Abstract
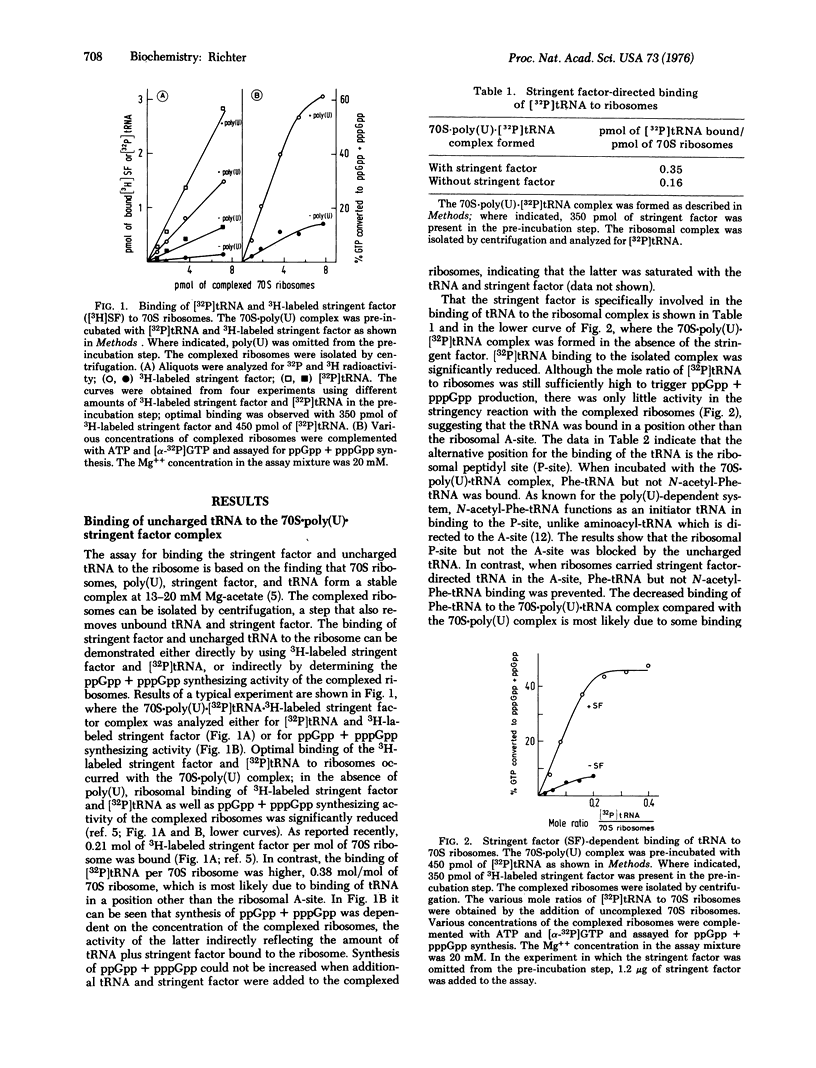
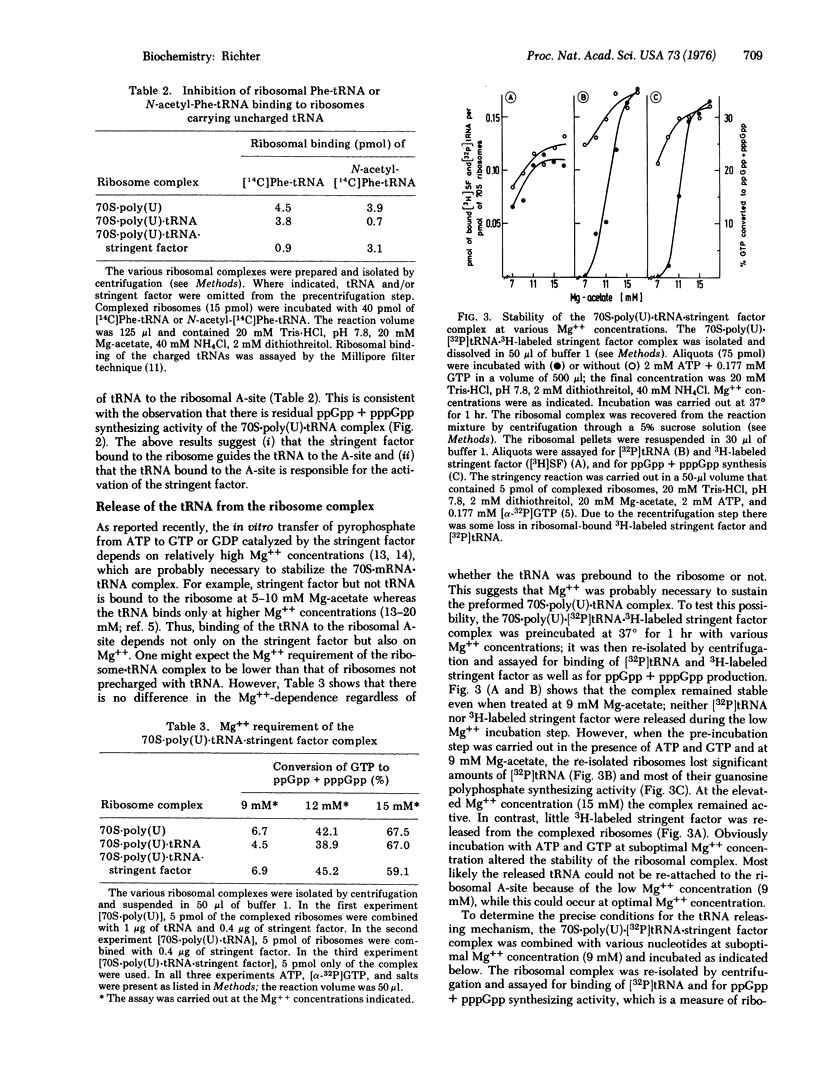
Uncharged tRNA is preferentially bound to the peptidyl site of the ribosome in the absence of stringent factor ,but in its presence is directed to the acceptor site. The synthesis of pppGpp and ppGpp is initiated by tRNA bound in the acceptor but not in the peptidyl site. In this reaction, tRNA is not permanently attached to the acceptor site. Uncharged [32P] tRNA but not 3H-labeled stringent factor is released from the ribosome after each round of stringent factor-dependent hydrolysis of ATP. ATP-32PPi-exchange experiments reveal that exchange is independent of the presence of GTP but strongly enhanced by the addition of stringent factor and tRNA. The tRNA release is suppressed when ATP is replaced by beta, gamma-imido adenosine 5'-triphosphate, 5'-AMP, or GTP.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allende C. C., Allende J. E., Firtel R. A. The degradation of ribonucleic acids injected into Xenopus laevis oocytes. Cell. 1974 Jul;2(3):189–196. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(74)90093-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cashel M., Kalbacher B. The control of ribonucleic acid synthesis in Escherichia coli. V. Characterization of a nucleotide associated with the stringent response. J Biol Chem. 1970 May 10;245(9):2309–2318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochran J. W., Byrne R. W. Isolation and properties of a ribosome-bound factor required for ppGpp and ppGpp synthesis in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 25;249(2):353–360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gevers W., Kleinkauf H., Lipmann F. The activation of amino acids for biosynthesis of gramicidin S. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 May;60(1):269–276. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.1.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haseltine W. A., Block R., Gilbert W., Weber K. MSI and MSII made on ribosome in idling step of protein synthesis. Nature. 1972 Aug 18;238(5364):381–384. doi: 10.1038/238381a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haseltine W. A., Block R. Synthesis of guanosine tetra- and pentaphosphate requires the presence of a codon-specific, uncharged transfer ribonucleic acid in the acceptor site of ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 May;70(5):1564–1568. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.5.1564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henes C., Krauskopf M., Ofengand J. A simple one-step method for the preparation of highly purified formylmethionine transfer ribonucleic acid and methionine transfer ribonucleic acid from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1969 Jul;8(7):3024–3028. doi: 10.1021/bi00835a051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinert U., Richter D. The binding of the pyrophosphoryl transferase and the elongation factor Tu and G to ribosomes from Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1975 Jul 15;55(1):188–193. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80989-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas-Lenard J. Protein biosynthesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1971;40:409–448. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.40.070171.002205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y., Lipmann F. The interrelationship between guanosine triphosphatase and amino acid polymerization. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Sep 26;116(1):344–351. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(66)90040-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen F. S., Lund E., Kjeldgaard N. O. Codon specific, tRNA dependent in vitro synthesis of ppGpp and pppGpp. Nat New Biol. 1973 May 2;243(122):13–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter D., Erdmann V. A., Sprinzl M. A new transfer RNA fragment reaction: Tp psi pCpGp bound to a ribosome-messenger RNA complex induces the synthesis of guanosine tetra- and pentaphosphates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):3226–3229. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.3226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter D. Inability of E. coli ribosomes to interact simultaneously with the bacterial elongation factors EF Tu and EF G. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Mar 10;46(5):1850–1856. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90061-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter D., Nowak P., Kleinert U. Escherichia coli stringent factor binds to ribosomes at a site different from that of elongation factor Tu or G. Biochemistry. 1975 Oct 7;14(20):4414–4420. doi: 10.1021/bi00691a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sy J., Lipmann F. Identification of the synthesis of guanosine tetraphosphate (MS I) as insertion of a pyrophosphoryl group into the 3'-position in guanosine 5'-diphosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Feb;70(2):306–309. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.2.306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



