Abstract
Histone post-transcriptional modifications play essential roles in regulation of all DNA related processes. Among them, histone ubiquitination has been discovered for more than three decades. However, its functions are still less well understood than other histone modifications such as methylation and acetylation. In this review, we will summarize our current understanding of histone ubiquitination and deubiquitination. In particular, we will focus on how they are regulated by histone ubiquitin ligases and deubiquitinating enzymes. We will then discuss the roles of histone ubiquitination in transcription and DNA damage response and the crosstalk between histone ubiquitination and other histone modifications. Finally, we will review the important roles of histone ubiquitination in stem cell biology and cancer.
Keywords: ubiquitin ligases, deubiquitinating enzymes, DUBs, H2Aub, H2Bub, BRCA1, RNF20, USP22
Introduction
In the eukaryotic nucleus, genomic DNA is packaged into chromatin by forming nucleosomes. Each nucleosome core particle consists of a histone octamer which is wrapped by 146 base pairs of DNA (Luger et al., 1997). A histone octamer is composed of two copies of the core histones H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. The histone tails protrude from the nucleosome, and are subjected to a wide array of covalent modifications include methylation, acetylation, ubiquitination, phosphorylation, sumoylation, and ADP ribosylation (Strahl and Allis, 2000). These post-transcriptional modifications work together to regulate the chromatin structure, which affects biological processes including gene expression, DNA repair, and chromosome condensation. Recent advances have defined critical roles of histone ubiquitination in transcriptional regulation and DNA repair. The writers, erasers, and readers of histone ubiquitination have also been linked to cancer development.
Histone Ubiquitination
Histone H2A is the first protein identified to be modified by ubiquitin in cells (Goldknopf et al., 1975). We know now H2A and H2B are two of the most abundant ubiquitinated proteins in the nucleus. It is estimated that 5–15% of H2A and 1–2% of H2B are conjugated with ubiquitin in vertebrate cells, while about 10% of H2B are ubiquitinated in yeast cells (Goldknopf et al., 1975; Matsui et al., 1979; West and Bonner, 1980; Robzyk et al., 2000).
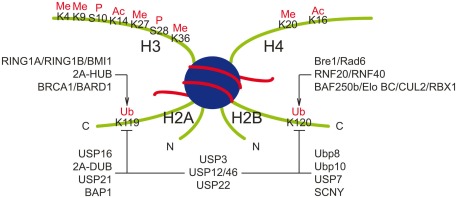
The dominant form of ubiquitinated histones are monoubiquitinated H2A (H2Aub) and H2B (H2Bub). A single molecule of ubiquitin is added to the highly conserved lysine residues: Lys-119 for H2A, and Lys-123 in yeast or Lys-120 in vertebrate for H2B (Figure 1; Goldknopf et al., 1975; West and Bonner, 1980). Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) experiments showed that monoubiquitinated H2A is enriched in the satellite regions of genome, while H2Bub binds to the gene body of transcriptional active genes (Minsky et al., 2008; Shema et al., 2008; Zhu et al., 2011).
Figure 1.
Ubiquitin ligases and deubiquitinating enzymes responsible for monoubiquitination of histones H2A and H2B. Major post-transcriptional modifications on histone H3 and H4 tails are also shown. Ac, acetylation; Me, methylation; P, phosphorylation.
In addition to H2A and H2B, core histones H3, H4, and linker histone H1 have also been reported to be modified by ubiquitin (Pham and Sauer, 2000; Jason et al., 2002; Wang et al., 2006; Jones et al., 2011). For example, H3 and H4 were polyubiquitinated in vivo by CUL4–DDB–RBX1 ubiquitin ligase complex after UV irradiation (Wang et al., 2006). But the biological function of these modifications has not been well elucidated.
Besides monoubiquitination, histone H2A and H2B can be modified by ubiquitin chains. K63-linked polyubiquitination of H2A and H2AX, a variant of H2A, is usually induced by DNA damage and is required for DNA repair response (Huen et al., 2007; Kolas et al., 2007; Mailand et al., 2007; Wang and Elledge, 2007; Doil et al., 2009; Stewart et al., 2009). Like other proteins, formation of K48-linked ubiquitin chains on histones targets them for proteasome mediated degradation. For example, during spermatogenesis, histones are degraded through this mechanism and replaced by transition proteins to permit chromatin condensation (Chen et al., 1998; Liu et al., 2005).
Histone Ubiquitination Enzymes
In this section, we will summarize our current knowledge on the histone modifying enzymes that can add ubiquitin to or remove it from histones (Figure 1; Table 1).
Table 1.
Functions of histone modifying enzymes for monoubiquitination.
| Enzyme | Species | Histone specificity | Enzymatic activity | Role in transcription | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RING1A/RING1B/BMI1 | Human | H2A | E3 | Repression | Cao et al. (2005); Gearhart et al. (2006) |
| 2A-HUB | Human | H2A | E3 | Repression | Zhou et al. (2008) |
| BRCA1/BARD1 | Human | H2A | E3 | Repression | Chen et al. (2002); Zhu et al. (2011) |
| UbcH5c | Human | H2A | E2 | N/A | Chen et al. (2002) |
| Bre1 | Yeast | H2B | E3 | Activation | Robzyk et al. (2000); Kao et al. (2004) |
| Rad6 | Yeast | H2B | E2 | Activation | Robzyk et al. (2000); Kao et al. (2004) |
| RNF20/40 | Human | H2B | E3 | Activation | Kim et al. (2005); Prenzel et al. (2011) |
| RAD6A/B | Human | H2B | E2 | Activation | Kim et al. (2005) |
| UbcH6 | Human | H2B | E2 | Activation | Zhu et al. (2005) |
| USP16 | Human | H2A | DUB | Activation | Joo et al. (2007); Shanbhag et al. (2010) |
| USP21 | Human | H2A | DUB | Activation | Nakagawa et al. (2008) |
| 2A-DUB | Human | H2A | DUB | Activation | Zhu et al. (2007) |
| BAP1 | Human Drosophila | H2A | DUB | Activation | Scheuermann et al. (2010) |
| Ubp8 | Yeast | H2B | DUB | Activation | Henry et al. (2003); Daniel et al. (2004) |
| Ubp10 | Yeast | H2B | DUB | Repression | Emre et al. (2005) |
| Ubp7 | Drosophila | H2B | DUB | Repression | van der Knaap et al. (2005) |
| SCNY | Drosophila | H2B | DUB | Repression | Buszczak et al. (2009) |
| UBP12/46 | Xenopus | H2A H2B | DUB | Activation | Joo et al. (2011) |
| USP3 | Human | H2A H2B | DUB | N/A | Nicassio et al. (2007) |
| USP22 | Human | H2A H2B | DUB | Activation | Zhang et al. (2008); Zhao et al. (2008) |
Histone ubiquitin ligases
Polycomb group protein RING1B is the first identified ubiquitin ligase (E3) responsible for monoubiquitination of H2A at lysine 119 (Wang et al., 2004; Cao et al., 2005). Loss of RING1B dramatically decreases H2A monoubiquitination globally and at the promoters of specific genes (Wang et al., 2004; Cao et al., 2005). Two other RING domain containing proteins in the PRC1 (Polycomb Repressive Complex 1) complex, RING1A, and BMI1, strongly stimulate the E3 ubiquitin ligase activity of RING1B (Cao et al., 2005; Buchwald et al., 2006). Another H2A-specific E3, 2A-HUB/hRUL138 is recruited by the NCoR/HDAC1/3 complex and catalyzes H2A monoubiquitination at Lysine 119 (Zhou et al., 2008). Breast cancer type 1 susceptibility gene (BRCA1) is also a potential E3 ubiquitin ligase for histone H2A. In an in vitro ubiquitination assay, BRCA1 cooperates with ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme (E2) UbcH5c to catalyze monoubiquitination of H2A/H2AX (Chen et al., 2002). In an in vivo study, BRCA1 co-localizes with H2Aub on satellite DNA, and loss of BRCA1 results in the decrease of H2Aub occupation in these regions (Zhu et al., 2011). Another RING finger containing protein BARD1, which carries an enzyme dead mutation in its RING finger, binds to BRCA1 and enhances its E3 activity (Xia et al., 2003). Although several ubiquitin ligases can catalyze H2A monoubiquitination, loss of RING1A, RING1B, or BMI1 leads to global decrease of H2Aub, suggesting the RING1A/RING1B/BMI1 complex is the major E3 in mammalian cells (de Napoles et al., 2004; Wang et al., 2004; Cao et al., 2005; Stock et al., 2007).
