Fig. 5.
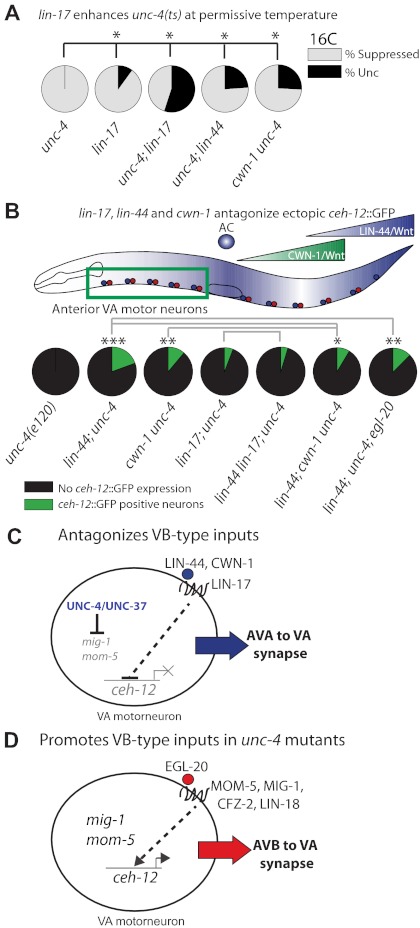
lin-17 promotes VA-type inputs in opposition to egl-20 signaling. (A) unc-4(e2322ts) shows wild-type backward locomotion at 16°C. Mutations in lin-17, lin-44 and cwn-1 enhance Unc-4 backward movement. lin-44 and cwn-1 single mutants show wild-type movement (data not shown). (B) LIN-44 is expressed in the tail and in the anchor cell (AC); CWN-1 is expressed in posterior cells. Mutations in cwn-1 and lin-44 enhance ectopic ceh-12::GFP expression in anterior VAs in unc-4(e120). ***P<0.001, **P<0.01, *P<0.05 versus unc-4. n≥16 for each neuron. Green box denotes group of anterior VA neurons scored in B. Gray brackets denote no significant difference (P>0.05, Fisher’s Exact Test) between compared strains. (C) LIN-44, CWN-1 and LIN-17 inhibit ceh-12 expression to preserve AVA inputs to anterior VAs. UNC-4 and UNC-37 antagonize mig-1 and mom-5 activity by transcriptional repression or by an indirect mechanism involving an intermediate target gene. (D) EGL-20 signaling promotes the creation of AVB inputs to VAs. Elevated expression or function of MOM-5 and MIG-1 in unc-4 and unc-37 mutants confers sensitivity to a local EGL-20 cue that activates ceh-12 expression and the creation of VB-type inputs. CFZ-2 and LIN-18 might also function in this pathway (Fig. 2).