Abstract
The present paper describes a sequential study of the leukocyte profiles and the changes in morphometry and morphology of erythrocytes in the tadpoles of Polypedates teraiensis during their development and metamorphosis, that is, transfer from an aquatic mode to a terrestrial mode of life. Blood smears of 21 different stages (Gosner stage 26 to 46) of tadpoles were investigated. Population of erythrocytes was heterogeneous in population represented by various forms (oval, elliptical or rounded cells, comma shaped, teardrop shaped, schistocytes, senile erythrocytes, crenulated RBCs). Correlation between various morphometric values of erythrocytes was determined with different developing stages of tadpoles. Amongst the leucocytes, the lymphocytes were the most abundant cells followed by neutrophils. Neutrophils and monocytes showed varied morphologic forms. The percentage of lymphocytes and neutrophils showed a negative whereas percentage of eosinophil, basophil, and monocytes showed a positive correlation with the developmental stages of tadpoles. Blood platelets were also observed, which were rounded in shape and found in aggregates.
1. Introduction
Anuran metamorphosis is an interesting physiological phenomenon where the aquatic tadpoles become terrestrial froglets. It is a rapid process to meet the demands of a new life form [1]. During early larval development, tissues are formed and body size increases, but later there is a massive tissue restructuring and breakdown leading to a reduction in overall body size [2]. As a part of metamorphosis, blood cell populations are renewed [1], and number of leukocytes changes [2]. Metamorphosis thus provides physiologists an opportunity to understand the processes involved in hematopoiesis. From a developmental and physiological point of view, the changes in the number of leucocytes and the changes in the morphology and morphometry of erythrocytes during the larval development are of great interest and importance. Apart from this, anuran larvae (tadpoles) are study of interest, as they have been widely used as bioindicators to detect the presence of mutagenic agents in water [3–7]. The general nature of blood cell responses to the aquatic environment emphasizes the role of the peripheral blood in tadpoles as a sensitive indicator regarding contamination in aquatic environments [8]. Since anurans are environmentally sensitive animals [8–10] and variation in white blood cell parameters is subjected to environmental stress [11–15], there is a recent interest by ecologists and wildlife researchers in their hematology.
Abundance of different leucocytes under normal metamorphosis [2] and thyroid-induced metamorphosis [16, 17] has been studied in the tadpoles of Rana catesbeiana. Granulopoiesis of basophils and heterophils (neutrophils) in the tadpoles of Rana esculenta [18] and presence of leucocytes in tissue sections in the tadpoles of Xenopus laevis [19] have been reported. Moreover, changes in the number of leucocytes in response to stress in the tadpoles of Rana esculenta [8], Rana catesbeiana [20], and Rana pipiens [21] have been observed.
In larval anurans, two general types of erythrocytes, that is, larval and adult forms, are found, which are differentiated by size and morphology during development [22–24]. The larval form is elongated while the adult form is smaller and rounder [23]. The transition from larval to adult cells has been reported to begin at the onset of metamorphosis in various anuran species like Rana pipiens [22] and Rana catesbeiana [25–28]. Thyroid-induced destruction of erythrocytes during metamorphosis in the tadpoles of Hyla crucifer, Hyla versicolor, Rana clamitans, and Bufo americanus has also been described earlier [29].
Sequential study on the leukocyte profile and changes in the morphometry and morphology of erythrocytes in different larval stages of anurans is not well documented. Moreover, blood cell profile of Indian anurans is restricted to few adult species, namely, Bufo melanostictus (new name: Duttaphrynus melanostictus) [30–33], Rana tigerina (new name: Hoplobatrachus tigerinus) [34], and Polypedates maculatus [35]. There is no report on the blood cell profiles of tadpoles of any Indian anuran. Thus, aim of the present study was to estimate changes in the leukocyte profile and changes in the morphometry and morphology of the erythrocytes in the laboratory reared anuran tadpoles. This paper describes blood cell profile of the laboratory-reared tadpoles (Gosner stages 26 to 46, [36]) of the Dubois's tree frog Polypedates teraiensis (Dubois, 1986) (Anura: Rhacophoridae).
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Rearing of Tadpoles
The foam nests of Dubois's tree frog Polypedates teraiensis [37] were collected during the month of August 2010 from their natural habitat from Choudwar (20°31′11′′N, 85°49′11′′E), Odisha, India. The tadpoles were reared following standardized procedure [38]. After hatching, the tadpoles were fed with boiled Amaranthus leaves ad libitum.
2.2. Tadpoles Investigated
For the study, tadpoles from Gosner stages 26 to 46 [36] were considered which were comparable to the Taylor and Kollros stages I to XXV [39, 40]. Ten tadpoles for each stage were selected for investigation.
2.3. Preparation of Blood Smears
Tadpoles were anesthetized by immersing them in 1% MS-222 (Tricaine Methane Sulphonate) solution. The blood of tadpoles from stage 26 to 44 was obtained from tail amputation through the middle of the tail. For stages 45 and 46, blood was collected from the heart using a fine syringe. Blood smears were prepared using push slide technique. The dried blood smears were stained with Giemsa's stain and were observed under light microscope (Hund H500).
2.4. Identification and Counting of Blood Cells
Different types of blood cells present in the smear were identified following Hadji-Azimi et al. [41], Turner [42] and Heatley and Johnson [43]. Slides were viewed in zigzag pattern, covering all parts of the blood smear, and leukocytes were counted in each field of view until 100 cells were counted. 150 fields of view per blood smear were assessed for each stage. Photos of the blood cells were taken with the help of a Canon EOS 450 12.2 Mega pixel camera (EF-S 18-55 1S Kit) connected to Hund H500 WETZLAR microscope. The sizes of red blood cells (RBCs) and their nuclei were measured by an ocular micrometer that was standardized against a stage micrometer (ERMA, Japan made). For morphometry of the erythrocytes, the formulae described by Arserim and Mermer [44] were followed.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
The relationship between developmental stages and blood cell profile was assessed by drawing scatter plots. The correlation coefficient “r” was calculated in each case by Karl Pearson's method [45].
