Abstract
Purpose
We analyzed the outcome of 47 patients with superficial facial rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) treated on Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Study Group (IRSG) Protocols-III, -IV-Pilot, and -IV.
Methods
We reviewed patients’ records. Clinico-pathologic features, treatment, and outcome were examined to identify prognostic factors.
Results
Thirty-two patients were males; 35 patients were 1–9 years old at diagnosis. Tumor sites were buccal/cheek (N = 21), external nasal/nasolabial (N = 12), lip/chin (N = 9), and masseter (N = 5). Patients (46/47) had localized disease: 18 biopsy only (Group III), 17 microscopic residual tumor (Group II), and 11 complete resection without residual tumor (Group I). Eight-year estimated event-free survival (EFS) and overall survival (OAS) rates were 61% and 65%. Patients <12 months old had inferior EFS, 21%, compared to ~68% in older patients (P = 0.077). Eight-year EFS rates were 80% for females and 50% for males (P = 0.096). Eight-year EFS rates were 72% in 33 patients without regional lymph-nodal tumor and 39% in 14 patients with regional nodal tumor (P = 0.07). Eight-year EFS rates were 72% for 22 patients with embryonal RMS and 53% for 23 patients with alveolar RMS (P = 0.28). Location of the primary tumor was not significantly related to outcome.
Conclusions
Patients with superficial facial RMS often have localized, grossly resectable lesions at the time of presentation. Favorable prognostic factors include age >12 months, female gender, embryonal histology, and no lymph-nodal tumor.
Keywords: childhood/adolescent superficial facial rhabdomyosarcoma, IRSG protocols
INTRODUCTION
The Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Study Group (IRSG) was formed in 1972 to investigate the biology of rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) and to improve treatment results for newly diagnosed patients <21 years of age. Sequential multidisciplinary protocols were designated as IRS-I through IRS-IV [1–8]. As patients accrued, differences in outcome were related to site, size, and histologic subtype of the primary tumor, and extent of the disease. Patients whose tumor was localized and completely removed before beginning chemotherapy had the greatest likelihood of cure.
We reviewed patients with superficial facial RMS to look for differences in outcome according to patient age/gender, histology, disease extent, and primary site, and to provide recommendations for treating future similar patients.
METHODS
Definition of Primary Sites
We included certain primary sites for review. Patients with cranial parameningeal sarcomas have been published previously [9]. Patients with orbit/eyelid tumors have been reviewed [10]. Patients with palatal, pharyngeal [11], and parotid tumors have more deeply seated lesions [12]. The upper face/forehead and pinna are contiguous with the scalp. This review includes patients with primary tumors bounded superiorly by a line from the external auditory meatus extending to the lateral canthus of the ipsilateral eye, crossing the top of the nasal bridge to the contralateral canthus and external auditory meatus. Lateral and inferior borders include tissues extending medially and inferiorly from the tragus down to the mandibular angle over to the anterior chin, stopping inferiorly where the horizontal part of the mandible joins its vertical part. We separated patients with tumors near the nasolabial fold (including 1 cm on either side) from those with buccal/cheek tumors, placed more laterally (Supplemental Fig. 1A,B).
Primary Sites Review
Two authors (BR, MC) reviewed the reports of 47 patients with tumors in one of the included sites, and agreed initially in 26 patients (55%); the remaining were decided after second review.
Clinical and Pathologic Characteristics
Patients’ information was reviewed by Surgical Subcommittee members to assess extent of disease and. categorized by TNM and Surgico-pathologic Grouping systems shown in Tables I and IV of Reference [13]. Pathology Subcommittee members reached consensus about histologic subtype. Definitions of response to treatment were outlined in the protocols [1–8].
TABLE I.
