Abstract
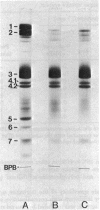
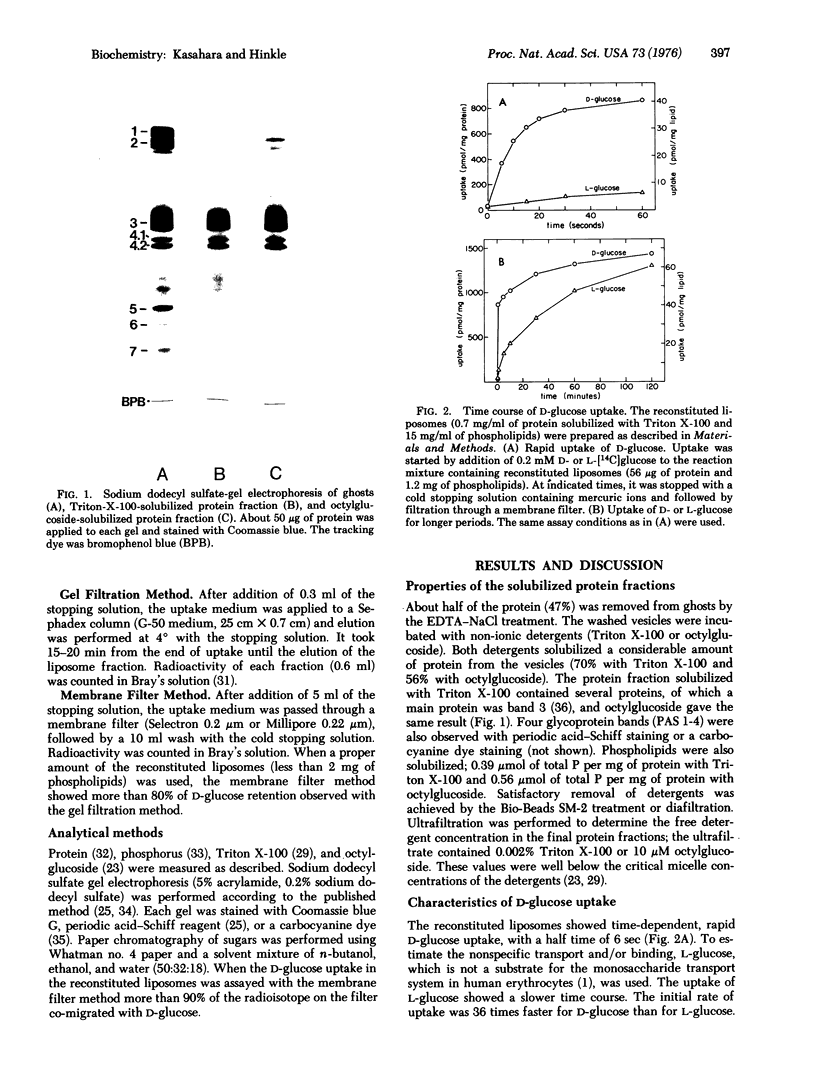
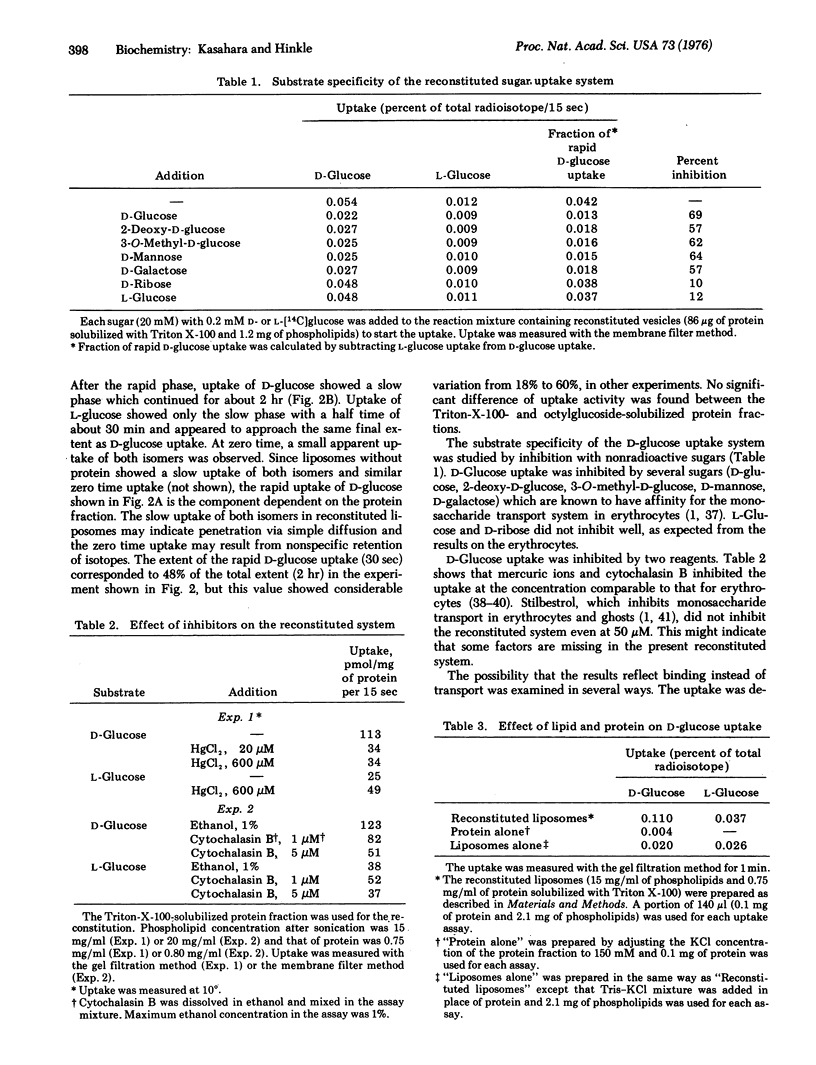
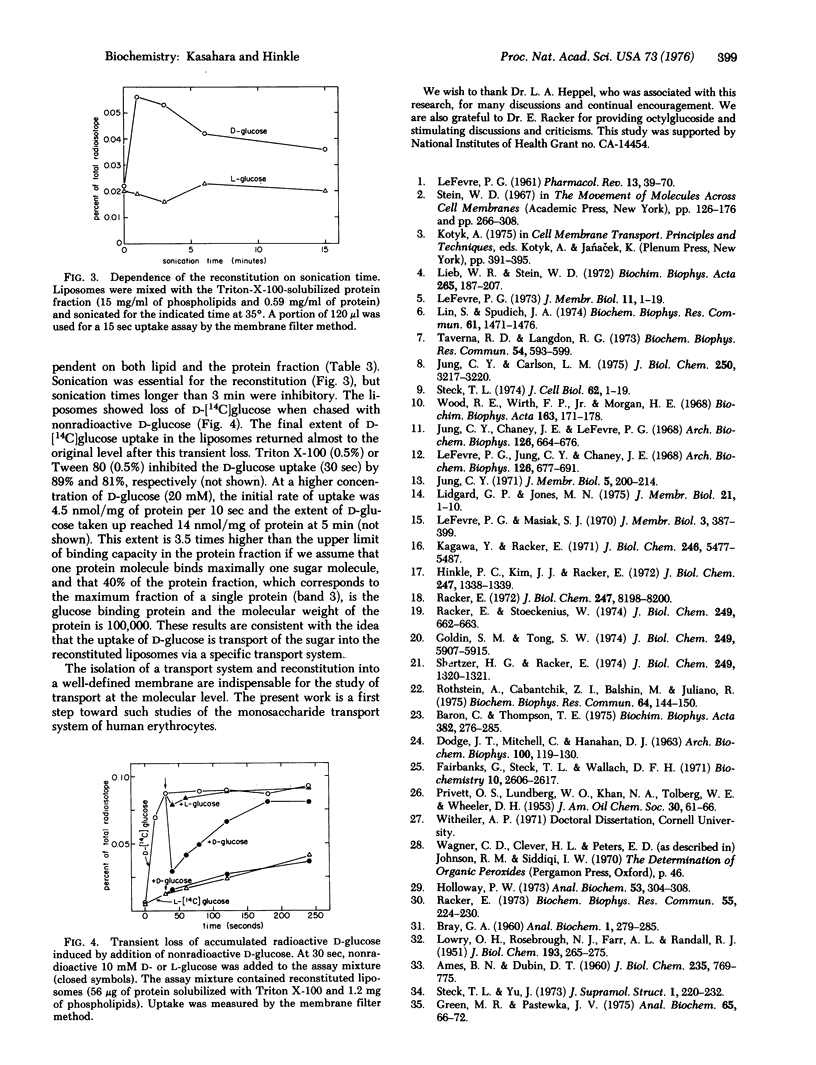
A protein fraction was obtained from human erythrocyte ghosts by solubilization with Triton X-100 or octylglucoside. Triton X-100 was removed from the protein by Bio-Beads SM-2 and octylglucoside, by diafiltration. The solubilized protein fraction catalyzed D-glucose uptake when reconstituted in sonicated liposomes. The uptake was time dependent and inhibited by mercuric ions or cytochalasin B. The results indicate that the uptake represents transport of the sugar into the liposomes rather than binding to the reconstituted liposomes.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMES B. N., DUBIN D. T. The role of polyamines in the neutralization of bacteriophage deoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1960 Mar;235:769–775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnett J. E., Holman G. D., Munday K. A. Structural requirements for binding to the sugar-transport system of the human erythrocyte. Biochem J. 1973 Feb;131(2):211–221. doi: 10.1042/bj1310211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron C., Thompson T. E. Solubilization of bacterial membrane proteins using alkyl glucosides and dioctanoyl phosphatidylcholine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 25;382(3):276–285. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90270-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloch R. Inhibition of glucose transport in the human erythrocyte by cytochalasin B. Biochemistry. 1973 Nov 6;12(23):4799–4801. doi: 10.1021/bi00747a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DODGE J. T., MITCHELL C., HANAHAN D. J. The preparation and chemical characteristics of hemoglobin-free ghosts of human erythrocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1963 Jan;100:119–130. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(63)90042-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldin S. M., Tong S. W. Reconstitution of active transport catalyzed by the purified sodium and potassium ion-stimulated adenosine triphosphatase from canine renal medulla. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 25;249(18):5907–5915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R., Pastewka J. V. Identification of sialic acid-rich glycoproteins on polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1975 May 12;65(1-2):66–72. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90491-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinkle P. C., Kim J. J., Racker E. Ion transport and respiratory control in vesicles formed from cytochrome oxidase and phospholipids. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 25;247(4):1338–1339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway P. W. A simple procedure for removal of Triton X-100 from protein samples. Anal Biochem. 1973 May;53(1):304–308. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90436-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung C. Y., Carlson L. M. Glucose transport carrier in human erythrocyte membranes. Dinitrophenylation of a membrane component modified by D-glucose. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 10;250(9):3217–3220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung C. Y., Carlson L. M., Whaley D. A. Glucose transport carrier activities in extensively washed human red cell ghosts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Aug 13;241(2):613–627. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung C. Y., Chaney J. E., LeFevre P. G. Enhanced migration of glucose from water into chloroform in presence of phospholipids. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Aug;126(2):664–676. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90454-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEFEVRE P. G. Sugar transport in the red blood cell: structure-activity relationships in substrates and antagonists. Pharmacol Rev. 1961 Mar;13:39–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeFevre P. G. A model for erythrocyte sugar transport based on substrate-conditioned "introversion" of binding sites. J Membr Biol. 1973 Jan 23;11(1):1–19. doi: 10.1007/BF01869810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeFevre P. G., Jung C. Y., Chaney J. E. Glucose transfer by red cell membrane phospholipids in H2O-CHCl-3-H2O three-layer systems. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Aug;126(2):677–691. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90455-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lidgard G. P., Jones M. N. D-glucose permeability of black lipid membranes modified by human erythrocyte membrane fractions. J Membr Biol. 1975 Apr 23;21(1-2):1–10. doi: 10.1007/BF01941058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieb W. R., Stein W. D. Carrier and non-carrier models for sugar transport in the human red blood cell. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Apr 18;265(2):187–207. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(72)90002-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin S., Spudich J. A. Binding of cytochalasin B to a red cell membrane protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Dec 23;61(4):1471–1476. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80449-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racker E. A new procedure for the reconstitution of biologically active phospholipid vesicles. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Nov 1;55(1):224–230. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(73)80083-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racker E. Reconstitution of a calcium pump with phospholipids and a purified Ca ++ - adenosine triphosphatase from sacroplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 25;247(24):8198–8200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racker E., Stoeckenius W. Reconstitution of purple membrane vesicles catalyzing light-driven proton uptake and adenosine triphosphate formation. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 25;249(2):662–663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein A., Cabantchik Z. I., Balshin M., Juliano R. Enhancement of anion permeability in lecithin vesicles by hydrophobic proteins extracted from red blood cell membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 May 5;64(1):144–150. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90230-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shertzer H. G., Racker E. Adenine nucleotide transport in submitochondrial particles and reconstituted vesicles derived from bovine heart mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 25;249(4):1320–1321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck T. L. The organization of proteins in the human red blood cell membrane. A review. J Cell Biol. 1974 Jul;62(1):1–19. doi: 10.1083/jcb.62.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck T. L., Yu J. Selective solubilization of proteins from red blood cell membranes by protein perturbants. J Supramol Struct. 1973;1(3):220–232. doi: 10.1002/jss.400010307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taverna R. D., Langdon R. G. D-glucosyl isothiocyanate, an affinity label for the glucose transport proteins of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Sep 18;54(2):593–599. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91464-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taverna R. D., Langdon R. G. Reversible association of cytochalasin B with the human erythrocyte membrane. Inhibition of glucose transport and the stoichiometry of cytochalasin binding. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Oct 11;323(2):207–219. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90145-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood R. E., Wirth F. P., Jr, Morgan H. E. Glucose permeability of lipid bilayer membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Sep 17;163(2):171–178. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(68)90095-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu J., Fischman D. A., Steck T. L. Selective solubilization of proteins and phospholipids from red blood cell membranes by nonionic detergents. J Supramol Struct. 1973;1(3):233–248. doi: 10.1002/jss.400010308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]