Abstract
Background
The influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 virus has been a challenge for public health surveillance systems in all countries. In Antananarivo, the first imported case was reported on August 12, 2009. This work describes the spread of A(H1N1)pdm09 in Madagascar.
Methods
The diffusion of influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 in Madagascar was explored using notification data from a sentinel network. Clinical data were charted to identify peaks at each sentinel site and virological data was used to confirm viral circulation.
Results
From August 1, 2009 to February 28, 2010, 7,427 patients with influenza-like illness were reported. Most patients were aged 7 to 14 years. Laboratory tests confirmed infection with A(H1N1)pdm09 in 237 (33.2%) of 750 specimens. The incidence of patients differed between regions. By determining the epidemic peaks we traced the diffusion of the epidemic through locations and time in Madagascar. The first peak was detected during the epidemiological week 47-2009 in Antananarivo and the last one occurred in week 07-2010 in Tsiroanomandidy.
Conclusion
Sentinel surveillance data can be used for describing epidemic trends, facilitating the development of interventions at the local level to mitigate disease spread and impact.
Introduction
The transmission of A(H1N1)pdm09-person to person-is similar to that of other seasonal influenza viruses. Influenza viruses spread rapidly through infected air-borne droplets that are generated by coughing or sneezing. Hands are a major alternative route of viral spread, and can be contaminated “directly”, when droplets land on the hands from an infected person coughing nearby, or “indirectly”, when hands pick up the virus by touching contaminated objects or surfaces. The infectious period for a confirmed case is from one day before the onset of symptoms to seven days after onset [1]–[2].
As concerns community-wide diffusion, influenza epidemics are widespread outbreaks of highly contagious respiratory disease that appear suddenly. Influenza pandemics are characterized by the rapid worldwide spread of a virus to which humans have had no previous exposure.
In infectious disease epidemiology, diffusion is an important concept depicting the dynamics of the spread of a microorganism through time and space [3]. To understand the spread of influenza in a community, it is necessary to study epidemiological and virological conditions and the geographical determinants of influenza during a pandemic [4]. Diverse factors influence the spread of epidemics through human populations, particularly the characteristics of the pathogen responsible for the infection [5], human mobility patterns [6], [7], the sociodemographic structure of the population [4], [8] and intervention measures.
On a population level, influenza spreads both by contagious diffusion (wave-like from one or more central foci) and hierarchical diffusion (movement from larger to smaller towns) [9]. The spread of influenza epidemics is linked more to the rates of movement of people to and from work than to geographical distance or air travel [10]. Also, the virus spreads more rapidly in more densely populated locations.
Recently, the A(H1N1)pdm09 influenza virus swept rapidly across the world after its first detection in humans in April 2009 in Mexico and the US [11], [12]. The A(H1N1)pdm09 pandemic virus is now well-characterized biologically, clinically and epidemiologically [13]. However, little is known about the timing and impact of pandemic influenza in Africa.
The first reported case of A(H1N1)pdm09 influenza to be imported into Madagascar was August 12th, 2009. The first laboratory-confirmed cases without travel history were detected on October 8th, 2009: three teenagers attending one of the largest schools in Antananarivo [14]. The first wave of A(H1N1)pdm09 peaked in November 2009 in Antananarivo.
Here, we report an analysis of the diffusion pattern of influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 virus by examining all clinical cases reported to the sentinel network. This network allowed the pandemic to be monitored nationwide in real time.
Results
Characteristics of the data from sentinel visits
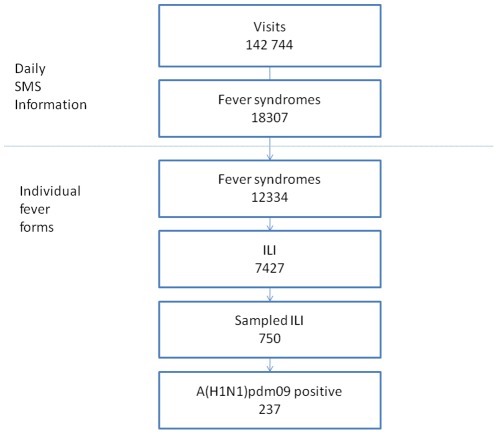
The data, collected on a daily basis between August 1st, 2009 and February 28th, 2010 from the 24 sentinel centers, corresponded to 142,744 visits (Figure 1); 81.0% of the data were transmitted within 24 h to IPM.
