Abstract
We associated Laguna Negra virus with hantavirus pulmonary syndrome in Mato Grosso State, Brazil, and a previously unidentified potential host, the Calomys callidus rodent. Genetic testing revealed homologous sequencing in specimens from 20 humans and 8 mice. Further epidemiologic studies may lead to control of HPS in Mato Grosso State.
Keywords: Viruses, hantavirus, Laguna Negra, hantaviral pulmonary syndrome, respiratory infections, rodents, zoonoses, microenvironment, Brazil
Hantavirus pulmonary syndrome (HPS) is a manifestation of an emerging zoonosis caused by New World viruses of the family Bunyaviridae, genus Hantavirus. Hantavirus is transmitted to humans by inhalation of aerosols of excreta from infected rodents of the subfamily Sigmodontinae (Rodentia, Cricetidae) (1,2). HPS was initially reported during an epidemic of severe respiratory disease that occurred in the southwestern United States in 1993 (1). HPS was subsequently identified in Brazil and other Latin American countries, which facilitated the recognition of new hantavirus species such as Laguna Negra virus (LNV), Andes virus, Choclo virus, Juquitiba virus, Araraquara virus, Castelo dos Sonhos virus, Anajatuba virus, as well as several other viruses detected in wild rodents which are not associated with HPS (3–9). Like particles of other bunyaviruses, hantavirus particles are spherical or pleomorphic and measure 80–120 nm in diameter; their genome comprises 3 RNA segments, and the small RNA fragment is used to characterize the nucleoprotein (N) gene and the hantavirus species (2).
During 1993–2009, a total of 1,246 cases of HPS were reported in Brazil; the state of Mato Grosso reported the fourth highest case count, diagnosed mainly in the municipalities of Tangará da Serra and Campo Novo do Parecis. However, the circulating hantavirus species and its host remained unknown, and identification of these factors were the main objectives of this study.
The Study
Mato Grosso comprises 903,357.9 km2 and has an estimated population of 2,803,274 inhabitants living in 141 municipalities. Nineteen municipalities have reported cases of HPS, mainly near Brazil’s BR-364 highway, located between the north and southwestern sections of the state. The climate is equatorial subhumid, with an annual rainfall of 1,700 mm, and temperature range 24°–40°C; the landscape consists of savannah (Cerrado) and pre-Amazon rainforest. The economic activities are agricultural production and ecologic tourism.
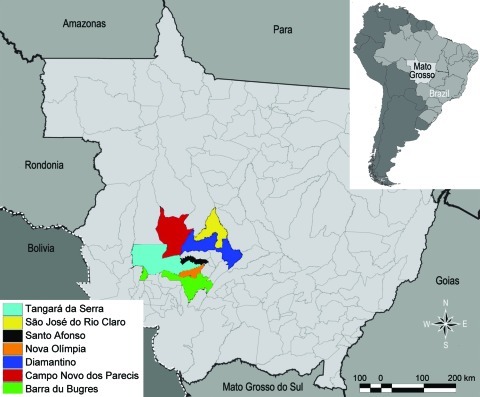
HPS was diagnosed in 24 persons who were IgM positive for LNV during 2001–2006 in the municipalities of Barra do Bugres (n = 1), Campo Novo do Parecis (n = 13), Diamantino (n = 3), Nova Olímpia (n = 1), Santo Afonso (n = 1), São José do Rio Claro (n = 1), and Tangará da Serra (n = 4) (Figure 1). Detailed information of patient samples submitted for nucleotide sequencing is provided in the Table.
Figure 1.
State of Mato Grosso, Brazil, indicating municipalities where hanta pulmonary syndrome cases occurred.
During a 2001 ecological–epidemiologic study conducted in the municipalities of Tangará da Serra and Campo Novo do Parecis, researchers obtained blood and viscera samples from wild rodents (10). The researchers followed Brazilian Institute for the Environment and Renewable Natural Resources guidelines for the capture and handling of rodents and using biosafety level 3 protocols. The samples were tested for hantavirus; animals with positive test results were identified taxonomically by morphometry and molecular analysis of mitochondrial DNA (cytochrome b gene) (10,11).