Characteristics of 47 Patients With Superficial Facial Rhabdomyosarcoma and Outcome
| Pt. no. | Study no. | Age, years | Gender | Primary site | Pathology | Group | Local therapy | Outcome, yrs. alive |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | IRS-III | 2 | M | Cheek | Emb | IIA | S, RT | 17.7+ |
| 2 | IRS-III | 3 | M | Nasolab | Alv | III | RT | L, 3.11 |
| 3 | IRS-III | 12 | M | Nasolab | Alv | II | RT | 16.2+ |
| 4 | IRS-III | 2 | M | Nasolab | Alv | IIA | S, RT | 1.26+ |
| 5 | IRS-III | 4 | M | Cheek | Emb | III | RT | 2.13+ |
| 6 | IRS-III | 10 | F | Buccal | Emb | III | RT | 17.1+ |
| 7 | IRS-III | 1 | M | Cheek | Alv | III | RT | 5.73+ |
| 8 | IRS-III | 2 | M | Cheek | Emb | II | RT | L&D, 15.3+ |
| 9 | IRS-III | 2 | F | Buccal | Emb | IA | S | L, 16.5+ |
| 10 | IRS-III | 5 | M | Nose tip | Alv | IA | S | 16.8+ |
| 11 | IRS-III | <1 | M | Cheek | SNOS | III | RT | L, 2.81 |
| 12 | IRS-III | 2 | M | Nasolab | Alv | III | ? | L, 3.69 |
| 13 | IRS-III | 2 | M | Cheek | Emb | III | RT | 5.00+ |
| 14 | IRS-III | 5 | F | Chin | Emb | IIA | S, RT | 13.4+ |
| 15 | IRS-III | 4 | F | Nose | Alv | IIA | S, RT | D, 1.84 |
| 16 | IRS-III | 3 | M | Masseter | Emb | IA | S | 1.93+ |
| 17 | IV-P | <1 | M | Lip | Emb | III | Bx., no RT | R, 3.19 |
| 18 | III | 1 | M | Cheek | Emb | IIC | S, RT | L, 9.89+ |
| 19 | IV-P | 12 | M | Cheek | Alv | III | Bx., no RT | L&D, 1.37 |
| 20 | III | 5 | M | Lip | Emb | IIA | S, RT | 10.5+ |
| 21 | III | 1 | F | Buccal | Alv | IIC | S, RT | 5.55+ |
| 22 | III | <1 | M | Nasolab | Alv | IIB | S, no RT | 2.74 |
| 23 | III | 5 | M | Lip | Emb | IIC | S, RT | 13.1+ |
| 24 | III | 8 | M | Buccal | Emb | IA | S | D, 1.92 |
| 25 | III | 12 | M | Nose tip | Emb | IA | S | 4.28+ |
| 26 | III | 11 | M | Masseter | Emb | IIA | S, RT | D, 5.69 |
| 27 | III | 6 | F | Masseter | Alv | IIC | S, RT | 6.61+ |
| 28 | III | 9 | F | Buccal | Emb | III | RT | 12.5+ |
| 29 | IV | 7 | M | Cheek | Emb | IIC | RT | 9.08+ |
| 30 | IV | 1 | F | Lip | Alv | III | RT | 9.97+ |
| 31 | IV | <1 | M | heek | Alv | IV | No RT | D, 0.85 |
| 32 | IV | <1 | F | Buccal | Emb | IA | S | 4.81+ |
| 33 | IV | <1 | M | Lip | Alv | IIB | S, RT | 1.02+ |
| 34 | IV | 8 | F | Masseter | Emb | III | RT | 6.90+ |
| 35 | IV | 15 | F | Buccal | Bot | IA | S | 6.42+ |
| 36 | IV | 1 | F | Nose | Alv | IA | S | 9.69+ |
| 37 | IV | 2 | M | Nasolab | Alv | IIA | S, RT | R, 4.67 |
| 38 | IV | 1 | F | Nasal | Alv | IA | S | 7.07+ |
| 39 | IV | 8 | M | Masseter | Bot | IIA | S, RT | 2.48+ |
| 40 | IV | 4 | M | Lip | Alv | IA | S | R&D, 3.67 |
| 41 | IV | 2 | M | Cheek | Alv | III | RT | D, 6.41 |
| 42 | IV | 2 | F | Lip | Alv | IIC | S, RT | 1.97 |
| 43 | IV | 1 | M | Nose | RNOS | III | RT | 5.46+ |
| 44 | IV | 3 | M | Cheek | Alv | III | RT | 7.23+ |
| 45 | IV | 5 | M | Buccal | Emb | IIA | S, RT | 4.44+ |
| 46 | IV | 2 | F | Lip | Emb | IA | S | 5.30+ |
| 47 | IV | 1 | M | Cheek | Alv | III | No RT | 6.00+ |
Pt., patient; no., number; IV-P, IRS-IV Pilot Study; M, male; F, female; Nasolab, nasolabial; Emb, embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS); Alv, alveolar RMS; SNOS, sarcoma not otherwise specified; Bot, botryoid RMS; RNOS, RMS not otherwise specified; S, surgery; RT, radiation therapy; Bx, biopsy; yrs., years; L, local recurrence; D, distant metastasis; R, regional lymph node metastasis; &, simultaneous recurrence in >1 site; +, alive; absence of +, dead.