The enzymes responsible for H2B monoubiquitination were first identified in yeast: Rad6 as a ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme and Bre1 as a ubiquitin ligase (Robzyk et al., 2000; Hwang et al., 2003; Wood et al., 2003; Kao et al., 2004). There are two homologs of Bre1 in mammalian cells: RNF20 and RNF40 (Koken et al., 1991; Kim et al., 2005). RNF20 and RNF40 form a complex in vivo, associate with yRad6 homologs hRAD6A and hRAD6B, or another ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme UbcH6, and catalyze monoubiquitination of H2B at lysine 120 in vitro (Kim et al., 2005, 2009; Zhu et al., 2005). Knockdown of RNF20 or RNF40 significantly reduces H2Bub globally in human cells (Kim et al., 2005; Zhu et al., 2005). The SWI/SNF-A subunit BAF250b associates with Elongin B and C, CUL2, and RBX1 to form a canonical Elongin BC containing ubiquitin ligase complex similar to the VHL or E4orf6 complex (Kamura et al., 1999; Querido et al., 2001; Yan et al., 2004). This BAF250b complex can also catalyze H2B monoubiquitination (Li et al., 2010).
Histones H2A and H2AX can also be polyubiquitinated by a related ubiquitin ligase complex. RNF8 and RNF168 catalyze formation of K63-linked polyubiquitination chain in histones H2A and H2AX at the site of DNA damage during DNA damage repair (Stewart et al., 2009). Polyubiquitination of H2A and H2AX facilitates the accumulation of DNA repair proteins including 53BP1 and BRCA1 at the DNA damage foci (Huen et al., 2007; Kolas et al., 2007; Mailand et al., 2007; Wang and Elledge, 2007; Doil et al., 2009; Stewart et al., 2009).
Histone deubiquitinating enzymes
Like other histone modifications, monoubiquitination of histones H2A and H2B is reversible. The ubiquitin modification can be removed by ubiquitin specific peptidases known as deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs).
Several DUBs, including USP16, 2A-DUB, USP21, and BRCA1 associated protein 1 (BAP1) were identified as H2A-specific. USP16 catalyzes H2A deubiquitination in vitro and in vivo, and plays important roles in H2Aub mediated HOX gene silencing, X chromosome inactivation, cell cycle progression, and DNA damage repair (Joo et al., 2007; Shanbhag et al., 2010). 2A-DUB interacts with PCAF and is required for full activation of androgen receptor-dependent genes (Zhu et al., 2007). Another H2A-specific DUB, USP21, was identified as a regulator of liver regeneration by deubiquitination of H2Aub at the promoters of regeneration related genes (Nakagawa et al., 2008). The polycomb protein BAP1, was identified as an H2A-specific histone C-terminal hydrolase. BAP1 removes monoubiquitin from H2A but not H2B in vivo and in vitro. Loss of BAP1 significantly increases H2Aub level and abolishes the repression of HOX genes in flies (Scheuermann et al., 2010).
Ubp8 and Ubp10 were identified as histone H2B DUBs in yeast (Henry et al., 2003; Daniel et al., 2004; Emre et al., 2005), but they have very different functions. Ubp8 co-localizes with H3K4me3, while Ubp10 binds to H3K79me3 enriched sites, as well as telomere and rDNA locus (Emre et al., 2005; Schulze et al., 2011). Ubp8 catalyzes H2B deubiquitination in vitro and loss of Ubp8 increases the global level of H2Bub (Henry et al., 2003; Daniel et al., 2004), suggesting that Ubp8 is the major H2Bub DUB in yeast. Furthermore, as a component of the SAGA acetylation complex, Ubp8 is required for the transcription of SAGA-regulated genes (Henry et al., 2003). In addition, USP7 has been shown to catalyze H2B deubiquitination and mediate epigenetic silencing of homeotic genes (van der Knaap et al., 2005). Drosophila ubiquitin protease SCNY, a homolog of yeast Ubp10, deubiquitinates monoubiquitinated H2B in vitro (Buszczak et al., 2009). Loss of SCNY increases monoubiquitinated H2B in larvae (Buszczak et al., 2009). Interestingly, SCNY is required for maintaining multiple types of adult stem cells (Buszczak et al., 2009).
In addition to H2A or H2B specific DUBs, several DUBs display dual specificity toward both H2Aub and H2Bub, such as USP3, USP12, and USP46. USP3 is required for cell cycle progression and genome stability, while USP12 and USP46 regulate Xenopus development (Nicassio et al., 2007; Joo et al., 2011). The Ubp8 homolog USP22 is a subunit of coactivator acetyltransferase hSAGA complex. It is recruited to the promoters by activators to deubiquitinate H2A and H2B, and is required for transcription activation (Zhang et al., 2008; Zhao et al., 2008).
Multiple histone DUBs were identified, suggesting that they may have redundant functions or act in a context-dependent manner. Although their redundancy was not extensively investigated, current literature supports the notion that these DUBs have context-dependent functions in various processes. Their functions may also be dictated by their expression patterns in different tissues and stages during development.
Function of Histone Ubiquitination
As histones are the most abundant ubiquitinated proteins, their ubiquitination plays critical roles in many processes in the nucleus, including transcription, maintenance of chromatin structure, and DNA repair.
Transcription
Monoubiquitination of H2A and H2B have been clearly implicated in transcriptional regulation. H2Aub occupation is more frequently correlated with gene silencing, while H2Bub is mostly associated with transcription activation.
H2A ubiquitin ligases were found in transcription repressor complexes, such as the PRC1, BCoR, E2F6.com-1, and 2A-HUB complexes (Ogawa et al., 2002; Wang et al., 2004; Cao et al., 2005; Gearhart et al., 2006; Zhou et al., 2008). RING1B mediated H2Aub is required for polycomb targeted gene silencing (Cao et al., 2005). Furthermore, in an in vitro assay, H2Aub represses transcriptional initiation and inhibits the formation of transcriptional active markers H3K4me2 and me3 (Nakagawa et al., 2008). The fact that H2A DUBs are usually required for genes activation (Joo et al., 2007; Zhu et al., 2007; Zhao et al., 2008) provides a second line of evidence for the gene silencing function of H2Aub.
In contrast, H2Bub occupation is strongly correlated with active gene expression in most cases, likely through multiple mechanisms, including promoting other active histone modifications and Pol II elongation. In a ChIP-on-Chip experiment, H2B monoubiquitination was found in the transcribed regions of highly expressed genes (Minsky et al., 2008). In yeast, monoubiquitinated H2B is required for the COMPASS complex for di- and tri-methylation of H3 at lysine 4 (Dover et al., 2002; Sun and Allis, 2002; Lee et al., 2007a), which are active markers for transcription (Klose et al., 2007; Blair et al., 2011). Loss of E2, E3, or the ubiquitination site (K123) within H2B inhibits H3K4 methylation by the COMPASS complex (Sun and Allis, 2002; Wood et al., 2003). In mammalian cells, E2 UbcH6 and E3 complex RNF20/RNF40 are recruited to transcriptionally active genes (Zhu et al., 2005). RNF20 also binds to transcription factors such as p53 directly and functions as a coactivator (Kim et al., 2005). Overexpression of RNF20 leads to elevated H2B monoubiquitination globally, which leads to subsequent increase of methylation at lysine 4 and 79 in H3, and stimulation of HOX gene expression (Zhu et al., 2005). Conversely, knockdown of RNF20 decreases endogenous H2Bub, H3K4, and K79 methylation, and therefore transcription (Kim et al., 2005). Moreover, transcriptional regulation by RNF20 is dependent on its E3 ligase activity (Shema et al., 2011).
