Abstract
This study aims to determine the epigenetic mechanism regulating Kiss1 gene expression in the anteroventral periventricular nucleus (AVPV) to understand the mechanism underlying estrogen-positive feedback action on gonadotropin-releasing hormone/gonadotropin surge. We investigated estrogen regulation of the epigenetic status of the mouse AVPV Kiss1 gene locus in comparison with the arcuate nucleus (ARC), in which Kiss1 expression is down-regulated by estrogen. Histone of AVPV Kiss1 promoter region was highly acetylated, and estrogen receptor α was highly recruited at the region by estrogen. In contrast, the histone of ARC Kiss1 promoter region was deacetylated by estrogen. Inhibition of histone deacetylation up-regulated in vitro Kiss1 expression in a hypothalamic non–Kiss1-expressing cell line. Gene conformation analysis indicated that estrogen induced formation of a chromatin loop between Kiss1 promoter and the 3′ intergenic region, suggesting that the intergenic region serves to enhance estrogen-dependent Kiss1 expression in the AVPV. This notion was proved, because transgenic reporter mice with a complete Kiss1 locus sequence showed kisspeptin neuron-specific GFP expression in both the AVPV and ARC, but the deletion of the 3′ region resulted in greatly reduced GFP expression only in the AVPV. Taken together, these results demonstrate that estrogen induces recruitment of estrogen receptor α and histone acetylation in the Kiss1 promoter region of the AVPV and consequently enhances chromatin loop formation of Kiss1 promoter and Kiss1 gene enhancer, resulting in an increase in AVPV-specific Kiss1 gene expression. These results indicate that epigenetic regulation of the Kiss1 gene is involved in estrogen-positive feedback to generate the gonadotropin-releasing hormone/gonadotropin surge.
Keywords: metastin, GPR54, DNA methylation
The gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) surge is well established as the cause of the luteinizing hormone (LH) surge (1). The continuous release of GnRH might be caused by the continuous excitation of GnRH neurons triggered by the estrogen-positive feedback action on the brain. Recently, investigations of kisspeptin, a neuropeptide encoded by the Kiss1 gene, shed light on the mechanism mediating GnRH/LH surges (2–7). One of the major kisspeptin neuronal populations in rodents is found in the anteroventral periventricular nucleus (AVPV) (8, 9), which has been suggested as the brain region involved in the surge generation in rodents (10). GnRH neurons express GPR54, a kisspeptin receptor (11). Preovulatory and estrogen-induced LH surges are blocked by the infusion of anti-kisspeptin antibody in rats (8, 12). Therefore, the estrogen-induced increase in Kiss1 gene expression in the AVPV might be closely associated with the induction of GnRH/LH surges in rodents. Primates may have a surge-generating mechanism different from that in rodents. The mediobasal hypothalamus might play a crucial role in surge induction (13, 14).
Estrogen signals responsible for the positive feedback are mediated by estrogen receptor (ER) α, because the LH surge is evoked by exogenous estrogen in ERβ-KO mice but not in ERα-KO mice (15–17). Kisspeptin neurons in the AVPV express ERα, and estrogen positively regulates kisspeptin expression (8, 9, 18), suggesting that the AVPV kisspeptin neurons would be a target of the estrogen action exerting a positive feedback effect on GnRH/LH release. On the other hand, estrogen negatively regulates kisspeptin expression in another population of kisspeptin neurons that are located in the arcuate nucleus (ARC) and coexpress ERα (8, 19). The molecular mechanism involved in these opposite effects of estrogen on AVPV and ARC kisspeptin neurons should be clarified to understand the estrogen-positive feedback mechanism more clearly.
Epigenetic modification of genomic DNA and histones has been tightly linked to chromatin organization and transcriptional regulation. Histone acetylation in gene promoter/enhancer regions generally is correlated with transcriptional activation (20–22). On the other hand, in mammals, genomic DNA is methylated at cytosine residues predominantly in CG dinucleotides (CpGs) (23). Methylation of DNA is essential for mammalian development and is associated with gene silencing in conjunction with histone core modifications, probably through chromatin remodeling (20, 22, 24, 25). These epigenetic mechanisms reportedly mediate estrogen actions in the brain. For example, estrogen decreased levels of histone deacetylase (HDAC) protein and increased DNA methyltransferase expression in the dorsal hippocampus, leading to impaired formation of hippocampal-dependent memory (26). Furthermore, the histone acetylation status during the early postnatal period plays a critical role in sexual differentiation of the brain, because masculinization of sexual behavior and the volume of the nucleus of the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis, a sexual dimorphic nucleus, were blocked by neonatal administration of HDAC inhibitors (27, 28).
The present study aims to determine the epigenetic regulatory mechanism underlying the effect of estrogen-positive feedback on Kiss1 gene expression in the AVPV. We first identified the Kiss1 gene promoter functioning in the mouse hypothalamus. To investigate the effect of estrogen on epigenetic status in the Kiss1 promoter, the histone acetylation and DNA methylation status of the Kiss1 gene locus in the mouse AVPV were analyzed in comparison with that in the ARC. A chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay with ERα antibody was used to investigate if ERα is recruited at the AVPV Kiss1 promoter region in the presence of estrogen. Further, we investigated the effect of estrogen on the interaction between the Kiss1 promoter region and intergenic DNA regions of the Kiss1 locus by a gene conformational analysis to obtain the candidate(s) for the AVPV-specific Kiss1 enhancer region. Finally, we generated transgenic (Tg) mice carrying DNA containing the GFP-labeled Kiss1 gene locus with or without a candidate 3′ intergenic region to determine whether the Kiss1 gene 3′ intergenic region, an enhancer candidate locus, functions as an estrogen-dependent AVPV-specific Kiss1 enhancer.
Results
Determination of the Core Promoter Region Driven In Hypothalamic Cells.
The AVPV and ARC express two splice variants that were identified in the present study (DNA Data Bank of Japan, EMBL, and Genbank nucleotide database, accession nos. AY707858 and AY182231) (Fig. 1 A and B and Fig. S1). Representative splice variants including the kisspeptin amino acid sequence within the ORF derived from University of California, Santa Cruz database (http://genome.ucsc.edu/) are shown in Fig. S1A. The RT-PCR analysis for AVPV and ARC tissues showed the same positive bands in both brain regions (Fig. 1B). Kiss1 mRNA were highly expressed in the AVPV of the ovariectomized (OVX) mice implanted with estradiol-17β (E2) (the OVX+E2 model) and in the ARC of OVX mice without E2 implantation (the OVX model). The variants were the products of alternative splicing from the same transcription start site (TSS), but their functional relevance is unknown.
Fig. 1.