3. Results
A cumulative account of the blood cell profiles of tadpoles of Polypedates teraiensis from Gosner stages 26 to 46 is represented in Tables 1 and 2.
Table 1.
Morphometry of erythrocytes during development of the tadpoles of Polypedates teraiensis.
| Stages | Size of cell | Size of nuclei | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gosner | Taylor and Kollros | Length (L ± SD) (μm) | Breadth (B ± SD) (μm) | L/B ± SD | Area (A ± SD) (μm²) | Length (L′ ± SD) (μm) | Breadth (B′± SD) (μm) | L′/B′± SD | Area (A′± SD) (μm²) | A′/A ± SD |
| 26 | I | 22.22 ± 1.26 | 21.30 ± 2.11 | 1.043 ± 0.14 | 371.529 ± 40.61 | 11.69 ± 1.51 | 10.60 ± 1.32 | 1.102 ± 0.12 | 97.373 ± 12.39 | 0.261 ± 0.12 |
| 27 | II | 23.24 ± 1.31 | 22.14 ± 1.61 | 1.049 ± 0.16 | 403.908 ± 43.16 | 12.12 ± 1.11 | 10.90 ± 1.41 | 1.111 ± 0.11 | 168.290 ± 18.12 | 0.416 ± 0.03 |
| 28 | III | 21.81 ± 1.35 | 20.60 ± 2.53 | 1.066 ± 0.12 | 353.254 ± 50.47 | 12.12 ± 1.91 | 10.30 ± 1.48 | 1.382 ± 0.17 | 99.488 ± 27.51 | 0.390 ± 1.41 |
| 29 | IV | 21.81 ± 2.53 | 18.78 ± 3.95 | 1.20 ± 0.301 | 321.549 ± 80.77 | 10.90 ± 1.65 | 10.90 ± 1.65 | 1 ± 0 | 95.075 ± 27.71 | 0.306 ± 0.11 |
| 30 | V | 23.02 ± 2.71 | 15.15 ± 0 | 1.52 ± 0.17 | 274.005 ± 32.24 | 9.09 ± 0 | 9.09 ± 0 | 1 ± 0 | 64.720 ± 0 | 0.239 ± 0.033 |
| 31 | VI | 21.21 ± 2.14 | 21.21 ± 2.14 | 1.016 ± 0.206 | 350.130 ± 30.66 | 10.90 ± 2.71 | 12.12 ± 2.14 | 0.9 ± 0.13 | 106.605 ± 44.76 | 0.247 ± 0.17 |
| 32 | VII | 21.81 ± 2.53 | 18.78 ± 4.97 | 1.21 ± 0.30 | 321.596 ± 87.66 | 12.12 ± 2.14 | 9.09 ± 0 | 1.33 ± 0.23 | 86.521 ± 15.30 | 0.276 ± 0.06 |
| 33 | VIII | 21.61 ± 2.16 | 17.87 ± 1.1 | 1.209 ± 0.21 | 303.143 ± 32.12 | 11.96 ± 1.26 | 9.39 ± 1.12 | 1.273 ± 0.21 | 88.158 ± 11.62 | 0.290 ± 0.02 |
| 34 | IX | 21.21 ± 2.14 | 15.75 ± 2.53 | 1.35 ± 0.12 | 265.352 ± 64.77 | 11.51 ± 1.35 | 9.69 ± 1.35 | 1.19 ± 0.18 | 87.951 ± 17.94 | 0.350 ± 0.11 |
| 35 | X | 19.24 ± 1.41 | 16.87 ± 1.21 | 1.140 ± 0.11 | 254.794 ± 41.12 | 10.96 ± 1.35 | 9.93 ± 1.21 | 1.103 ± 0.17 | 80.787 ± 12.91 | 0.317 ± 0.05 |
| 36 | XI | 20.60 ± 2.53 | 15.75 ± 2.53 | 1.35 ± 0.34 | 252.321 ± 31.41 | 9.69 ± 1.35 | 9.69 ± 1.35 | 1.01 ± 0.20 | 73.529 ± 11.86 | 0.293 ± 0.05 |
| 37 | XII | 22.42 ± 2.71 | 18.18 ± 2.14 | 1.248 ± 0.22 | 318.711 ± 41.54 | 11.51 ± 1.35 | 11.51 ± 1.35 | 1.016 ± 0.20 | 103.798 ± 15.76 | 0.326 ± 0.04 |
| 38 | XIII | 21.12 ± 1.31 | 19.20 ± 1.2 | 1.10 ± 0.22 | 318.320 ± 32.61 | 11.51 ± 1.61 | 10.75 ± 1.12 | 1.070 ± 0.21 | 97.130 ± 11.12 | 0.305 ± 0.04 |
| 39 | XIV | 20.63 ± 1.41 | 20.60 ± 1.61 | 1.00 ± 0.11 | 333.607 ± 31.41 | 10.64 ± 1.11 | 9.63 ± 1.11 | 1.104 ± 0.25 | 80.4333 ± 9.31 | 0.241 ± 0.06 |
| 40 | XV-XVII | 20.60 ± 2.53 | 21.81 ± 2.53 | 0.96 ± 0.22 | 350.336 ± 35.89 | 11.51 ± 1.35 | 10.30 ± 1.65 | 1.14 ± 0.26 | 92.284 ± 12.87 | 0.267 ± 0.06 |
| 41 | XVIII-XIX | 23.63 ± 3.95 | 16.96 ± 2.71 | 1.43 ± 0.39 | 310.058 ± 35.69 | 11.51 ± 1.35 | 9.69 ± 1.35 | 1.21 ± 0.25 | 86.528 ± 0 | 0.282 ± 0.03 |
| 42 | XX | 24.24 ± 2.14 | 16.36 ± 1.65 | 1.49 ± 0.20 | 311.500 ± 40.59 | 9.69 ± 1.35 | 9.09 ± 0 | 1.06 ± 0.14 | 69.196 ± 9.68 | 0.227 ± 0.06 |
| 43 | XXI | 22.42 ± 2.11 | 18.93 ± 0.21 | 1.184 ± 0.21 | 333.162 ± 30.69 | 10.93 ± 1.32 | 9.09 ± 0 | 1.202 ± 0.12 | 77.992 ± 9.29 | 0.234 ± 0.05 |
| 44 | XXII | 20.64 ± 2.12 | 17.63 ± 0.69 | 1.170 ± 0.20 | 285.648 ± 31.41 | 10.90 ± 1.51 | 9.09 ± 0 | 1.199 ± 0.14 | 77.778 ± 9.48 | 0.272 ± 0.06 |
| 45 | XXIII-XXIV | 19.39 ± 3.45 | 16.96 ± 2.71 | 1.15 ± 0.22 | 259.565 ± 66.31 | 10.90 ± 1.65 | 9.09 ± 0 | 1.19 ± 0.18 | 77.862 ± 11.86 | 0.304 ± 0.04 |
| 46 | XXV | 20.60 ± 2.53 | 16.36 ± 2.71 | 1.27 ± 0.19 | 266.768 ± 64.49 | 10.30 ± 1.65 | 9.09 ± 0 | 1.13 ± 0.18 | 73.529 ± 11.86 | 0.280 ± 0.05 |
|
| ||||||||||
| Correlation coefficient (r) | −0.257 | −0.389 | 0.191 | −0.471 | −0.322 | −0.509 | 0.087 | −0.520 | −0.305 | |
SD: standard deviation.