Figure 1. Flow charts of cases from visits to influenza results.
A total of 18,307 cases (12.8%) presented a fever syndrome. A fever-specific form was completed by 12,334 of these patients (67.4%). The sex ratio (male/female) of those with fever syndrome was 0.8; age was available for 12,136 patients (98.4%), and the mean age of these patients was 12.7 years (95%CI: [12.4–12.9]).
Of the patients with a completed fever-specific form, 7,427 cases (60.2%) presented an ILI. The sex ratio (male/female) for those with ILI was 0.9; age was available for 7,316 patients (98.5%), and their mean age was 10.9 years (95%CI: [10.7–11.3]).
Of the patients who presented with ILI, 750 (10.1%) were sampled for laboratory confirmation. Infection with A(H1N1)pdm09 virus was confirmed for 237 (33.2%) patients. The age was available for 233 of these patients (98.3%), and their mean age was 12.6 years (95%CI: [11.1–14.1]).
The age distribution by overall number of visits and febrile syndromes is listed in Table 1. ILI, sampling and laboratory results differed significantly between age groups (p-value<0.01). The proportion of ILI among those with fever syndromes was lower in the population over 25 years old, and the proportion of positive results was higher in the age 5–14year-old group (logistic regression: p-value<0.01).
Table 1. Distribution of overall visits, fever-related illnesses, influenza-1-like illnesses, and positive results by age.
| Age group | All visits (n = 142,563) | Fever syndromes (n = 12,136) | ILI syndromes (n = 7,316) | Sampled ILI (n = 740) | A(H1N1)pdm positive (n = 233) | ||||||||
| n | (%) | n | (%) | n | (%) | p | n | (%) | p | n | (%) | P* | |
| <1 year | 14,142 | (9.9) | 1,394 | (11.5) | 951 | (68.2) | <0.01 | 53 | (6.1) | <0.01 | 11 | (20.7) | --- |
| 1–4 years | 23,774 | (16.7) | 3,249 | (26.8) | 2,212 | (68.1) | <0.01 | 223 | (11.2) | 0.1 | 52 | (23.3) | 0.7 |
| 5–14 years | 24,579 | (17.2) | 3,485 | (28.7) | 2,175 | (62.4) | <0.01 | 237 | (11.3) | 0.1 | 97 | (40.9) | <0.01 |
| 15–24 years | 26,415 | (18.5) | 1,944 | (16.0) | 1,028 | (52.8) | <0.01 | 110 | (11.2) | 0.2 | 36 | (32.7) | 0.1 |
| ≥25 years | 53,653 | (37.6) | 2,064 | (17.0) | 950 | (46.0) | --- | 117 | (13.1) | --- | 37 | (31.6) | 0.2 |
comparison of A(H1N1)pdm positivity by age using logistic regression analysis.
The clinical symptoms are shown in Table 2. The most frequent symptoms presented by A(H1N1)pdm09-positive patients were fever (100%), cough (99.1%), headache (40.1%) and runny nose (38.0%). However, logistic regression analysis of the main symptoms (cough, headache, runny nose, asthenia, sore throat, vomiting, shivering) adjusted for age group only identified a relationship between A(H1N1)pdm09 positivity and runny nose (OR = 1.5; p = 0.03).
Table 2. Distribution of symptoms among ILI and confirmed cases of influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 virus infection declared by the sentinel network in Madagascar.
