Figure 4.
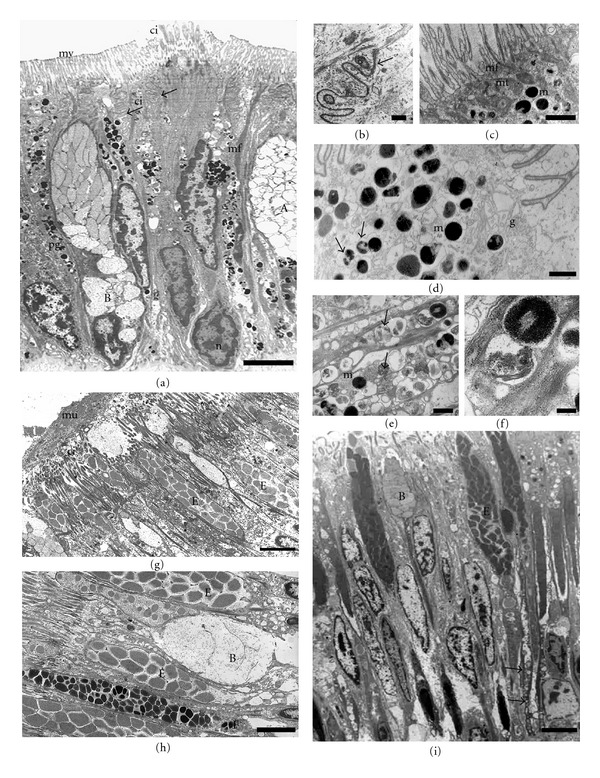
Transmission electron microphotographs of the side (a–f) and sole (g–i) foot epithelia. (a) General view showing secretory cells (types (a) and (b)) and pigmented epithelial cells with a prominent microvillus border (mv), a small group of cilia (ci) projecting from the apical surface. Note the highly infolded lateral membrane (arrows). Nucleus (n), pigmented granules (pg). Bar: 5 μm. (b) Detail of the apical region of adjacent cells, cell junctions which a zonula adherens can be observed (arrow). Bar: 0.5 μm. (c) Detail of microvillus border, microfilaments (mf) extend from the apical surface and comprise the core of the microvilli. At the apical surface mitochondria (mt) and melanosomes (m) are concentrated. Bar: 5 μm. (d) Melanosomes (m) and partially melanized granules (arrows) from a pigmented cell located on a groove. Golgi complex (g) Bar: 1 μm. (e) A pigmented epithelial cell located on the crests showing phycobilin-like pigmented granules (arrows) and a few melanosomes at different developmental stages (m) Bar: 0.3 μm. (f) Detail of both pigmented granules. Bar: 0.1 μm. (g) The mucus (mu) layer over the ciliated sole cells. Cilia (ci) Bar: 3 μm. (h) Three types of secretory cells (B, E, F) interspersed with ciliated cells. Bar: 2 μm. (i) General view of the ciliated sole foot epithelium. Type (b) and (e) secretory cells are located among ciliated epithelial cells. Observe the long necks (arrows) extending to the basal membrane. Bar: 3 μm.