Recent work implicated the function of H2Bub in regulating transcriptional elongation, suggesting that it is also a mechanism by which H2Bub plays a positive role in gene expression. H2B ubiquitination is associated with elongating RNA Polymerase II, and is necessary for reassembly of nucleosomes and restoration of the chromatin structure during the transcription elongation, thus influencing the kinetic properties of elongating Pol II (Xiao et al., 2005). Using a reconstituted chromatin transcription system, Reinberg and colleagues showed that H2Bub stimulates elongation by Pol II through the chromatin by promoting the replacement of H2A/H2B dimers from the core nucleosomes (Pavri et al., 2006). A recent study showed that monoubiquitinated H2B cooperates with acetylated H4 to disrupt chromatin compaction, which leads to an open and accessible chromatin structure (Fierz et al., 2011). Furthermore, yeast mutants carrying defects in H2B ubiquitination pathway display transcription elongation defects (Xiao et al., 2005).
However, H2B monoubiquitination may also repress gene expression in some cases. H2B DUBs, for example, were found in some coactivator complexes and they are required for coactivator-dependent gene activation in both yeast and mammalian cells (Henry et al., 2003; Zhang et al., 2008; Zhao et al., 2008). One of these DUBs, Ubp8, promotes Pol II CTD phosphorylation, which is a mark of transcription elongation and is required for co-transcriptional mRNA processing (Wyce et al., 2007). Both E3s and DUBs of H2Bub showed a positive effect on gene activation, suggesting the ubiquitination and deubiquitination cycle of H2B is required for full gene induction (Henry et al., 2003; Wyce et al., 2007).
Many studies demonstrated that histone ubiquitination and other histone modifications are inter-connected and they act in combination and/or sequentially to regulate transcription. For example, H2B monoubiquitination is required for both H3K4 methylation and H3K79 methylation (Dover et al., 2002; Sun and Allis, 2002; Lee et al., 2007a). H3K27 demethylase UTX was shown to suppress the recruitment of PRC1 and subsequent H2A monoubiquitination (Lee et al., 2007b). It was also shown that H2A monoubiquitination is coupled to H3K36me2 demethylation (Lagarou et al., 2008). These findings indicate that precise transcriptional control requires the concerted actions of multiple histone modifications.
DNA damage response
Current studies suggest that histone ubiquitination is a general histone modification induced by DNA damage and plays important roles in DNA damage response. DNA damage has emerged as a major culprit in cancer and many other diseases. Inherited impairments in DNA repair usually leads to a higher risk of cancer. Cells developed a defense system against DNA damage, called DNA damage response, which includes recruitment of DNA repair machinery, cell cycle arrest, and lesion tolerance or apoptosis (Hoeijmakers, 2001).
One of the classic models to trigger DNA damage response is to introduce DNA double-strand break (DSB). Following DSBs, the histone variant H2AX is rapidly phosphorylated at the γ position (γH2AX) along chromatin tracks flanking DSBs by ATM, ATR, and DNA-PK (Falck et al., 2005). H2AX phosphorylation facilitates the accumulation of DNA damage response regulators, Mdc1/NFBD1(Stewart et al., 2003; Xu and Stern, 2003), RNF8 and RNF168. RNF8 and RNF168 catalyze the K63-linked polyubiquitination chain formation on histone H2A and H2AX (Huen et al., 2007; Kolas et al., 2007; Mailand et al., 2007; Stewart et al., 2009). K63-linked polyubiquitinated histones provide a recognition element that recruits RAP80 through its ubiquitin interaction motif (Kim et al., 2007; Sobhian et al., 2007; Wang et al., 2007). The subsequent recruitment of BRCA1 and the intact IR induced G2/M checkpoint are dependent on RAP80 and its ubiquitin binding motif that recognizes K63-linked polyubiquitin chains on H2A and H2AX (Kim et al., 2007; Sobhian et al., 2007; Wang and Elledge, 2007; Wang et al., 2007). Consistent with these findings, knockdown of histone ubiquitination enzymes impairs DSB-associated polyubiquitination of H2A and H2AX, inhibits retention of 53BP1 and BRCA1 at the DSB sites, and sensitizes cells to ionizing radiation (Huen et al., 2007; Kolas et al., 2007; Mailand et al., 2007; Stewart et al., 2009).
In addition to polyubiquitination, monoubiquitination of histones H2A, H2B, and H2AX also occurs at the sites of DNA damage. RING1B/BMI1 and RNF20/RNF40 are recruited to DSB site and catalyze H2A/H2AX monoubiquitination at lysine 119 and H2B monoubiquitination at lysine 120, respectively (Bergink et al., 2006; Marteijn et al., 2009; Wu et al., 2009, 2011; Ginjala et al., 2011; Moyal et al., 2011; Pan et al., 2011). Furthermore, depletion of RNF20 or interference with histone H2B monoubiquitination disrupts the recruitment of DNA repair machine proteins in both non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) and homologous recombination repair (HRR) pathways to the DSB (Moyal et al., 2011). Histone DUBs, such as USP3 and K63-ub DUB BRCC36, are also critical for efficient DNA repair, suggesting that a dynamic regulation of histone ubiquitination and deubiquitination is required for DNA damage response (Shao et al., 2009). It was proposed that monoubiquitination of histones H2A and H2B interferes with chromatin compaction and therefore facilitates assembly of the repair machinery on the DNA damage foci (Moyal et al., 2011), but the mechanisms of action remain elusive.
Other functions
H2A monoubiquitination occurs on the inactive X chromosome in female mammals (de Napoles et al., 2004; Fang et al., 2004). Both RING1B and H2Aub are involved in the initiation of imprinted and random X chromosome inactivation (de Napoles et al., 2004; Fang et al., 2004).
In addition to transcription regulation, monoubiquitinated H2B is required for chromatin function in other ways. H2Bub is required for chromatin boundary integrity, and loss of H2Bub leads to the spreading of other histone modifications (Ma et al., 2011). The present of H2Bub also interferes with chromatin compaction and results in an open chromatin structure (Fierz et al., 2011). H2Bub is also shown to play an important role in homologous recombination through chromatin remodeling by recruiting chromatin remodeling factors. Cells lacking RNF20 or expressing H2B K120R, which lacks ubiquitin conjugation site, exhibit defects in HRR (Nakamura et al., 2011).
Histone ubiquitination and deubiquitination play essential roles in stem cell maintenance and differentiation, likely through controlling the expression of key pluripotency and differentiation genes. BMI1 is required for the self-renewal and maintenance of hematopoietic stem cells (Lessard and Sauvageau, 2003; Park et al., 2003) and neural stem cells (Molofsky et al., 2003). In flies, H2B DUB SCNY is required for the maintenance of germline stem cells, follicle stem cells, and intestinal stem cells. SCNY mutant animals display reduced number and half-life of germline stem cells (Buszczak et al., 2009). In mouse embryonic stem cells, ubiquitinated H2A restrains poised RNA polymerase II at a subset of developmental regulator genes. Loss of RING1A and RING1B releases poised RNA polymerase II and subsequent gene de-repression (Stock et al., 2007).