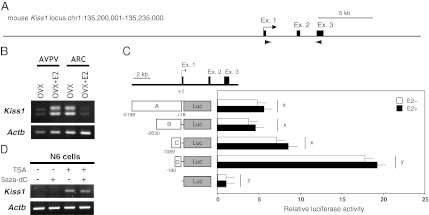
Characterization of the Kiss1 gene expressed in the mouse AVPV and ARC. (A) Schematic illustration of the genomic structure around the mouse Kiss1 gene. Filled boxes and arrowheads show exons and primer regions, respectively, used in RT-PCR analyses. (B) Expression pattern of Kiss1 mRNA. RT-PCR analysis of Kiss1 expression in the AVPV and ARC is shown. RT-PCR analysis of AVPV and ARC tissues showed the same positive bands in both brain regions. (C) Identification of the core promoter region of Kiss1 expression in the hypothalamus. (Upper) A map of the Kiss1 locus. (Lower) Empty plasmid (pGL4-mock) or constructs carrying different lengths of the Kiss1 5′-flanking regions (labeled A–D) were transfected into immortalized hypothalamic N7 cells, together with pcDNA-ERα plasmids. Luciferase activities were determined relative to that of pGL4-mock. Open and filled bars indicate the absence and presence of E2 treatment, respectively. Each bar represents the mean of triplicate experiments ± SEM. x, y, z, significantly different from each other (P < 0.01). (D) Effects of inhibitors of histone deacetylation and/or DNA methylation on Kiss1 expression in the immortalized hypothalamic cell line. RT-PCR analysis of Kiss1 gene expression in N6 cells treated with 200 nM of TSA (an inhibitor of histone deacetylation) and/or 1 μM of 5-aza-dC (an inhibitor of DNA methylation). Total RNA (1 μg) extracted from cells was used for RT-PCR analyses.
To determine the region for epigenetic analyses, the Kiss1 promoter was analyzed with luciferase reporter assays using the N7 cell line, a mouse hypothalamic immortalized neuronal cell line. All the constructs containing the Kiss1 region upstream of −5198 (pGL4-A), −2630 (pGL4-B), −1089 (pGL4-C), and −180 (pGL4-D) showed a significant increase in luciferase activity compared with controls (pGL4-mock) (Fig. 1C). The D sequence region had the strongest promoter activity, and a sequence with repressive effects was located in the upstream region of D. E2 treatment did not affect promoter activity, although ERα was expressed in the cells.
Induction of in Vitro Kiss1 Gene Expression in Hypothalamic Cell Lines by Treatment with Reagents Affecting Epigenetic Status.
Fig. 1D shows the effects of trichostatin A (TSA), an inhibitor of histone deacetylation, and/or 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine (5-aza-dC), an inhibitor of DNA methylation, on Kiss1 expression in N6 cells, a mouse hypothalamic cell line that does not express Kiss1 mRNA (Fig. S2). TSA induced Kiss1 expression in the cell line, but 5-aza-dC alone had no effect on Kiss1 gene repression.
Estrogen-Induced Brain Region-Specific Alteration of the Histone Acetylation Status of the Kiss1 Gene Locus.
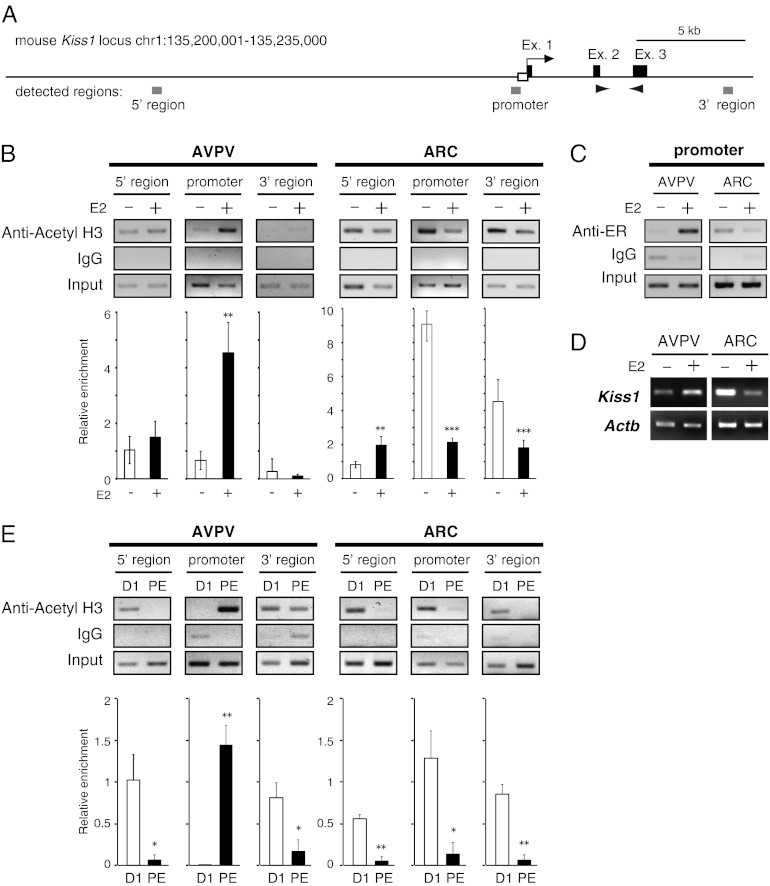
To determine the brain region-specific alteration of estrogen-induced change in the histone acetylation status at the Kiss1 locus, ChIP assays with anti-acetylated histone H3 antibody were performed using three sets of primers across the Kiss1 gene locus (Fig. 2A): a further region upstream of the Kiss1 gene (5′ region, −17588 to −17242), a region upstream of the Kiss1 promoter (−707 to −270), and an intergenic region downstream of the Kiss1 gene (3′ region, +9238 to +9670). Estrogen treatment significantly increased H3 acetylation at the Kiss1 promoter region in the AVPV (Fig. 2B), but significantly decreased H3 acetylation of the same promoter region in the ARC. Estrogen treatment also significantly increased and decreased ARC histone acetylation at 5′ and 3′ regions, respectively. ChIP assays using anti-ERα antibody further showed that estrogen treatment increased ERα binding within the Kiss1 promoter in the AVPV but not in the ARC (Fig. 2C). Kiss1 expression was up-regulated by estrogen in the AVPV and was down-regulated by estrogen in the ARC (Fig. 2D). Furthermore, the histone acetylation status within the AVPV Kiss1 promoter was significantly higher during proestrus than during diestrus (Fig. 2E), whereas histones of the ARC Kiss1 promoter were significantly higher during diestrus than during proestrus. Histones of the 5′ and 3′ regions of both the AVPV and ARC were more highly acetylated during diestrus than during proestrus (Fig. 2E).
Fig. 2.