| Symptoms | All ILI (n = 7,427) | Sampled ILI (n = 750) | Confirmed Cases (n = 237) | |||
| n | (%) | n | (%) | n | (%) | |
| GENERAL | ||||||
| Fever | 7,427 | (100.0) | 750 | (100.0) | 237 | (100.0) |
| Headache | 3,236 | (58.1) | 281 | (47.1) | 95 | (40.1) |
| Muscle pain | 486 | (11.9) | 52 | (10.7) | 20 | (8.4) |
| Join pain | 870 | (20.5) | 68 | (13.9) | 13 | (5.5) |
| Asthenia | 1,047 | (14.1) | 93 | (12.4) | 32 | (13.5) |
| Shiver | 1,445 | (19.5) | 130 | (17.3) | 37 | (15.5) |
| RESPIRATORY | ||||||
| Cough | 6,816 | (92.6) | 743 | (99.1) | 235 | (99.1) |
| Sore throat | 1,425 | (19.2) | 96 | (12.8) | 31 | (13.1) |
| Runny nose | 2,283 | (30.7) | 239 | (31.8) | 90 | (38.0) |
| Shortness of breath | 287 | (3.9) | 42 | (5.2) | 5 | (2.1) |
| GASTRO INTESTINAL | ||||||
| Diarrhea | 770 | (10.4) | 85 | (11.3) | 22 | (9.3) |
| Vomiting | 984 | (13.2) | 88 | (11.7) | 31 | (13.1) |
| Nausea | 564 | (7.6) | 55 | (7.3) | 12 | (5.1) |
| OTHERS | ||||||
| Retro-orbital pain | 81 | (2.1) | 10 | (2.2) | 2 | (0.8) |
| Hemorrhagic sign | 57 | (1.5) | 4 | (0.8) | 2 | (0.8) |
| Skin rash | 137 | (3.6) | 7 | (1.5) | 0 | (0.0) |
No case with pneumonia or respiratory failure, requiring ventilation, was reported. Other severe symptoms such as multiple organ failure were not reported.
Spatio-temporal diffusion patterns: the road of the peaks
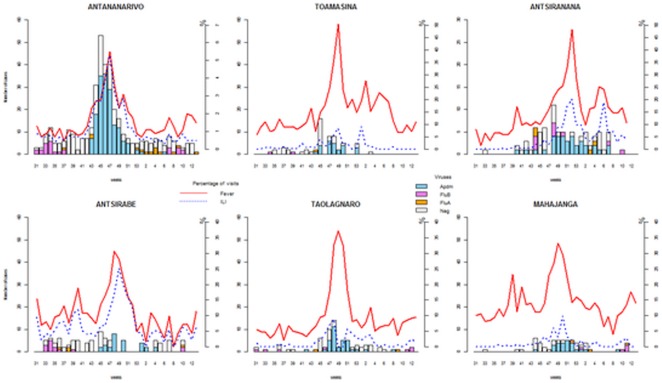
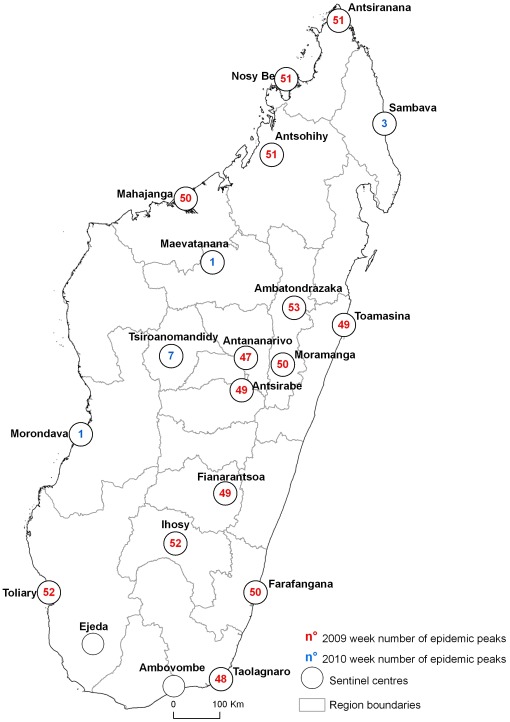
Figure 2 shows the progress of the epidemic as assessed from the cases of ILI reported to IPM by the sentinel network. The first peak of ILI (989.3 per thousand visits with fever) was detected during Week 47-2009, in Antananarivo. In this city, cases were confirmed between Week 34 and the first week of 2010 (Table 3). Most cases were confirmed during the first school outbreak which occurred in Week 42-2009. The peak of confirmed cases in Antananarivo occurred in Week 45 (Figure 3) after which systematic detection of all suspected cases ceased.
Figure 2. Time series distribution of the fever syndromes, ILI and confirmed influenza cases in the major cities of Madagascar.
