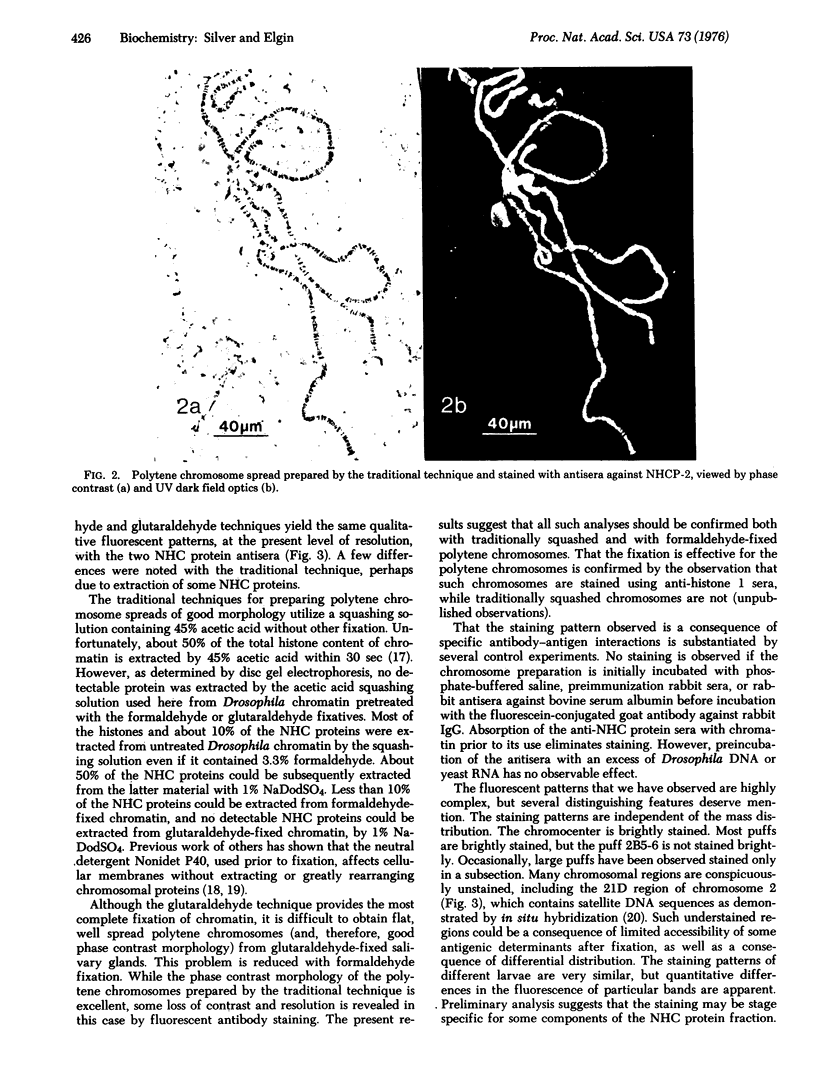
Abstract
A technique has been developed for "staining" cytological preparations by indirect immunofluorescent methods that permits determination of the in situ distribution of chromosomal proteins. The method is particularly oriented to the use of polytene chromosome squashes from Drosophila salivary glands. Control experiments indicate that the fixation methods used allow little or no extraction or rearrangement of the chromosomal proteins. The results obtained demonstrate the specific in vivo chromosomal locations of nonhistone proteins purified from isolated chromatin. The technique is apparently capable of resolution at the level of the chromomere or band, the unit of genetic organization in Drosophila.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cohen L. H., Gotchel B. V. Histones of polytene and nonpolytene nuclei of Drosophila melanogaster. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 25;246(6):1841–1848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daneholt B. Transcription in polytene chromosomes. Cell. 1975 Jan;4(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90127-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dick C., Johns E. W. The effect of two acetic acid containing fixatives on the histone content of calf thymus deoxyribonucleoprotein and calf thymus tissue. Exp Cell Res. 1968 Aug-Sep;51(2-3):626–632. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(68)90150-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgin S. C., Hood L. E. Chromosomal proteins of Drosophila embryos. Biochemistry. 1973 Nov 20;12(24):4984–4991. doi: 10.1021/bi00748a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gall J. G., Pardue M. L. Formation and detection of RNA-DNA hybrid molecules in cytological preparations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jun;63(2):378–383. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.2.378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman R. D., Lazarides E., Pollack R., Weber K. The distribution of actin in non-muscle cells. The use of actin antibody in the localization of actin within the microfilament bundles of mouse 3T3 cells. Exp Cell Res. 1975 Feb;90(2):333–344. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(75)90323-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. Interphase chromosomal deoxyribonucleoprotein isolated as a discrete structure from cultured cells. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jul 5;86(3):649–663. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90187-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochman B. Analysis of a whole chromosome in Drosophila. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1974;38:581–589. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.038.01.062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Judd B. H., Shen M. W., Kaufman T. C. The anatomy and function of a segment of the X chromosome of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1972 May;71(1):139–156. doi: 10.1093/genetics/71.1.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefevre G., Jr The one band-one gene hypothesis: evidence from a cytogenetic analysis of mutant and nonmutant rearrangement breadpoints in Drosophila melanogaster. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1974;38:591–599. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.038.01.063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGillivray A. J., Cameron A., Krauze R. J., Rickwood D., Paul J. The non-histone proteins of chromatin, their isolation and composition in a number of tissues. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Aug 25;277(2):384–402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie S. L., Henikoff S., Meselson M. Localization of RNA from heat-induced polysomes at puff sites in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1117–1121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardue M. L., Gall J. G. Molecular hybridization of radioactive DNA to the DNA of cytological preparations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Oct;64(2):600–604. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.2.600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peacock W. J., Brutlag D., Goldring E., Appels R., Hinton C. W., Lindsley D. L. The organization of highly repeated DNA sequences in Drosophila melanogaster chromosomes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1974;38:405–416. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.038.01.043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stumph W. E., Elgin S. C., Hood L. Antibodies to proteins dissolved in sodium dodecyl sulfate. J Immunol. 1974 Dec;113(6):1752–1756. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tata J. R., Hamilton M. J., Cole R. D. Membrane phospholipids associated with nuclei and chromatin: melting profile, template activity and stability of chromatin. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jun 20;67(2):231–246. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90238-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]