TABLE IV.
Series of Young Patients With Head/Neck Rhabdomyosarcoma
| References | No. of Pts. | Primary sites | Percent alive |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wharam et al. [11] | 21 | Cheek, parotid | 95% at 5 years |
| Rao et al. [17] | 7 | Cheek, parotid | 29%, ? interval |
| Lyos et al. [19] | 56 | Head/neck | 63% at 5 years |
| Simon et al. [20] | 12 | Cranial, non-PM, non-orbit | 55% at 5 years |
| Pappo et al. [13] | 164 | Cheek+other non-PM, non-orbit sites | 83% at 5 years |
| Current series | 47 | Superficial facial sites | 65% at 8 years |
No., number; Pts., patients; PM, parameningeal.
Statistical Considerations
Event-free survival (EFS) was defined as the time from study enrollment to disease recurrence or death as a first event. Overall survival (OAS) was defined as the time from enrollment to death from any cause. EFS and OAS for patients without an event were censored at the patient’s last contact. The Kaplan–Meier method was used to estimate the EFS and OAS distributions [14]. Differences between survival curves were analyzed using the log-rank test [15]. The distribution of categorical characteristics such as gender, histology, regional lymph-nodal involvement, were compared using Chi-square tests. Analyses were based on data available by May 2004. P-values of less than 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
Patients and Tumors
Forty-seven patients with superficial facial rhabdomyosarcoma were treated on Protocols IRS-III, -IV-Pilot, and -IV, 1984–1997 (Table I).
Gender/age
The 32 males and 15 females (M:F 2.1/1) had a median age of ~5 years. Thirty-five patients (74%) were 1–9 years old; six each were <1 year and 10–20 years at diagnosis. There was no significant difference among age categories by gender (Supplemental Table I).
Tumor sites
Sites included cheek (N = 13 region patients), buccal (N = 8), external nasal/nasolabial region (N = 12), lip/labial region (N = 8), masseter muscle (N = 5), and chin (N = 1).
Disease extent
Forty-six patients had localized disease; one had distant metastases in the soft tissues of the neck, trunk, and extremities.
Surgical procedures
Eighteen patients with localized disease underwent only biopsy before beginning chemotherapy (Group III). Seventeen patients underwent gross total removal of the primary lesion with microscopic residual tumor and/or resected involved regional lymph nodes (Group II); 11 patients had complete resection of the primary tumor (Group I).
Regional lymph nodes
Thirty-three patients had no clinical evidence of tumor-involved regional nodes (N0 status); 14 patients had regional lymph node involvement (N1). There were no significant differences by gender or histology regarding numbers with tumor-involved lymph nodes (Supplemental Table II).
Tumor histology
Twenty-three patients had alveolar RMS, 22 had embryonal RMS, and 2 had RMS not otherwise specified.
Tumor size
Forty tumors were ≤5 cm in widest diameter, four were >5 cm, three were unspecified.
