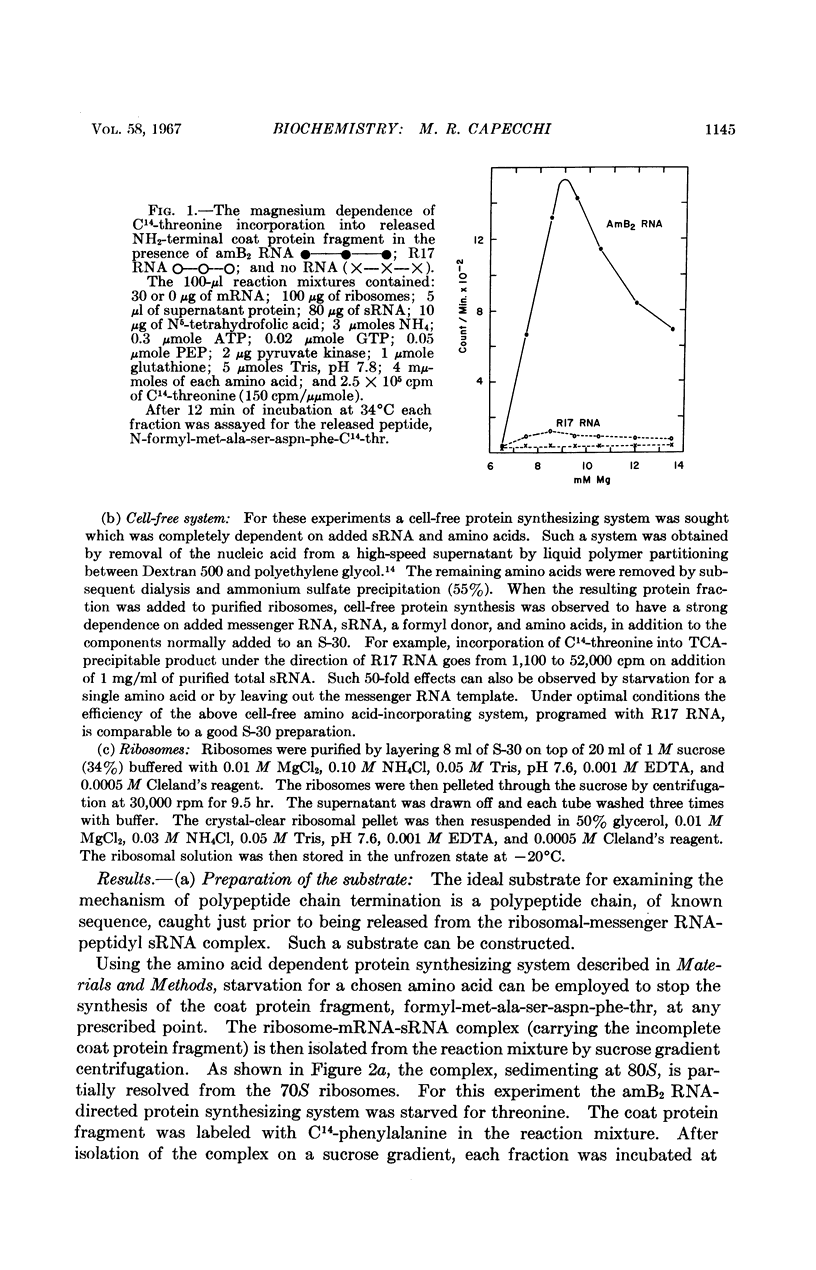
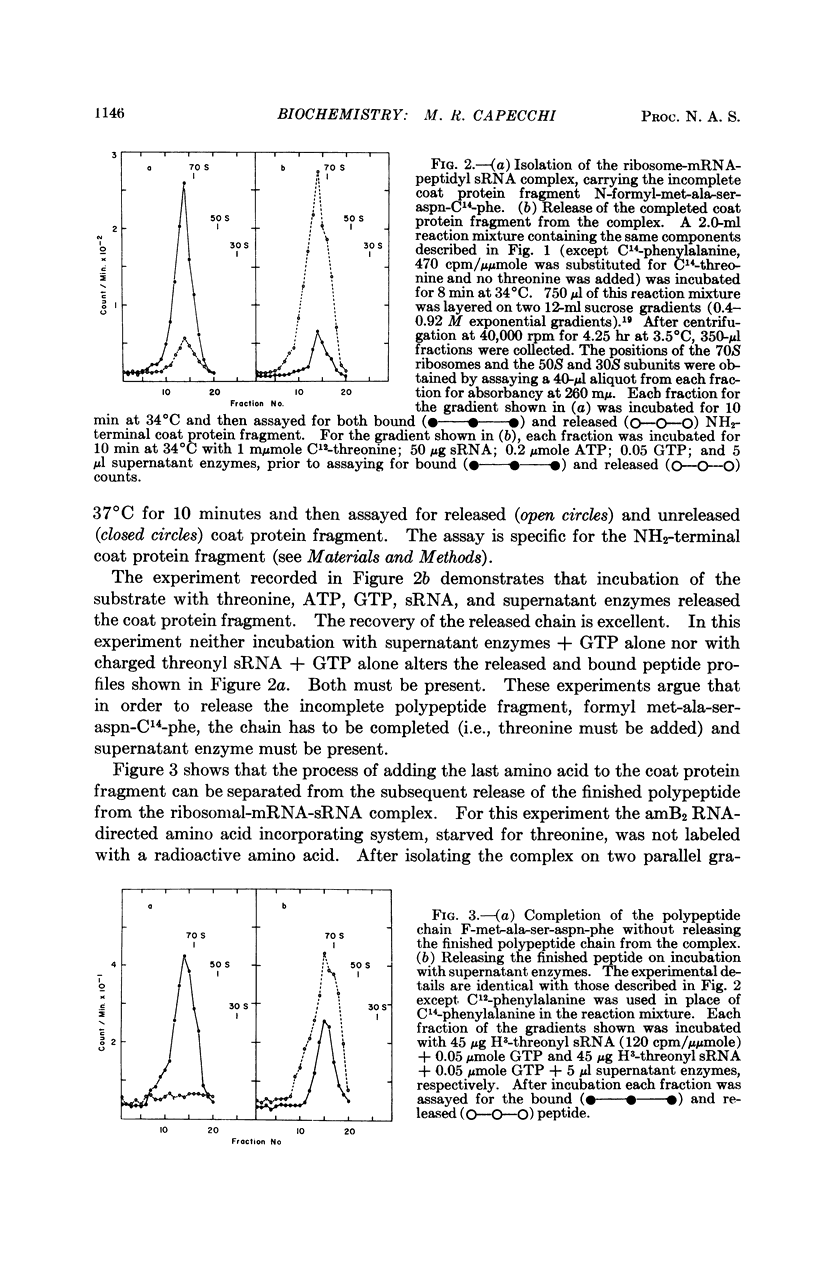
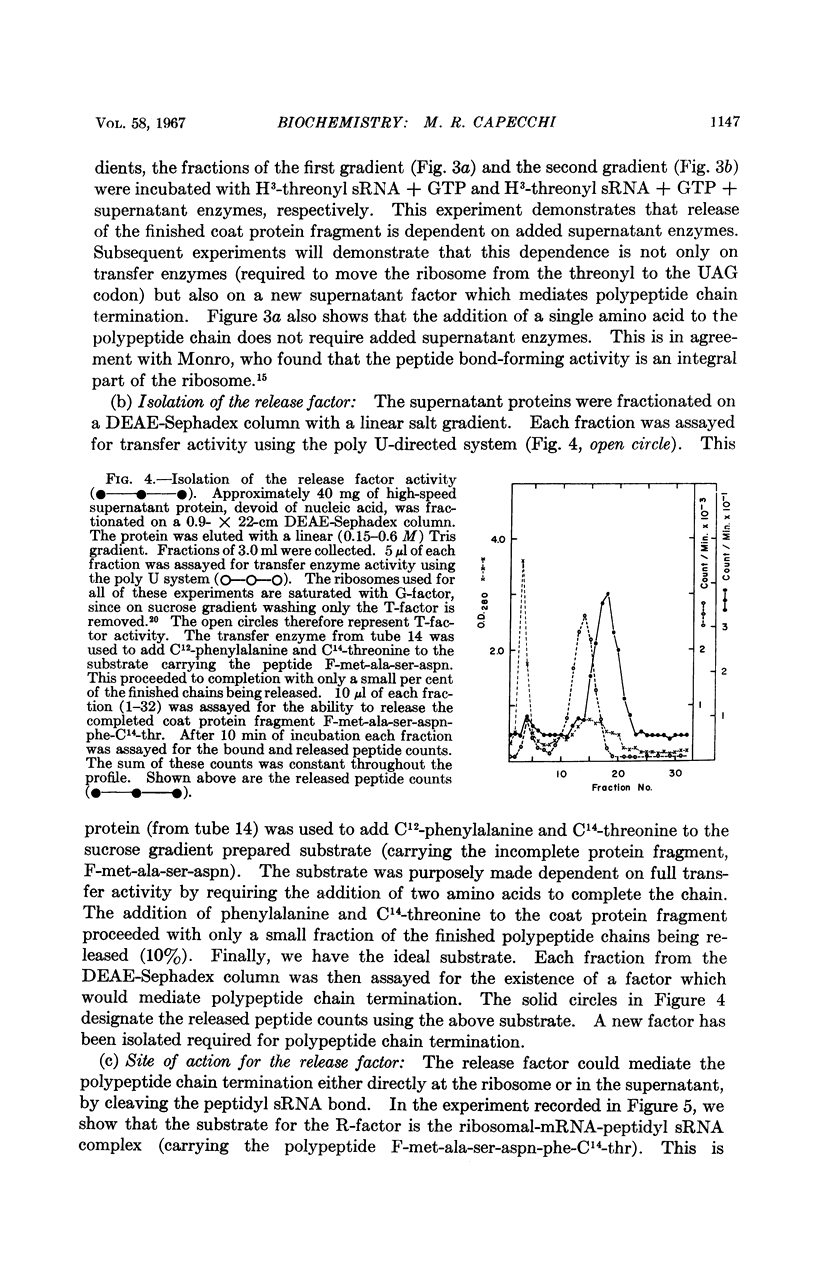
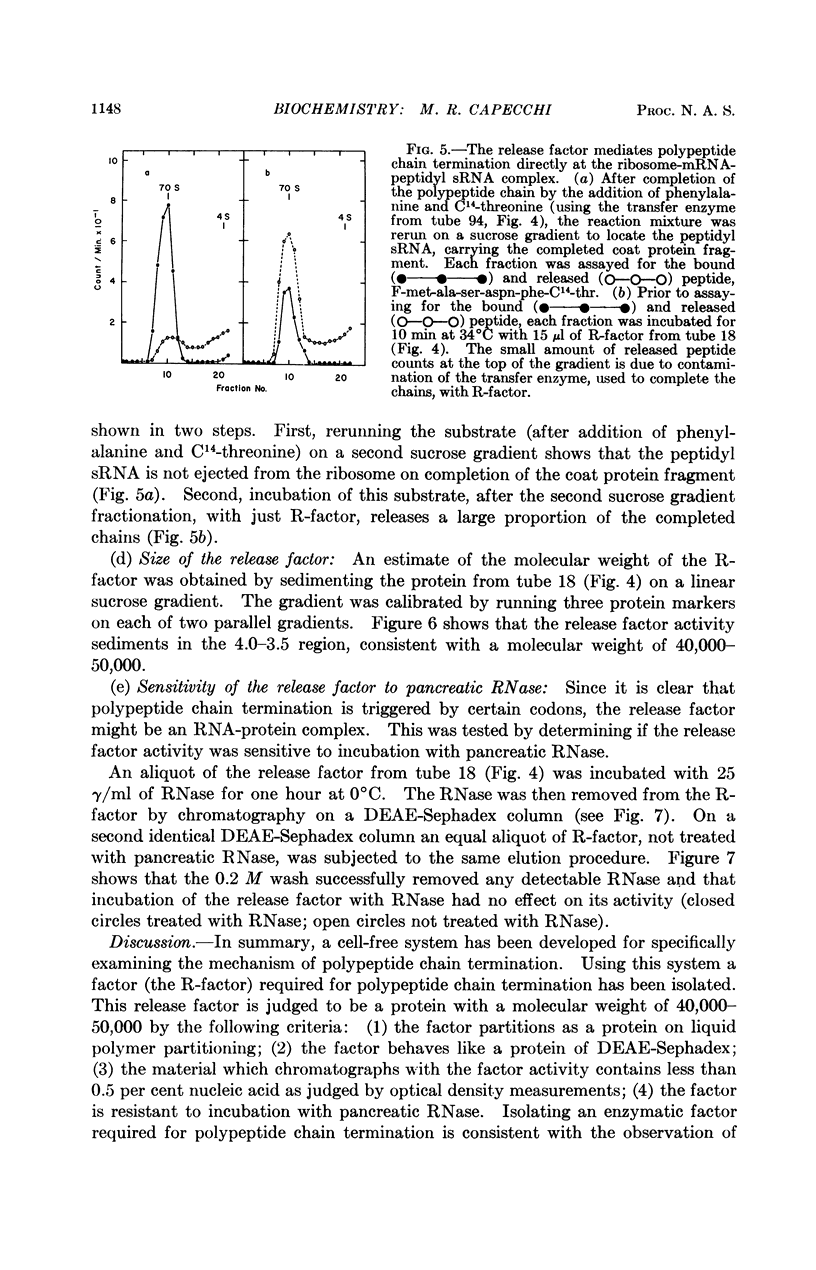
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bretscher M. S., Goodman H. M., Menninger J. R., Smith J. D. Polypeptide chain termination using synthetic polynucleotides. J Mol Biol. 1965 Dec;14(2):634–639. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80219-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILBERT W. Polypeptide synthesis in Escherichia coli. II. The polypeptide chain and S-RNA. J Mol Biol. 1963 May;6:389–403. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80051-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganoza M. C., Nakamoto T. Studies on the mechanism of polypeptide chain termination in cell-free extracts of E. coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jan;55(1):162–169. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.1.162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganoza M. C. Polypeptide chain termination in cell-free extracts of E. coli. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1966;31:273–278. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1966.031.01.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Last J. A., Stanley W. M., Jr, Salas M., Hille M. B., Wahba A. J., Ochoa S. Translation of the genetic message, IV. UAA as a chain termination codon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Apr;57(4):1062–1067. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.4.1062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks E. Use of miniature transistor oscillators in dental research. Nature. 1965 May 29;206(987):944–945. doi: 10.1038/206944a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monro R. E. Catalysis of peptide bond formation by 50 S ribosomal subunits from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1967 May 28;26(1):147–151. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90271-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SARABHAI A. S., STRETTON A. O., BRENNER S., BOLLE A. CO-LINEARITY OF THE GENE WITH THE POLYPEPTIDE CHAIN. Nature. 1964 Jan 4;201:13–17. doi: 10.1038/201013a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sambrook J. F., Fan D. P., Brenner S. A strong suppressor specific for UGA. Nature. 1967 Apr 29;214(5087):452–453. doi: 10.1038/214452a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. D., Abelson J. N., Clark B. F., Goodman H. M., Brenner S. Studies on amber suppressor tRNA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1966;31:479–485. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1966.031.01.062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WETTSTEIN F. O., NOLL H. BINDING OF TRANSFER RIBONUCLEIC ACID TO RIBOSOMES ENGAGED IN PROTEIN SYNTHESIS: NUMBER AND PROPERTIES OF RIBOSOMAL BINDING SITES. J Mol Biol. 1965 Jan;11:35–53. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80169-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinder N. D., Engelhardt D. L., Webster R. E. Punctuation in the genetic code. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1966;31:251–256. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1966.031.01.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