Table 2.
Percentage of leucocytes throughout larval development in Polypedates teraiensis.
| Stages | Lymphocytes ± SD | Neutrophils ± SD | Monocytes ± SD | Eosinophils ± SD | Basophils ± SD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gosner stage | Taylor and Kollros stages | |||||
| 26 | I | 60.5 ± 1.2 | 32.5 ± 0.9 | 1 ± 0 | 5 ± 0.1 | 1 ± 0.0 |
| 27 | II | 61.7 ± 1.1 | 29.7 ± 0.9 | 0 ± 0 | 6.3 ± 0.12 | 2.3 ± 0.11 |
| 28 | III | 58.2 ± 1.01 | 31.5 ± 0.85 | 0 ± 0 | 7.8 ± 0.12 | 2.5 ± 0.11 |
| 29 | IV | 59.1 ± 0.9 | 32 ± 0.75 | 1.9 ± 0.1 | 4 ± 0.21 | 3 ± 0.12 |
| 30 | V | 62.1 ± 0.98 | 31.2 ± 0.75 | 1 ± 0 | 2.7 ± 0.1 | 3 ± 0.12 |
| 31 | VI | 61.5 ± 0.9 | 29 ± 1.75 | 0.4 ± 0 | 3.9 ± 0.2 | 5.2 ± 0.21 |
| 32 | VII | 63 ± 0.89 | 22.5 ± 0.75 | 1 ± 0 | 8.5 ± 0.55 | 5 ± 0.21 |
| 33 | VIII | 58.1 ± 0.89 | 23.2 ± 0.75 | 2.9 ± 0.1 | 7.9 ± 0.12 | 7.9 ± 0.75 |
| 34 | IX | 55.9 ± 0.97 | 24.6 ± 0.85 | 3.7 ± 0.11 | 9.5 ± 0.25 | 6.3 ± 0.75 |
| 35 | X | 58.9 ± 1.01 | 17 ± 1.2 | 6.9 ± 0.21 | 11.3 ± 0.55 | 5.9 ± 0.25 |
| 36 | XI | 61.1 ± 1.2 | 18.9 ± 1.1 | 5 ± 0.11 | 10.9 ± 0.25 | 4.1 ± 0.25 |
| 37 | XII | 61.8 ± 1.2 | 14.8 ± 0.75 | 7 ± 0.12 | 12.8 ± 0.26 | 3.6 ± 0.12 |
| 38 | XIII | 59.1 ± 1.3 | 18 ± 0.75 | 7 ± 0.12 | 13.9 ± 0.35 | 2 ± 0.11 |
| 39 | XIV | 55.2 ± 1.5 | 18 ± 0.55 | 8.9 ± 0.12 | 13.9 ± 0.35 | 4 ± 0.25 |
| 40 | XV-XVII | 57.1 ± 1.5 | 9 ± 2.5 | 12 ± 0.11 | 15.9 ± 1.12 | 6 ± 0.75 |
| 41 | XVIII-XIX | 57.9 ± 1.1 | 17 ± 1.20 | 10 ± 0.13 | 12 ± 1.10 | 3.1 ± 0.12 |
| 42 | XX | 59.2 ± 0.95 | 17 ± 1.25 | 10.9 ± 0.11 | 9.9 ± 0.75 | 3 ± 0.12 |
| 43 | XXI | 58.1 ± 0.95 | 19 ± 1.5 | 10 ± 0.11 | 8 ± 0.75 | 4.9 ± 0.25 |
| 44 | XXII | 57.2 ± 0.75 | 20 ± 1.25 | 7.8 ± 0.12 | 10 ± 0.55 | 5 ± 0.25 |
| 45 | XXIII-XXIV | 59.3 ± 1.25 | 17 ± 1.25 | 7.8 ± 0.12 | 10.9 ± 0.75 | 5 ± 0.25 |
| 46 | XXV | 60.1 ± 1.10 | 20 ± 1.25 | 6.9 ± 0.2 | 9 ± 0.75 | 4 ± 0.55 |
|
| ||||||
| Correlation coefficient (r) | −0.330 | −0.789 | 0.865 | 0.611 | 0.237 | |
SD: standard deviation.