Outcome
Event-free survival (EFS) and overall survival (OAS)
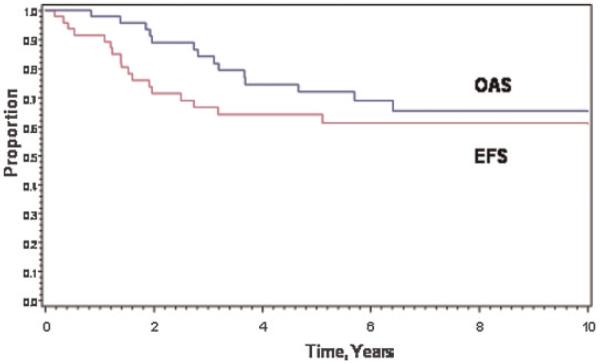
The estimated 8-year EFS and OAS rates were 61% (95% Confidence Interval [CI], 45%, 74%) and 65% (95% CI, 48%, 78%; Fig. 1).
Fig. 1.
Event-free survival (EFS) and overall survival (OAS) in 47 patients with superficial facial rhabdomyosarcoma.
Prognostic Factors
Table II shows patients’ distribution by age, gender, nodal involvement, Surgico-pathologic Group, pathologic subtype, and primary site group.
TABLE II.
Clinical and Pathological Characteristics and Outcome of 47 Patients With Facial RMS
| Age at diagnosis, years | No. Pts. | % | % Event-free at 8 years |
P-value | % Alive at 8 years |
P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <1 | 6 | 13 | 21 | 0.077 | 21 | 0.0029 |
| 1–9 | 35 | 74 | 67 | 73 | ||
| 10–20 | 6 | 13 | 67 | 63 | ||
| Gender | ||||||
| Male | 32 | 68 | 50 | 0.096 | 53 | 0.065 |
| Female | 15 | 32 | 80 | 87 | ||
| Node status | ||||||
| N0 | 33 | 70 | 72 | 0.07 | 75 | 0.06 |
| N1 | 14 | 30 | 39 | 45 | ||
| Histology | ||||||
| Embryonal | 22 | 49 | 72 | 0.28 | 83 | 0.03 |
| Alveolar | 23 | 51 | 53 | 51 | ||
| Surg-path Group | ||||||
| I | 11 | 24 | 73 | 0.85 | 81 | 0.73 |
| II | 17 | 37 | 58 | 63 | ||
| III | 18 | 39 | 60 | 62 | ||
| 1° Site group | ||||||
| Buccal/cheek | 21 | 50 | 60 | 0.98 | 73 | 0.26 |
| Nasal/labial/chin | 21 | 50 | 55 | 55 |
No. Pts., number of patients; Surg-path, Surgico-pathologic; 1°, primary tumor.
Age
Patients <12 months had inferior 8-year EFS and OAS rates, 21%, compared to ~68% in those older (P = 0.077 and 0.0029).
Gender
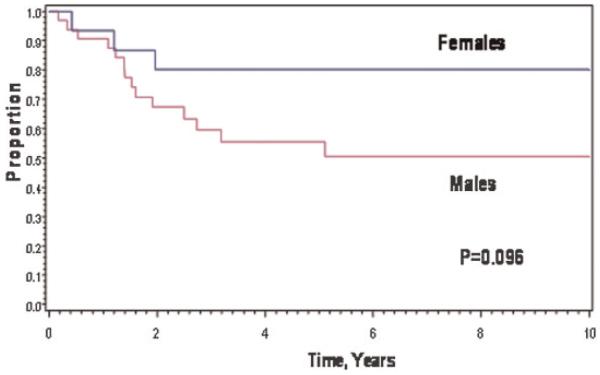
Females fared somewhat better in 8-year EFS and OAS, 80% and 87%, compared to males, whose 8-year EFS and OAS rates were 50% and 53%; P = 0.096 for EFS (Fig. 2) and 0.065 for OAS.
Fig. 2.
Event-free survival of patients by gender.