Chromatin modification status of the Kiss1 locus. (A) Schematic diagram of the Kiss1 gene locus (exons 1–3 indicated by black squares; promoter region indicated by open square) and location of three regions for ChIP assay (5′, promoter, and 3′ regions indicated by gray squares). Arrowheads show primer regions used in RT-PCR analysis in Fig. 2D. (B) Histone acetylation status of the Kiss1 locus in the AVPV and ARC nuclei before and after E2 replacement. (Upper) Punched-out brain tissues from OVX (E2−) and estrogen-treated OVX (E2+) mice were subjected to ChIP assays with antibody against acetylated histone H3 (Acetyl H3). Normal mouse IgG was used as a negative control for the specificity of immunoprecipitation. An amount of chromatin fragments equal to that used for each immunoprecipitation also was subjected to PCR without immunoprecipitation as a positive control (input). (Lower) Semiquantitative analysis of the relative levels of histone acetylation was performed. The intensity of each band in the gel images was measured using the ImageJ program and normalized by input. Each bar represents the mean ± SEM of two independent experiments performed in triplicate. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.005. (C) ChIP analysis of ERα binding with the Kiss1 gene locus. Brain tissues punched out from OVX and OVX+E2 mice were subjected to ChIP assays with antibody against ERα. PCR products were analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis. (D) Expression pattern of the Kiss1 gene in the AVPV and ARC following E2 replacement. RT-PCR analysis using AVPV and ARC tissues taken from OVX and OVX+E2 mice. (E) Histone acetylation status of the Kiss1 locus in the AVPV and ARC nuclei at diestrous and proestrous stages. (Upper) Punched-out brain tissues from diestrous and proestrous mice were subjected to ChIP assays with antibody of acetyl H3. (Lower) Semiquantitative analysis of relative levels of histone acetylation was performed. The intensity of each band in gel images was measured using the ImageJ program and normalized by input. Each bar represents the mean ± SEM performed in triplicate. D1, diestrus-1 phase; PE, proestrus. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.
DNA Methylation Status of Kiss1 Core Promoter in Vivo and in Vitro.
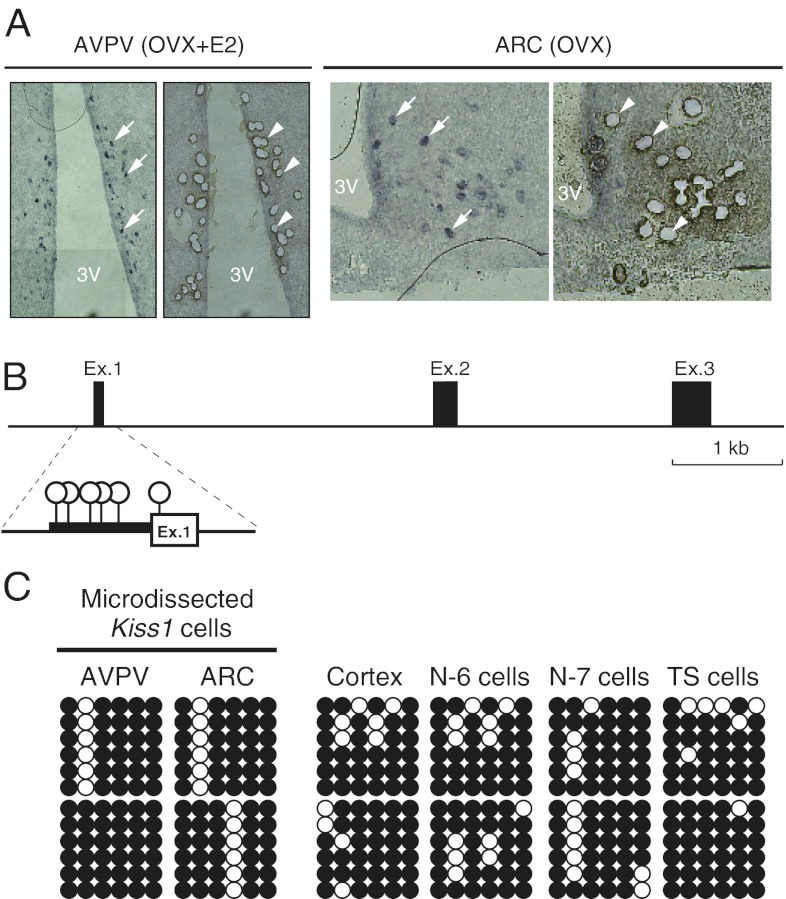
Kiss1 neurons visualized by in situ hybridization were isolated from the AVPV and ARC sections by microdissection (Fig. 3A). Bisulfite sequencing analysis of the Kiss1 upstream region harboring strong promoter activity (−180 to +29) revealed that the CpGs upstream of the TSS (Fig. 3B) appeared hypermethylated in all samples examined (Fig. 3C). No apparent difference was found between Kiss1-expressing cells (AVPV, ARC, N7, and differentiated trophoblast stem cells) and non–Kiss-expressing cells (cortex and N6 cells) (Fig. S2).
Fig. 3.
DNA methylation status of the Kiss1 promoter region in Kiss1-expressing or -nonexpressing cells. (A) Images of sections including AVPV or ARC nuclei before (Left in AVPV and ARC) and after (Right in AVPV and ARC) laser microdissection. Kiss1 neurons were visualized by in situ hybridization and were isolated based on in situ hybridization signals (indicated by arrows in left panels and by arrowheads in right panels). Kiss1-positive cells were collected from the AVPV in OVX+E2 mice and from the ARC in OVX mice. 3V, third ventricle. (B) Six CpG sites in the Kiss1 core promoter region analyzed by bisulfite sequencing. Open circles indicate CpG sites. (C) DNA methylation status of individual CpGs at the Kiss1 core promoter region in each sample. Bisulfite sequencing analysis was performed with DNA extracted from each sample. Each row of circles represents a single clone randomly picked from each of two independent PCRs. Open and filled circles represent unmethylated and methylated cytosines, respectively. TS cells, trophoblast stem cells.
Effects of Estrogen on Chromatin Loop Formation in AVPV and ARC Kiss1 Loci.
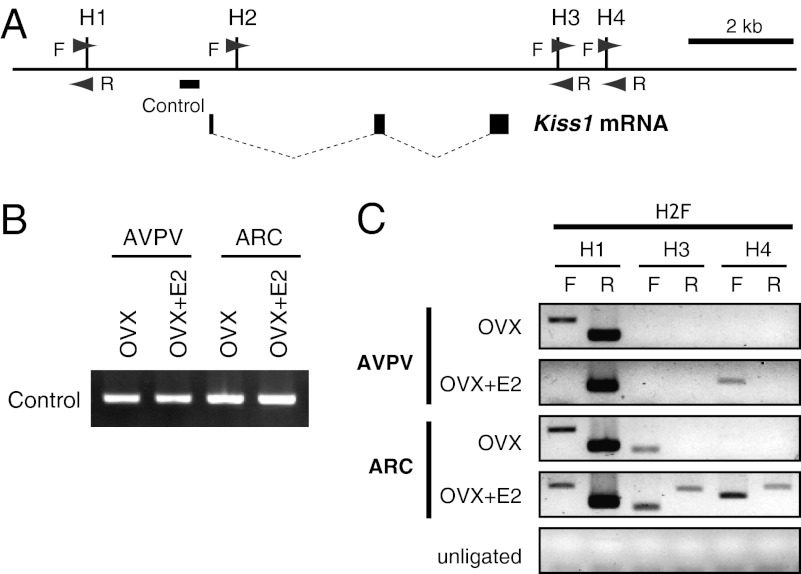
We analyzed the effects of estrogen on chromatin conformation of the Kiss1 locus in the AVPV and ARC by a chromatin conformation capture (3C) assay using 3C primers as indicated in Fig. 4A. PCR for loading control showed no difference in the amount of samples among groups (Fig. 4B). The 3C assay with AVPV tissue showed that estrogen treatment increased 3′ PCR products with H2F–H4F primers, but no band was detected without estrogen treatment (Fig. 4C). These results indicate that estrogen enhances the formation of the chromatin loop between the promoter and the 3′ intergenic region. The assay also showed an estrogen-dependent decrease in 5′ PCR products (H2F–H1F) in the AVPV, indicating the presence of another association between the promoter region and the 5′ region at the Kiss1 locus in the AVPV.
