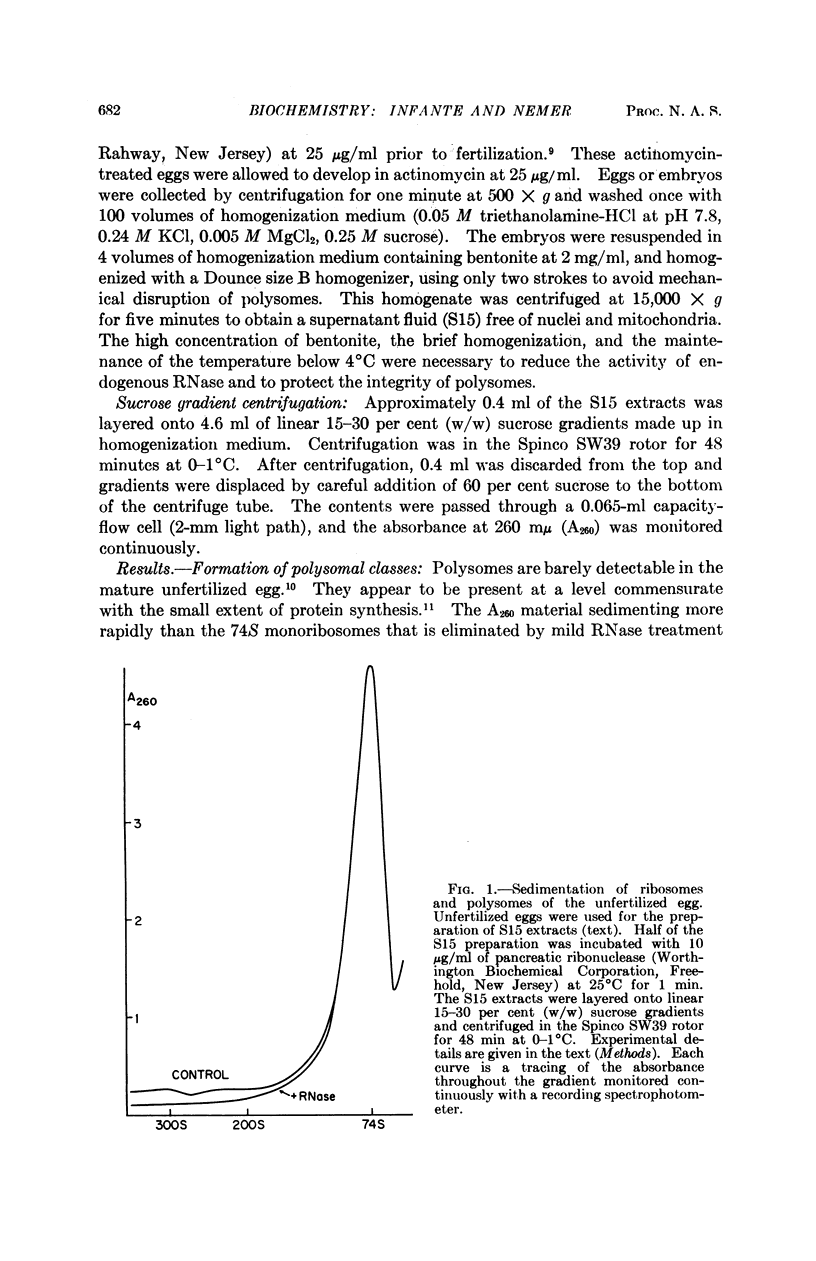
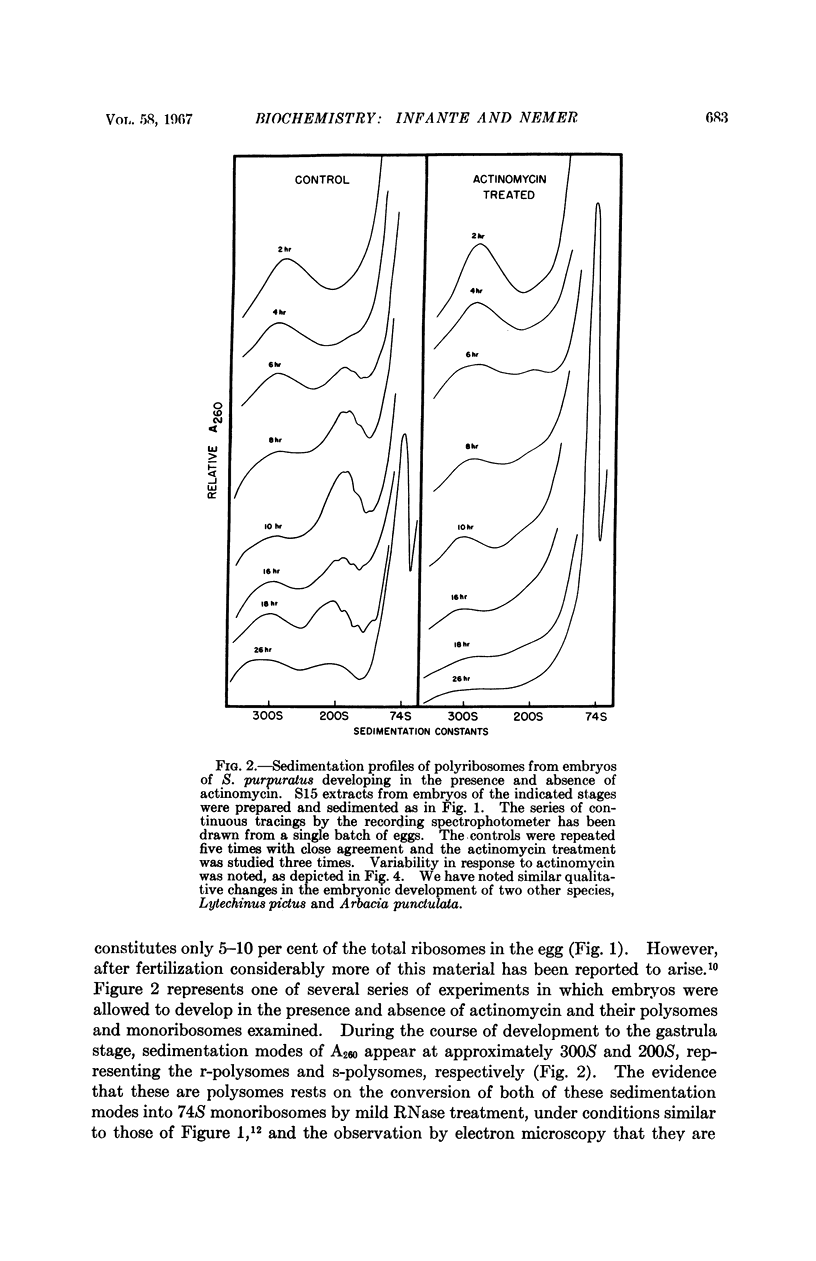
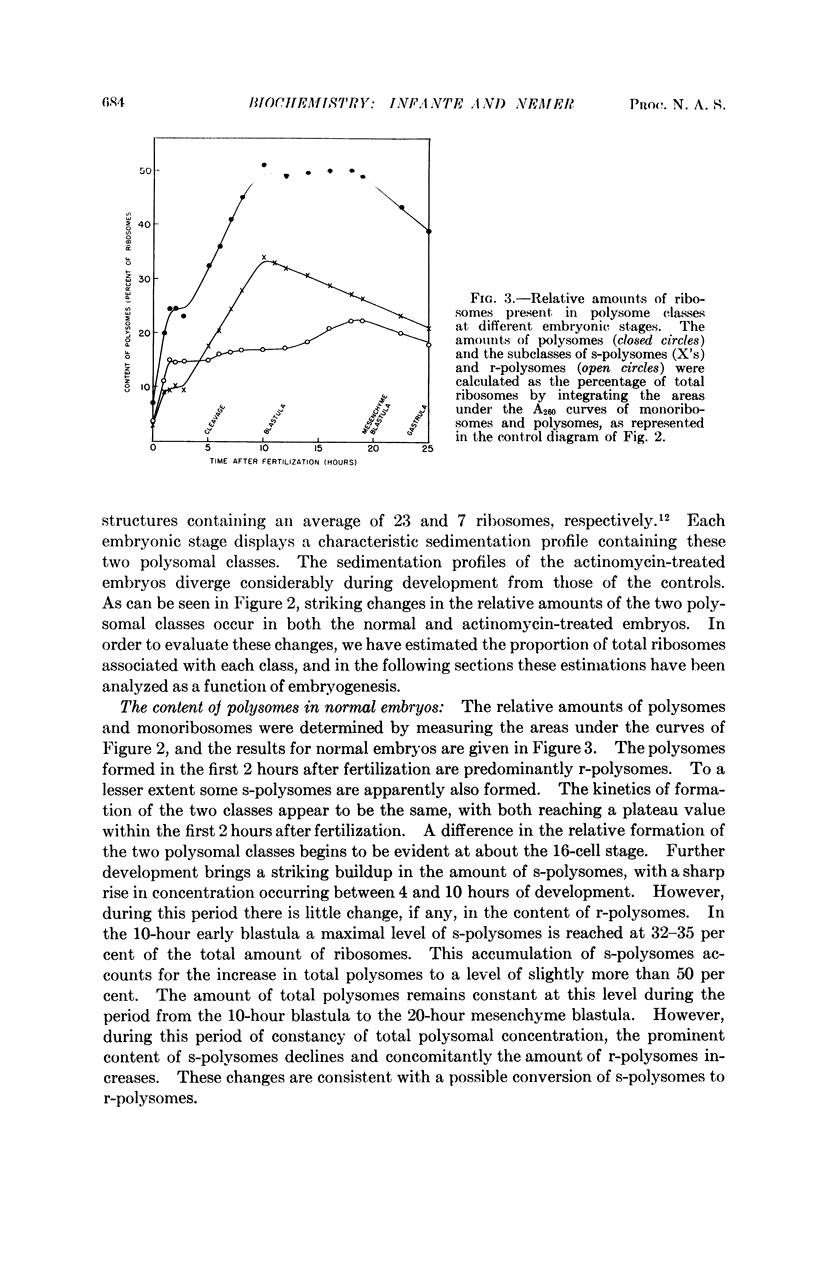
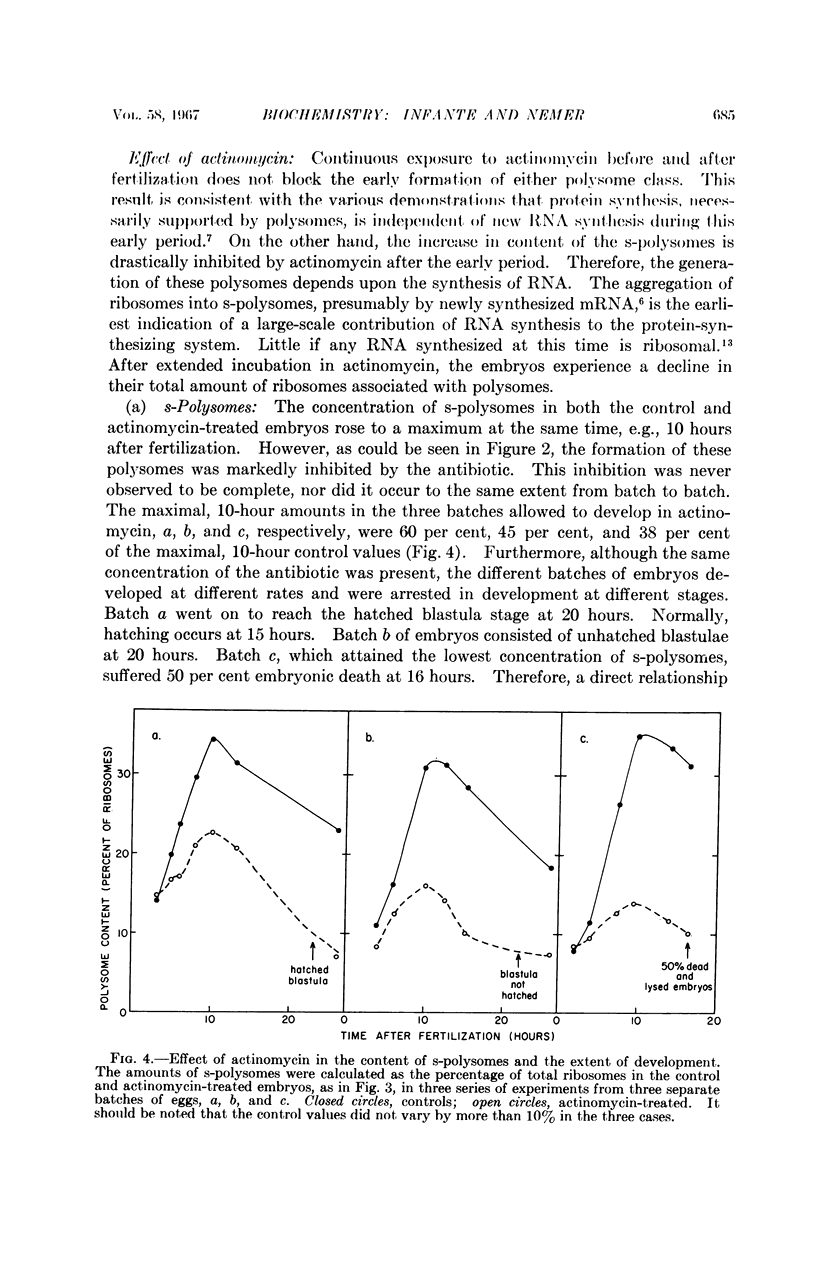
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRACHET J., FICQ A., TENCER R. AMINO ACID INCORPORATION INTO PROTEINS OF NUCLEATE AND ANUCLEATE FRAGMENTS OF SEA URCHIN EGGS: EFFECT OF PARTHENOGENETIC ACTIVATION. Exp Cell Res. 1963 Oct;32:168–170. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(63)90081-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barros C., Hand G. S., Jr, Monroy A. Control of gastrulation in the starfish, Asterias forbesii. Exp Cell Res. 1966 Aug;43(1):167–183. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(66)90390-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEBELLIS R. H., GLUCK N., MARKS P. A. SYNTHESIS OF RIBONUCLEIC ACID IN RABBIT BLOOD CELLS IN VIVO. J Clin Invest. 1964 Jul;43:1329–1337. doi: 10.1172/JCI105008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL VALLE M. R., ARONSON A. I. Evidence for the synthesis of stable informational RNA required for bacterial spore formation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1962 Nov 27;9:421–425. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(62)90027-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epel D. Protein synthesis in sea urchin eggs: a "late" response to fertilization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Apr;57(4):899–906. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.4.899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSS P. R., COUSINEAU G. H. Effects of actinomycin D on macromolecule synthesis and early development in sea urchin eggs. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1963 Feb 18;10:321–326. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(63)90532-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSS P. R., MALKIN L. I., MOYER W. A. TEMPLATES FOR THE FIRST PROTEINS OF EMBRYONIC DEVELOPMENT. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Mar;51:407–414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.3.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSS P. R. THE IMMEDIACY OF GENOMIC CONTROL DURING EARLY DEVELOPMENT. J Exp Zool. 1964 Oct;157:21–41. doi: 10.1002/jez.1401570107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HULTIN T. Activation of ribosomes in sea urchin eggs in response to fertilization. Exp Cell Res. 1961 Nov;25:405–417. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(61)90290-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONROY A., TYLER A. FORMATION OF ACTIVE RIBOSOMAL AGGREGATES (POLYSOMES) UPON FERTILIZATON AND DEVELOPMENT OF SEA URCHIN EGGS. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1963 Dec;103:431–435. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(63)90433-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEMER M. OLD AND NEW RNA IN THE EMBRYOGENESIS OF THE PURPLE SEA URCHIN. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Aug;50:230–235. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.2.230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemer M., Infante A. A. Messenger RNA in early sea-urchin embryos: size classes. Science. 1965 Oct 8;150(3693):217–221. doi: 10.1126/science.150.3693.217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papaconstantinou J., Stewart J. A., Koehn P. V. A localized stimulation of lens protein synthesis by actinomycin D. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Feb 21;114(2):428–430. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90328-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spirin A. S., Nemer M. Messenger RNA in early sea-urchin embryos: cytoplasmic particles. Science. 1965 Oct 8;150(3693):214–217. doi: 10.1126/science.150.3693.214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sussman M., Loomis W. F., Jr, Ashworth J. M., Sussman R. R. The effect of actinomycin D on cellular slime mold morphogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Feb 8;26(3):353–359. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90131-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sussman M., Sussman R. R. The regulatory program for UDPgalactose polysaccharide transferase activity during slime mold cytodifferentiation: requirement for specific synthesis of ribonucleic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Nov 8;108(3):463–473. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(65)90038-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILT F. H. REGULATION OF THE INITIATION OF CHICK EMBRYO HEMOGLOBIN SYNTHESIS. J Mol Biol. 1965 Jun;12:331–341. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80257-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilde C. E., Jr, Crawford R. B. Cellular differentiation in the anamniota. 3. Effects of actinomycin D and cyanide on the morphogenesis of Fundulus. Exp Cell Res. 1966 Nov-Dec;44(2):471–488. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(66)90453-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