Regional nodes
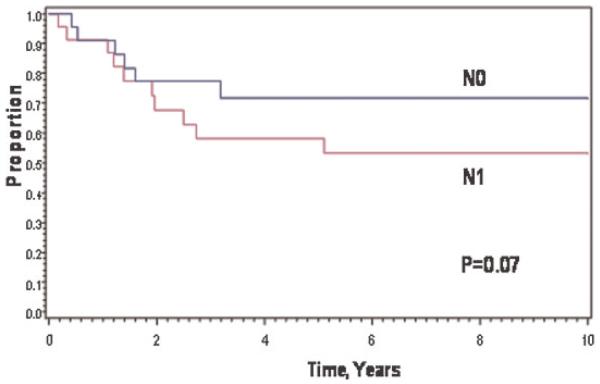
Nineteen (40%) patients underwent biopsy of regional lymph nodes; 11 patients had 1–3 tumor-involved lymph nodes (N1); eight patients had 1–22 negative lymph nodes (N0). Twenty-eight patients’ regional lymph-node status was assessed clinically: 25 were N0 and 3 were N1. Eight-year EFS and OAS rates were 72% and 75% for 33 N0 patients compared to 39% and 45% for 14 N1 patients; P = 0.07 for EFS (Fig. 3) and 0.06 for OAS. Survival was not related to whether lymph node biopsy was performed.
Fig. 3.
Event-free survival by regional lymph node status at diagnosis.
Histology
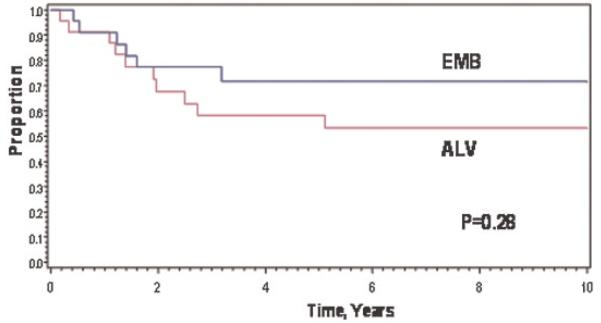
Patients with embryonal RMS had 8-year EFS and OAS rates of 72% and 83%, compared to 53% and 51% for patients with alveolar RMS; P = 0.28 for EFS (Fig. 4) and 0.03 for OAS.
Fig. 4.
Event-free survival of patients with embryonal RMS versus alveolar RMS.
Surgico-pathologic Group
There was no significant difference among EFS rates according to Group (Supplemental Fig. 2).
Primary site and tumor size
There was no significant difference in 8-year EFS rates of the two primary site groups (Table II) or by tumor size.
Recurrence and Outcome
Table III shows data in the 16 patients who experienced recurrence within the major histologic subtypes. The small number of patients precluded a multivariate analysis.
TABLE III.
Failure and Outcome Among 16 Patients With Facial Rhabdomyosarcoma
| Histology | Age at diagnosis, yrs. | Gender, no. of patients |
Surg/Path Group, no. |
Regional lymph nodes |
Tumor size (cm) | Site group | Years alive; survival status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Embryonal RMS, N=6 patients |
<1, 1; 1–9, 4; >9,1 | Male, 5; female, 1 | I, 2; II, 2; III, 2 | N0, 4; N1, 2 | ≤5, 4; ?, 2 | BC, 4; NL, 1; masseter, 1 | 1.9-5.69, dead (N=3); 9.8+−16+, alive (N=3) |
| Alveolar RMS. N=10 patients |
<1, 2; 1–9, 7; >9, 1 | Male, 8; female, 2 | I, 1; II, 4; III, 4; IV, 1 | N0, 5; N1, 5 | ≤5, 9; > 5, 1 | BC, 3; NL, 7 | 0.8–6.4; all dead of tumor (N=10) |
| Totals | <1, 3; 1–9, 11; >9, 2 | Male, 13; female, 3 | I, 3; II, 6; III, 6; IV, 1 | N0, 9; N1, 7 | ≤ 5, 13; >5, 1; ?, 2 | BC, 7; NL, 8; masseter, 1 | 13 dead of tumor, 3 alive |
BC, buccal/cheek, NL, nasal/labial/chin, +, alive at last contact; ?, unknown.