Fig. 4.
Chromatin conformational change at the Kiss1 gene locus in the AVPV and ARC. (A) Diagram of the Kiss1 locus; filled boxes indicate exons, and thin dotted lines indicate introns. HindIII restriction endonuclease sites are indicated by vertical lines (labeled by H1–H4). Arrowheads show positions of primers used in 3C assays. The thick horizontal bar indicates the region used in loading control PCR. (B) PCR for loading control. OVX mice with (OVX+E2) or without (OVX) E2 treatment were subjected to AVPV and ARC tissue sampling. (C) 3C analysis of the Kiss1 locus obtained from AVPV and ARC tissues in the absence and presence of E2 stimulation. 3C assays were performed, and PCR products were analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis. PCR products were generated using primer H2 forward (H2F) in combination with one of the other HindIII primers (H1–H4) as indicated.
The 3C assay of the ARC showed a pattern of loop formation within Kiss1 locus different from that seen in the AVPV. In the ARC, the 5′ region (H2F–H1F) and 3′ proximal region (H2F–H3F) were associated with a promoter region regardless of E2 treatment. Furthermore, an extensive range of the 3′ region (H2F–H3R, H2F–H4F, and H2F–H4R) was associated with the promoter region after E2 treatment (Fig. 4C).
In Vivo Reporter Assay to Confirm the Candidate Estrogen-Dependent AVPV-Specific Enhancer Region in Tg Mice.
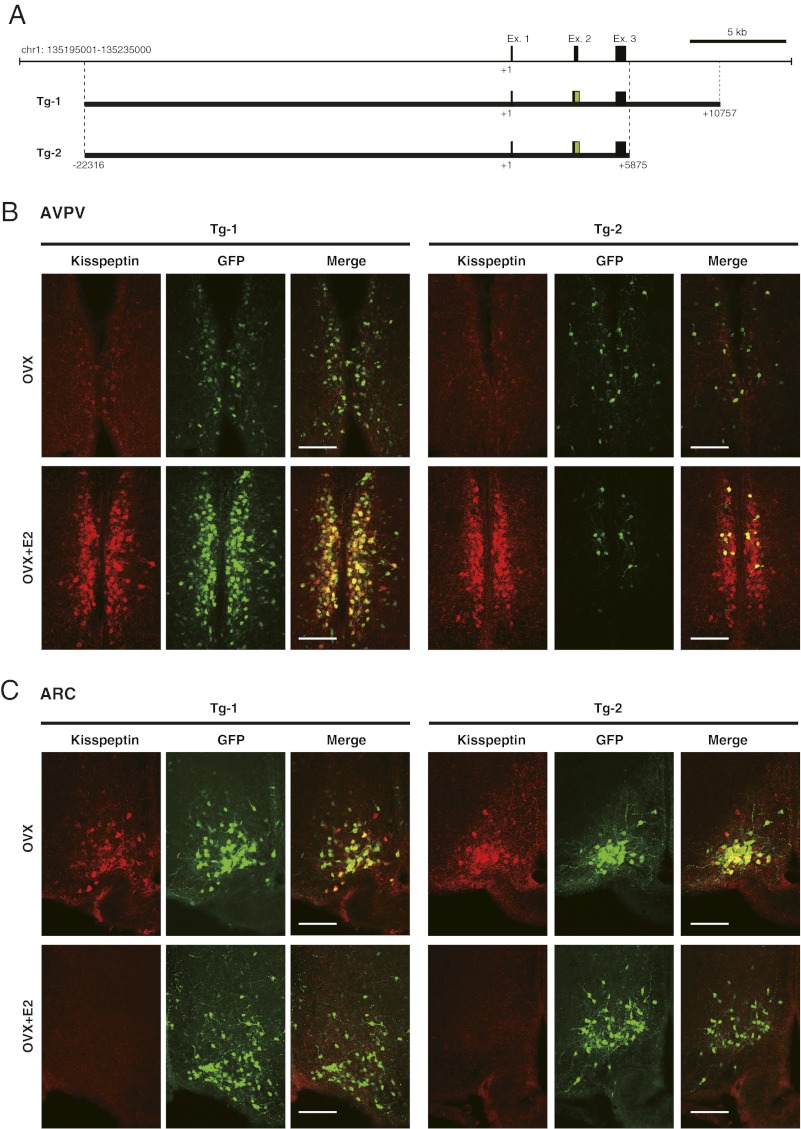
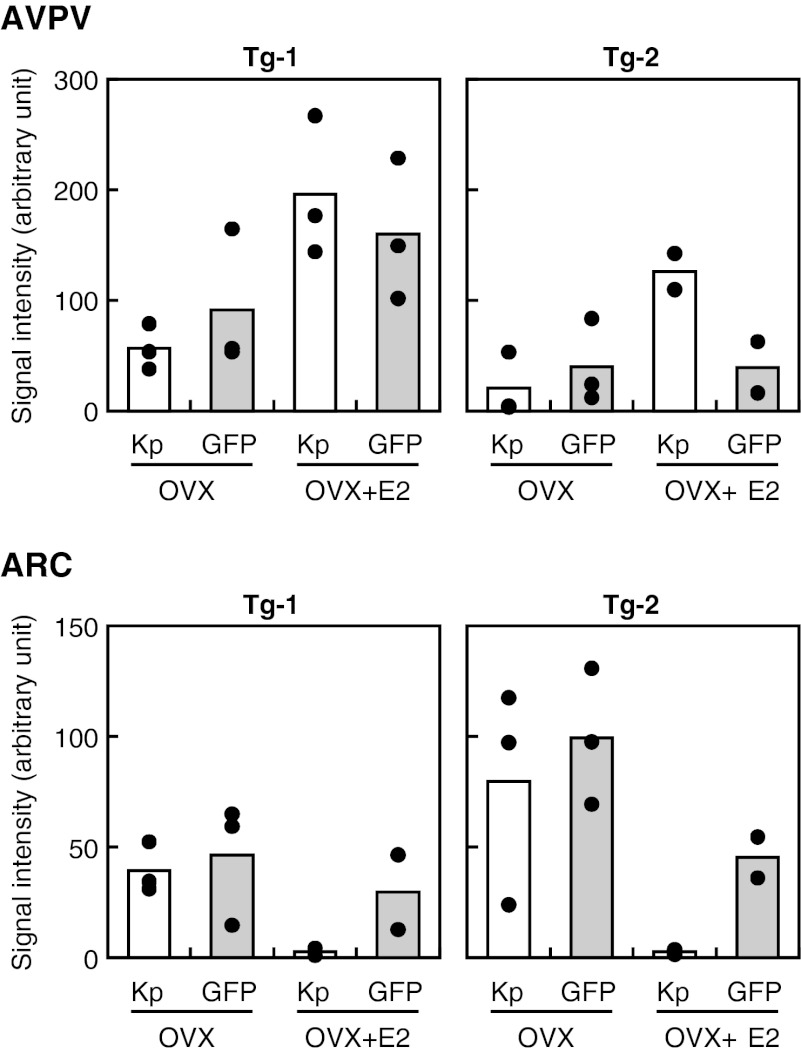
Two lines of Tg mice were generated using DNA constructs, the 22-kb upstream and 10- kb downstream sequence from the Kiss1 gene TSS (Tg-1) and the same sequence without the 3′ region of the third exon (Tg-2) (Fig. 5A). Dual-labeling immunohistochemistry revealed that GFP-positive neurons are located in two predicted nuclei, the AVPV and ARC. Photomicrographs show kisspeptin and GFP immunoreactivity in the AVPV (Fig. 5B) and ARC (Fig. 5C) of representative Tg-1 and Tg-2 mice. Fig. 6 shows the integrated density of fluorescence values for kisspeptin and GFP determined by Image J software in each nucleus. Tg-1 mice showed E2-enhanced GFP immunoreactivity in the AVPV (Fig. 6), most of which overlapped with kisspeptin immunoreactivity (Fig. 5B and Fig. S3). GFP immunoreactivity was greatly reduced, even with E2 treatment, in Tg-2 mice (which lacked the 3′ region) as compared with Tg-1 mice (Figs. 5B and 6 and Fig. S3). In the ARC, E2 reduced kisspeptin expression but did not cause an obvious reduction in GFP expression (Figs. 5B and 6 and Fig. S3).
Fig. 5.