Furthermore, a recent landmark paper showed that H2Bub can function in trans independent of transcription (Latham et al., 2011). During mitosis, H2Bub is required for the kinetochore protein Dam1 methylation (Latham et al., 2011). Depletion of E2, E3 for H2B monoubiquitination or mutation of Lys-123 in H2B inhibits methylation of Dam1 (Latham et al., 2011). These results suggest that H2Bub also plays important roles outside of chromatin and is required for chromosome segregation.
Histone Ubiquitination and Cancer
Histone modifications play critical roles in genes expression and DNA repair. Aberrations of these processes often cause cancers (Jones and Baylin, 2007). Many histone modifying enzymes have been identified as oncogene or tumor suppressors (Chandrasekharappa et al., 1997; Yokoyama et al., 2004; Wissmann et al., 2007; Lin et al., 2011). Therefore, it is not a surprise that more and more connections between histone ubiquitination and cancer have been discovered. Monoubiquitinated histone H2A and H2B were found to be dramatically down-regulated in prostate and breast tumors, respectively (Zhu et al., 2007; Prenzel et al., 2011). Recently advances have also linked the writers, erasers, and readers of histone ubiquitination to tumorigenesis.
BRCA1
Inactivation of tumor suppressor BRCA1 leads to breast and ovarian cancer. Female individuals carrying a mutated BRCA1 allele have an estimated risk of 87% for breast cancer and 44% for ovarian cancer by age 70 (Ford et al., 1994). BRCA1 associated protein BAP1 is also a tumor suppressor in multiple cancers, including lung cancer, breast cancer, uveal melanoma, and mesothelioma (Harbour et al., 2010; Testa et al., 2011; Wiesner et al., 2011).
The BRCA1 protein is a RING finger domain containing E3 ubiquitin ligase. H2A and H2B were identified as BRCA1 substrates in an in vitro assay (Chen et al., 2002; Mallery et al., 2002). A more recently report showed that BRCA1 binds to satellite DNA regions and catalyzes monoubiquitination of H2A in vivo (Zhu et al., 2011). Loss of BRCA1 is associated with loss of H2A ubiquitination at satellite repeats and de-repression of satellite transcription. Cells lacking BRCA1 are impaired in organization of heterochromatin structure. More interestingly, ectopic expression of H2A fused to ubiquitin, which is a mimic of natural monoubiquitinated H2A, rescues BRCA1 phenotypes (Zhu et al., 2011). These findings indicate that BRCA1 maintains heterochromatin structure via monoubiquitination of H2A. Furthermore, the fact that satellite DNA transcripts are increased in BRCA1 mutant breast cancer samples, and the relationship between monoubiquitination of H2A and satellite DNA repression suggest that dysregulation of H2Aub plays important roles in tumorigenesis.
RNF20 and RNF40
RNF20 is the major H2B specific E3 ubiquitin ligase in mammalian cells. Besides a significant decrease in the cellular pool of monoubiquitinated H2B, RNF20 depletion causes increased expression of some proto-oncogenes and growth-related genes including c-myc and c-Fos (Shema et al., 2008). Further study discovered that RNF20 represses gene expression by disrupting the interaction between TFIIS and PAF1 elongation complex and inhibiting transcriptional elongation. Those effects are also dependent on the E3 ligase activity of RNF20 (Shema et al., 2011). In addition, RNF20 depleted cells showed decreased expression of the p53 tumor suppressor, and increased cell migration and tumorigenesis. Moreover, hypermethylation of RNF20 promoter was observed in tumor samples (Shema et al., 2008). These findings suggest that H2B ubiquitin ligase RNF20 is a putative tumor suppressor. Furthermore, the RNF40, a binding partner of RNF20 and another major E3 for H2B monoubiquitination also showed tumor suppressive activity in breast cancer cells (Prenzel et al., 2011).
USP22
USP22 is a ubiquitin hydrolase and catalyzes the removal of ubiquitin from monoubiquitinated histones H2A and H2B (Zhang et al., 2008, 2011; Zhao et al., 2008). USP22 is a putative cancer stem cell marker and was found to be highly expressed in malignant tumor samples. High level of USP22 in tumor tissues is associated with poor clinical outcome, including high risk of recurrence, metastasis, and resistance to chemotherapy (Glinsky, 2005; Glinsky et al., 2005; Zhang et al., 2011). Further studies determined that USP22 is recruited to the gene promoters by Myc and is required for the activation of Myc target genes (Zhang et al., 2008). Depletion of USP22 compromises Myc functions, including transformation. USP22 also play roles in cell cycle regulation, where depletion of USP22 increases the expression of p53 and p21, inhibits proliferation, and induces cell cycle arrest at G1 phase (Zhang et al., 2008; Lv et al., 2011).
Conclusion
It is now well established that histone modifications and enzymes catalyzing their addition or removal are essential for normal cellular functions. Rapid advances of this field revealed that fine tuning of histone ubiquitination and deubiquitination is required for gene expression, DNA repair, and many other biological processes. Therefore aberrations of histone ubiquitination or deubiquitination lead to multiple human diseases including cancer. However, the precise mechanisms by which histone ubiquitination contributes to these biological processes are still poorly understood and require further investigation. Related essential questions include the crosstalk between histone ubiquitination and DNA methylation or other chromatin marks. Future studies that help decipher the essential roles of epigenetic regulation by histone ubiquitination in cellular homeostasis and pathological conditions like cancer will definitely benefit the identification of “druggable” targets for personalized cancer therapies.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
We thank members of the Yan laboratory for critical reading of the manuscript. This work was supported in part by V Scholar Award, Breast Cancer Alliance Young Investigator Grant, Melanoma Research Foundation Career Development Award, the Alexander and Margaret Stewart Trust Fellowship, CTSA Scholar Award from Yale Center for Clinical Investigation, a Pilot Grant from the Yale Comprehensive Cancer Center (all to Qin Yan), and NIH grant CA16359 (to the Yale Comprehensive Cancer Center). This publication was made possible by CTSA Grant Number UL1 RR024139 from the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS), a component of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), and NIH roadmap for Medical Research. Its contents are solely the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official view of NCATS or NIH. We apologize to our colleagues whose work could not be cited due to space limitation.