Embryonal RMS
Patients (6/22) with embryonal RMS (27%) recurred; three died. Three patients survived; including one alive 3.8 years following treatment of secondary osteosarcoma, diagnosed 12.7 years after RMS.
Alveolar RMS
Patients (10/23) with alveolar RMS (43%) recurred; all died of tumor at a median of 1.9 years after study enrollment.
RMS not otherwise specified
One patient recurred at 1.5 years and died 1.3 years later. The other patient survived relapse-free 5.4 years after study enrollment.
DISCUSSION
Compared to patients with parameningeal lesions, those with superficial tumors were more likely to have grossly complete resection of the tumor before chemotherapy (28/47, ~ 60%) [9]. But the favorable effect of up-front surgical removal was offset by the fact that nearly 50% of superficial facial tumors were alveolar RMS, which confers a worse prognosis than embryonal RMS.
The relevant reports are summarized in Table IV. Twenty of 21 IRS-I patients with parotid/cheek tumors (95%) were diseasefree at 5 years [11]. Females fared worse than males, opposite to our findings here. However, a later article stated that 11/21 patients with cheek tumors treated on IRS-I and -II had embryonal RMS and 10/21 had alveolar RMS, a distribution similar to this report [16].
It is difficult to compare other series, because sites other than the ones reviewed here were usually not separated in this way (Table IV). Only 2/7 patients at St. Jude with cheek/parotid rhabdomyosarcomas survived (29%) [17]. At Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, mortality was reduced from 50% during 1970–1979 to 23% from 1980 to 1989 [18]. The 5-year survival rate was 63% in 56 pediatric patients with head/neck RMS treated at the M.D Anderson Cancer Center [19]. The 5-year survival rate for 12 nonparameningeal patients in Iowa was 55%; chemotherapy was not given to all patients [20].
In 2003 the IRSG reported 164 patients with localized, nonorbital, nonparameningeal head/neck RMS treated on IRS-III and -IV [13]. Ninety-nine patients (60%) had embryonal RMS; 58 had alveolar RMS, and 7 had other histologies. The estimated 5-year survival rate was 83%. Patients with embryonal RMS fared better than those with alveolar RMS. Females and patients with N0 status fared better than males and those with N1 status, similar to our findings here. The nearly equal number of alveolar and embryonal RMS patients in this series may be the reason for our lower 8-year survival rate of 65%.
In summary, we believe that if feasible and cosmetically acceptable, gross total removal of superficial facial RMS should be undertaken before instituting chemotherapy. Clinically suspicious regional lymph nodes should be removed, to assess prognosis and to plan radiation therapy to those node-bearing areas containing demonstrable tumor.
Supplementary Material
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
This study was supported in part by grants CA-24507, CA-29511, and CA-72989 from the National Cancer Institute, Bethesda, Maryland. A complete listing of grant support for research conducted by CCG and POG before initiation of the COG grant in 2003 is available online at http://www.childrensoncologygroup.org/admin/grantinfo.htm.
Footnotes
Presented in part at the 36th Meeting of the International Society for Pediatric Oncology in Oslo, Norway, on September 17, 2004.
This article contains Supplementary Material available at http://www.interscience.wiley.com/jpages/1545-5009/suppmat.
