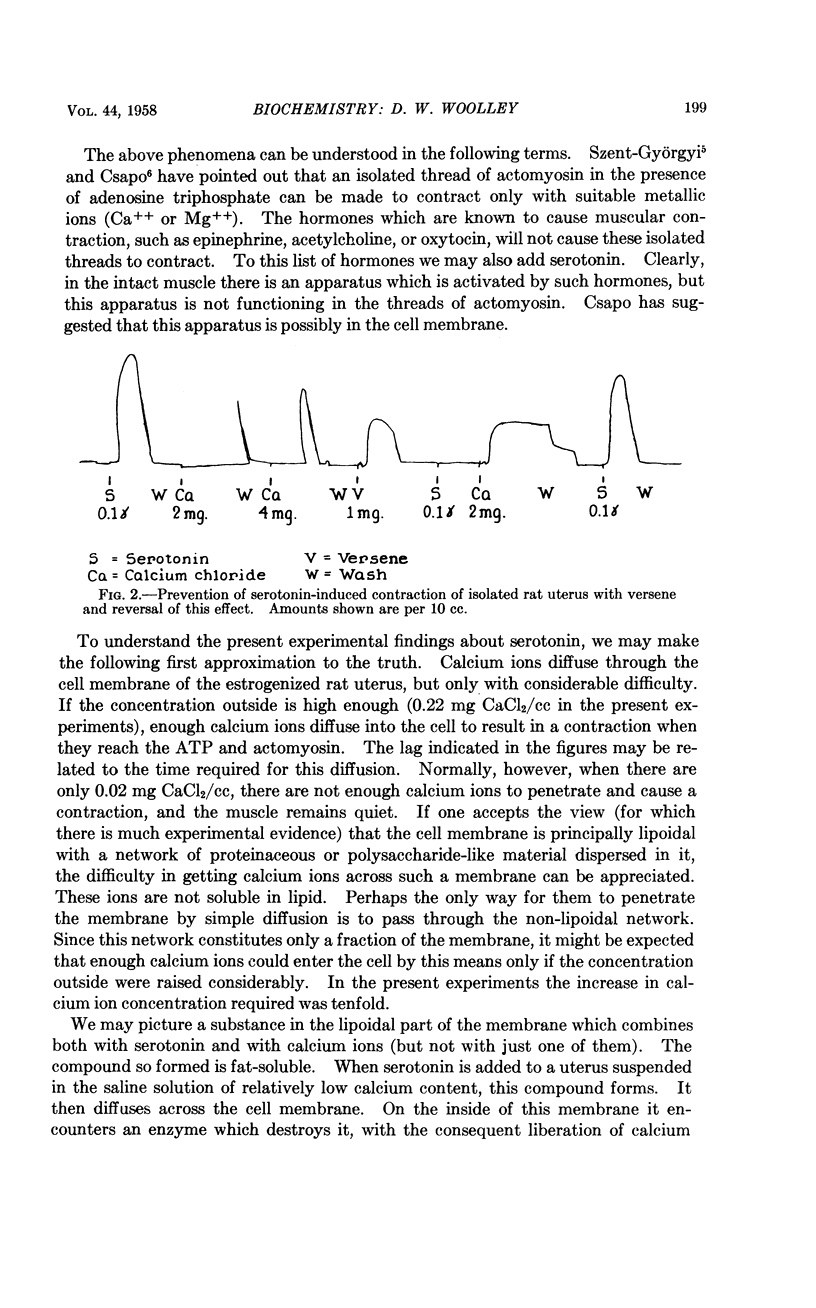
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- GADDUM J. H., HAMEED K. A. Drugs which antagonize 5-hydroxytryptamine. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1954 Jun;9(2):240–248. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1954.tb00848.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHAW E., WOOLLEY D. W. Pharmacological properties of some antimetabolites of serotonin having unusually high activity on isolated tissues. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1954 May;111(1):43–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGT W. Pharmacologically active lipidsoluble acids of natural occurrence. Nature. 1957 Feb 9;179(4554):300–passim. doi: 10.1038/179300a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOOLLEY D. W. Probable evolutionary relationship of serotonin and indoleacetic acid, and some practical consequences therefrom. Nature. 1957 Sep 28;180(4587):630–633. doi: 10.1038/180630a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



