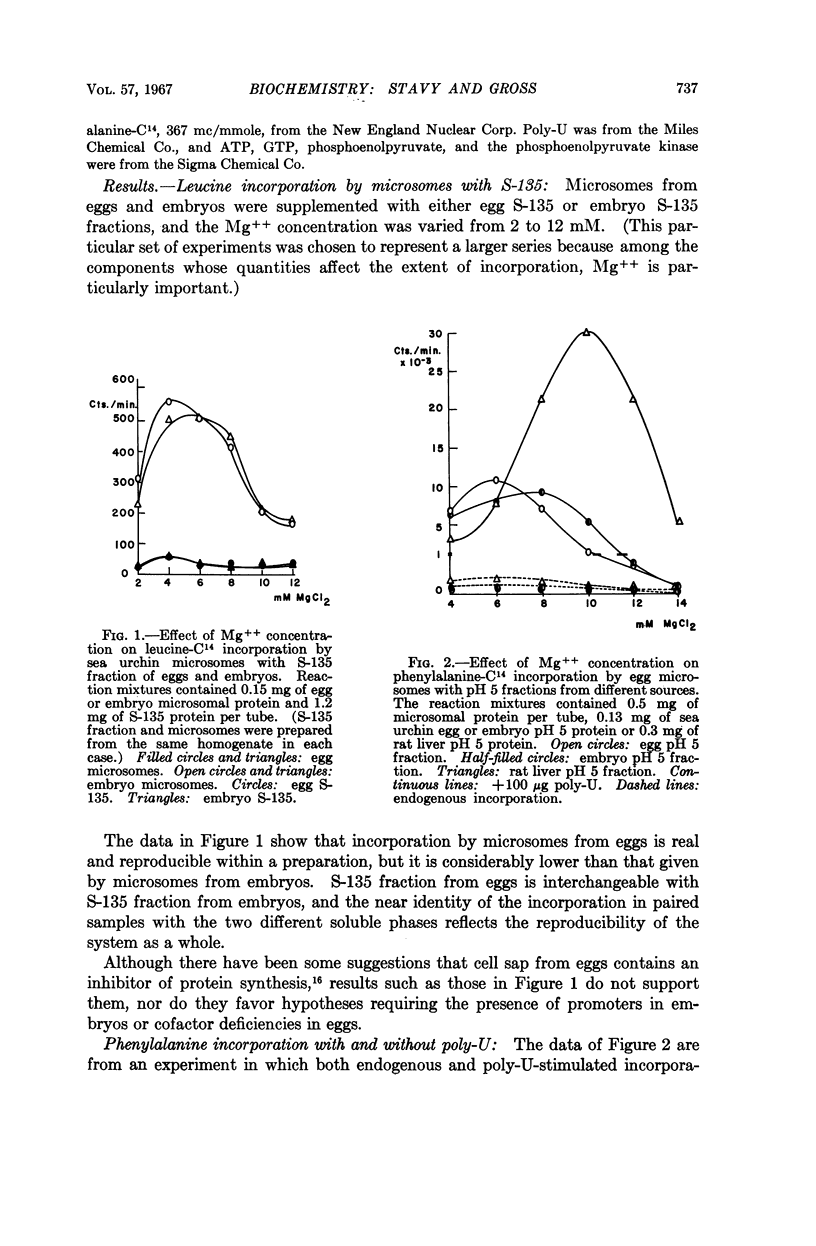
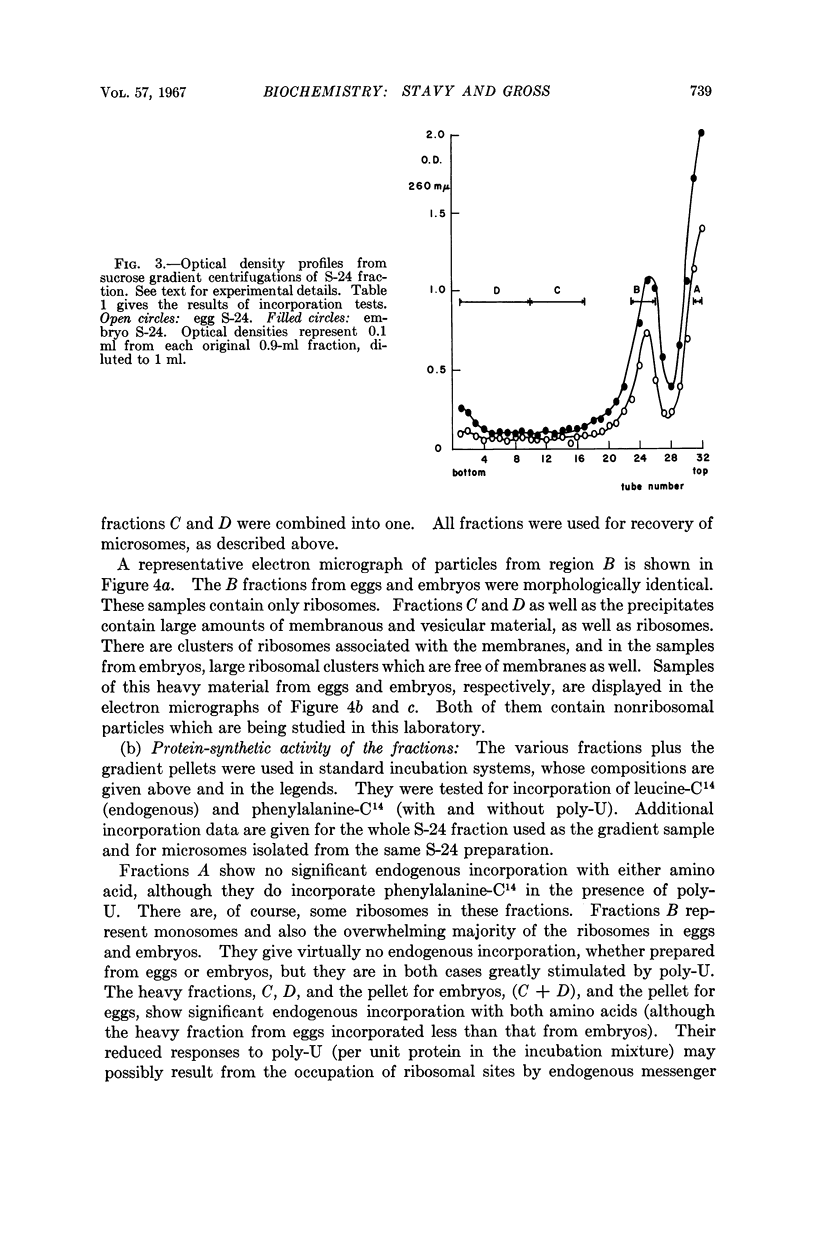
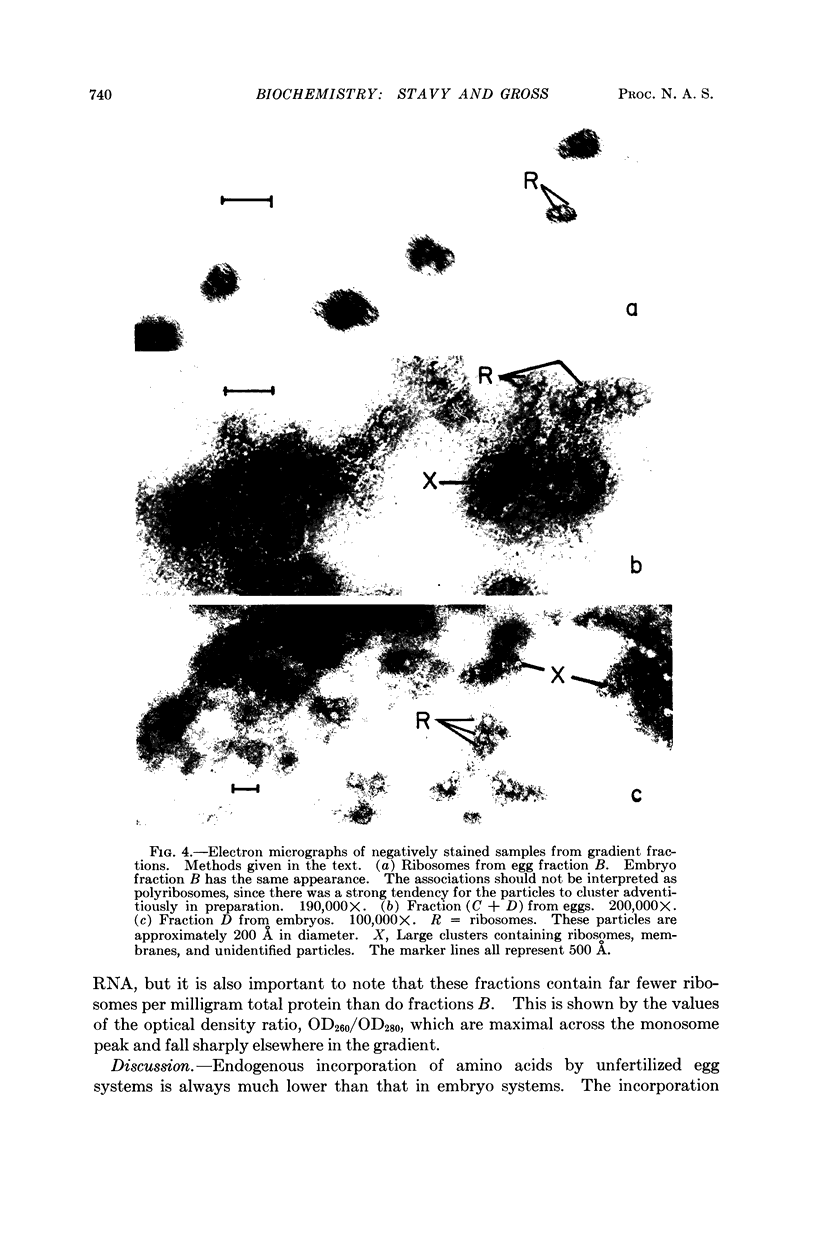
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Candelas G. C., Iverson R. M. Evidence for translational level control of protein synthesis in the development of sea urchin eggs. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Sep 22;24(6):867–871. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90328-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSS P. R., MALKIN L. I., MOYER W. A. TEMPLATES FOR THE FIRST PROTEINS OF EMBRYONIC DEVELOPMENT. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Mar;51:407–414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.3.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSS P. R. THE IMMEDIACY OF GENOMIC CONTROL DURING EARLY DEVELOPMENT. J Exp Zool. 1964 Oct;157:21–41. doi: 10.1002/jez.1401570107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glisin V. R., Glisin M. V., Doty P. The nature of messenger RNA in the early stages of sea urchin development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jul;56(1):285–289. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.1.285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross P. R., Malkin L. I., Hubbard M. Synthesis of RNA during oogenesis in the sea urchin. J Mol Biol. 1965 Sep;13(2):463–481. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80110-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HULTIN T. Activation of ribosomes in sea urchin eggs in response to fertilization. Exp Cell Res. 1961 Nov;25:405–417. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(61)90290-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HULTIN T. ON THE MECHANISM OF RIBOSOMAL ACTIVATION IN NEWLY FERTILIZED SEA URCHIN EGGS. Dev Biol. 1964 Oct;10:305–328. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(64)90047-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MALKIN L. I., GROSS P. R., ROMANOFF P. POLYRIBOSOMAL PROTEIN SYNTHESIS IN FERTILIZED SEA URCHIN EGGS: THE EFFECT OF ACTINOMYCIN TREATMENT. Dev Biol. 1964 Dec;10:378–394. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(64)90051-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONROY A., TYLER A. FORMATION OF ACTIVE RIBOSOMAL AGGREGATES (POLYSOMES) UPON FERTILIZATON AND DEVELOPMENT OF SEA URCHIN EGGS. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1963 Dec;103:431–435. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(63)90433-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggio R., Vittorelli M. L., Rinaldi A. M., Monroy A. In vitro incorporation of amino acids into proteins stimulated by RNA from unfertilized sea urchin eggs. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1964 Apr 22;15(5):436–441. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(64)90481-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mano Y., Nagano H. Release of maternal RNA from some particles as a mechanism of activation of protein synthesis fertilization in sea urchin eggs. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Oct 20;25(2):210–215. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90582-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mano Y. Role of a trypsin-like protease in "informosomes" in a trigger mechanism of activation of protein synthesis by fertilization in sea urchin eggs. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Oct 20;25(2):216–221. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90583-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monroy A., Maggio R., Rinaldi A. M. Experimentally induced activation of the ribosomes of the unfertilized sea urchin egg. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Jul;54(1):107–111. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.1.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEMER M., BARD S. G. Polypeptide synthesis in sea urchin embryogenesis: an examination with synthetic polyribonucleotides. Science. 1963 May 10;140(3567):664–666. doi: 10.1126/science.140.3567.664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STAFFORD D. W., SOFER W. H., IVERSON R. M. DEMONSTRATION OF POLYRIBOSOMES AFTER FERTILIZATION OF THE SEA URCHIN EGG. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Aug;52:313–316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.2.313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salb J. M., Marcus P. I. Translational inhibition in mitotic HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Nov;54(5):1353–1358. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.5.1353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater D. W., Spiegelman S. An estimation of genetic messages in the unfertilized echinoid egg. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jul;56(1):164–170. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.1.164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILT F. H., HULTIN T. Stimulation of phenylalanine incorporation by polyuridylic acid in homogenates of sea urchin eggs. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1962 Oct 31;9:313–317. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(62)90046-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteley A. H., McCarthy B. J., Whiteley H. R. Changing populations of messenger RNA during sea urchin development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Mar;55(3):519–525. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.3.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]