Abstract
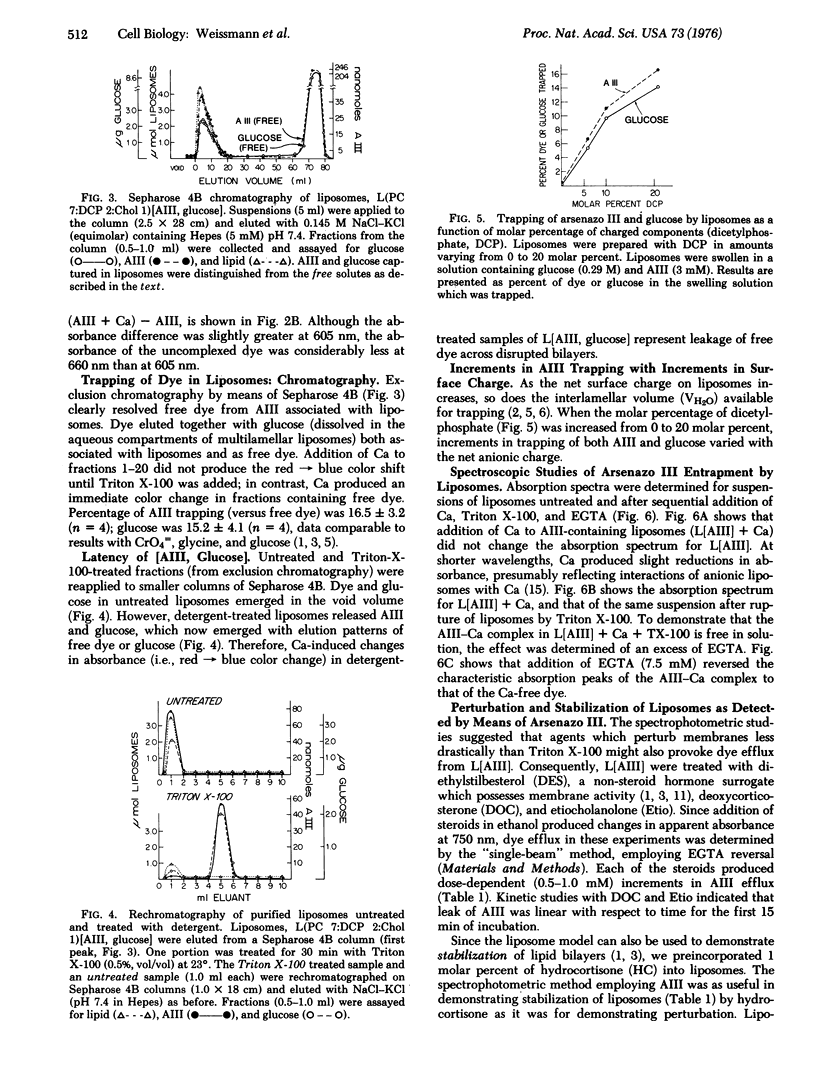
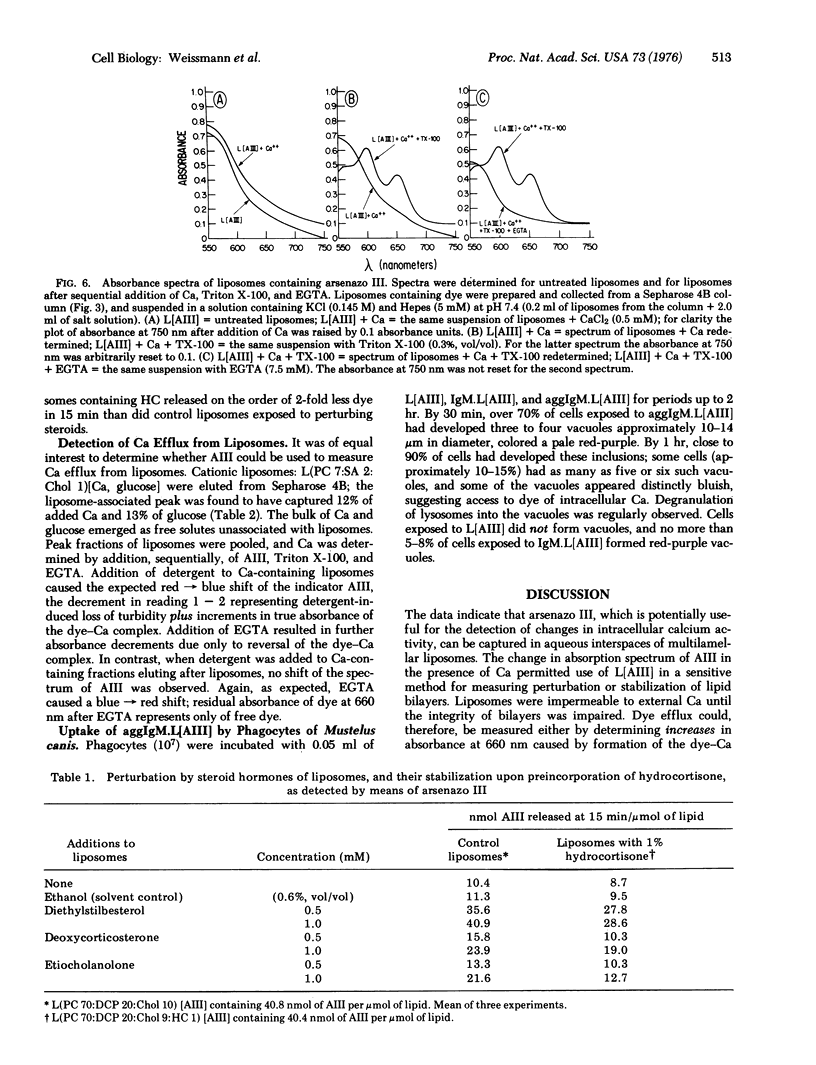
A metallochromic dye, arsenazo III [2,7-bis-(2-arsonophenylazo)-1,8-dihydroxynaphthalene-3,6-disulfonic acid], has been incorporated into the aquenous interspaces of multilamellar liposomes. multilamellar liposomes. Addition of Ca produced no shift in the absorbance spectrum of dye captured by liposomes, whereas disruption of liposomes by Triton X-100, followed by Ca, produced the spectrum chracteristic of the dye-Ca complex: evidence of latency. Addition of excess ethyleneglycol-bis(beta-aminoethyl ether)-N,N'-tetraacetic acid (EGTA) reversed the spectal shift. Differences between spectra obtained in this sequence yielded dye efflus. To measure Ca efflux, difference spectra (+/-EGTA) were obtained from cationic liposomes containing Ca after detergent lysis (sensitivity less than 10 mmol/ml). Since liposomes were impermeable either to dye or Ca until perturbed, it was possible to test a variety of membrane-active steroids (diethylstilbesterol, deoxycorticosterone, etiocholanolone) for their capacity to provoke dye efflux from liposomes; preincorporation of cortisol stablized liposomes against dye leak. Immunoglobulin-coated liposomes containing dye were taken up by phagocytes of Mustelus canis, and phagocytic vacuoles stained red-purple after ingestions. Liposomes containing the calcium-sensitive dye constitute a simple, accurate means for determining membrane perturbation and Ca fluxes; their uptake by cells or organelles remains to be exploited further.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bangham A. D., Standish M. M., Weissmann G. The action of steroids and streptolysin S on the permeability of phospholipid structures to cations. J Mol Biol. 1965 Aug;13(1):253–259. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80094-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. E., Cohen L. B., De Weer P., Pinto L. H., Ross W. N., Salzberg B. M. Rapid changes in intracellular free calcium concentration. Detection by metallochromic indicator dyes in squid giant axon. Biophys J. 1975 Nov;15(11):1155–1160. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(75)85891-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbell W. L., McConnell H. M. Molecular motion in spin-labeled phospholipids and membranes. J Am Chem Soc. 1971 Jan 27;93(2):314–326. doi: 10.1021/ja00731a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson K., Papahadjopoulos D. Phase transitions and phase separations in phospholipid membranes induced by changes in temperature, pH, and concentration of bivalent cations. Biochemistry. 1975 Jan 14;14(1):152–161. doi: 10.1021/bi00672a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg R. D., McNamee M. G., McConnell H. M. Measurement of transmembrane potentials in phospholipid vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1508–1513. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence D. K., Gill E. W. Structurally specific effects of some steroid anesthetics on spin-labeled liposomes. Mol Pharmacol. 1975 May;11(3):280–286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lussan C., Faucon J. F. Effects of ions on vesicles and phospholipid dispersions studied by polarization of fluorescence. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Apr 12;345(1):83–90. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90248-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDougall I. R., Dunnick J. K., McNamee M. G., Kriss J. P. Distribution and fate of synthetic lipid vesicles in the mouse: a combined radionuclide and spin label study. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3487–3491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sessa G., Weissmann G. Incorporation of lysozyme into liposomes. A model for structure-linked latency. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jul 10;245(13):3295–3301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Six H. R., Young W. W., Jr, Uemura K., Kinsky S. C. Effect of antibody-complement on multiple vs. single compartment liposomes. Application of a fluorometric assay for following changes in liposomal permeability. Biochemistry. 1974 Sep 10;13(19):4050–4058. doi: 10.1021/bi00716a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissmann G., Bloomgarden D., Kaplan R., Cohen C., Hoffstein S., Collins T., Gotlieb A., Nagle D. A general method for the introduction of enzymes, by means of immunoglobulin-coated liposomes, into lysosomes of deficient cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):88–92. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.88. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissmann G., Brand A., Franklin E. C. Interaction of immunoglobulins with liposomes. J Clin Invest. 1974 Feb;53(2):536–543. doi: 10.1172/JCI107587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissmann G., Rita G. A. Molecular basis of gouty inflammation: interaction of monosodium urate crystals with lysosomes and liposomes. Nat New Biol. 1972 Dec 6;240(101):167–172. doi: 10.1038/newbio240167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissmann G., Sessa G. The action of polyene antibiotics on phospholipid-cholesterol structures. J Biol Chem. 1967 Feb 25;242(4):616–625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissmann G., Sessa G., Weissmann S. The action of steroids and triton X-100 upon phospholipid/cholesterol structures. Biochem Pharmacol. 1966 Oct;15(10):1537–1551. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(66)90198-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



