Abstract
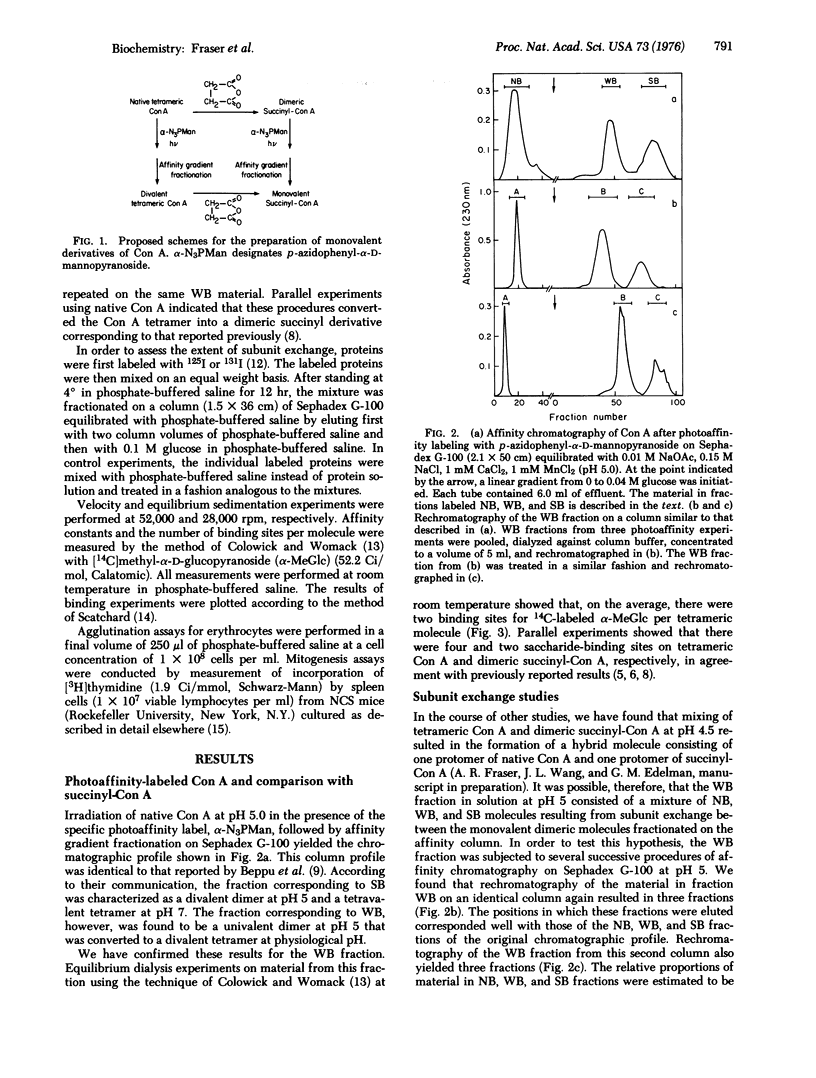
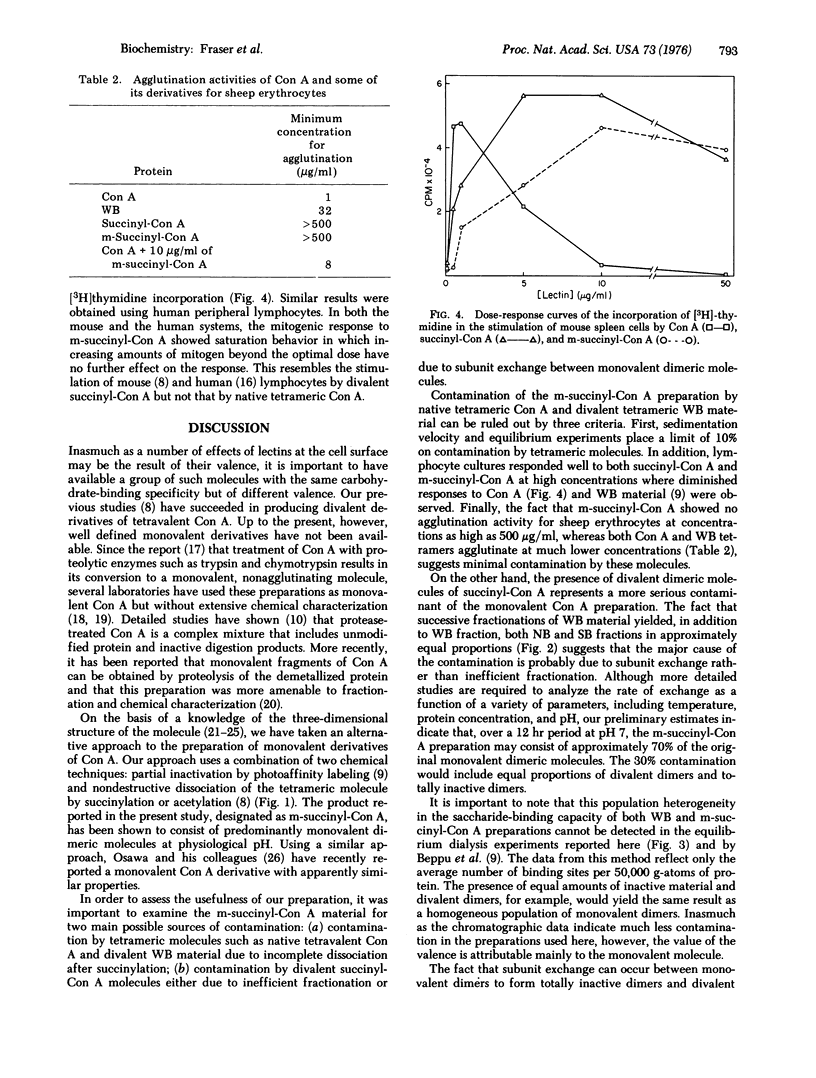
Monovalent dimers of concanavalin A (Con A) have been prepared by a combination of succinylation and photoaffinity labeling. Partial derivatization of native Con A using the photoaffinity label, p-azidophenyl-alpha-D-mannopyranoside, followed by affinity chromatography yielded a fraction that consisted of dimers with a single saccharide-binding site at pH 5. These monovalent dimers formed divalent tetramers at pH 7. In order to achieve a monovalent dimer at this pH, the divalent tetramers were succinylated by previously developed methods. Ultracentrifugation, equilibrium dialysis, and chromatographic experiments indicated that the resultant preparations consisted mainly of monovalent dimers which showed subunit exchange to yield about 15% divalent dimers after 12 hr at physiological pH. Freshly prepared material failed to agglutinate sheep erythrocytes at concentrations 500-fold higher than native tetravalent Con A. In addition, they showed saturating dose-response curves of mitogenic stimulation of mouse splenic lymphocytes. These curves resembled those of divalent succinyl-Con A but not those of the native molecule. Further development of methods for preparing stable monovalent derivatives of Con A should allow a refined analysis of the effects of lectin valence at the cell surface.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Becker J. W., Reeke G. N., Jr, Wang J. L., Cunningham B. A., Edelman G. M. The covalent and three-dimensional structure of concanavalin A. III. Structure of the monomer and its interactions with metals and saccharides. J Biol Chem. 1975 Feb 25;250(4):1513–1524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beppu M., Terao T., Osawa T. Photoaffinity labeling of concanavalin A. Preparation of a concanavalin A derivative with reduced valence. J Biochem. 1975 Nov;78(5):1013–1019. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger M. M., Noonan K. D. Restoration of normal growth by covering of agglutinin sites on tumour cell surface. Nature. 1970 Nov 7;228(5271):512–515. doi: 10.1038/228512a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colowick S. P., Womack F. C. Binding of diffusible molecules by macromolecules: rapid measurement by rate of dialysis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Feb 25;244(4):774–777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham B. A., Wang J. L., Pflumm M. N., Edelman G. M. Isolation and proteolytic cleavage of the intact subunit of concanavalin A. Biochemistry. 1972 Aug 15;11(17):3233–3239. doi: 10.1021/bi00767a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham B. A., Wang J. L., Waxdal M. J., Edelman G. M. The covalent and three-dimensional structure of concanavalin A. II. Amino acid sequence of cyanogen bromide fragment F3. J Biol Chem. 1975 Feb 25;250(4):1503–1512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M., Cunningham B. A., Reeke G. N., Jr, Becker J. W., Waxdal M. J., Wang J. L. The covalent and three-dimensional structure of concanavalin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2580–2584. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M., Yahara I., Wang J. L. Receptor mobility and receptor-cytoplasmic interactions in lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 May;70(5):1442–1446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.5.1442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans P. M., Jones B. M. Studies on cellular adhesion-aggregation. Consideration of involvement of concanavalin A receptors. Exp Cell Res. 1974 Sep;88(1):56–62. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90617-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunther G. R., Wang J. L., Edelman G. M. The kinetics of cellular commitment during stimulation of lymphocytes by lectins. J Cell Biol. 1974 Aug;62(2):366–377. doi: 10.1083/jcb.62.2.366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunther G. R., Wang J. L., Yahara I., Cunningham B. A., Edelman G. M. Concanavalin A derivatives with altered biological activities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Apr;70(4):1012–1016. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.4.1012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardman K. D., Ainsworth C. F. Structure of concanavalin A at 2.4-A resolution. Biochemistry. 1972 Dec 19;11(26):4910–4919. doi: 10.1021/bi00776a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalb A. J., Lustig A. The molecular weight of concanavalin A. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Oct 21;168(2):366–367. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(68)90161-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. A method of trace iodination of proteins for immunologic studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000229699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeke G. N., Jr, Becker J. W., Edelman G. M. The covalent and three-dimensional structure of concanavalin A. IV. Atomic coordinates, hydrogen bonding, and quaternary structure. J Biol Chem. 1975 Feb 25;250(4):1525–1547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharon N., Lis H. Lectins: cell-agglutinating and sugar-specific proteins. Science. 1972 Sep 15;177(4053):949–959. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4053.949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinburg M. S., Gepner I. A. Are concanavalin A receptor sites mediators of cell-cell adhesion? Nat New Biol. 1973 Feb 21;241(112):249–251. doi: 10.1038/newbio241249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomasson D. L., Doyle R. J. Monovalent concanavalin A. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Dec 15;67(4):1545–1552. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90202-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. L., Cunningham B. A., Edelman G. M. Unusual fragments in the subunit structure of concanavalin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1130–1134. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. L., Cunningham B. A., Waxdal M. J., Edelman G. M. The covalent and three-dimensional structural of concanavalin A. I. Amino acid sequence of cyanogen bromide fragments F1 and F2. J Biol Chem. 1975 Feb 25;250(4):1490–1502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. L., McClain D. A., Edelman G. M. Modulation of lymphocyte mitogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1917–1921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yariv J., Kalb A. J., Levitzki A. The interaction of concanavalin A with methyl alpha-D-glucopyranoside. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Sep 3;165(2):303–305. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(68)90063-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



