Abstract
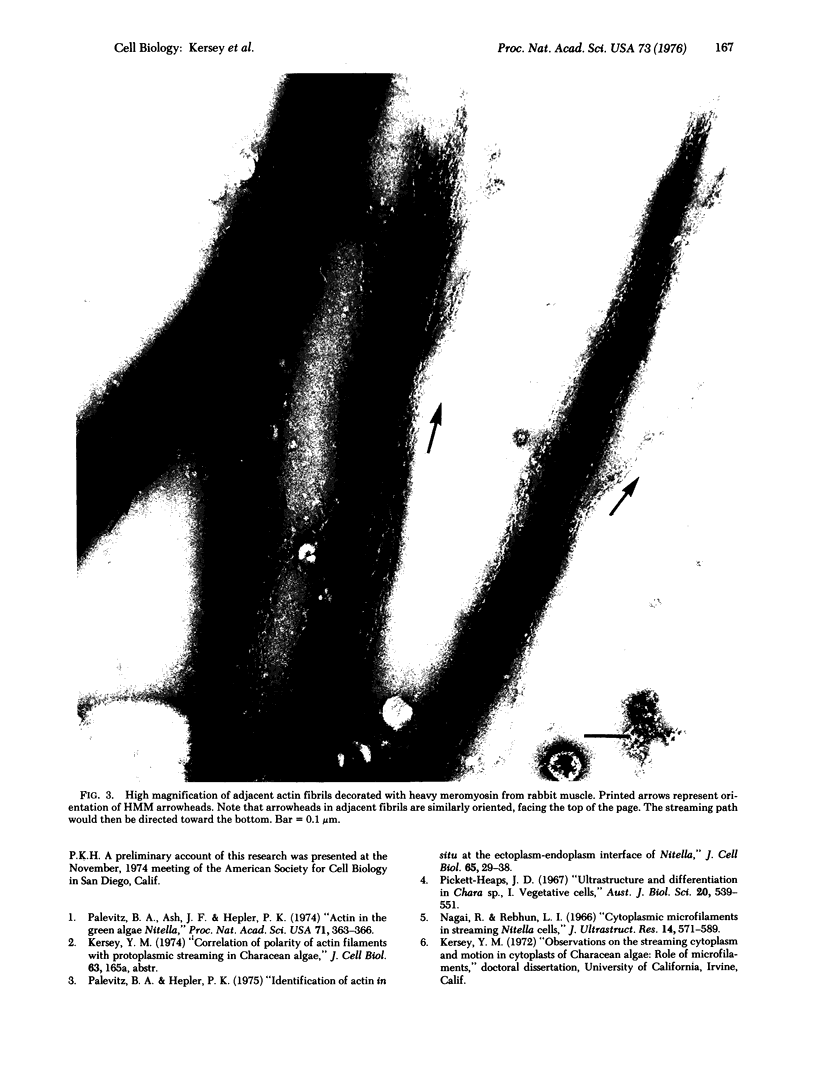
Heavy meromyosin from rabbit muscle combines with oriented Nitella and Chara actin in vitro to form arrowhead structures directed opposite to the cytoplasmic flow in the living plant cell. All filaments and all bundles of filaments in the apically directed stream are similarly oriented; polarity with respect to the axis of the thallus is reversed in the downward stream. The actin filaments are attached to the chloroplasts at the ectoplasm-endoplasm interface, where the motive force for streaming is known to be generated.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Nagai R., Rebhun L. I. Cytoplasmic microfilaments in streaming Nitella cells. J Ultrastruct Res. 1966 Mar;14(5):571–589. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(66)80083-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palevitz B. A., Ash J. F., Hepler P. K. Actin in the green alga, Nitella. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Feb;71(2):363–366. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.2.363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palevitz B. A., Hepler P. K. Identification of actin in situ at the ectoplasm-endoplasm interface of Nitella. Microfilament-chloroplast association. J Cell Biol. 1975 Apr;65(1):29–38. doi: 10.1083/jcb.65.1.29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]