In vivo reporter assay using constructs including the Kiss1 gene locus. (A) Schematic illustration of constructs for the generation of Tg mice. Green boxes indicate the inserted AcGFP sequence. (B and C) Kisspeptin and GFP expression in the AVPV and ARC of OVX and OVX+E2 Tg mice. Photomicrographs show sections of the AVPV and ARC stained by immunohistochemistry for kisspeptin (Left) and GFP (Center). Computer-aided merged images of immunoreactive signals for kisspeptin and GFP are shown on the right. (Scale bars, 100 μm.)
Fig. 6.
Expressions of kisspeptin (Kp) and GFP in the AVPV and ARC of Tg-1 and Tg-2 mice with or without E2 replacement. Integrated density of fluorescence in each microscopic field was determined by Image J software. Each bar represents the mean value, and solid circles indicate individual values.
Discussion
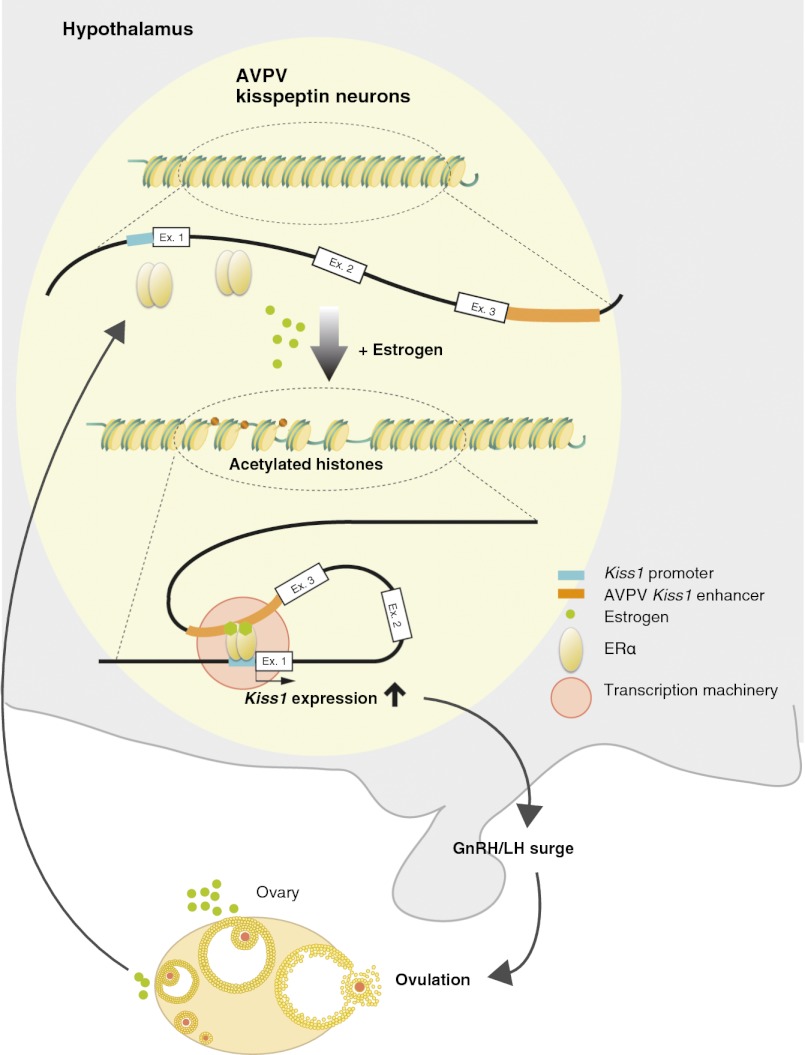
This study demonstrates that epigenetic regulation of Kiss1 is involved in the up-regulation of Kiss1 expression in the AVPV in response to estrogen. Histone H3 acetylation in the Kiss1 promoter region in the AVPV, which is increased by estrogen, is closely associated with an increase in Kiss1 expression in the AVPV. Indeed, histone H3 acetylation in the Kiss1 promoter region of the AVPV was much higher in proestrous animals than in diestrous animals. These results suggest that estrogen in the AVPV causes the Kiss1 promoter region to switch from an inactive to an active, open chromatin structure. In support of this idea, in vitro Kiss1 expression in hypothalamic cell lines was induced by TSA, an inhibitor of histone deacetylation, indicating that histone acetylation is involved in Kiss1 expression. Importantly, the present study demonstrates that the 3′ intergenic region of Kiss1 is essential for activation of the estrogen-induced Kiss1 promoter in the AVPV. This requirement is demonstrated clearly by the present in vivo reporter assay. Tg-1 mice, with the complete sequence of Kiss1 locus, showed GFP expression in kisspeptin neurons in both the AVPV and ARC, but the deletion of the 3′ region in Tg-2 mice greatly reduced estrogen-induced GFP expression in the AVPV, indicating that the 3′ region of the Kiss1 gene functions as an estrogen-responsive enhancer. The 3C assay showed interaction between the promoter and 3′ region of Kiss1 via a chromatin loop in the AVPV in the presence of estrogen, indicating that the 3′ region enhances the induction of estrogen-dependent AVPV Kiss1 promoter activity. Taken together, these results demonstrate that estrogen induces histone acetylation in the region of the Kiss1 promoter in the AVPV and consequently enhances the formation of a chromatin loop in the Kiss1 promoter, resulting in an increase in the estrogen-dependent, AVPV-specific expression of Kiss1. Functional in vivo data would be ultimately needed to completely demonstrate the role of histone acetylation in generating GnRH/LH surges.