For hantavirus detection, we conducted reverse transcription PCR to synthesize complementary DNA with generic hantavirus primers as described (1,2). We obtained N gene partial nucleotide sequences by using the Sanger method with the same primers (3,4,6,9). At least 3 amplicons per sample were sequenced in both directions to improve coverage and confidence for results. The obtained sequences were aligned with other hantavirus sequences available at the GenBank database (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov) with ClustalW software in BioEdit version 7.1.3 (www.mbio.ncsu.edu/BioEdit/bioedit.html). We implemented the maximum-likelihood and Bayesian methods by using PHYML (www.atgc-montpellier.fr/phyml/versions.php) and Mr. Bayes version 3.2 (http://mrbayes.scs.fsu.edu) software, respectively, for phylogenetic reconstructions. We used Modeltest version 3.7 (http://gel.ahabs.wisc.edu/mauve) to determine the best nucleotide substitution model. We analyzed 2 million replicates, with the sample fixed at every 1,000 trees generated, and used TRACER (www.evolve.zoo.ox.ac.uk) to determine whether the Bayesian analysis reached appropriate convergence (3,6,9,12).
We obtained amplicons from 20 of the 24 samples from persons with HPS and partial sequence of the N gene (≈434 bp) from 16 of the 24 samples from patients who were symptomatic at the time of sampling. During the ecologic study, 126 rodents were captured: 68 (53.9%) commensal synanthropic species, 49 (38.8%) wild rodents [Calomys callidus (n = 46), Proechimys sp. (n = 1), and Necromys lasiurus (n = 2)], and 9 (7.1%) unidentified species. IgG was detected in 8 (17.4%) C. callidus rodents (2 captured in Campo Novo do Parecis, 6 in Tangará da Serra). Amplicons were produced in lung/heart samples from 7 of the 8 IgG-positive rodents; 3 of those were selected for nucleotide sequencing of the N gene (Table).
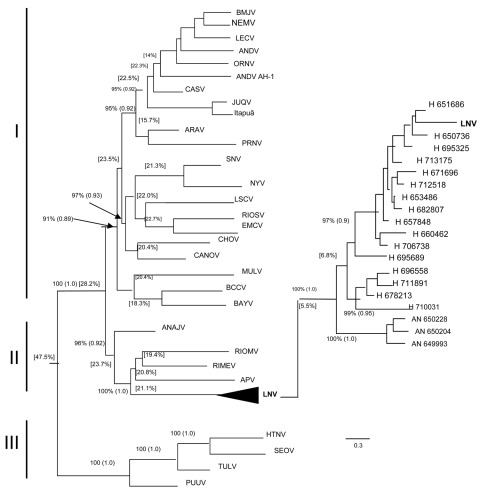
All strains recovered from human and C. callidus rodent specimens were related and formed a monophylogenetic cluster with the LNV (GenBank accession no. AF005727), with a mean genetic divergence of 4.8%. These strains were included in subclade II, which comprises Anajatuba, Rio Mamore, Rio Mearim, and Alto Paraguay viruses (Figure 2). The genetic distance between strains recovered from rodents and humans was 5.5%, whereas the genetic distance between the human strains was 6.8%. Analysis of homology showed no difference between the partial amino acid sequences of human and rodent strains and LNV (100% homology). The homology of nucleotide sequences between the LNV strains was 89.9%–93.4% (Table A1). Most changes were silent mutations in the nucleotide sequences, indicated by the genetic divergence between LNV strains (Δdiv = 0.2%–9.8%).
Figure 2.