References
- Bergink S., Salomons F. A., Hoogstraten D., Groothuis T. A., de Waard H., Wu J., Yuan L., Citterio E., Houtsmuller A. B., Neefjes J., Hoeijmakers J. H., Vermeulen W., Dantuma N. P. (2006). DNA damage triggers nucleotide excision repair-dependent monoubiquitylation of histone H2A. Genes Dev. 20, 1343–1352 10.1101/gad.373706 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair L. P., Cao J., Zou M. R., Sayegh J., Yan Q. (2011). Epigenetic regulation by lysine demethylase 5 (KDM5) enzymes in cancer. Cancers 3, 1383–1404 10.3390/cancers3011383 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchwald G., van der Stoop P., Weichenrieder O., Perrakis A., van Lohuizen M., Sixma T. K. (2006). Structure and E3-ligase activity of the ring-ring complex of polycomb proteins Bmi1 and Ring1b. EMBO J. 25, 2465–2474 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601144 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buszczak M., Paterno S., Spradling A. C. (2009). Drosophila stem cells share a common requirement for the histone H2B ubiquitin protease scrawny. Science 323, 248–251 10.1126/science.1165678 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao R., Tsukada Y., Zhang Y. (2005). Role of Bmi-1 and Ring1A in H2A ubiquitylation and Hox gene silencing. Mol. Cell 20, 845–854 10.1016/j.molcel.2005.12.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandrasekharappa S. C., Guru S. C., Manickam P., Olufemi S. E., Collins F. S., EmmertBuck M. R., Debelenko L. V., Zhuang Z. P., Lubensky I. A., Liotta L. A., Crabtree J. S., Wang Y. P., Roe B. A., Weisemann J., Boguski M. S., Agarwal S. K., Kester M. B., Kim Y. S., Heppner C., Dong Q. H., Spiegel A. M., Burns A. L., Marx S. J. (1997). Positional cloning of the gene for multiple endocrine neoplasia-type 1. Science 276, 404–407 10.1126/science.276.5311.404 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen A., Kleiman F. E., Manley J. L., Ouchi T., Pan Z. Q. (2002). Autoubiquitination of the BRCA1-BARD1 RING ubiquitin ligase. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 22085–22092 10.1074/jbc.M202076200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen H. Y., Sun J. M., Zhang Y., Davie J. R., Meistrich M. L. (1998). Ubiquitination of histone H3 in elongating spermatids of rat testes. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 13165–13169 10.1074/jbc.273.19.11887 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel J. A., Torok M. S., Sun Z. W., Schieltz D., Allis C. D., Yates J. R., 3rd, Grant P. A. (2004). Deubiquitination of histone H2B by a yeast acetyltransferase complex regulates transcription. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 1867–1871 10.1074/jbc.C300494200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Napoles M., Mermoud J. E., Wakao R., Tang Y. A., Endoh M., Appanah R., Nesterova T. B., Silva J., Otte A. P., Vidal M., Koseki H., Brockdorff N. (2004). Polycomb group proteins Ring1A/B link ubiquitylation of histone H2A to heritable gene silencing and X inactivation. Dev. Cell 7, 663–676 10.1016/j.devcel.2004.10.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doil C., Mailand N., Bekker-Jensen S., Menard P., Larsen D. H., Pepperkok R., Ellenberg J., Panier S., Durocher D., Bartek J., Lukas J., Lukas C. (2009). RNF168 binds and amplifies ubiquitin conjugates on damaged chromosomes to allow accumulation of repair proteins. Cell 136, 435–446 10.1016/j.cell.2008.12.041 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dover J., Schneider J., Tawiah-Boateng M. A., Wood A., Dean K., Johnston M., Shilatifard A. (2002). Methylation of histone H3 by COMPASS requires ubiquitination of histone H2B by Rad6. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 28368–28371 10.1074/jbc.C200348200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emre N. C., Ingvarsdottir K., Wyce A., Wood A., Krogan N. J., Henry K. W., Li K., Marmorstein R., Greenblatt J. F., Shilatifard A., Berger S. L. (2005). Maintenance of low histone ubiquitylation by Ubp10 correlates with telomere-proximal Sir2 association and gene silencing. Mol. Cell 17, 585–594 10.1016/j.molcel.2005.01.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falck J., Coates J., Jackson S. P. (2005). Conserved modes of recruitment of ATM, ATR and DNA-PKcs to sites of DNA damage. Nature 434, 605–611 10.1038/nature03442 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fang J., Chen T., Chadwick B., Li E., Zhang Y. (2004). Ring1b-mediated H2A ubiquitination associates with inactive X chromosomes and is involved in initiation of X inactivation. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 52812–52815 10.1074/jbc.M313855200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fierz B., Chatterjee C., McGinty R. K., Bar-Dagan M., Raleigh D. P., Muir T. W. (2011). Histone H2B ubiquitylation disrupts local and higher-order chromatin compaction. Nat. Chem. Biol. 7, 113–119 10.1038/nchembio.501 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford D., Easton D. F., Bishop D. T., Narod S. A., Goldgar D. E., Haites N., Milner B., Allan L., Ponder B. A. J., Peto J., Smith S., Stratton M., Lenoir G. M., Feunteun J., Lynch H., Arason A., Barkardottir R., Egilsson V., Black D. M., Kelsell D., Spurr N., Devilee P., Cornelisse C. J., Varsen H., Birch J. M., Skolnick M., Santibanezkoref M. S., Teare D., Steel M., Porter D., Cohen B. B., Carothers A., Smyth E., Weber B., Newbold B., Boehnke M., Collins F. S., Cannonalbright L. A., Goldgar D. (1994). Risks of cancer in BRCA1-mutation carriers. Lancet 343, 692–695 10.1016/S0140-6736(94)91578-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gearhart M. D., Corcoran C. M., Wamstad J. A., Bardwell V. J. (2006). Polycomb group and SCF ubiquitin ligases are found in a novel BCOR complex that is recruited to BCL6 targets. Mol. Cell. Biol. 26, 6880–6889 10.1128/MCB.00630-06 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginjala V., Nacerddine K., Kulkarni A., Oza J., Hill S. J., Yao M., Citterio E., van Lohuizen M., Ganesan S. (2011). BMI1 is recruited to DNA breaks and contributes to DNA damage-induced H2A ubiquitination and repair. Mol. Cell. Biol. 31, 1972–1982 10.1128/MCB.00981-10 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glinsky G. V. (2005). Death-from-cancer signatures and stem cell contribution to metastatic cancer. Cell Cycle 4, 1171–1175 10.4161/cc.4.9.2001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glinsky G. V., Berezovska O., Glinskii A. B. (2005). Microarray analysis identifies a death-from-cancer signature predicting therapy failure in patients with multiple types of cancer. J. Clin. Invest. 115, 1503–1521 10.1172/JCI23412 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldknopf I. L., Taylor C. W., Baum R. M., Yeoman L. C., Olson M. O., Prestayko A. W., Busch H. (1975). Isolation and characterization of protein A24, a “histone-like” non-histone chromosomal protein. J. Biol. Chem. 250, 7182–7187 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harbour J. W., Onken M. D., Roberson E. D., Duan S., Cao L., Worley L. A., Council M. L., Matatall K. A., Helms C., Bowcock A. M. (2010). Frequent mutation of BAP1 in metastasizing uveal melanomas. Science 330, 1410–1413 10.1126/science.1194472 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry K. W., Wyce A., Lo W. S., Duggan L. J., Emre N. C., Kao C. F., Pillus L., Shilatifard A., Osley M. A., Berger S. L. (2003). Transcriptional activation via sequential histone H2B ubiquitylation and deubiquitylation, mediated by SAGA-associated Ubp8. Genes Dev. 17, 2648–2663 10.1101/gad.1144003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeijmakers J. H. J. (2001). Genome maintenance mechanisms for preventing cancer. Nature 411, 366–374 10.1038/35077232 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huen M. S., Grant R., Manke I., Minn K., Yu X., Yaffe M. B., Chen J. (2007). RNF8 transduces the DNA-damage signal via histone ubiquitylation and checkpoint protein assembly. Cell 131, 901–914 10.1016/j.cell.2007.09.041 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang W. W., Venkatasubrahmanyam S., Ianculescu A. G., Tong A., Boone C., Madhani H. D. (2003). A conserved RING finger protein required for histone H2B monoubiquitination and cell size control. Mol. Cell 11, 261–266 10.1016/S1097-2765(02)00826-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jason L. J., Moore S. C., Lewis J. D., Lindsey G., Ausio J. (2002). Histone ubiquitination: a tagging tail unfolds? Bioessays 24, 166–174 10.1002/bies.10038 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. M., Bhattacharyya A., Simkus C., Vallieres B., Veenstra T. D., Zhou M. (2011). The RAG1 V(D)J recombinase/ubiquitin ligase promotes ubiquitylation of acetylated, phosphorylated histone 3.3. Immunol. Lett. 136, 156–162 10.1016/j.imlet.2011.01.