3.1. Morphology of Blood Cells
3.1.1. Erythrocytes
The erythrocytes were observed to occur in various forms. They were either elongated or circular (round) in shape. Elongated cells were oval (cells with perfect and smooth curves at both the ends) (Figure 1(A)) and elliptical (cells with more of a rectangular look) (Figures 1(B) and 1(C)). Oval (Figure 1(A)), elliptical (Figures 1(B) and 1(C)), and circular (Figure 1(D)) erythrocytes were observed in all stages. Nuclei in the erythrocytes were either centrally (Figures 1(A), 1(B), 1(C), and 1(D)) or eccentrically (Figure 1(E)) placed. Besides, some irregular forms such as comma-shaped (Figure 1(F)) and dacrocyte, that is, teardrop-shaped (Figure 1(G)) erythrocytes were observed in tadpoles of stages 37 to 40. Senile erythrocytes (without nucleus) and schistocytes (erythrocyte fragments) were observed in the tadpoles of stages 41 and 42 (Figures 1(H) and 1(I)). Dividing RBCs (Figures 1(J) and 1(K)) were present in all the metamorphic stages (39 to 44). In stages 42 to 45, larger erythrocytes were observed (Figure 1(L)). However, poikilocytosis was seen in the early stages from stage 26 to stage 31 (Figures 2(A) and 2(B)). Aggregation of the erythrocyte (Figure 2(C)) or rouleaux formation was observed in almost all stages of tadpoles investigated. During the metamorphic stages (stages 41 to 45), crenulation (short blunt projections or throne-like spicules of variable size distributed over the surface of the cell) of the erythrocytes (Figures 2(D) and 2(E)) and destruction of erythrocyte membranes (Figures 2(F), 2(G), and 2(H)) was distinct.
Figure 1.
Erythrocytes of the tadpoles of Polypedates teraiensis. (A) Oval cell with centrally placed nucleus, (B) and (C) elliptical cells with centrally placed nuclei, (D) round cell with centrally placed nucleus, (E) oval cells with eccentrically placed nuclei, (F) comma-shaped cell, (G) tear-drop-shaped cell, (H) senile erythrocytes (without nucleus), (I) schistocytes (fragmented erythrocytes), (J) and (K) dividing erythrocytes, and (L) large erythrocytes (scale bar = 10 μm).
Figure 2.

(A) and (B) Poikilocytosis, (C) aggregation of erythrocytes or rouleaux formation, (D) crenulated erythrocytes (resembling echinocytes), (E) crenulated erythrocytes (resembling acanthocytes), (F), (G), and (H) destruction of erythrocyte membrane (scale bar = 10 μm).
3.1.2. Leucocytes
The leucocytes observed in the present study were of five types, that is, lymphocytes (large and small), monocytes, eosinophils, basophils, and neutrophils. The first two being agranulocytes and the rest were granulocytes. Most of the lymphocytes were rounded in shape. The nuclei were rounded in shape both in large (Figure 3(A)) and small lymphocytes (Figure 3(B)). In both the cells, the nuclei occupied the entire cell leaving a narrow rim of light violet cytoplasm towards the periphery. Monocytes were rounded in shape with either round-shaped nuclei (Figure 3(C)) or indented nuclei (Figure 3(D)). A few monocytes had pseudopod-like cytoplasmic extensions (Figure 3(E)). Eosinophils had bilobed nuclei, which were located at one end of cells (Figure 3(F)). Basophils were round cells having large dark violet-stained granules over the irregular nuclei and also entire cells (Figure 3(G)). Neutrophils showed bilobed, trilobed, or U-shaped nuclei (band neutrophils) (Figures 3(H), 3(I), 3(J), and 3(K)).
Figure 3.
Leucocytes and platelets of the tadpoles of Polypedates teraiensis. (A) Large lymphocyte, (B) small lymphocyte, (C) monocyte with eccentrically placed round nucleus, (D) monocyte with intended nucleus, (E) monocyte with pseudopodia-like cytoplasmic extensions, (F) eosinophil, (G) basophil (H) neutrophil with bilobed nucleus, (I) neutrophil with eccentrically placed trilobed nucleus, (J) neutrophil with U-shaped nucleus (band neutrophil), (K) neutrophil with distinct trilobed nucleus, and (L) round platelets in cluster (scale bar = 10 μm).
3.1.3. Platelets
Blood platelets were rounded in shape and found in clusters (Figure 3(l)).
3.2. Morphometry of Erythrocytes
The length and breadth of red blood cells ranged from 19.24 ± 1.41 μm (Gosner stage 35) to 24.24 ± 2.14 μm (Gosner stage 42) and 15.15 ± 0 μm (Gosner stage 30) to 22.14 ± 1.61 μm (Gosner stage 27), respectively (Table 1). Similarly, the length and breadth of the nuclei ranged from 9.09 ± 0 μm (Gosner stage 30) to 12.12 ± 1.11 μm (Gosner stage 27) and 9.09 ± 0 μm (Gosner stage 30, 32, 42 to 46) to 12.12 ± 2.14 μm (Gosner stage 31), respectively, in different developmental stages (Table 1). Moreover, area occupied by the red blood cells ranged from 252.321 ± 31.41 μm2 (Gosner stage 36) to 403.908 ± 43.16 μm2 (Gosner stage 27), while the nuclear area ranged from 64.720 ± 0 μm2 (Gosner stage 30) to 168.290 ± 18.12 μm2 (Gosner stage 28) in the tadpoles of different developmental stages (Table 1).
