Abstract
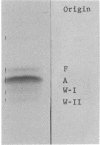
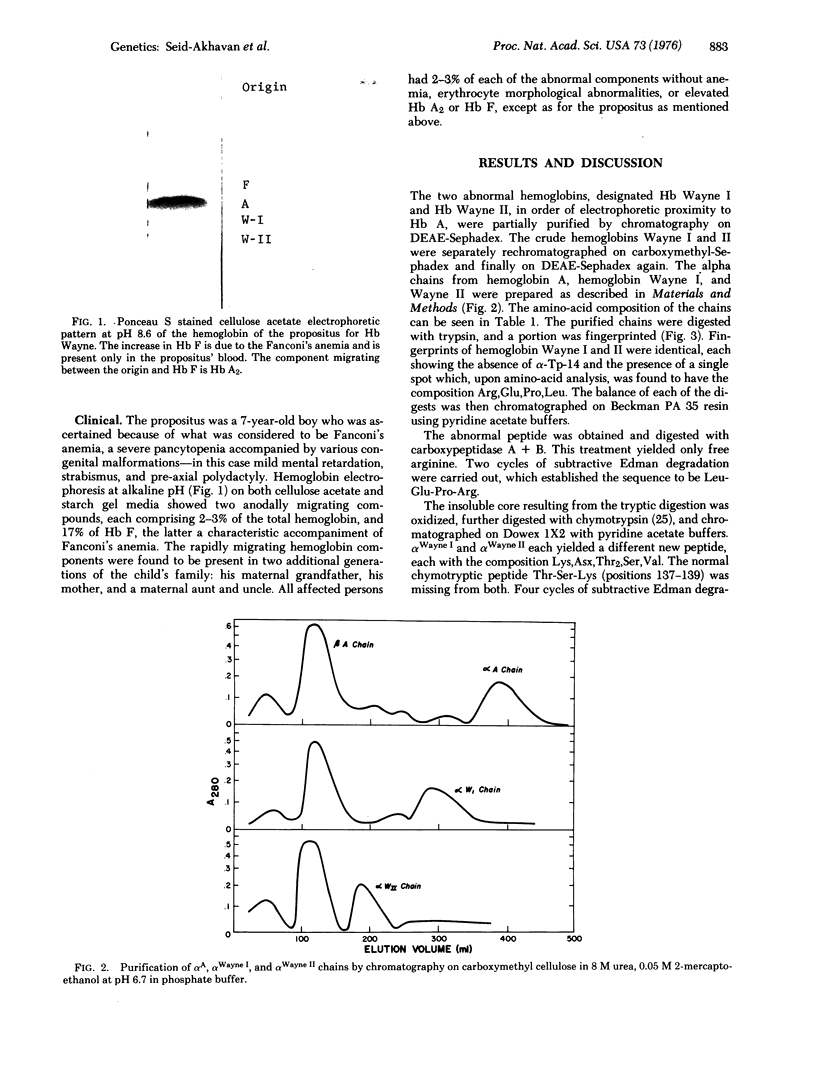
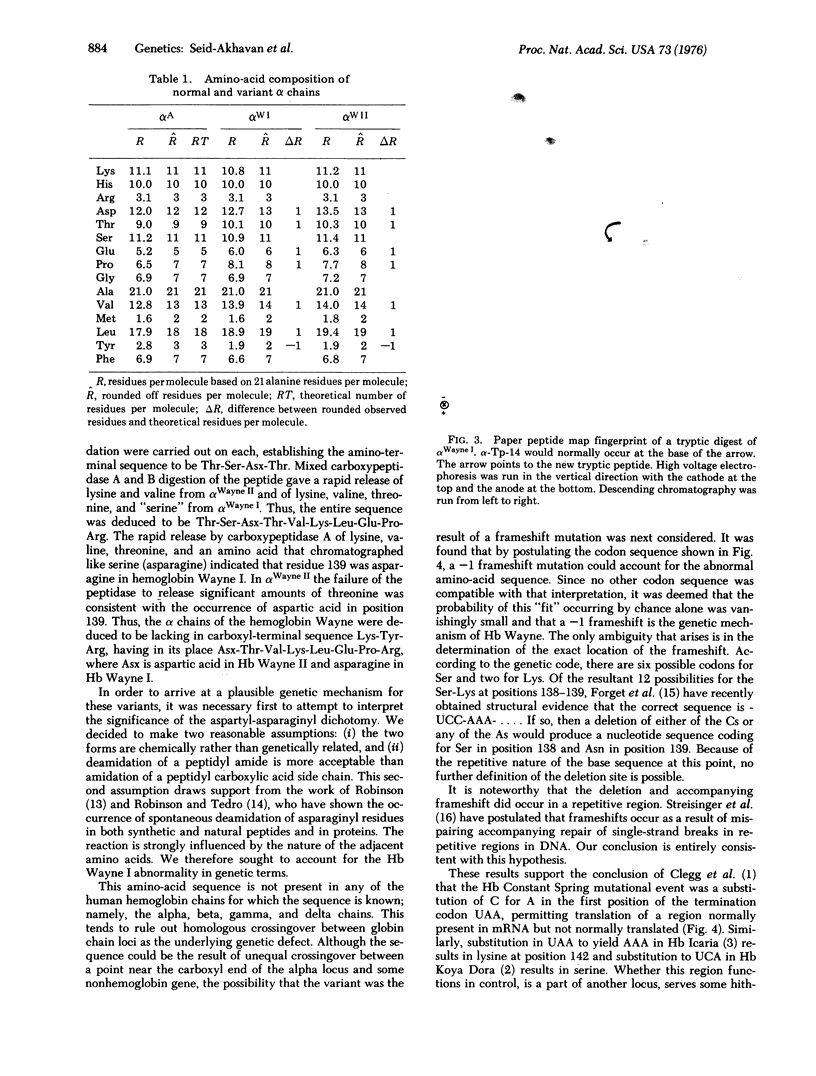
Hemoglobin Wayne is an alpha chain variant which manifests itself as two minor hemoglobin (Hb) components that migrate more rapidly than Hb A on electrophoresis at pH 8.6. It has been found in a child with Fanconi's anemia and in three generations of the child's family. Each of the minor components yields an alpha chain in which the carboxyl-terminal tripeptide sequence, Lys-Tyr-Arg, has been replaced by the octapeptide sequence Asx-Thr-Val-Lys-Leu-Glu-Pro-Arg. In alpha Wayne I, the slower of the pair, Asx is asparagine, whereas in alpha Wayne II it is aspartic acid. Comparison of the alpha Wayne sequences with the amino-acid sequences of alpha A and alpha Constant Spring leads to the conclusion that Hb Wayne I is the result of a -1 frameshift mutation in the alpha chain and that Hb Wayne II is formed secondarily by spontaneous deamidation of the new asparagine residue. A frameshift is consistent with a single mRNA base sequence for the last eight codons involved and supports the view of Clegg, Weatherall, and Milner [Nature (1971) 234, 337-341] that Hb Constant Spring is the result of a terminator mutation leading to translation of 31 codons not normally translated.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams J. G., 3rd, Winter W. P., Rucknagel D. L., Spencer H. H. Biosynthesis of hemoglobin Ann Arbor: evidence for catabolic and feedback regulation. Science. 1972 Jun 30;176(4042):1427–1429. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4042.1427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg J. B., Naughton M. A., Weatherall D. J. An improved method for the characterization of human haemoglobin mutants: identification of alpha-2-beta-2-95GLU, haemoglobin N (Baltimore). Nature. 1965 Aug 28;207(5000):945–947. doi: 10.1038/207945a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg J. B., Weatherall D. J., Contopolou-Griva I., Caroutsos K., Poungouras P., Tsevrenis H. Haemoglobin Icaria, a new chain-termination mutant with causes alpha thalassaemia. Nature. 1974 Sep 20;251(5472):245–247. doi: 10.1038/251245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg J. B., Weatherall D. J., Milner P. F. Haemoglobin Constant Spring--a chain termination mutant? Nature. 