Table 3. Incidence of ILI during each regional peak.
| Sentinel Center | Weeks of viral circulation (first-last) | Week of the ILI peak | Incidence of fever syndromes per thousand visits | Incidence of ILI per thousand visits with fever |
| Antananarivo | 34th 2009–01st 2010 | 47th 2009 | 62.3 | 989.3 |
| Taolagnaro | 42nd 2009–02nd 2010 | 48th 2009 | 326.8 | 273.8 |
| Toamasina | 42nd 2009–50th 2009 | 49th 2009 | 503.2 | 562.3 |
| Antsirabe | 44th 2009–02nd 2010 | 49th 2009 | 281.0 | 891.7 |
| Fianarantsoa | 48th 2009–52nd 2010 | 49th 2009 | 222.2 | 200.0 |
| Moramanga | 48th 2009–52nd 2010 | 50th 2009 | 424.2 | 46.3 |
| Mahajanga | 44th 2009–09th 2010 | 50th 2009 | 294.5 | 336.6 |
| Farafangana | 46th 2009 | 50th 2009 | 215.7 | 597.4 |
| Antsiranana | 43rd 2009–03rd 2010 | 51st 2009 | 330.1 | 543.5 |
| Nosy Be | No swab | 51st 2009 | 461.0 | 538.5 |
| Antsohihy | 36th 2009 | 51st 2009 | 391.3 | 111.1 |
| Ihosy | No swab | 52nd 2009 | 435.9 | 117.6 |
| Toliara | 47th 2009–06th 2010 | 52nd 2009 | 38.2 | 333.3 |
| Ambatondrazaka | No swab | 53rd 2009 | 135.1 | 600.0 |
| Morondava | 52th 2009–01st 2010 | 01st 2010 | 124.7 | 150.9 |
| Maevatanana | 49th 2009–08th 2010 | 01st 2010 | 221.7 | 446.9 |
| Sambava | No swab | 03rd 2010 | 271.3 | 57.9 |
| Tsiroanomandidy | 49th 2009–08th 2010 | 07th 2010 | 195.1 | 250.0 |
Figure 3. A(H1N1)pdm09 diffusion in Madagascar-the “peaks road.”.
The incidence of ILI was also evaluated by region (Table 3). The peaks were observed through the various sentinel centers in Madagascar and occurred from Weeks 47-2009 to 07-2010 (Figure 2).
Discussion
We studied the epidemiology of the current pandemic of influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 virus in Madagascar, including the temporal and geographic pattern of spread and the clinical characteristics of A(H1N1)pdm09 disease among ILI patients. We characterized the range and chronology of the pandemic in Madagascar with real-time data from a sentinel network.
This is the first description of overall trends of pandemic influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 infection in Madagascar. This country was one of the first countries in Africa to report laboratory-confirmed cases of this new influenza virus: cases of pandemic influenza were detected in Madagascar before mass gatherings occurred. All of the initial sporadic cases identified were imported (from India, Mauritius and Reunion Island). The sentinel surveillance networks which have been operational since 2007 [15] presumably contributed to this because coverage was good in high density population settings; the updated information given to health care professionals in June 2009 during an influenza workshop organized by Institut Pasteur from Madagascar may also have contributed.
The pattern of spread of A(H1N1)pdm09 in Madagascar was dominated by a wave that emanated from the capital, Antananarivo. The early dynamics of this wave might have been associated with a high frequency of international travel, increasing the risks of a major epidemic in the capital city [10].
It was challenging to implement the early phase of the WHO recommendations concerning the epidemic. Thus, epidemiological investigation was crucial to monitor the epidemic better, particularly to identify risk groups and factors that contributed to the development of the epidemic. An understanding of the epidemiology of past pandemics, and in particular the last A(H1N1)pdm09 pandemic, may help health authorities to prepare and implement response programs to subsequent waves and pandemics [16].
Collecting relevant information on pre-existing chronic conditions and complications among hospitalized cases could be valuable to fill the gaps in the existing epidemiological data. However, in Madagascar, like in others developing countries, the level of hospital care is poor, and there is a lack of influenza surveillance in hospitals (e.g. concerning severe cases). This weakness with regard to surveillance, and hospitalization costs for patients, need to be considered and overcome so as strengthen surveillance systems with data from hospitals.