3.3. Differential Leukocyte Count
Lymphocytes were the most abundant cells amongst the leucocytes (Table 2). Percentage of lymphocytes ranged from 55.2 ± 1.5 (39) to 63 ± 0.89 (stage 32). Neutrophils were the second abundant cells after lymphocytes. The percentage of neutrophils ranged from 9 ± 2.5 (stage 40) to 32.5 ± 0.9 (stages 26). There was an abrupt decline in the percentage of neutrophils from stage 39 to stage 40, that is, 18 ± 0.55 to 9 ± 2.5 percent, which further increased and fluctuated between 17 to 20 within stages 41 to 46. The neutrophil percentage was observed to be high during the early larval period (stage 26 to 34). The percentage of monocytes ranged from 0 to 12 ± 0.11, and interestingly the maximum percentage was observed at stage 40. At stages 27 and 28, no monocytes were observed whereas the percentage remained higher in stages 40 to 43 (10–12). The percentage of eosinophils ranged from 2.7 ± 0.1 (stage 30) to 15.9 ± 1.12 (stage 40). Tadpoles from stage 34 to stage 42 showed a comparatively higher percentage of eosinophils (9.5 ± 0.25 to 15.9 ± 1.12). Basophil percentage ranged from 1 to 7.9 ± 0.75 with a minimum at stage 26 and maximum at stage 33.
3.4. Statistical Analysis
A negative correlation was observed between different stages of tadpoles with respect to length (r = −0.257, P = 0.137), breadth (r = −0.389, P = 0.125), and area (r = −0.471, P = 0.114) of the erythrocytes. Similar negative correlation was observed for nuclear length (r = −0.322, P = 0.131), breadth (r = −0.509, P = 0.109), and area (−0.520, P = 0.107). However, the aspect ratio (length/breadth) of erythrocytes was positively correlated both for cells (r = 0.191, P = 0.141) as well as nuclei (r = 0.087, P = 0.146) (Figures 4(a)–4(h)).
Figure 4.
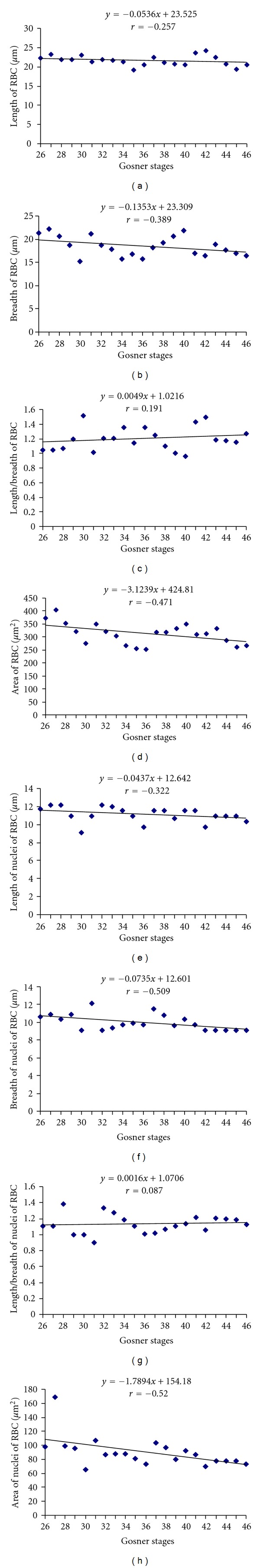
Correlation between different morphometric values of erythrocyte and stages of tadpoles.
The monocytes (r = 0.865, P = 0.03), basophils (r = 0.237, P = 0.13), and eosinophils (r = 0.6111, P = 0.09) showed a positive correlation, whereas neutrophil (r = −0.789, P = 0.05) and lymphocytes (r = −0.330, P = 0.13) showed a negative correlation with different stages during development (Figures 5(a)–5(e)). The percentage of neutrophils, eosinophils, and monocytes showed a significant correlation with different stages during development.
Figure 5.
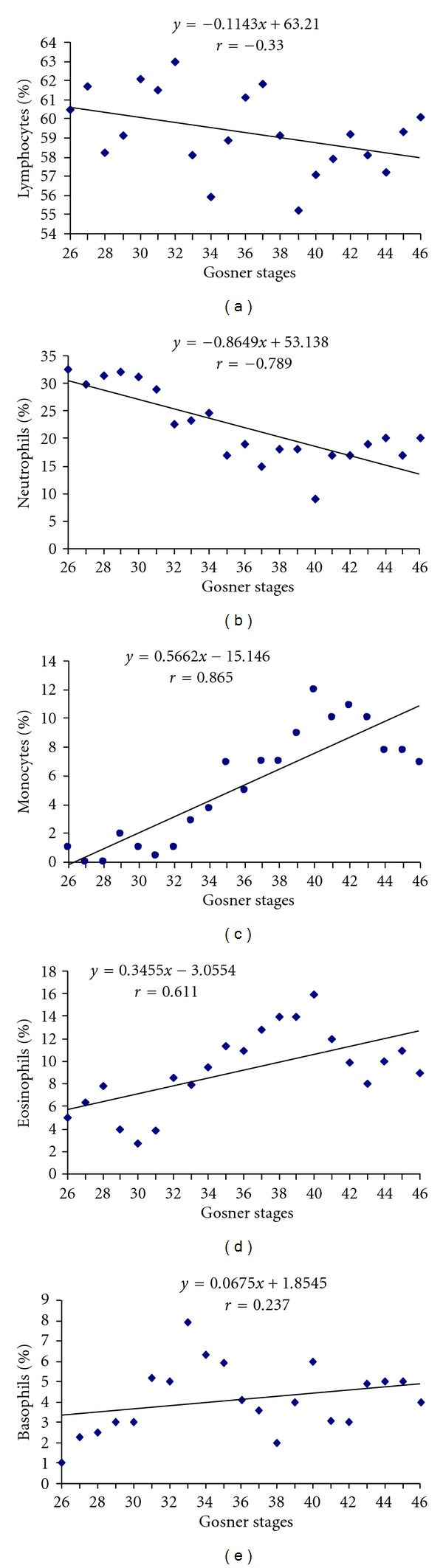
Correlation between percentage of different leucocytes and stages of tadpoles.
4. Discussion
Present investigation describes changes in the shape, size, and number of blood cells during development and metamorphosis in the tadpoles of Polypedates teraiensis. The erythrocytes constituted an entirely heterogeneous population. They appeared in different shapes such as elliptical, oval, and rounded. Depending on the position of the nuclei in the cells, it was observed that there existed oval or elliptical cells with nuclei of varying degree of eccentricity (Figure 1(E)), oval or elliptical cells with centrally placed nuclei (Figures 1(A), 1(B), and 1(C)) or rounded cells with centrally placed nuclei (Figure 1(D)).