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. A., Baylin S. B. (2007). The epigenomics of cancer. Cell 128, 683–692 10.1016/j.cell.2007.01.029 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joo H. Y., Jones A., Yang C., Zhai L., Smith A. D. T., Zhang Z., Chandrasekharan M. B., Sun Z. W., Renfrow M. B., Wang Y., Chang C., Wang H. (2011). Regulation of histone H2A and H2B deubiquitination and Xenopus development by USP12 and USP46. J. Biol. Chem. 286, 7190–7201 10.1074/jbc.M111.221382 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joo H. Y., Zhai L., Yang C., Nie S., Erdjument-Bromage H., Tempst P., Chang C., Wang H. (2007). Regulation of cell cycle progression and gene expression by H2A deubiquitination. Nature 449, 1068–1072 10.1038/nature06256 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamura T., Conrad M. N., Yan Q., Conaway R. C., Conaway J. W. (1999). The Rbx1 subunit of SCF and VHL E3 ubiquitin ligase activates Rub1 modification of cullins Cdc53 and Cul2. Genes Dev. 13, 2928–2933 10.1101/gad.13.22.2928 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao C. F., Hillyer C., Tsukuda T., Henry K., Berger S., Osley M. A. (2004). Rad6 plays a role in transcriptional activation through ubiquitylation of histone H2B. Genes Dev. 18, 184–195 10.1101/gad.1149604 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H., Chen J., Yu X. (2007). Ubiquitin-binding protein RAP80 mediates BRCA1-dependent DNA damage response. Science 316, 1202–1205 10.1126/science.1139621 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J., Guermah M., McGinty R. K., Lee J. S., Tang Z., Milne T. A., Shilatifard A., Muir T. W., Roeder R. G. (2009). RAD6-mediated transcription-coupled H2B ubiquitylation directly stimulates H3K4 methylation in human cells. Cell 137, 459–471 10.1016/j.cell.2009.02.045 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J., Hake S. B., Roeder R. G. (2005). The human homolog of yeast BRE1 functions as a transcriptional coactivator through direct activator interactions. Mol. Cell 20, 759–770 10.1016/j.molcel.2005.11.012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klose R. J., Yan Q., Tothova Z., Yamane K., Erdjument-Bromage H., Tempst P., Gilliland D. G., Zhang Y., Kaelin W. G., Jr. (2007). The retinoblastoma binding protein RBP2 is an H3K4 demethylase. Cell 128, 889–900 10.1016/j.cell.2007.02.013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koken M. H., Reynolds P., Jaspers-Dekker I., Prakash L., Prakash S., Bootsma D., Hoeijmakers J. H. (1991). Structural and functional conservation of two human homologs of the yeast DNA repair gene RAD6. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88, 8865–8869 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3832 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolas N. K., Chapman J. R., Nakada S., Ylanko J., Chahwan R., Sweeney F. D., Panier S., Mendez M., Wildenhain J., Thomson T. M., Pelletier L., Jackson S. P., Durocher D. (2007). Orchestration of the DNA-damage response by the RNF8 ubiquitin ligase. Science 318, 1637–1640 10.1126/science.1150034 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagarou A., Mohd-Sarip A., Moshkin Y. M., Chalkley G. E., Bezstarosti K., Demmers J. A., Verrijzer C. P. (2008). dKDM2 couples histone H2A ubiquitylation to histone H3 demethylation during polycomb group silencing. Genes Dev. 22, 2799–2810 10.1101/gad.484208 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latham J. A., Chosed R. J., Wang S., Dent S. Y. (2011). Chromatin signaling to kinetochores: transregulation of Dam1 methylation by histone H2B ubiquitination. Cell 146, 709–719 10.1016/j.cell.2011.07.025 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. S., Shukla A., Schneider J., Swanson S. K., Washburn M. P., Florens L., Bhaumik S. R., Shilatifard A. (2007a). Histone crosstalk between H2B monoubiquitination and H3 methylation mediated by COMPASS. Cell 131, 1084–1096 10.1016/j.cell.2007.11.037 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. G., Villa R., Trojer P., Norman J., Yan K. P., Reinberg D., Di Croce L., Shiekhattar R. (2007b). Demethylation of H3K27 regulates polycomb recruitment and H2A ubiquitination. Science 318, 447–450 10.1126/science.1149042 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lessard J., Sauvageau G. (2003). Bmi-1 determines the proliferative capacity of normal and leukaemic stem cells. Nature 423, 255–260 10.1038/nature01572 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li X. S., Trojer P., Matsumura T., Treisman J. E., Tanese N. (2010). Mammalian SWI/SNF–a subunit BAF250/ARID1 is an E3 ubiquitin ligase that targets histone H2B. Mol. Cell. Biol. 30, 1673–1688 10.1128/MCB.00183-09 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin W., Cao J., Liu J., Beshiri M. L., Fujiwara Y., Francis J., Cherniack A. D., Geisen C., Blair L. P., Zou M. R., Shen X., Kawamori D., Liu Z., Grisanzio C., Watanabe H., Minamishima Y. A., Zhang Q., Kulkarni R. N., Signoretti S., Rodig S. J., Bronson R. T., Orkin S. H., Tuck D. P., Benevolenskaya E. V., Meyerson M., Kaelin W. G., Jr., Yan Q. (2011). Loss of the retinoblastoma binding protein 2 (RBP2) histone demethylase suppresses tumorigenesis in mice lacking Rb1 or Men1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 108, 13379–13386 10.1073/pnas.1014026108 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Z., Oughtred R., Wing S. S. (2005). Characterization of E3Histone, a novel testis ubiquitin protein ligase which ubiquitinates histones. Mol. Cell. Biol. 25, 2819–2831 10.1128/MCB.25.9.3475-3482.2005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luger K., Mader A. W., Richmond R. K., Sargent D. F., Richmond T. J. (1997). Crystal structure of the nucleosome core particle at 2.8 A resolution. Nature 389, 251–260 10.1038/38444 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lv L., Xiao X. Y., Gu Z. H., Zeng F. Q., Huang L. Q., Jiang G. S. (2011). Silencing USP22 by asymmetric structure of interfering RNA inhibits proliferation and induces cell cycle arrest in bladder cancer cells. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 346, 11–21 10.1007/s11010-010-0585-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma M. K., Heath C., Hair A., West A. G. (2011). Histone crosstalk directed by H2B ubiquitination is required for chromatin boundary integrity. PLoS Genet. 7, e1002175. 