Phylogenetic comparison of the partial nucleotide sequences of nucleoprotein (N) gene of the small (S) RNA segment of different hantavirus strains from the Old World and New World by using the maximum-likelihood method and Bayesian analysis, with detail of the phylogenetic relationship between LNV strains isolated from humans and rodents in the state of Mato Grosso, Brazil. Bootstrap and Bayesian values (within parentheses) are shown for each respective knot. The arrows indicate the exact position of the values. Numbers within brackets correspond to the divergence between groups. Scale bar indicates 30% divergence of nucleotide sequences. APV, Alto Paraguay; ANAJV, Anajatuba, ANDV, Andes; BMJV, Andes Bermejo, NEMV, Andes Neembuco, LECV, Andes Lechiguanas; ORNV, Andes Oran; ARAV, Araraquara; BAYV, Bayou; BCCV, Black Creek Canal; CANOV, Cano Delgadito; CASV, Castelo dos Sonhos; CHOV, Choclo; EMCV, El Moro Canyon; HTNV, Hantaan; JUQV; Juquitiba-Araucaria; LNV, Laguna Negra; LSCV, Limestone Canyon; MULV, Muleshoe; NYV, New York; PRNV, Pergamino; PUUV, Puumala; RIOMV, Rio Mamoré; RIMEV, Rio Mearim; RIOSV, Rio Segundo; SEOV, Seoul; SNV, Sin Nombre; TULV, Tula.
LNV was initially confirmed in 1997 by serologic testing of a patient with HPS who died. The patient lived in Santiago, Chile, but was probably infected in Santa Cruz, Bolivia (13). In 1999, molecular analysis of the small N gene and medium Gn and Gc gene segments of the hantavirus genome in samples from HPS patients from Bolivia, western Paraguay, and Chile facilitated the genetic characterization of LNV and its association with the small vesper mouse Calomys laucha, which is considered the primary host of LNV. Subsequent studies in Argentina have also demonstrated the circulation of LNV in patients with HPS and in the large vesper mouse Calomys callosus (4,9,13–15).
Conclusions
Our phylogenetic analysis of partial sequences of the N gene showed LNV as the cause of HPS, and the possible association of the organism with C. callidus rodents in western Brazil. These findings highlight the intense circulation of LNV in Matto Grosso municipalities located near the BR-364 highway. The vegetation and the equatorial climate of the area provide an excellent microenvironment for the maintenance of C. callidus rodents, as do areas in Bolivia Paraguay, and northern Argentina, where HPS caused by LNV has been reported (4,9,13–15).
The high nucleotide and amino acid homology between strains recovered from humans and the C. callidus rodent in Matto Grosso and the LNV prototype detected in Paraguay and Argentina suggest that LNV was transmitted by the rodent host C. callidus and led to the HPS cases that occurred in the vicinity of the highway BR-364 in southwestern Matto Grosso. No correlation was observed between the human LNV strains and year, geographic distribution, or between the severity of disease and the genetic diversity of LNV found in Brazil. The genetic data obtained in this study provide a better understanding of the molecular characterization of LNV and its association with HPS in southwestern Matto Grosso. Finally, on the basis of the phylogenetic analysis, the rodent species C. callidus is suggested as a potential reservoir for LNV. Further analyses of complete genome data are needed to confirm this result and to assess whether the C. callidus rodent is the sole carrier of of LNV in Matto Grosso.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to João Paulo da Silva, Reginaldo Alves da Silva, Irene Maria Mendes, Jason Batista, and Noeli Negrão; and Mato Grosso State Health Department for logistical support. Thanks are also due to the LabGeo at Instituto Evandro Chagas for helping with Figure 1.
This study was partially supported by Conselho Nacional para o Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (grants 301641/2010-2 8 and 302987/2008-8), Conselho Nacional para o Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico/Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Pará/Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Ensino Superior grant 573739/2008-0, Instituto Nacional de Ciência e Tecnologia para Febres Hemorrágicas Virais, Secretaria de Ciência Tecnologia e Meio Ambiente/Fundo Estadual de Ciência e Tecnologia/EDITAL PPRH 2003 CT, and by Instituto Evandro Chagas, Fundação Oswaldo Cruz, and Secretaria de Vigilância em Saúde.
Biography
Dr Travassos da Rosa is a senior researcher at the Evandro Chagas Institute, Ananindeua, Brazil. Her research interests are diagnosis, epidemiology, and molecular epidemiology of arboviruses, hantaviruses, and rabies virus.