The present study shows that, in the presence of estrogen, ERα is highly recruited at the region of the Kiss1 promoter in the AVPV (Fig. 2C), suggesting that the estrogen–ERα complex recruited to the region may be responsible for the histone acetylation at the Kiss1 promoter region and the subsequent expression of Kiss1 in the AVPV. Indeed, a potential estrogen-responsive element half-site was located within the predicted promoter region. The present finding is consistent with previous studies showing that ERα has a critical role in transcriptional activation of Kiss1 in the AVPV (8, 17, 18, 29). Furthermore, previous studies using knockin mice expressing a mutant form of ERα lacking a functional estrogen-responsive element-binding domain also suggesed that estrogen-positive feedback is mediated via the classical estrogen receptor pathway, whereas estrogen-negative feedback is mediated via the nonclassical pathway (30, 31). An increase in estrogen-induced ERα binding in the Kiss1 promoter region in the AVPV might recruit some histone acetyl-transferases (HATs) and other transcription regulators within the Kiss1 promoter in the AVPV. Indeed, the previous study using the human pS2 promoter as a model indicates that liganded ERα induced transcriptional activation of pS2 involving an orchestrated recruitment of components of basal transcriptional machinery and intermediate factors, such as HATs and the ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling complex, concomitant with an alteration in local chromatin structure (32). In vitro reporter analysis showed that E2 treatment failed to enhance Kiss1 promoter activity even in the presence of ERα (Fig. 1C). This result is consistent with the 3C and Tg analyses indicating that the 3′ region is a possible enhancer region.
An interesting issue in the mechanism of Kiss1 regulation in the hypothalamus is the opposite responses to circulating estrogen in kisspeptin neurons in the ARC and AVPV (8, 33). Here, we show that, in the AVPV, estrogen increased the histone H3 acetylation level in the Kiss1 promoter as correlated with the estrogen-dependent transcriptional activation of Kiss1. In contrast, estrogen decreased the histone acetylation level in the ARC, where estrogen negatively regulates Kiss1 expression. Indeed, the acetylation level of the Kiss1 promoter in the AVPV was higher during proestrus than during diestrous, whereas the level in the ARC was higher during diestrus than during proestrus (Fig. 2E). Unlike the AVPV, the histone H3 acetylation level in the ARC also was affected by estrogen in the 5′ and 3′ regions of Kiss1 (Fig. 2 B and E). It is possible that estrogen induces a broad range of changes in the Kiss1 locus in the ARC. We detected formation of an ARC-specific chromatin loop within the 3′ region of the Kiss1 locus after E2 treatment, suggesting that the 3′ region is involved in the suppression of Kiss1 expression in the ARC. Therefore, we speculate that the transcriptional cofactors that control Kiss1 gene expression could be different in the AVPV and ARC. Interestingly, we detected ERα binding to the Kiss1 promoter region taken from the ARC of OVX mice without E2 treatment (Fig. 2C), suggesting that unliganded ERα may have a role in Kiss1 regulation, as previously reported (34–36). The ligand-independent ERα activity was increased by phosphorylation at specific serine residues in the N-terminal domain as activated by the growth factor pathway (37, 38). Furthermore, ERα is known to interact with other transcription factors, such as Sp1 and AP-1, and it may use the constitutive transcriptional function of these factors (39, 40). Thus, unliganded ERα may play a role in regulating basal Kiss1 transcription in the ARC. Estradiol reduced kisspeptin expression in the ARC but did not cause an obvious reduction of GFP expression in the ARC (Figs. 5C and 6 and Fig. S3). The long half-life of conventional GFP may prevent the repression of reporter expression. Another possibility is that the cis element regulating the action of estrogen-negative feedback in the Kiss1 expression in the ARC might not be included within the transgene. The precise mechanism involved in the down-regulation of Kiss1 in the ARC by estrogen should be clarified in the future.
In the present study, we put more emphasis on the regulation of the Kiss1 gene by histone acetylation than by DNA methylation. In vitro Kiss1 expression was not affected by 5-aza-dC, an inhibitor of DNA methylation, in N6 hypothalamic cell lines. The Kiss1 promoter region was hypermethylated even in the Kiss1-expressing cells microdissected from both AVPV and ARC regions. However, we could not exclude the possibility that DNA methylation is involved in Kiss1 gene regulation. Our DNA methylation analysis did not cover the entire region of the Kiss1 locus, and transient cyclical change of DNA methylation status in the pS2 promoter in MCF-7 cells has been reported (41, 42). Further studies will be needed to elucidate the involvement of DNA methylation in regulating the Kiss1 gene.
In conclusion, the present study demonstrates an epigenetic mechanism underlying the estrogen regulation of AVPV Kiss1 expression to mediate estrogen positive feedback action to induce GnRH/LH surges. Our results suggest that estrogen stimulates ERα recruitment on the Kiss1 promoter region to induce histone H3 acetylation and the formation of a chromatin loop between the Kiss1 promoter and the 3′ enhancer region, leading to Kiss1 up-regulation in the AVPV. This notion suggests that epigenetic regulation of Kiss1 is involved in the estrogen-positive feedback generating the GnRH/gonadotropin surge.
Materials and Methods
Animals and tissue preparation, cell culture, RNA analyses, transient transfection, luciferase assays, and immunohistochemistry, including validity of the current E2 treatment (Fig. S4) and specificity of anti-kisspeptin antibody (Fig. S5), are described in detail in SI Materials and Methods.
Microdissection of Kiss1-Expressing Cells from Hypothalamus.
To dissect out Kiss1-positive cells, Kiss1 mRNA was visualized by in situ hybridization in coronal sections (20-μm thickness) of the hypothalamus taken from OVX or OVX+E2 mice as previously described (8, 43). Briefly, the hypothalamic tissues were sectioned on a cryostat. Digoxigenin (DIG)-labeled antisense and sense cRNA probes for mouse Kiss1 were synthesized by in vitro transcription from the cDNA clones. Hybridization with DIG-labeled cRNA probes was carried out at 60 °C overnight, and hybridized probes were detected using an alkaline phosphatase-conjugated anti-DIG Fab fragment (Roche Diagnostics) and 5-Bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl phosphate/Nitro blue tetrazolium chloride (Roche Diagnostics). Signal-positive cells were taken from the sections with the PALM MicroBeam System (Carl Zeiss Microimaging) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. About 100 cells for each nucleus were pooled and stored at −80 °C until used for DNA extraction.