Poikilocytosis of RBC with irregular shapes was observed in patches only during early stages, that is, 26 to 31 (Figures 2(A) and 2(B)). Disappearance of these cells at later stage seems to be a normal phenomenon. Another interesting observation was aggregation of erythrocytes or rouleaux formation (Figure 2(C)). In contrast to poikilocytosis, rouleaux formation occurred throughout the larval period. Abnormal shapes of erythrocytes such as teardrop (Figure 1(F)) and comma shaped (Figure 1(E)) were observed in the tadpoles of stages 37 to 40. Apart from this, cells with crenulations (projections over surface of cell) were seen (Figures 2(D) and 2(E)), in stages 41 to 45, which resembled the echinocytes and acanthocytes seen in mammals [46]. Similar, crenulations in red blood cells have been reported in different ranid frogs studied by Hollyfield [22]. He has described small crenulated erythrocytes to appear in the circulation of Rana pipiens during metamorphosis, which increases in number as metamorphosis proceeds, and gradually lose their wrinkled appearance. At the end of metamorphosis, the entire red cell population is replaced by these new cells. Vankin et al. [47] have observed cell outlines to be more irregular and crenulated with many cytoplasmic projections in thyroid-treated tadpoles of R. catesbeiana and have correlated it with anemic conditions and death of tadpoles during metamorphosis. In vertebrates, the abnormal cells (echinocytes, acanthocytes, schistocytes, teardrop cells, and comma shaped cells) have been reported to be present during anemic conditions [48], and the ectothermic animals are capable of withstanding the anemic conditions for a long period without mortality [49]. Thus, the present findings indicate the tadpoles to pass through a critical condition where erythrocytes show variations in shapes.
Senile erythrocytes (without nuclei) and schistocytes (erythrocytes fragments) were common in stages 41 and 42. Presence of the senile erythrocytes has been reported during metamorphosis in tadpoles of Hyla crucifer, Hyla versicolor, Rana clamitans, and Bufo americanus [29]. Schistocytes described in the present study may be due to the fragmentation of the erythrocytes as a result of passage through the blood vessels due to change in the metabolic activities during metamorphosis at stages 41 and 42.
Apart from this, division of erythrocytes was also observed from stages 39 to 44. This may be due to increase in erythropoietic activity during metamorphosis as reported earlier by Maniatis and Ingram [50] in Rana catesbeiana. Comparatively larger erythrocytes observed in stages 42 to 45 of the present study resembled the immature erythrocytes described in the tadpoles of Rana catesbeiana [50].
Size (length and breadth) of erythrocytes and their nuclei was observed to be negatively correlated with the developmental stages of the tadpoles (Figures 4(a), 4(b), 4(e), and 4(f)). The aspect ratio (length/breadth) of both the erythrocytes and their nuclei showed a positive correlation (Figures 4(c) and 4(g)), which indicated the formation of rounded cells with the growth of tadpoles. Several other workers have reported that during anuran metamorphosis larger larval cells were replaced by smaller adult erythrocytes [51, 52]. In the present study, the area of erythrocytes decreased with the development of the tadpoles (Figure 4(d)). Similar decrease in the erythrocyte area has been reported in tadpoles of Rana catesbeiana [22, 23, 28]. Decrease in area of erythrocytes during metamorphosis seems to be associated with the transfer from an aquatic to a terrestrial mode of life of the tadpole larva.
The leukocyte population (the nonspecific immune system) is reported to be one of the primary lines of defense against invading pathogens and is made up of five different types of white blood cells, each performing different tasks in the immune process [53, 54] in anurans. Out of the five types of leucocytes studied, the lymphocytes showed a negative correlation with the developmental stages (Figure 5(a)). Davis [2] has reported higher percentage of lymphocytes (70%) in the tadpoles of stages 30 to 33 in Rana catesbeiana, which declined with the onset of metamorphosis. Neutrophils also showed a negative correlation with the developmental stages (Figure 5(b)). Since, neutrophils are regarded as the first cell to respond to the site of infections [55], presence of a higher percentage of neutrophil in the early developmental stages represents requirement of more nonspecific immunity. Similar observation is seen in tadpoles of Rana catesbeiana [2]. A positive correlation was observed between the monocyte percentage and developmental stages. Monocyte percentage remained higher from stage 40 to stage 43, suggesting their involvement in the early stages of metamorphosis. Elevation in the percentage of monocytes is suggested to be correlated with increase in cellular debris resulted during remodeling of the larval structures. The percentage of eosinophils was positively correlated with progress in development. Eosinophils are known to produce a number of chemicals to initiate and modulate the immune and inflammation response [56, 57]. Thus, eosinophils may act to modulate the process of lysis of tissue during metamorphosis, which behave in a way similar to the inflammation response [2]. Basophils showed a positive correlation (Figure 5(e)), which was not significant. In the tadpoles of Rana catesbeiana [2], general increase in the number of basophils has been reported, and the author suggested the trend to be related to their formation and entrance in circulation rather than a direct association with metamorphosis.
Thus, the present study provides information regarding the blood cells of the tadpoles of Polypedates teraiensis during their development and metamorphosis, that is, their transfer from an aquatic to a terrestrial mode of life. As this is the first study to examine the hematological values of the tadpoles of Polypedates teraiensis, it establishes a baseline data that can be used as general reference values for future investigations involving this species and other anuran tadpoles.
Acknowledgments
Authors thank the Head of the P.G. Department of Zoology, Utkal University, for providing necessary facilities. Authors thank Dr. Pratyush P. Mohapatra, wildlife biologist, NTCA, New Delhi, for his help in collection and identification of foam nests. M. Das would like to thank UGC for a Research Fellowship (RFSMS).