Table A1. Homology between hantavirus strains originating from Mato Grosso, Brazil, and other hantaviruses from South America*.
| Strains | H 651686 | H 650736 | H 695325 | H 713175 | H 712518 | H 671696 | H 653486 | H 682807 | H 657848 | H 660462 | H 706738 | H 695689 | H 696558 | H 711891 | H 678213 | H 710031 | AN 649993 | AN 650204 | AN 650228 | LNV | APV | RIMEV | RIOM | ANAJV | CASV | JUQV | ARAV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H 651686 | 98.1 | 96.8 | 95.1 | 95 | 94.1 | 95.6 | 95 | 95.7 | 93.5 | 94.6 | 92.9 | 91.6 | 91.6 | 92.1 | 90.1 | 92.4 | 93.4 | 92.8 | 96.8 | 71.1 | 72.7 | 76.9 | 72.7 | 75 | 72.7 | 77.2 | |
| H 650736 | 100 | 96.9 | 95.3 | 95.6 | 94.7 | 95.9 | 95.6 | 94.9 | 92.8 | 93.8 | 92.4 | 91.3 | 91.3 | 91.8 | 89.7 | 92.1 | 92.8 | 92.1 | 96.5 | 70.5 | 72.5 | 76.1 | 73.2 | 75.2 | 72.9 | 77.2 | |
| H 695325 | 100 | 100 | 97.1 | 95.2 | 94.6 | 96 | 95.7 | 95.9 | 93.8 | 94.9 | 92.7 | 91.6 | 91.6 | 92.1 | 90 | 94.3 | 95.2 | 94.4 | 94.1 | 71.3 | 71.8 | 76.3 | 72.5 | 74.8 | 73 | 76.7 | |
| H 713175 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 96.6 | 95.7 | 97.2 | 96.9 | 97.1 | 95.9 | 97.8 | 94.7 | 94.6 | 94.6 | 94 | 92.1 | 92.2 | 93.1 | 92.4 | 92.8 | 70.7 | 73.3 | 75.6 | 75 | 74.5 | 72.6 | 78.4 | |
| H 712518 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 98.5 | 99.1 | 98.5 | 98.7 | 96.8 | 97.8 | 96.3 | 95.3 | 95.3 | 95.7 | 93.7 | 91.8 | 91.8 | 91.8 | 93.8 | 70.8 | 73 | 76.3 | 77.4 | 75.5 | 73 | 78.2 | |
| H 671696 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 98.5 | 97.9 | 97.8 | 95.7 | 96.8 | 95.3 | 94.4 | 94.4 | 94.9 | 92.8 | 90.9 | 90.9 | 90.9 | 93.1 | 71.3 | 73.3 | 76.4 | 77.1 | 75.2 | 72.1 | 77.2 | |
| H 653486 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 99.4 | 99 | 96.9 | 97.9 | 96.3 | 95.3 | 95.3 | 95.7 | 93.7 | 91.8 | 91.8 | 91.9 | 93.5 | 71 | 73.5 | 76.4 | 76.9 | 75.5 | 73.3 | 77.2 | |
| H 682807 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 98.4 | 96.3 | 97.4 | 95.7 | 94.7 | 94.7 | 95.2 | 93.1 | 91.2 | 91.2 | 91.3 | 93.4 | 70.8 | 73.3 | 76 | 76.8 | 75.7 | 73 | 77.5 | |
| H 657848 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 97.8 | 98.8 | 96.6 | 95.6 | 95.6 | 96 | 94 | 91.9 | 92.2 | 92.1 | 92.8 | 70.7 | 73 | 75.9 | 77.1 | 75.2 | 72.6 | 77.7 | |
| H 660462 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 98.1 | 95.4 | 94.9 | 94.9 | 95.2 | 96.2 | 90.7 | 91 | 90.9 | 90.9 | 70.4 | 72.2 | 75.9 | 79.2 | 76 | 73.2 | 78.2 | |
| H 706738 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 96.6 | 96.8 | 96.8 | 96.2 | 94.3 | 91.9 | 92.2 | 92.1 | 91.9 | 70.5 | 72.7 | 76 | 77.2 | 75 | 72.6 | 77.5 | |
| H 695689 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 96.2 | 96.2 | 96.8 | 95.3 | 93.7 | 95.3 | 94.6 | 90.9 | 71.3 | 72.5 | 76.4 | 78 | 75 | 73.6 | 77.5 | |
| H 696558 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 99 | 96.8 | 94.4 | 92.5 | 92.5 | 90.2 | 71.1 | 73.5 | 76.7 | 78.3 | 76.2 | 73.2 | 77.7 | |