Sodium Bisulfite Sequencing.
The conditions for using the bisulfite reaction to determine DNA methylation status have been described previously (22). The DNA fragment covering the 5′-flanking sequence of the Kiss1 gene was amplified by PCR using the forward primer GGGTATTGAGGAGTTTTTGGGTTAGATTGT and the reverse primer ACCTACTTCTCCAAACCCTCCCTAAATCAA. The PCR products were cloned into pCR2.1 TOPO (Invitrogen), and six clones randomly picked from each of two independent PCRs were sequenced using the BigDye Terminator v.3 System (Applied Biosystems) and an ABI3100 sequencer (Applied Biosystems).
ChIP Assay.
The ChIP assay was performed with 10 mg of punched-out tissue per assay using the ChIP Assay Kit (Millipore) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Fixed tissues were homogenized, lysed, and sonicated until chromatin fragments became 200–1,000 bp in size. Antibody against acetylated histone H3 (Millipore) or ERα (Millipore) was used for immunoprecipitation. Mouse nonimmunized IgG (Millipore) was used as a negative control to check the specificity of immunoprecipitation. After immunoprecipitation, recovered chromatin samples were subjected to PCR with the primers TACAGCACCAGGAAAGTTGAGA and GAAGAATCCGAGACTGCAGAAC for 5′ region, promoter CAACCACCCAGGAGGTAGAA and GAAGAGAAAGTGGCTGAGCAG for the promoter region, and GAGCTAGTGTACCCGCTTCTGT and GAAGTGACTCAAAGGTCCTGCT for the 3′ region. The PCR products were run on agarose gel, and the intensity of each band was measured using ImageJ software v. 1.40G (National Institutes of Health). Results from two independent experiments performed in triplicate were quantified and averaged.
3C Assay.
The 3C assay was conducted as described by Dekker et al. (44) with some modification. Crosslinked chromatin was digested with 500 U of HindIII (Roche) overnight at 37 °C, and was ligated in 6 mL of 1× ligation buffer. The 3C products were extracted by phenol/chloroform, precipitated by ethanol, and dissolved in Tris-EDTA buffer. The Kiss1 locus contains four HindIII sites; the primers flanking HindIII sites were designated as H1F (GCAGCTGGTGACATCAAGAA), H1R (CACCGACAGTCCAAGTTCAA), H2F (CAGGGCTTATCTGAGCCTTTC), H3F (GAGACTTCCCTTCTTTCCTGGT), H3R (GTTCGGGATGATTACAAAGAGC), H4F (AACATGTTTGGGCAGTAGTGTG), and H4R (AACTAGGGATGCACTTGGTTG). The Kiss1 chromatin loop was detected using primer H2F in combination with one of the other primers. A region serving as a loading control was amplified with GTTGTTTGGGGTGGAATGAGTC and TGGCTCCTGGGCTTACTCTA. Each PCR was performed under the following conditions: 95 °C for 5 min; 35 cycles of 95 °C for 30 s, 60 °C for 1 min, and 72 °C for 1 min; final extension 72 °C for 10 min. PCR products were analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis.
Generation of Transgenic Mice.
To generate transgenic mice, the two types of DNA construction shown in Fig. 5A were subcloned from BAC clone RP24-299J2 (BACPAC Resources). All final constructs were verified by sequencing. The linearized DNA fragments were purified by precipitation with ethanol and injected into fertilized eggs of the B6D2F1 mouse strain. Manipulated eggs were transplanted into foster mothers. We generated two types of Tg mice containing the Kiss1 locus sequence, Tg-1 and Tg-2. Tg-1 includes the sequences 22-kb upstream and 10-kb downstream from the Kiss1 TSS. Tg-2 also has a 22-kb upstream sequence but lacks the downstream sequence of the third exon. Both Tg mice contained the AcGFP sequence within the second exon of the Kiss1 gene. Mouse ear DNA was screened by PCR to check the presence of the transgenes using primers for the DNA sequence of AcGFP, AAGTTCATCTGCACCACCG and CCTGGGTATCTCTCAAGTGCAGAAA. F1 and F2 mice were identified by PCR analysis.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank Drs. Toru Takahashi, Yoshihiro Wakabayashi, and Tamami Homma (National Institute of Agrobiological Sciences) for technical advice and Tetsuhiro Kanazawa, Kae Yoshida, and Sho Nakamura (Nagoya University) for technical support. This study was supported in part by a grant from the Program for Promotion of Basic Research Activities for Innovative Biosciences (to K.-i.M.) and by Grants-in Aid from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science 23380163 (to H.T.), 23580402 (to Y.U.), and 23780292 (to N. Inoue). K.-i.M. received support from the Cooperative Study Program of National Institute for Physiological Sciences, Japan.
Footnotes
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Data deposition: The sequence reported in this paper has been deposited in the DNA Data Bank of Japan, EMBL, and Genbank nucleotide database [accession no. AB666166 (Kiss1 mRNA)].
This article is a PNAS Direct Submission.
See Author Summary on page 7609 (volume 109, number 20).
This article contains supporting information online at www.pnas.org/lookup/suppl/doi:10.1073/pnas.1114245109/-/DCSupplemental.