Our report demonstrates that the signs and symptoms in ILI or confirmed cases are similar to those observed in patients with seasonal influenza [16], [17]. We observed that sampling children aged under 1 year old was much less effective than that for other groups. The proportions of patients sampled did not differ between the other age groups, and the positivity rate for A(H1N1)pdm09 was high in patients aged between 4 and 15 years. One characteristic of this pandemic is that it disproportionately affected children and young adults [18]; indeed, a study in the USA reported that 60% of confirmed A(H1N1)pdm09 cases were aged 18 years or younger [19].
We also observed that transmission of the influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 virus during the pandemic in Madagascar, like in other countries, appeared to be inevitable, presumably due to the nature of the infection: the virus spread despite preparations to mitigate the situation, including systematic detection of all suspected cases, social distancing options (such as school closure) and antiviral treatment of all confirmed cases and their contacts during the early stage of the epidemic. However, in Madagascar like in other remote areas, the impact of vaccination or timely oseltamivir use on influenza transmission was probably low because these measures were unavailable throughout the country.
As in other countries [20]–[22], there were regional differences in the trend of the epidemic and the timeline of A(H1N1)pdm09 spread, and the causes are not easily explained. These differences may be associated with the demographic structure or population density of these regions. The region specificity of the pattern requires further examination.
Data from Madagascar, like those from others countries [23], suggest that the A(H1N1)pdm09 virus spreads rapidly through communities once introduced from an affected area. For the specific case of Madagascar Island, the principal spread of infection took approximately 3–4 months. This rapid spread of pandemic influenza infection across the whole country underscores the need for real-time surveillance systems to track viral activity across regions and districts.
In conclusion, the sentinel data allowed description of the pattern of disease activity. Both seasonal and pandemic influenza surveillance, using sentinel data, is informative when combined with laboratory testing. We advocate (i) enhancing the surveillance capacity with the aim of mitigating the course of future epidemics early, (ii) strengthening surveillance efforts, and (iii) promoting information sharing in Africa because the influenza epidemiology on the continent is largely unknown. In addition population-based serological surveys should be performed to generate more accurate estimates of the epidemic's impact.
Methods
Subjects
Before the pandemic was declared in Madagascar, the surveillance aimed to identify cases in travelers returning from affected areas to allow prompt implementation of control measures around each case (nasal swab, and antiviral treatment if case was confirmed) and to contain viral spread. Antiviral prophylaxis was recommended for close contacts of confirmed cases, who were asked to quarantine themselves at home.
The case management protocol was updated according to the general dissemination of the virus and the start of transmission in the community; ultimately, the protocol was limited to patients with known risk factors and hospitalized cases.
As described previously [15], the sentinel surveillance network was based on daily declaration by volunteer general practitioners (GPs) throughout the 22 regions of Madagascar. Participating GPs reported daily the total number of consultations and any patients who presented with influenza-like illness (ILI), defined as observed fever (>38°C) and cough or sore throat.
With the emergence of the influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 virus, the following case definitions of suspected and confirmed cases were used:
A suspected case of influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 virus infection was defined as a person with ILI who meets at least one of the following epidemiological criteria of the WHO case definition protocol [24]: (i) returned from a country or region with an epidemic of influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 virus within the last seven days, (ii) was in close contact with a confirmed case within the past seven days, or (iii) handled samples suspected of containing influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 virus in a laboratory or other setting within the past seven days. A confirmed case of influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 virus infection was defined as a person with laboratory confirmation by real-time PCR. For each case, we collected demographic (including age and sex) and clinical (fever, cough) data on a dedicated fever case report form.
Laboratory confirmation
Nose and throat swabs were collected from all suspected cases during the first step of the spread and on a random basis during community spread. Respiratory specimens were placed in universal transport media (Copan, Italia), and transported at 4°C twice per week from sentinel sites to the National Influenza Center (NIC) at the Institut Pasteur of Madagascar (IPM) for confirmation. Specimens were stored at 4°C before being tested by PCR.
Samples were also tested for other seasonal influenza viruses during the period (Influenza types B and A, and subtypes AH1 seasonal and AH3 seasonal)
The CDC Real-Time RT-PCR Protocol for the detection and characterization of human and swine influenza was used to confirm cases. It includes panels of oligonucleotide primers and dual-labeled hydrolysis (Taqman®) probes for in vitro qualitative detection and characterization of human and swine influenza viruses in respiratory specimens [25]. The Ambion Ag-Path One-Step RT-PCR kit was used for this assay.