| H 711891 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 99 | 96.8 | 94.4 | 92.5 | 92.5 | 90.2 | 71.1 | 73.5 | 76.7 | 78.3 | 76.2 | 73.2 | 77.7 | |
| H 678213 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 96.6 | 94.6 | 93.1 | 93.1 | 90.6 | 71.1 | 73 | 76.6 | 78.1 | 75.5 | 73.3 | 77.5 | |
| H 710031 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 94.6 | 92.6 | 92.6 | 88.7 | 71.3 | 72.9 | 77 | 81 | 76.5 | 74.2 | 79.4 | |
| AN 649993 | 99.6 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 97.5 | 98.1 | 90.9 | 71.9 | 71.3 | 77.3 | 74.8 | 75.5 | 74.2 | 78.2 | |
| AN 650204 | 99.6 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 98.4 | 91.6 | 72.3 | 71.5 | 77.5 | 75 | 74.3 | 74.4 | 77.2 | |
| AN 650228 | 99.6 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 90.7 | 72.5 | 71.3 | 78.6 | 75 | 74 | 74.6 | 77 | |
| LNV | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 72.3 | 72.7 | 77.9 | 74.4 | 75.5 | 75.3 | 77.7 | |
| APV | 96.7 | 96.7 | 96.7 | 96.7 | 96.7 | 96.7 | 96.7 | 96.7 | 96.7 | 96.7 | 96.7 | 96.7 | 96.7 | 96.7 | 96.7 | 96.7 | 96.3 | 96.3 | 96.3 | 96.7 | 76.6 | 76.6 | 79 | 76 | 72.6 | 76.2 | |
| RIMEV | 94.8 | 94.8 | 94.8 | 94.8 | 94.8 | 94.8 | 94.8 | 94.8 | 94.8 | 94.8 | 94.8 | 94.8 | 94.8 | 94.8 | 94.8 | 94.8 | 94.2 | 94.2 | 94.2 | 94.8 | 96.2 | 76.8 | 78.9 | 72.8 | 70 | 72.8 | |
| RIOMV | 97.7 | 97.7 | 97.7 | 97.7 | 97.7 | 97.7 | 97.7 | 97.7 | 97.7 | 97.7 | 97.7 | 97.7 | 97.7 | 97.7 | 97.7 | 97.7 | 97.1 | 97.1 | 97.1 | 97.7 | 99.1 | 97.3 | 81 | 74.3 | 73.2 | 79.9 | |
| ANAJV | 96.2 | 96.2 | 96.2 | 96.2 | 96.2 | 96.2 | 96.2 | 96.2 | 96.2 | 96.2 | 96.2 | 96.2 | 96.2 | 96.2 | 96.2 | 96.2 | 96 | 96 | 96 | 96.2 | 96.7 | 95 | 93.8 | 76.2 | 75.7 | 77.2 | |
| CASV | 91.5 | 91.5 | 91.5 | 91.5 | 91.5 | 91.5 | 91.5 | 91.5 | 91.5 | 91.5 | 91.5 | 91.5 | 91.5 | 91.5 | 91.5 | 91.5 | 91 | 91 | 91 | 91.5 | 89.7 | 56.6 | 56 | 57.5 | 79.4 | 77 | |
| JUQV | 92 | 92 | 92 | 92 | 92 | 92 | 92 | 92 | 92 | 92 | 92 | 92 | 92 | 92 | 92 | 92 | 91.5 | 91.5 | 91.5 | 92 | 90.6 | 86.4 | 86.7 | 89.1 | 96.3 | 79.2 | |
| ARAV | 90.6 | 90.6 | 90.6 | 90.6 | 90.6 | 90.6 | 90.6 | 90.6 | 90.6 | 90.6 | 90.6 | 90.6 | 90.6 | 90.6 | 90.6 | 90.6 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90.6 | 90.6 | 56.1 | 56 | 57.5 | 95.6 | 93.9 |
*Numbers above the diagonal indicate nucleotide sequence identity and numbers below the diagonal indicate amino acid sequence identity. Gray shading corresponds to the genetic relationship (nucleotides and amino acids) of hantavirus strains isolated from humans (H) and rodents (AN) with the Laguna Negra virus. APV, Alto Paraguay virus; ARAV, Araraquara virus; ANAJV, Anajatuba virus; CASV, Castelo dos Sonhos virus; JUQV, Juquitiba-Araucaria virus; LNV, Laguna Negra virus; RIOMV, Rio Mamore virus; RIMEV, Rio Mearim virus.