REFERENCES
- 1.Maurer HM, Beltangady M, Gehan EA, et al. The Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Study-I. A final report. Cancer. 1988:209–220. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19880115)61:2<209::aid-cncr2820610202>3.0.co;2-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Maurer HM, Gehan EA, Beltangady M, et al. The Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Study-II. Cancer. 1993;71:1904–1922. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19930301)71:5<1904::aid-cncr2820710530>3.0.co;2-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Crist WM, Raney RB, Ragab A, et al. Intensive chemotherapy including cisplatin with or without etoposide for children with soft-tissue sarcomas. Med Pediatr Oncol. 1987;15:51–57. doi: 10.1002/mpo.2950150202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Crist W, Gehan EA, Ragab AH, et al. The Third Inter-group Rhabdomyosarcoma Study. J Clin Oncol. 1995;13:610–630. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1995.13.3.610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ortega JA, Ragab AH, Gehan EA, et al. A feasibility, toxicity, and efficacy study of ifosfamide, actinomycin D, and vincristine for the treatment of childhood rhabdomyosarcoma: A report of the Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Study IV Pilot Study. Am J Pediatr Hematol/Oncol. 1993;15:S15–S20. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ruymann FB, Vietti T, Gehan E, et al. Cyclophosphamide dose escalation in combination with vincristine and actinomycin D (VAC) in gross residual sarcoma: A pilot study without hema-topoietic growth factor support evaluating toxicity and response. J Pediatr Hematol/Oncol. 1995;17:331–337. doi: 10.1097/00043426-199511000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Arndt C, Tefft M, Gehan E, et al. A feasibility, toxicity, and early response study of etoposide, ifosfamide, and vincristine for the treatment of children with rhabdomyosarcoma: A report from the Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Study (IRS) IV pilot study. J Pediatr Hematol/Oncol. 1997;19:124–129. doi: 10.1097/00043426-199703000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Crist WM, Anderson JR, Meza JL, et al. Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Study IV: Results for patients with nonmetastatic disease. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19:2091–2102. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2001.19.12.3091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Raney RB, Meza J, Anderson JR, et al. Treatment of children and adolescents with localized parameningeal sarcoma: Experience of the Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Study Group protocols IRS-II through -IV, 1978–1997. Med Pediatr Oncol. 2002;38:22–32. doi: 10.1002/mpo.1259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Wharam M, Beltangady M, Hays D, et al. Localized orbital rhabdomyosarcoma: An interim report of the Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Study Committee. Ophthalmology. 1987;94:251–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Wharam MD, Foulkes MA, Lawrence W, Jr., et al. Soft tissue sarcoma of the head and neck in childhood: A report of the Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Study (IRS-I) Cancer. 1984;53:1016–1019. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19840215)53:4<1016::aid-cncr2820530432>3.0.co;2-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Walterhouse DO, Pappo AS, Baker KS, et al. Rhabdomyosarcoma of the parotid region occurring in childhood and adolescence: A report from the Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Study Group. Cancer. 2001;92:3135–3146. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(20011215)92:12<3135::aid-cncr10172>3.0.co;2-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Pappo AS, Meza JL, Donaldson SS, et al. Treatment of localized nonorbital, nonparameningeal head and neck rhabdomyosarcoma: Lessons learned from Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Studies III and IV. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:638–645. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2003.01.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kaplan GL, Meier P. Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observations. J Am Stat Assoc. 1958;53:457–481. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Peto R, Pike MC, Armitage P, et al. Design and analysis of randomized clinical trials requiring prolonged observation of each patient. II: Analysis and examples. Br J Cancer. 1977;35:1–39. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1977.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Wharam MD, Beltangady MS, Heyn RM, et al. Pediatric orofacial and laryngopharyngeal rhabdomyosarcoma. An Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Study report. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1987;113:1225–1227. doi: 10.1001/archotol.1987.01860110091014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Rao BN, Santana VM, Fleming ID, et al. Management and prognosis of head and neck sarcomas. Am J Surg. 1989;158:373–377. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(89)90136-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Anderson GJ, Tom LWC, Womer RB, et al. Rhabdomyosarcoma of the head and neck in children. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1990;116:428–431. doi: 10.1001/archotol.1990.01870040050012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Lyos AT, Goepfert H, Luna MA, et al. Soft tissue sarcoma of the head and neck in children and adolescents. Cancer. 1996;77:193–200. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0142(19960101)77:1<193::AID-CNCR31>3.0.CO;2-Z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Simon JH, Paulino AC, Smith RB, et al. Prognostic factors in head and neck rhabdomyosarcoma. Head Neck. 2002;24:468–473. doi: 10.1002/hed.10070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.