Abstract
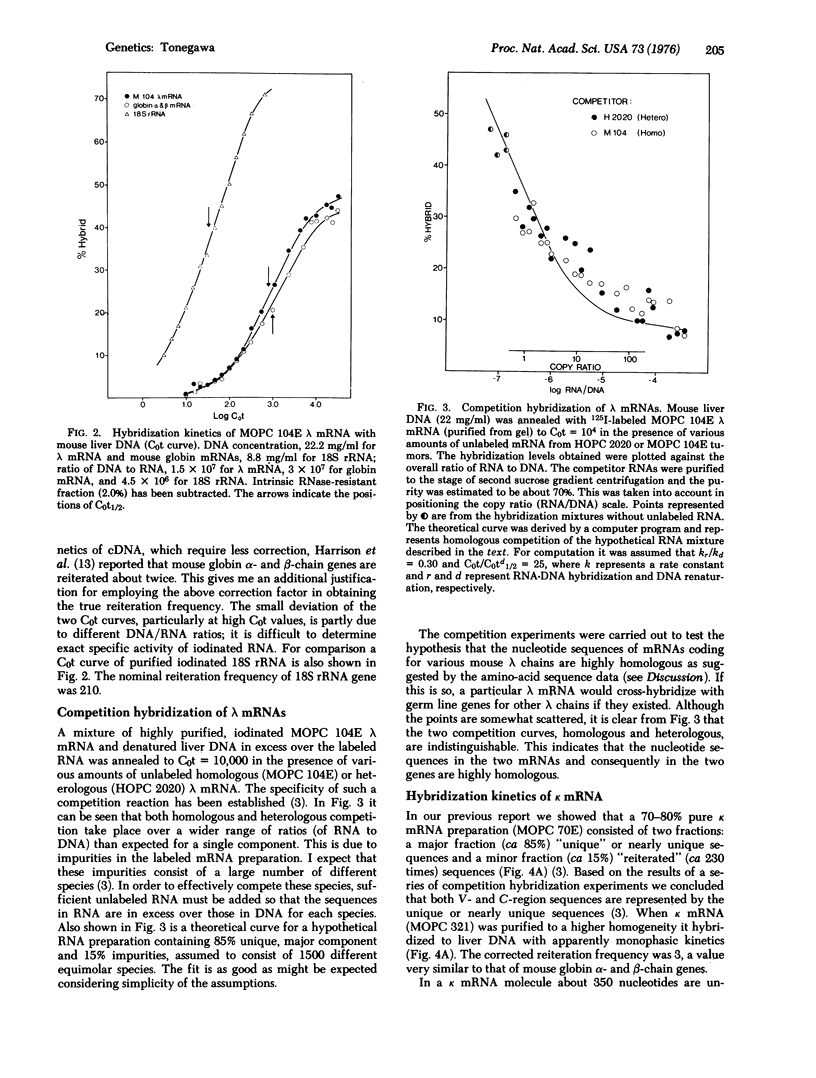
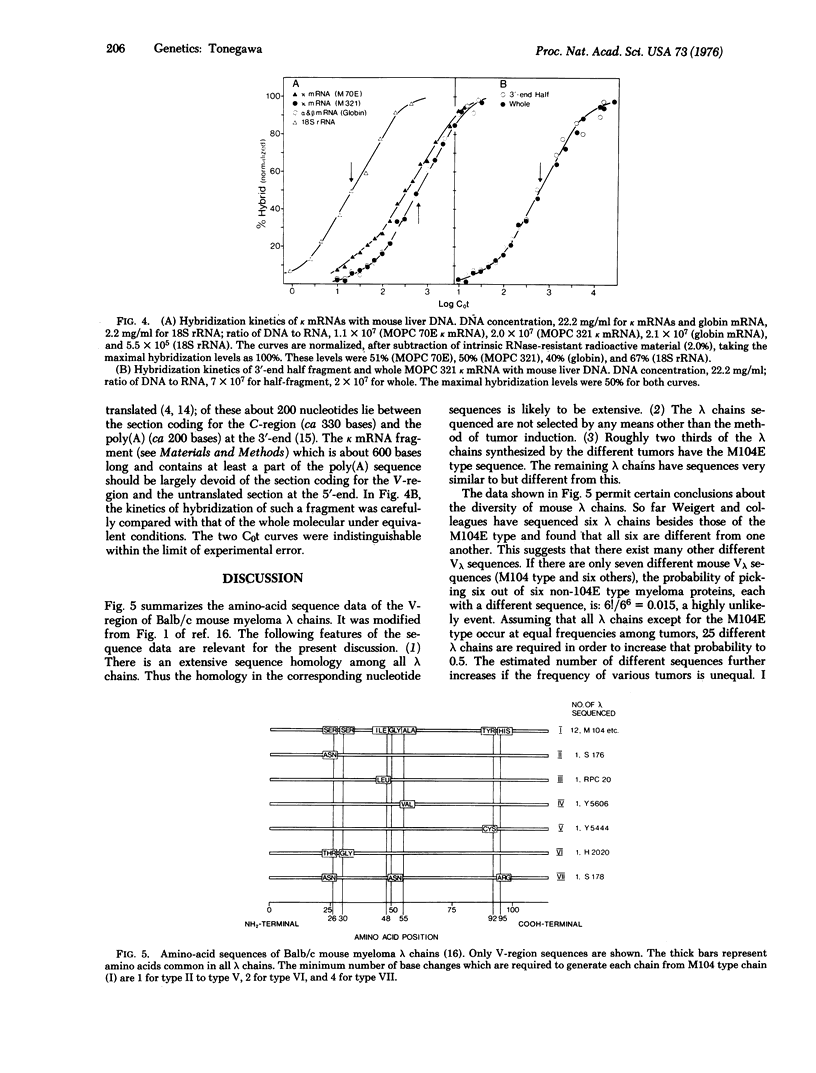
Methods have been developed for preparing mouse immunoglobulin light chain mRNA of better than 90% purity. Hybridization of both lambda and kappa mRNAs to excess liver DNA yielded results compatible with gene reiteration frequencies of two to three. There was no evidence of hybridization of these highly purified mRNAs to reiterated DNA, and, in fact, the kinetics of hybridization were very similar to that of purified globin mRNA. Purified lambda mRNA from tumors producing structurally different lambda chains were used in competition hybridization experiments. An unlabeled lambda mRNA competed with another, labeled lambda mRNA to the same extent as homologous unlabeled lambda mRNA. That is, base sequence homology among lambda mRNAs is so high that any lambda mRNA should cross-hybridize with all germ line variable (Vlambda) genes at least for those V-regions which are represented among myelomas. From amino-acid sequence data, it is argued that there are probably more than 25 different lambda V regions. Hence it is concluded that the number of germ line genes is too small to account for the diversity of lambda chains. A similar conclusion is drawn for kappa chains.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berns A., Jansen P., Bloemendal H. The separation of alpha- and beta-rabbit globin mRNA by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. FEBS Lett. 1974 Oct 15;47(2):343–347. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)81044-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. O., Pemberton R., Baglioni C. Reiteration frequency of haemoglobin genes in the duck. Nat New Biol. 1972 Feb 23;235(60):231–234. doi: 10.1038/newbio235231a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Potter V. R. Relation of ribonuclease and ribonuclease inhibitor to the isolation of polysomes from rat liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 May;55(5):1283–1288. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.5.1283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner T. I., Brenner D. J., Neufeld B. R., Britten R. J. Reduction in the rate of DNA reassociation by sequence divergence. J Mol Biol. 1973 Dec 5;81(2):123–135. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90184-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownlee G. G., Cartwright E. M., Cowan N. J., Jarvis J. M., Milstein C. Purification and sequence of messenger RNA for immunoglobulin light chains. Nat New Biol. 1973 Aug 22;244(138):236–240. doi: 10.1038/newbio244236a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capra J. D., Kehoe J. M. Editorial: Antibody diversity: is it all coded for by the germ line genes? Scand J Immunol. 1974;3(1):1–4. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1974.tb01226.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delovitch T., Baglioni C. Immunoglobulin genes: a test of somatic vs. germ line hypothesis by RNA-DNA hybridization. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1974;38:739–751. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.038.01.079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faust C. H., Diggelmann H., Mach B. Estimation of the number of genes coding for the constant part of the mouse immunoglobulin kappa light chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jun;71(6):2491–2495. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.6.2491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison P. R., Hell A., Birnie G. D., Paul J. Evidence for single copies of globin genes in the mouse genome. Nature. 1972 Sep 22;239(5369):219–221. doi: 10.1038/239219a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honjo T., Packman S., Swan D., Nau M., Leder P. Organization of immunoglobulin genes: reiteration frequency of the mouse kappa chain constant region gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3659–3663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leder P., Honjo T., Packman S., Swan D., Nau M., Norman B. The organization and diversity of immunoglobulin genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):5109–5115. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.5109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melli M., Whitfield C., Rao K. V., Richardson M., Bishop J. O. DNA-RNA hybridization in vast DNA excess. Nat New Biol. 1971 May 5;231(18):8–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milstein C., Brownlee G. G., Cartwright E. M., Jarvis J. M., Proudfoot N. J. Sequence analysis of immunoglobulin light chain messenger RNA. Nature. 1974 Nov 29;252(5482):354–359. doi: 10.1038/252354a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milstein C., Munro A. J. The genetic basis of antibody specificity. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1970;24:335–358. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.24.100170.002003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabbitts T. H., Bishop J. O., Milstein C., Brownlee G. G. Comparative hybridization studies iwth an immunoglobulin light chain mRNA fraction and non-immunoglobulin mRNA of mouse. FEBS Lett. 1974 Mar 15;40(1):157–160. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80917-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabbitts T. H. Hybridization characteristics of enzymatically synthesised DNA complementary to mouse immunoglobulin messenger RNA. FEBS Lett. 1974 Jun 15;42(3):323–326. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80756-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabbitts T. H., Milstein C. Mouse immunoglobulin genes: studies on the reiteration frequency of light-chain genes by hybridisation procedures. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Mar 3;52(1):125–133. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb03980.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stavnezer J., Huang R. C., Stavnezer E., Bishop J. M. Isolation of messenger RNA for an immunoglobulin kappa chain and enumeration of the genes for the constatn region of kappa chain in the mouse. J Mol Biol. 1974 Sep 5;88(1):43–63. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90294-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storb U. Evidence for multiple immunoglobulin genes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Mar 15;57(1):31–38. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80353-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonegawa S., Baldi I. Electrophoretically homogeneous myeloma light chain mRNA and its translation in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Mar 5;51(1):81–87. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90510-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonegawa S., Bernardini A., Weimann B. J., Steinberg C. Reiteration frequency of antibody genes. Studies with k-chain mRNA. FEBS Lett. 1974 Mar 15;40(1):92–96. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80901-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonegawa S., Steinberg C., Dube S., Bernardini A. Evidence for somatic generation of antibody diversity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):4027–4031. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.4027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigzell H. Editorial: Antibody diversity: is it all coded for by the germ line genes? Scand J Immunol. 1973;2(3):199–206. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1973.tb02030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson R., Morrison M., Lanyon G., Eason R., Paul J. Properties of mouse globin messenger ribonucleic acid and its preparation in milligram quantities. Biochemistry. 1971 Aug 3;10(16):3014–3021. doi: 10.1021/bi00792a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