Table. Characteristics of human patients and Calomys callidus rodents with positive serologic results for hantavirus and partial nucleotide sequence of gene N, Mato Grosso, Brazil*.
| ID no. | Age, y/sex | Sample | Date of sample collection | Outcome | GenBank accession no. | Municipality |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Humans | ||||||
| H 678213 | 38/M | Serum | 2005 Mar 10 | Cure | JQ775513 | Barra do Bugres (15°4′21′′S; 57°10′52′′W) |
| H 650736 | 33/M | Serum | 2001 Dec 19 | Death | JQ775504 | Campo Novo do Parecis (13°40′31′′S; 57°53′31′′W) |
| H 660462 | 23/F | Serum | 2002 Jul 8 | Cure | JQ775506 | |
| H 671696 | 20/F | Serum | 2003 Aug 23 | Death | JQ775505 | |
| H 682807 | 20/M | Serum | 2004 Aug 22 | Death | JQ775507 | |
| H 695689 | 27/F | Serum | 2005 Aug 22 | Cure | JQ775508 | |
| H 696558 | 22/M | Blood | 2005 | Cure | JQ775512 | |
| H 711891 | 42/M | Serum | 2006 Aug 17 | Death | JQ775503 | |
| H 657848 | 42/M | Serum | 2002 May 14 | Cure | JQ775517 | Diamantino (14°24′31′′S; 56°26′46′′W) |
| H 706738 | 13/F | Serum | 2006 May 22 | Cure | JQ775516 | |
| H 712518 | 33/M | Serum | 2006 Aug 29 | Cure | JQ775518 | |
| H 653486 | 13/F | Serum | 2002 Feb 22 | Cure | JQ775514 | Nova Olímpia (14°47′50′′S; 57°17′17′′W) |
| H 695325 | 24/M | Serum | 2005 Nov 11 | Cure | JQ775515 | Santo Afonso (14°29′51′′S; 7°0′7′′W) |
| H 713175 | 17/M | Serum | 2006 Sep 26 | Cure | JQ775509 | São José do Rio Claro (13°26′48′′S; 56°43′17′′W) |
| H 651686 | 31/M | Serum | 2002 Jan 22 | Cure | JQ775511 | Tangará da Serra (14°37′10′′S; 57°29′9′′W) |
| H 710031 | 7/F | Serum | 2006 Jul 18 | Death | JQ775510 | |
| Rodents | ||||||
| AN 650204 | NA | Lung | NA | NA | JQ775500 | Campo Novo do Parecis |
| AN 650228 | NA | Lung | NA | NA | JQ775502 | |
| AN 649993 | NA | Heart | NA | NA | JQ775501 | Tangará da Serra |
*Source: Secretaria de Vigilância Epidemiológica do Estado do Mato Grosso and Instituto Evandro Chagas, Secretaria de Vigilância em Saúde), and Ministério da Saúde. NA, data not available.