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002175 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mailand N., Bekker-Jensen S., Faustrup H., Melander F., Bartek J., Lukas C., Lukas J. (2007). RNF8 ubiquitylates histones at DNA double-strand breaks and promotes assembly of repair proteins. Cell 131, 887–900 10.1016/j.cell.2007.09.040 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallery D. L., Vandenberg C. J., Hiom K. (2002). Activation of the E3 ligase function of the BRCA1/BARD1 complex by polyubiquitin chains. EMBO J. 21, 6755–6762 10.1093/emboj/cdf691 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marteijn J. A., Bekker-Jensen S., Mailand N., Lans H., Schwertman P., Gourdin A. M., Dantuma N. P., Lukas J., Vermeulen W. (2009). Nucleotide excision repair-induced H2A ubiquitination is dependent on MDC1 and RNF8 and reveals a universal DNA damage response. J. Cell Biol. 186, 835–847 10.1083/jcb.200902150 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui S. I., Seon B. K., Sandberg A. A. (1979). Disappearance of a structural chromatin protein A24 in mitosis: implications for molecular basis of chromatin condensation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 76, 6386–6390 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6386 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minsky N., Shema E., Field Y., Schuster M., Segal E., Oren M. (2008). Monoubiquitinated H2B is associated with the transcribed region of highly expressed genes in human cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 10, 483–488 10.1038/ncb1712 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molofsky A. V., Pardal R., Iwashita T., Park I. K., Clarke M. F., Morrison S. J. (2003). Bmi-1 dependence distinguishes neural stem cell self-renewal from progenitor proliferation. Nature 425, 962–967 10.1038/nature02060 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyal L., Lerenthal Y., Gana-Weisz M., Mass G., So S., Wang S. Y., Eppink B., Chung Y. M., Shalev G., Shema E., Shkedy D., Smorodinsky N. I., van Vliet N., Kuster B., Mann M., Ciechanover A., Dahm-Daphi J., Kanaar R., Hu M. C., Chen D. J., Oren M., Shiloh Y. (2011). Requirement of ATM-dependent monoubiquitylation of histone H2B for timely repair of DNA double-strand breaks. Mol. Cell 41, 529–542 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.02.015 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa T., Kajitani T., Togo S., Masuko N., Ohdan H., Hishikawa Y., Koji T., Matsuyama T., Ikura T., Muramatsu M., Ito T. (2008). Deubiquitylation of histone H2A activates transcriptional initiation via trans-histone cross-talk with H3K4 di- and trimethylation. Genes Dev. 22, 37–49 10.1101/gad.1609708 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura K., Kato A., Kobayashi J., Yanagihara H., Sakamoto S., Oliveira D. V., Shimada M., Tauchi H., Suzuki H., Tashiro S., Zou L., Komatsu K. (2011). Regulation of homologous recombination by RNF20-dependent H2B ubiquitination. Mol. Cell 41, 515–528 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.02.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicassio F., Corrado N., Vissers J. H., Areces L. B., Bergink S., Marteijn J. A., Geverts B., Houtsmuller A. B., Vermeulen W., Di Fiore P. P., Citterio E. (2007). Human USP3 is a chromatin modifier required for S phase progression and genome stability. Curr. Biol. 17, 1972–1977 10.1016/j.cub.2007.10.034 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa H., Ishiguro K., Gaubatz S., Livingston D. M., Nakatani Y. (2002). A complex with chromatin modifiers that occupies E2F- and Myc-responsive genes in G0 cells. Science 296, 1132–1136 10.1126/science.1069861 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan M. R., Peng G., Hung W. C., Lin S. Y. (2011). Monoubiquitination of H2AX protein regulates DNA damage response signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 286, 28599–28607 10.1074/jbc.M111.218990 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park I. K., Qian D., Kiel M., Becker M. W., Pihalja M., Weissman I. L., Morrison S. J., Clarke M. F. (2003). Bmi-1 is required for maintenance of adult self-renewing haematopoietic stem cells. Nature 423, 302–305 10.1038/nature01587 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavri R., Zhu B., Li G., Trojer P., Mandal S., Shilatifard A., Reinberg D. (2006). Histone H2B monoubiquitination functions cooperatively with FACT to regulate elongation by RNA polymerase II. Cell 125, 703–717 10.1016/j.cell.2006.04.029 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pham A. D., Sauer F. (2000). Ubiquitin-activating/conjugating activity of TAFII250, a mediator of activation of gene expression in Drosophila. Science 289, 2357–2360 10.1126/science.289.5488.2357 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prenzel T., Begus-Nahrmann Y., Kramer F., Hennion M., Hsu C., Gorsler T., Hintermair C., Eick D., Kremmer E., Simons M., Beissbarth T., Johnsen S. A. (2011). Estrogen-dependent gene transcription in human breast cancer cells relies upon proteasome-dependent monoubiquitination of histone H2B. Cancer Res. 71, 5739–5753 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-1896 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Querido E., Blanchette P., Yan Q., Kamura T., Morrison M., Boivin D., Kaelin W. G., Conaway R. C., Conaway J. W., Branton P. E. (2001). Degradation of p53 by adenovirus E4orf6 and E1B55K proteins occurs via a novel mechanism involving a Cullin-containing complex. Genes Dev. 15, 3104–3117 10.1101/gad.926401 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robzyk K., Recht J., Osley M. A. (2000). Rad6-dependent ubiquitination of histone H2B in yeast. Science 287, 501–504 10.1126/science.287.5452.501 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheuermann J. C., de Ayala Alonso A. G., Oktaba K., Ly-Hartig N., McGinty R. K., Fraterman S., Wilm M., Muir T. W., Muller J. (2010). Histone H2A deubiquitinase activity of the polycomb repressive complex PR-DUB. Nature 465, 243–247 10.1038/nature08966 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulze J. M., Hentrich T., Nakanishi S., Gupta A., Emberly E., Shilatifard A., Kobor M. S. (2011). Splitting the task: Ubp8 and Ubp10 deubiquitinate different cellular pools of H2BK123. Genes Dev. 25, 2242–2247 10.1101/gad.177220.111 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanbhag N. M., Rafalska-Metcalf I. U., Balane-Bolivar C., Janicki S. M., Greenberg R. A. (2010). ATM-dependent chromatin changes silence transcription in cis to DNA double-strand breaks. Cell 141, 970–981 10.1016/j.cell.2010.04.038 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shao G., Lilli D. R., Patterson-Fortin J., Coleman K. A., Morrissey D. E., Greenberg R. A. (2009). The Rap80-BRCC36 de-ubiquitinating enzyme complex antagonizes RNF8-Ubc13-dependent ubiquitination events at DNA double strand breaks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 106, 3166–3171 10.1073/pnas.0807485106 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shema E., Kim J., Roeder R. G., Oren M. (2011). RNF20 inhibits TFIIS-facilitated transcriptional elongation to suppress pro-oncogenic gene expression. Mol. Cell 42, 477–488 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.03.011 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shema E., Tirosh I., Aylon Y., Huang J., Ye C., Moskovits N., Raver-Shapira N., Minsky N., Pirngruber J., Tarcic G., Hublarova P., Moyal L., Gana-Weisz M., Shiloh Y., Yarden Y., Johnsen S. A., Vojtesek B., Berger S. L., Oren M. (2008). The histone H2B-specific ubiquitin ligase RNF20/hBRE1 acts as a putative tumor suppressor through selective regulation of gene expression. Genes Dev. 22, 2664–2676 10.1101/gad.1703008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobhian B., Shao G., Lilli D. R., Culhane A. C., Moreau L. A., Xia B., Livingston D. M., Greenberg R. A. (2007). RAP80 targets BRCA1 to specific ubiquitin structures at DNA damage sites. Science 316, 1198–1202 10.1126/science.1139516 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart G. S., Panier S., Townsend K., Al-Hakim A. K., Kolas N. K., Miller E. S., Nakada S., Ylanko J., Olivarius S., Mendez M., Oldreive C., Wildenhain J., Tagliaferro A., Pelletier L., Taubenheim N., Durandy A., Byrd P. J., Stankovic T., Taylor A. M., Durocher D. (2009). The RIDDLE syndrome protein mediates a ubiquitin-dependent signaling cascade at sites of DNA damage. Cell 136, 420–434 10.1016/j.cell.2008.12.042 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart G. S., Wang B., Bignell C. R., Taylor A. M., Elledge S. J. (2003). MDC1 is a mediator of the mammalian DNA damage checkpoint. Nature 421, 961–966 10.1038/nature01446 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J. K., Giadrossi S., Casanova M., Brookes E., Vidal M., Koseki H., Brockdorff N., Fisher A. G., Pombo A. (2007). Ring1-mediated ubiquitination of H2A restrains poised RNA polymerase II at bivalent genes in mouse ES cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 9, 1428–1435 10.1038/ncb1663 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strahl B. D., Allis C. D. (2000). The language of covalent histone modifications. Nature 403, 41–45 10.1038/47412 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun Z. W., Allis C. D. (2002). Ubiquitination of histone H2B regulates H3 methylation and gene silencing in yeast. Nature 418, 104–108 10.1038/nature00902 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Testa J. R., Cheung M., Pei J., Below J. E., Tan Y., Sementino E., Cox N. J., Dogan A. U., Pass H. I., Trusa S., Hesdorffer M., Nasu M., Powers A., Rivera Z., Comertpay S., Tanji M., Gaudino G., Yang H., Carbone M. (2011). Germline BAP1 mutations predispose to malignant mesothelioma. Nat. Genet. 