Data analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using R version 2.12.0 [26]. Arcview 9.2 was used for mapping.
Descriptive analyses comprised assessing frequency distributions and proportions for each variable category. Fisher's exact test for categorical variables was used for group comparisons, and ANOVA for continuous variables. P values were two-sided.
Logistic regression analysis was performed to measure the association between ILI or laboratory results and each independent variable (symptom, age group). Odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated from â coefficients and their standard errors.
Ethical clearance
The data were collected by routine surveillance and were anonymous; thus, the epidemiologists running the surveillance network had ethical and professional obligations to maximize the benefits of the studies to the participants and society, and minimize potential harm (such as loss of privacy and confidentiality). These risks were remote possibilities due to the steps that were taken to safeguard confidentiality: they included data encryption, written procedures for confidentiality, and appropriate staff training. Malagasy public health authorities can legally collect and receive information for the purposes of preventing and controlling disease, injury, and disability. Hence, no specific ethics approval is required for public health practice activities such as surveillance. Nevertheless, verbal informed consent-as noted on the form by the primary health care staff-was obtained from each patient, or from at least one parent for children, before sampling under the principle of respect for individual freedom.
Acknowledgments
We thank the staff of the Malagasy National Influenza Center for influenza testing. We would like to express our gratitude to the staff at the Direction des Urgences et de la Lutte contre les Maladies Négligées (Ministry of Health), Direction de la Veille Sanitaire et de la Surveillance Epidémiologique (Ministry of Health), and the Ministry of Health for supporting the influenza surveillance system. We are deeply endebted to all practitioners and nurses who are involved daily in the sentinel surveillance in Madagascar.
Disclaimer
The views expressed in this article are those of the authors.
Footnotes
Competing Interests: The authors have read the journal's policy and have the following conflicts: The authors have received some funds from Sanofi Pasteur for the training of virological staff. This does not alter the authors' adherence to all the PLoS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Funding: This work was feasible thanks to set-up of sentinel network supported by World Health Organization (WHO) Geneva (APW/Ref. OD/AP-08-02451), Sanofi-Pasteur, the French Ministry of Health, the United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (Cooperative Agreement Number: U51/IP000327-01), the United States Department of Health and Human Services (Grant Number 6 IDSEP060001-01-01) via the International Network of Pasteur Institutes, and the President Malaria Initiative program (USAIDS). The authors are therefore grateful to Wenqing Zhang from WHO Geneva, Béatrice Barret and Myriam Beigeaud from Sanofi Pasteur, and Kathleen Victoir and Marc Jouan from the International Network of Pasteur Institutes. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
References
- 1.World Health Organization Western Pacific Region. Avian influenza, including influenza A (H5N1) in humans: WHO interim infection control guideline for health care facilities. WHO: Manila, 2006. 2006;23 Available: http://www3.ha.org.hk/idctc/document/infectioncontrolaiinhumanswhointerimguidelinesfor2_(2).pdf. Accessed 2012 Apr. [Google Scholar]
- 2.United States Department of Health and Human Services. HHS pandemic influenza plan. Washington, DC: Department of Health and Human Services, 2005. 2005;23 Available: http://www.flu.gov/planning-preparedness/federal/hhspandemicinfluenzaplan.pdf. Accessed 2012 Apr. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Anderson RM, May RM. Oxford, UK: Oxford University; 1992. Infectious diseases of humans: dynamics and control.Press.768 [Google Scholar]
- 4.Merler S, Ajelli M. The role of population heterogeneity and human mobility in the spread of pandemic influenza. Proc Biol Sci. 2010;277:557–565. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2009.1605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bonhoeffer S, Nowak MA. Mutation and the evolution of virulence. Proc R Soc B. 1994;258:133–140. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Hufnagel L, Brockmann D, Geisel T. Forecast and control of epidemics in a globalized world. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:15124–15129. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0308344101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ajelli M, Merler S. The Impact of the Unstructured Contacts Component in Influenza Pandemic Modeling. PLoS ONE. 2008;3:e1519. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0001519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Mossong J, Hens N, Jit M, Beutels P, Auranen K, et al. Social contacts and mixing patterns relevant to the spread of infectious diseases. PLoS Med. 2008;5:e74. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0050074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Cliff AD, Haggett P, Ord KL, Versey G. The study of spatial diffusion. In: Spatial Diffusion: An Historical Geography of Epidemics in an Island Community. Chapter 2. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 1981;6–34 [Google Scholar]