References
- 1.Rosenkilde P, Sorensen I, Ussing AP. Amphibian hematology: metamorphosis-related changes in blood cells. Netherlands Journal of Zoology. 1994;45:213–215. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Davis AK. Metamorphosis-related changes in leukocyte profiles of larval bullfrogs (Rana catesbeiana) Comparative Clinical Pathology. 2009;18(2):181–186. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Jaylet A, Deparis P, Ferrier V. A new micronucleus test using peripheral blood erythrocytes of the newt Pleurodeles waltl to detect mutagens in fresh-water pollution. Mutation Research. 1986;164(4):245–257. doi: 10.1016/0165-1161(86)90058-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Fernandez M, L’Haridon J, Gauthier L, Zoll-Moreux C. Amphibian micronucleus test(s): a simple and reliable method for evaluating in vivo genotoxic effects of freshwater pollutants and radiations. Initial assessment. Mutation Research. 1993;292(1):83–99. doi: 10.1016/0165-1161(93)90010-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ralph S, Petras M, Pandrangi R, Vrzoc M. Alkaline single-cell (comet) assay and genotoxicity monitoring using two species of tadpoles. Environmental and Molecular Mutagenesis. 1996;28(2):112–120. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-2280(1996)28:2<112::AID-EM7>3.0.CO;2-H. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Campana MA, Panzeri AM, Moreno VJ, Dulout FN. Micronuclei induction in Rana catesbeiana tadpoles by the pyrethroid insecticide lambda-cyhalothrin. Genetics and Molecular Biology. 2003;26(1):99–103. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Wirz MVMA, Saldiva PH, Freire-Maia DV. Micronucleus test for monitoring genotoxicity of polluted river water in Rana catesbeiana tadpoles. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology. 2005;75(6):1220–1227. doi: 10.1007/s00128-005-0879-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Barni S, Boncompagni E, Grosso A, et al. Evaluation of Rana snk esculenta blood cell response to chemical stressors in the environment during the larval and adult phases. Aquatic Toxicology. 2007;81(1):45–54. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2006.10.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Cabagna MC, Lajmanovich RC, Stringhini G, Sanchez-Hernandez JC, Peltzer PM. Hematological parameters of health status in the common toad Bufo arenarum in agrosystems of Santa Fe Province, Argentina. Applied Herpetology. 2005;2(4):373–380. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Raffel TR, Rohr JR, Kiesecker JM, Hudson PJ. Negative effects of changing temperature on amphibian immunity under field conditions. Functional Ecology. 2006;20(5):819–828. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kiesecker JM. Synergism between trematode infection and pesticide exposure: a link to amphibian limb deformities in nature? Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2002;99(15):9900–9904. doi: 10.1073/pnas.152098899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Forbes MR, McRuer DL, Shutler D. White blood cell profiles of breeding American toads (Bufo americanus) relative to sex and body size. Comparative Clinical Pathology. 2006;15(3):155–159. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Forson DD, Storfer A. Atrazine increases ranavirus susceptibility in the tiger salamander, Ambystoma tigrinum . Ecological Applications. 2006;16(6):2325–2332. doi: 10.1890/1051-0761(2006)016[2325:airsit]2.0.co;2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Gervasi SS, Foufopoulos J. Costs of plasticity: responses to desiccation decrease post-metamorphic immune function in a pond-breeding amphibian. Functional Ecology. 2008;22(1):100–108. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Davis AK, Maney DL, Maerz JC. The use of leukocyte profiles to measure stress in vertebrates: a review for ecologists. Functional Ecology. 2008;22(5):760–772. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Jordan HE, Speidel CC. Blood cell formation and distribution in relation to the mechanism of thyroid-accelerated metamorphosis in the larval frog. The Journal of Experimental Medicine. 1923;38:529–543. doi: 10.1084/jem.38.5.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Jordan HE, Speidel CC. The behavior of the leucocytes during coincident regeneration and thyroid-induced metamorphosis in the frog larva, with a consideration of growth factors. The Journal of Experimental Medicine. 1924;40:1–11. doi: 10.1084/jem.40.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Frank G. Granulopoiesis in tadpoles of Rana esculenta. Ultrastructural observations on the morphology and development of heterophil and basophil granules. Journal of Anatomy. 1989;163:107–116. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Rollins-Smith LA, Barker KS, Davis AT. Involvement of glucocorticoids in the reorganization of the amphibian immune system at metamorphosis. Developmental Immunology. 1997;5(2):145–152. doi: 10.1155/1997/84841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Bennett MF, Harbottle JA. The effects of hydrocortisone on the blood of tadpoles and frogs, Rana catesbeiana . Biological Bulletin. 1968;135(1):92–95. doi: 10.2307/1539616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Bennett MF, Alspaugh JK. Some changes in the blood of frogs following administration of hydrocortisone. The Virginia Journal of Science. 1964;15:76–79. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hollyfield JG. Erythrocyte replacement at metamorphosis in the frog, Rana pipiens . Journal of Morphology. 1966;119(1):1–6. doi: 10.1002/jmor.1051190102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Benbassat J. Erythroid cell development during natural amphibian metamorphosis. Developmental Biology. 1970;21(4):557–583. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(70)90078-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Broyles RH, Johnson GM, Maples PB, Kindell GR. Two erythropoietic microenvironments and two larval red cell lines in bullfrog tadpoles. Developmental Biology. 1981;81(2):299–314. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90293-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Moss B, Ingram VM. Hemoglobin synthesis during amphibian metamorphosis. II. Synthesis of adult hemoglobin following thyroxine administration. Journal of Molecular Biology. 1968;32(3):493–504. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90337-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Dorn AR, Broyles RH. Erythrocyte differentiation during the metamorphic hemoglobin switch of Rana catesbeiana . Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 1982;79(18 I):5592–5596. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Just JJ, Klaus-Just J. Controls of thyroid hormones and their involvement in hemoglobin transistion during Xenopus and Rana metamorphosis. In: Tinsley RC, Kobel HR, editors. Biology of Xenopus. London, UK: Oxford University Press; 1996. pp. 213–229. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Hasebe T, Oshima H, Kawamura K, Kikuyama S. Rapid and selective removal of larval erythrocytes from systemic circulation during metamorphosis of the bullfrog, Rana catesbeiana . Development Growth and Differentiation. 1999;41(5):639–643. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-169x.1999.00461.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Speidel CC. Bile pigment production and erythrocyte destruction in thyroid-treated amphibian larvae. The Journal of Experimental Medicine. 1926;63:703–712. doi: 10.1084/jem.43.5.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Banerjee V, Banerjee M. Seasonal variations of erythrocyte number and haemoglobin content in the common Indian Toad, Bufo melanostictus . Proceedings of the Zoological Society (Calcutta) 1966;19:173–178. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Boral MC, Deb CC. Seasonal changes in body fluids and haematology in toad Bufo melanostictus a poikilothermic cold torpor. Proceedings of the Indian National Science Academy. 1970;36(6):369–379. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Banerjee V, Sinha PK. Notes on the differential leukocyte count in the female toad Bufo melanostictus with relation to body weight. Indian Journal of Animal Research. 1978;12(1):47–48. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Banerjee V, Singh PK, Ahmed M, Yadav DP. Some aspects of haematology of Bufo melanostictus with relation to body weight. Journal of the Zoological Society of India. 1980;31:55–60. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Mishra V, Banerjee V. Haematology of Rana tigerina. Erythrocytes and related parameters with relation to body weight. Annals of Zoology. 1983;20(1):25–32. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Mahapatra BB, Das M, Dutta SK, Mahapatra PK. Hematology of Indian rhacophorid tree frog Polypedates maculatus, Gray, 1833 (Anura: Rhacophoridae) Comparative Clinical Pathology. In press. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Gosner KL. A simplified table for staging anuran embryos and larvae. Herpetologica. 1960;16:183–190. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Dutta SK, Nair MV, Mohapatra PP, Mahapatra AK. Amphibians and reptiles of similipal biosphere reserves. Regional Plant Resource Centre. 2009:52–53. [Google Scholar]
- 38.Mohanty-Hejmadi P. Care and management of amphibian embryos. Prakruti-Utkal University Journal-Scienc. 1977;11:81–87. [Google Scholar]
- 39.Taylor AC, Kollros JJ. Stages in the normal development of Rana pipiens larvae. The Anatomical Record. 1946;94:2–23. doi: 10.1002/ar.1090940103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.McDiarmid W, Altig R. Tadpoles: The Biology of Anuran Larvae. Chicago, Ill, USA: The University of Chicago Press; 2000. [Google Scholar]
- 41.Hadji-Azimi I, Coosemans V, Canicatti C. Atlas of adult Xenopus laevis laevis hematology. Developmental and Comparative Immunology. 1987;11(4):807–874. doi: 10.1016/0145-305x(87)90068-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Turner RJ. Amphibians. In: Rawley AF, Ratcliff NA, editors. Vertebrate Blood Cells. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press; 1998. pp. 129–209. [Google Scholar]
- 43.Heatley JJ, Johnson M. Clinical technique: amphibian hematology: a practitioner’s guide. Journal of Exotic Pet Medicine. 2009;18(1):14–19. [Google Scholar]
- 44.Arserim SK, Mermer A. Hematology of the Uludağ frog, Rana macrocnemis Boulenger, 1885 in Uludağ National park (Bursa, Turkey) E. U. Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences. 2008;25(1):39–46. [Google Scholar]
- 45.Steel RGD, Torrie JN. Principles and Procedures of Statistics. London, UK: McGraw Hill; 1980. [Google Scholar]
- 46.Foglia A. The acanthocyte-echinocyte differential: the example of chorea-acanthocytosis. doi: 10.4414/smw.2010.13039. Swiss Medical Weekly. In press. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Vankin GL, Brandt EM, DeWitt W. Ultrastructural studies on red blood cells from thyroxin-treated Rana catesbeiana tadpoles. Journal of Cell Biology. 1970;47(3):767–772. doi: 10.1083/jcb.47.3.767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.College of American Pathologists. Blood cell identification. Hematology and Clinical Microscopy Glossary. 2010:3–21. [Google Scholar]
- 49.Feder ME, Burggren WW. Environmental Physiology of the Amphibians. University of Chicago Press; 1992. [Google Scholar]
- 50.Maniatis GM, Ingram VM. Erythropoiesis during amphibian metamorphosis—I. Site of maturation of erythrocytes in Rana catesbeiana . The Journal of Cell Biology. 1971;49:372–379. doi: 10.1083/jcb.49.2.372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Broyles RH. Changes in the blood during amphibian metamorphosis. In: Gilbert LI, Frieden E, editors. A Problem in Developmental Biology. New York, NY, USA: Plenum Press; 1981. pp. 461–490. [Google Scholar]
- 52.Duelleman WL, Trueb L. Biology of Amphibians. New York, NY, USA: McGraw Hill; 1986. [Google Scholar]
- 53.Jain NC. Schalm’s Vertebrate Hematology. Philadelphia, Pa, USA: Lea and Febiger; 1986. [Google Scholar]
- 54.Jain NC. Essentials of Veterinary Hematology. Philadelphia, Pa, USA: Blackwell; 1993. [Google Scholar]
- 55.Thrall MA. Hematology of amphibians. In: Thrall MA, Baker DC, Lassen ED, editors. Veterinary Hematology and Clinical Chemistry: Test and Clinical Test Presentations. Philadelphia, Pa, USA: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; 2004. [Google Scholar]
- 56.Adamko DJ, Odemuyiwa SO, Vethanayagam D, Moqbel R. The rise of the phoenix: the expanding role of the eosinophil in health and disease. Allergy. 2005;60(1):13–22. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.2005.00676.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Rothenberg ME, Hogan SP. The eosinophil. Annual Review of Immunology. 2006;24:147–174. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.24.021605.090720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