43, 1022–1025 10.1038/ng.912 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Knaap J. A., Kumar B. R., Moshkin Y. M., Langenberg K., Krijgsveld J., Heck A. J., Karch F., Verrijzer C. P. (2005). GMP synthetase stimulates histone H2B deubiquitylation by the epigenetic silencer USP7. Mol. Cell 17, 695–707 10.1016/j.molcel.2005.02.013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang B., Elledge S. J. (2007). Ubc13/Rnf8 ubiquitin ligases control foci formation of the Rap80/Abraxas/Brca1/Brcc36 complex in response to DNA damage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 104, 20759–20763 10.1073/pnas.0703676104 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang B., Matsuoka S., Ballif B. A., Zhang D., Smogorzewska A., Gygi S. P., Elledge S. J. (2007). Abraxas and RAP80 form a BRCA1 protein complex required for the DNA damage response. Science 316, 1194–1198 10.1126/science.1139366 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H., Wang L., Erdjument-Bromage H., Vidal M., Tempst P., Jones R. S., Zhang Y. (2004). Role of histone H2A ubiquitination in polycomb silencing. Nature 431, 873–878 10.1038/nature03016 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H., Zhai L., Xu J., Joo H. Y., Jackson S., Erdjument-Bromage H., Tempst P., Xiong Y., Zhang Y. (2006). Histone H3 and H4 ubiquitylation by the CUL4-DDB-ROC1 ubiquitin ligase facilitates cellular response to DNA damage. Mol. Cell 22, 383–394 10.1016/j.molcel.2006.03.034 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West M. H., Bonner W. M. (1980). Histone 2B can be modified by the attachment of ubiquitin. Nucleic Acids Res. 8, 4671–4680 10.1093/nar/8.20.4671 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiesner T., Obenauf A. C., Murali R., Fried I., Griewank K. G., Ulz P., Windpassinger C., Wackernagel W., Loy S., Wolf I., Viale A., Lash A. E., Pirun M., Socci N. D., Rutten A., Palmedo G., Abramson D., Offit K., Ott A., Becker J. C., Cerroni L., Kutzner H., Bastian B. C., Speicher M. R. (2011). Germline mutations in BAP1 predispose to melanocytic tumors. Nat. Genet. 43, 1018–1021 10.1038/ng.910 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wissmann M., Yin N., Muller J. M., Greschik H., Fodor B. D., Jenuwein T., Vogler C., Schneider R., Gunther T., Buettner R., Metzger E., Schule R. (2007). Cooperative demethylation by JMJD2C and LSD1 promotes androgen receptor-dependent gene expression. Nat. Cell Biol. 9, 347–353 10.1038/ncb1546 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood A., Krogan N. J., Dover J., Schneider J., Heidt J., Boateng M. A., Dean K., Golshani A., Zhang Y., Greenblatt J. F., Johnston M., Shilatifard A. (2003). Bre1, an E3 ubiquitin ligase required for recruitment and substrate selection of Rad6 at a promoter. Mol. Cell 11, 267–274 10.1016/S1097-2765(02)00802-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. Y., Kang H. Y., Yang W. L., Wu J., Jeong Y. S., Wang J., Chan C. H., Lee S. W., Zhang X., Lamothe B., Campos A. D., Darnay B. G., Lin H. K. (2011). Critical role of monoubiquitination of histone H2AX protein in histone H2AX phosphorylation and DNA damage response. J. Biol. Chem. 286, 30806–30815 10.1074/jbc.M110.174755 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J., Huen M. S., Lu L. Y., Ye L., Dou Y., Ljungman M., Chen J., Yu X. (2009). Histone ubiquitination associates with BRCA1-dependent DNA damage response. Mol. Cell. Biol. 29, 849–860 10.1128/MCB.01302-08 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyce A., Xiao T., Whelan K. A., Kosman C., Walter W., Eick D., Hughes T. R., Krogan N. J., Strahl B. D., Berger S. L. (2007). H2B ubiquitylation acts as a barrier to Ctk1 nucleosomal recruitment prior to removal by Ubp8 within a SAGA-related complex. Mol. Cell 27, 275–288 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.01.035 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xia Y., Pao G. M., Chen H. W., Verma I. M., Hunter T. (2003). Enhancement of BRCA1 E3 ubiquitin ligase activity through direct interaction with the BARD1 protein. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 5255–5263 10.1074/jbc.M208500200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao T. J., Kao C. F., Krogan N. J., Sun Z. W., Greenblatt J. F., Osley M. A., Strahl B. D. (2005). Histone H2B ubiquitylation is associated with elongating RNA polymerase II. Mol. Cell. Biol. 25, 637–651 10.1128/MCB.25.6.2384-2394.2005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu X. Z., Stern D. F. (2003). NFBD1/KIAA0170 is a chromatin-associated protein involved in DNA damage signaling pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 8795–8803 10.1074/jbc.M210775200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan Q., Kamura T., Cai Y., Jin J., Ivan M., Mushegian A., Conaway R. C., Conaway J. W. (2004). Identification of Elongin C and Skp1 sequences that determine Cullin selection. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 43019–43026 10.1074/jbc.M312810200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama A., Wang Z., Wysocka J., Sanyal M., Aufiero D. J., Kitabayashi I., Herr W., Cleary M. L. (2004). Leukemia proto-oncoprotein MLL forms a SET1-like histone methyltransferase complex with menin to regulate Hox gene expression. Mol. Cell. Biol. 24, 5639–5649 10.1128/MCB.24.13.5639-5649.2004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. Y., Varthi M., Sykes S. M., Phillips C., Warzecha C., Zhu W., Wyce A., Thorne A. W., Berger S. L., McMahon S. B. (2008). The putative cancer stem cell marker USP22 is a subunit of the human SAGA complex required for activated transcription and cell-cycle progression. Mol. Cell 29, 102–111 10.1016/j.molcel.2008.01.013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y. X., Yao L., Zhang X. Y., Ji H. F., Wang L. H., Sun S. S., Pang D. (2011). Elevated expression of USP22 in correlation with poor prognosis in patients with invasive breast cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 137, 1245–1253 10.1007/s00432-011-1048-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao Y., Lang G., Ito S., Bonnet J., Metzger E., Sawatsubashi S., Suzuki E., Le Guezennec X., Stunnenberg H. G., Krasnov A., Georgieva S. G., Schule R., Takeyama K., Kato S., Tora L., Devys D. (2008). A TFTC/STAGA module mediates histone H2A and H2B deubiquitination, coactivates nuclear receptors, and counteracts heterochromatin silencing. Mol. Cell 29, 92–101 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.12.011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou W., Zhu P., Wang J., Pascual G., Ohgi K. A., Lozach J., Glass C. K., Rosenfeld M. G. (2008). Histone H2A monoubiquitination represses transcription by inhibiting RNA polymerase II transcriptional elongation. Mol. Cell 29, 69–80 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.11.002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu B., Zheng Y., Pham A. D., Mandal S. S., Erdjument-Bromage H., Tempst P., Reinberg D. (2005). Monoubiquitination of human histone H2B: the factors involved and their roles in HOX gene regulation. Mol. Cell 20, 601–611 10.1016/j.molcel.2005.09.025 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu P., Zhou W., Wang J., Puc J., Ohgi K. A., Erdjument-Bromage H., Tempst P., Glass C. K., Rosenfeld M. G. (2007). A histone H2A deubiquitinase complex coordinating histone acetylation and H1 dissociation in transcriptional regulation. Mol. Cell 27, 609–621 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.07.024 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu Q., Pao G. M., Huynh A. M., Suh H., Tonnu N., Nederlof P. M., Gage F. H., Verma I. M. (2011). BRCA1 tumour suppression occurs via heterochromatin-mediated silencing. Nature 477, 179–184 10.1038/nature10371 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]