- 10.Colizza V, Barrat A, Barthélemy M, Vespignani A. The role of the airline transportation network in the prediction and predictability of global epidemics. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;7:2015–2020. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0510525103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Novel Swine-Origin Influenza A (H1N1) Virus Investigation Team, Dawood FS, Jain S, Finelli L, Shaw MW, et al. Emergence of a Novel Swine-Origin Influenza A (H1N1) Virus in Humans. N Engl J Med. 2009;360:2605–2615. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0903810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Swine Influenza A(H1N1) infection in Two Children – Southern California, March–April 2009. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2009;58:400–402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.World Health Organization. New influenza A(H1N1) virus: global epidemiological situation, June 2009. Wkly Epidemiol Rec. 2009;84:249–257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Rajatonirina S, Heraud JM, Randrianasolo L, Razanajatovo N, Ramandimbisoa T, et al. Pandemic influenza A(H1N1) 2009 virus outbreak among boarding school pupils in Madagascar: compliance and adverse effects of prophylactic oseltamivir treatment. J Infect Dev Ctries. 2011;5:156–162. doi: 10.3855/jidc.1318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Randrianasolo L, Raoelina Y, Ratsitorahina M, Ravolomanana L, Andriamandimby S, et al. Sentinel surveillance system for early outbreak detection in Madagascar. BMC Public Health. 2010;21:31. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-10-31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Lagacé-Wiens PR, Rubinstein E, Gumel A. Influenza epidemiology-past, present, and future. Crit Care Med. 2010;38:e1–9. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e3181cbaf34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Razanajatovo NH, Richard V, Hoffmann J, Reynes JM, Razafitrimo GM, et al. Viral Etiology of Influenza-Like Illnesses in Antananarivo, Madagascar, July 2008 to June 2009. PLoS ONE. 2011;6(3):e17579. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Dawood FS, Jain S, Finelli L, Shaw MW, Lindstrom S, et al. Emergence of a novel swine-origin influenza A (H1N1) virus in humans. N Engl J Med. 2009;360:2605–2615. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0903810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Jhung MA, Swerdlow D, Olsen SJ, Jernigan D, Biggerstaff M, et al. Epidemiology of 2009 Pandemic Influenza A(H1N1) in the United States. Clin Infect Dis. 2011;52:S13–26. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciq008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kwan-Gett TS, Baer A, Duchin JS. Spring 2009 H1N1 influenza outbreak in King country Washington. Disaster Med Pub Health Preparedness. 2009;3:S109–116. doi: 10.1097/DMP.0b013e3181c6b818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Wenger JD, Castrodale LJ, Bruden DL, Keck JW, Zulz T, et al. 2009 Pandemic Influenza A H1N1 in Alaska: Temporal and Geographic Characteristics of Spread and Increased Risk of Hospitalization among Alaska Native and Asian/Pacific Islander. Clin Infect Dis. 2011;52:S2–S5. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciq037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kim JH, Yoo HS, Lee JS, Lee EG, Park HK, et al. The spread of pandemic H1N1 2009 by age and region and the comparison among monitoring tools. J Korean Med Sci. 2010;25:1109–1112. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.7.1109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Harcourt SE, Smith GE, Elliot AJ, Pebody R, Charlett A, et al. Use of a large general practice syndromic surveillance system to monitor the progress of the influenza A(H1N1) pandemic 2009 in the UK. Epidemiol Infect. 2011;8:1–6. doi: 10.1017/S095026881100046X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.World Health Organization. 2009;23 Pandemic(H1N1) Available: http://www.who.int/csr/disease/swineflu/en/index.html. Accessed 2012 Apr. [Google Scholar]
- 25.23 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention protocol of realtime RTPCR for influenza A (H1N1) Available: http://www.who.int/csr/resources/publications/swineflu/CDCrealtimeRTPCRprotocol_20090428.pdf. Accessed 2012 Apr. [Google Scholar]
- 26.R Development Core Team. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, 2009, Vienna, Austria. 2011;23 ISBN 3-900051-07-0, URL http://www.r-project.org. Accessed 2012 April. [Google Scholar]