Footnotes
Suggested citation for this article: Travassos da Rosa ES, Medeiros DBA, Nunes MRT, Simith DB, Pereira A, Elkhoury MR, et al. Molecular epidemiology of Laguna Negra virus, Mato Grosso State, Brazil. Emerg Infect Dis [serial on the Internet]. 2012 Jun [date cited]. http://dx.doi.org/10.3201/eid1806.110948
References
- 1.Nichol ST, Spiropoulou CE, Morzunov S, Rollin PE, Ksiazek TG, Feldmann H, et al. Genetic identification of a hantavirus associated with an outbreak of acute respiratory illness. Science. 1993;262:914–7. 10.1126/science.8235615 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Schmaljohn CS, Nichol ST. Bunyaviridae. In: Knipe DM, Griffin DE, Lamb RA, Strauss SE, Howley PM, Martin MA, et al., editors. Fields virology, 5th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2007. p. 1741–89. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Levis S, Murzonov S, Rowe J, Enria D, Pini N, Calderon G, et al. Genetic diversity and epidemiology of hantaviruses in Argentina. J Infect Dis. 1998;177:529–38. 10.1086/514221 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Padula PJ, Colavecchia SB, Martínez VP, Valle MO, Edelstein A, Miguel SDL, et al. Genetic diversity, distribution, and serological features of hantavirus infection in five countries in South America. J Clin Microbiol. 2000;38:3029–35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Vincent MJ, Quiroz E, Gracia F, Sanchez AJ, Ksiazek TG, Kitsutani PT, et al. Hantavirus pulmonary syndrome in Panama: identification of novel hantaviruses and their likely reservoirs. Virology. 2000;277:14–9. 10.1006/viro.2000.0563 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Travassos da Rosa ES, Lemos ERS, Medeiros DBA, Smith DB, Pereira AS, Elkhoury MR, et al. Hantaviruses and hantavirus pulmonary syndrome, Maranhão, Brazil. Emerg Infect Dis. 2010;16:1952–5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Travassos da Rosa ES, Mills JM, Padula PJ, Elkhoury MR, Ksiazek TG, Mendes WS, et al. Newly recognized hantaviruses associated with hantavirus pulmonary syndrome in northern Brazil: partial genetic characterization of viruses and serologic implication of likely reservoirs. Vector-B Zoon Dis. 2005;5:11–9. 10.1089/vbz.2005.5.11 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Johnson AM, Souza LTM, Ferreira IB, Pereira LE, Ksiazek TG, Rollin PE, et al. Genetic investigation of novel hantaviruses causing fatal HPS in Brazil. J Med Virol. 1999;59:527–35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Johnson AM, Bowen MD, Ksiazek TG, Williams RJ, Bryan RT, Mills JN, et al. Laguna Negra virus associate with HPS in western Paraguay and Bolivia. Virology. 1997;238:115–27. 10.1006/viro.1997.8840 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Mills JN, Childs JE. Ecologic studies of rodent reservoirs: their relevance for human health. Emerg Infect Dis. 1998;4:529–37. 10.3201/eid0404.980403 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Bonvicino CR, Moreira MAM. Molecular phylogeny of the genus Oryzomys (Rodentia: Sigmodontinae) based on cytochrome b DNA sequences. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2001;18:282–92. 10.1006/mpev.2000.0878 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Huelsenbeck JP, Ronquist F. MrBAYES: Bayesian inference of phylogeny and its impact on evolutionary biology. Science. 2001;294:2310–4. 10.1126/science.1065889 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Espinoza R, Vial P, Noriega LM, Johnson A, Nichol ST, Rollin PE, et al. Hantavirus pulmonary syndrome in a Chilean patient with recent travel in Bolivia. Emerg Infect Dis. 1998;4:93–5. 10.3201/eid0401.980112 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Levis S, Garcia J, Pini N, Calderón G, Ramírez J, Bravo D, et al. Hantavirus pulmonary syndrome in northwestern Argentina: circulation of Laguna Negra virus associated with Calomys callosus. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2004;71:658–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Carroll DS, Mills JN, Montgomery JM, Bausch DG, Blair PJ, Burans JP, et al. Hantavirus pulmonary syndrome in central Bolivia: relationships between reservoir hosts, habitats, and viral genotypes. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2005;72:42–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]