Abstract
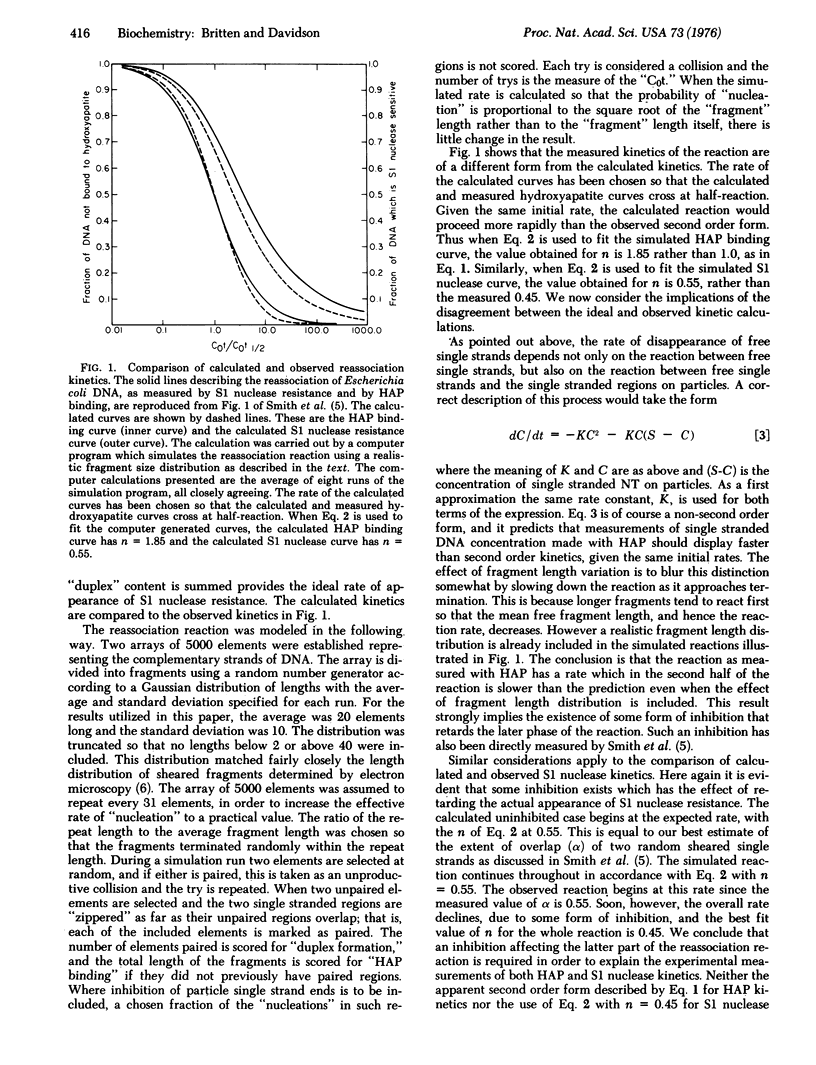
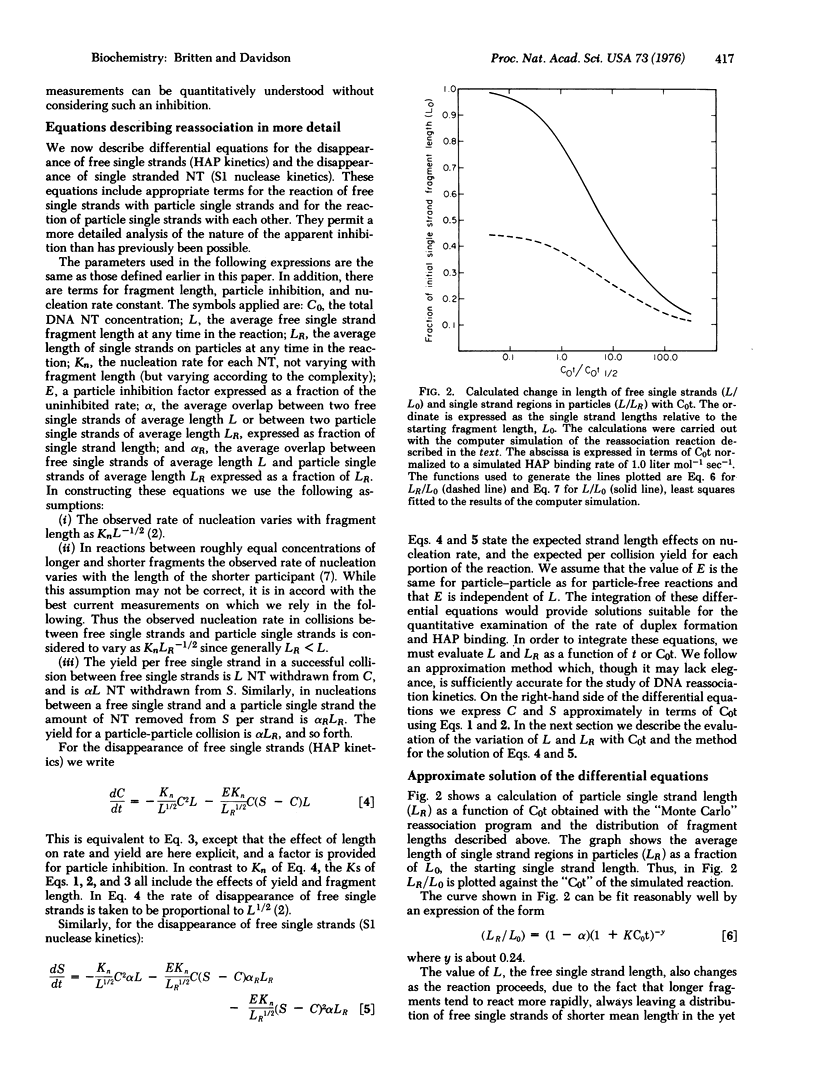
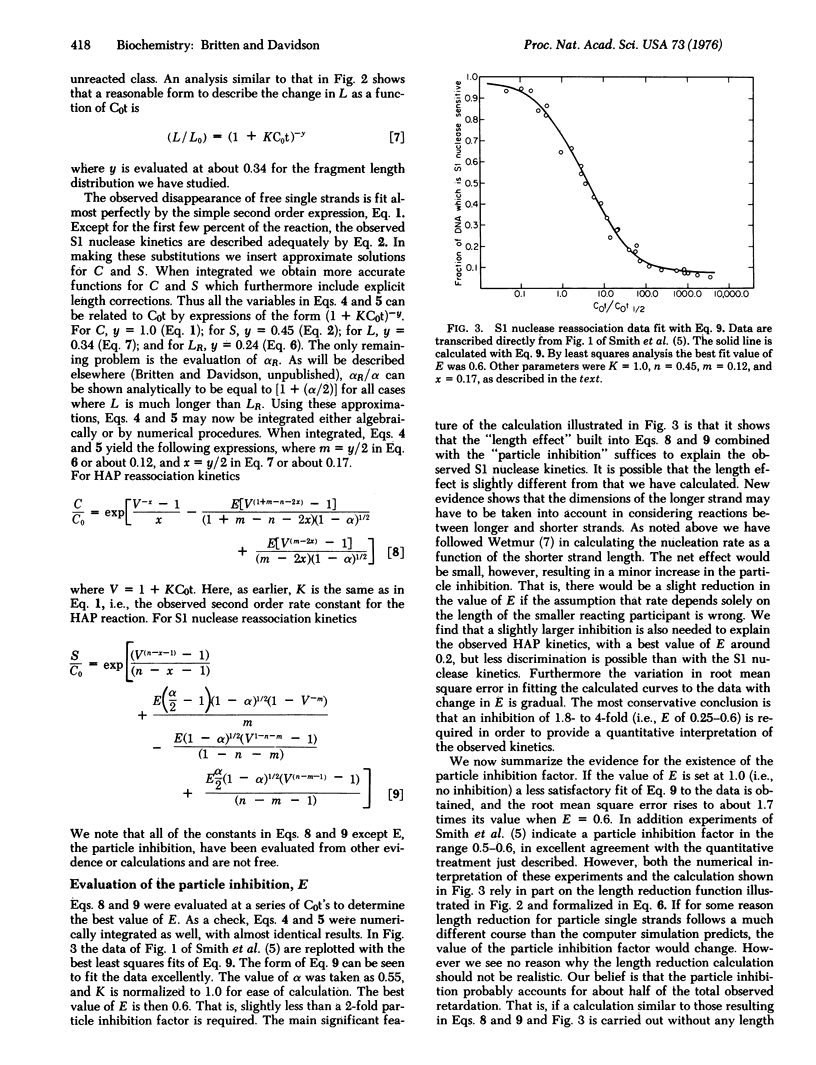
The rate of appearance of duplex DNA renaturation, measured with single strand specific nuclease, deviates significantly from a second order reaction. Measurements reported in paper I of this series indicate an inhibition in the rate of reassociation of single strand tails on partially reassociated molecules by a factor of at least two. Equations are derived that describe the observed form of reassociation kinetics as measured with hydroxyapatite and with single strand specific nuclease. The free parameter that describes the extent of inhibition of nucleation with single strand tails in these equations has been evaluated by least squares methods and agrees with the experimentally measured value.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chamberlin M. E., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Sequence organization in Xenopus DNA studied by the electron microscope. J Mol Biol. 1975 Aug 5;96(2):317–333. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90351-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. J., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Studies on nucleic acid reassociation kinetics: reactivity of single-stranded tails in DNA-DNA renaturation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4805–4809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetmur J. G., Davidson N. Kinetics of renaturation of DNA. J Mol Biol. 1968 Feb 14;31(3):349–370. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90414-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetmur J. G. Excluded volume effects on the rate of renaturation of DNA. Biopolymers. 1971;10(4):601–613. doi: 10.1002/bip.360100402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