References
- 1.Moenter SM, Caraty A, Karsch FJ. The estradiol-induced surge of gonadotropin-releasing hormone in the ewe. Endocrinology. 1990;127:1375–1384. doi: 10.1210/endo-127-3-1375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.de Roux N, et al. Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism due to loss of function of the KiSS1-derived peptide receptor GPR54. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003;100:10972–10976. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1834399100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Gottsch ML, et al. A role for kisspeptins in the regulation of gonadotropin secretion in the mouse. Endocrinology. 2004;145:4073–4077. doi: 10.1210/en.2004-0431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Navarro VM, et al. Developmental and hormonally regulated messenger ribonucleic acid expression of KiSS-1 and its putative receptor, GPR54, in rat hypothalamus and potent luteinizing hormone-releasing activity of KiSS-1 peptide. Endocrinology. 2004;145:4565–4574. doi: 10.1210/en.2004-0413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ohkura S, et al. Gonadotrophin-releasing hormone pulse generator activity in the hypothalamus of the goat. J Neuroendocrinol. 2009;21:813–821. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2826.2009.01909.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Seminara SB, et al. The GPR54 gene as a regulator of puberty. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:1614–1627. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa035322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Shahab M, et al. Increased hypothalamic GPR54 signaling: A potential mechanism for initiation of puberty in primates. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102:2129–2134. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0409822102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Adachi S, et al. Involvement of anteroventral periventricular metastin/kisspeptin neurons in estrogen positive feedback action on luteinizing hormone release in female rats. J Reprod Dev. 2007;53:367–378. doi: 10.1262/jrd.18146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Smith JT, Cunningham MJ, Rissman EF, Clifton DK, Steiner RA. Regulation of Kiss1 gene expression in the brain of the female mouse. Endocrinology. 2005;146:3686–3692. doi: 10.1210/en.2005-0488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Goodman RL. The site of the positive feedback action of estradiol in the rat. Endocrinology. 1978;102:151–159. doi: 10.1210/endo-102-1-151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Han SK, et al. Activation of gonadotropin-releasing hormone neurons by kisspeptin as a neuroendocrine switch for the onset of puberty. J Neurosci. 2005;25:11349–11356. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3328-05.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kinoshita M, et al. Involvement of central metastin in the regulation of preovulatory luteinizing hormone surge and estrous cyclicity in female rats. Endocrinology. 2005;146:4431–4436. doi: 10.1210/en.2005-0195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Plant TM, Ramaswamy S. Kisspeptin and the regulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis in the rhesus monkey (Macaca mulatta) Peptides. 2009;30:67–75. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2008.06.029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Smith JT, Shahab M, Pereira A, Pau KY, Clarke IJ. Hypothalamic expression of KISS1 and gonadotropin inhibitory hormone genes during the menstrual cycle of a non-human primate. Biol Reprod. 2010;83:568–577. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.110.085407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Couse JF, Yates MM, Walker VR, Korach KS. Characterization of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis in estrogen receptor (ER) Null mice reveals hypergonadism and endocrine sex reversal in females lacking ERalpha but not ERbeta. Mol Endocrinol. 2003;17:1039–1053. doi: 10.1210/me.2002-0398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Shivers BD, Harlan RE, Morrell JI, Pfaff DW. Absence of oestradiol concentration in cell nuclei of LHRH-immunoreactive neurones. Nature. 1983;304:345–347. doi: 10.1038/304345a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Wintermantel TM, et al. Definition of estrogen receptor pathway critical for estrogen positive feedback to gonadotropin-releasing hormone neurons and fertility. Neuron. 2006;52:271–280. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2006.07.023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Li D, et al. Estrogen regulates KiSS1 gene expression through estrogen receptor alpha and SP protein complexes. Endocrinology. 2007;148:4821–4828. doi: 10.1210/en.2007-0154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Huijbregts L, de Roux N. KISS1 is down-regulated by 17beta-estradiol in MDA-MB-231 cells through a nonclassical mechanism and loss of ribonucleic acid polymerase II binding at the proximal promoter. Endocrinology. 2010;151:3764–3772. doi: 10.1210/en.2010-0260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Hattori N, et al. Epigenetic control of mouse Oct-4 gene expression in embryonic stem cells and trophoblast stem cells. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:17063–17069. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M309002200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Jenuwein T, Allis CD. Translating the histone code. Science. 2001;293:1074–1080. doi: 10.1126/science.1063127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Tomikawa J, Fukatsu K, Tanaka S, Shiota K. DNA methylation-dependent epigenetic regulation of dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase 2 gene in trophoblast cell lineage. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:12163–12169. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M513782200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Gruenbaum Y, Stein R, Cedar H, Razin A. Methylation of CpG sequences in eukaryotic DNA. FEBS Lett. 1981;124:67–71. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80055-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Jones PL, et al. Methylated DNA and MeCP2 recruit histone deacetylase to repress transcription. Nat Genet. 1998;19:187–191. doi: 10.1038/561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Li E, Bestor TH, Jaenisch R. Targeted mutation of the DNA methyltransferase gene results in embryonic lethality. Cell. 1992;69:915–926. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90611-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Zhao Z, Fan L, Frick KM. Epigenetic alterations regulate estradiol-induced enhancement of memory consolidation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107:5605–5610. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0910578107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Matsuda KI, et al. Histone deacetylation during brain development is essential for permanent masculinization of sexual behavior. Endocrinology. 2011;152:2760–2767. doi: 10.1210/en.2011-0193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Murray EK, Hien A, de Vries GJ, Forger NG. Epigenetic control of sexual differentiation of the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis. Endocrinology. 2009;150:4241–4247. doi: 10.1210/en.2009-0458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Mayer C, et al. Timing and completion of puberty in female mice depend on estrogen receptor alpha-signaling in kisspeptin neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107:22693–22698. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1012406108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Glidewell-Kenney C, et al. Nonclassical estrogen receptor alpha signaling mediates negative feedback in the female mouse reproductive axis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104:8173–8177. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0611514104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Gottsch ML, et al. Regulation of Kiss1 and dynorphin gene expression in the murine brain by classical and nonclassical estrogen receptor pathways. J Neurosci. 2009;29:9390–9395. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0763-09.2009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Métivier R, et al. Estrogen receptor-alpha directs ordered, cyclical, and combinatorial recruitment of cofactors on a natural target promoter. Cell. 2003;115:751–763. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(03)00934-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Kauffman AS, et al. Sexual differentiation of Kiss1 gene expression in the brain of the rat. Endocrinology. 2007;148:1774–1783. doi: 10.1210/en.2006-1540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Alotaibi H, Yaman EC, Demirpençe E, Tazebay UH. Unliganded estrogen receptor-alpha activates transcription of the mammary gland Na+/I- symporter gene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006;345:1487–1496. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.05.049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Cardamone MD, et al. ERalpha as ligand-independent activator of CDH-1 regulates determination and maintenance of epithelial morphology in breast cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106:7420–7425. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0903033106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Cvoro A, et al. Distinct roles of unliganded and liganded estrogen receptors in transcriptional repression. Mol Cell. 2006;21:555–564. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2006.01.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Dutertre M, Smith CL. Ligand-independent interactions of p160/steroid receptor coactivators and CREB-binding protein (CBP) with estrogen receptor-alpha: Regulation by phosphorylation sites in the A/B region depends on other receptor domains. Mol Endocrinol. 2003;17:1296–1314. doi: 10.1210/me.2001-0316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Hafner F, Holler E, von Angerer E. Effect of growth factors on estrogen receptor mediated gene expression. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1996;58:385–393. doi: 10.1016/0960-0760(96)00054-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Han WD, et al. GC-rich promoter elements maximally confers estrogen-induced transactivation of LRP16 gene through ERalpha/Sp1 interaction in MCF-7 cells. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2008;109:47–56. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2007.12.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Webb P, et al. The estrogen receptor enhances AP-1 activity by two distinct mechanisms with different requirements for receptor transactivation functions. Mol Endocrinol. 1999;13:1672–1685. doi: 10.1210/mend.13.10.0357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Kangaspeska S, et al. Transient cyclical methylation of promoter DNA. Nature. 2008;452:112–115. doi: 10.1038/nature06640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Métivier R, et al. Cyclical DNA methylation of a transcriptionally active promoter. Nature. 2008;452:45–50. doi: 10.1038/nature06544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Tomikawa J, et al. Molecular characterization and estrogen regulation of hypothalamic KISS1 gene in the pig. Biol Reprod. 2010;82:313–319. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.109.079863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Dekker J, Rippe K, Dekker M, Kleckner N. Capturing chromosome conformation. Science. 2002;295:1306–1311. doi: 10.1126/science.1067799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]