1971 Dec 10;234(5328):337–340. doi: 10.1038/234337a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Jong W. W., Meera Khan P., Bernini L. F. Hemoglobin Koya Dora: high frequency of a chain termination mutant. Am J Hum Genet. 1975 Jan;27(1):81–90. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dozy A. M., Huisman T. H. Studies on the heterogeneity of hemoglobin. XIV. Chromatography of normal and abnormal human hemoglobin types on CM-Sephadex. J Chromatogr. 1969 Mar 11;40(1):62–70. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)96618-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dozy A. M., Kleihauer E. F., Huisman T. H. Studies on the heterogeneity of hemoglobin. 13. Chromatography of various human and animal hemoglobin types on DEAE-Sephadex. J Chromatogr. 1968 Feb 20;32(4):723–727. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)80551-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flatz G., Kinderlerer J. L., Kilmartin J. V., Lehmann H. Haemoglobin Tak: a variant with additional residues at the end of the beta-chains. Lancet. 1971 Apr 10;1(7702):732–733. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91994-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forget B. G., Marotta C. A., Weissman S. M., Verma I. M., McCaffrey R. P., Baltimore D. Nucleotide sequences of human globin messenger RNA. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 Nov 29;241(0):290–309. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb21888.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaskill P., Kabat D. Unexpectedly large size of globin messenger ribonucleic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jan;68(1):72–75. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.1.72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. T. Automatic peptide chromatography. Methods Biochem Anal. 1970;18:205–258. doi: 10.1002/9780470110362.ch4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laux B., Dennis D., White H. B., 3rd Human alpha-chain globin messenger: prediction of a nucleotide sequence. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Oct 1;54(3):894–898. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90778-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall R. E., Caskey C. T., Nirenberg M. Fine structure of RNA codewords recognized by bacterial, amphibian, and mammalian transfer RNA. Science. 1967 Feb 17;155(3764):820–826. doi: 10.1126/science.155.3764.820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rachmilewitz E. A. Denaturation of the normal and abnormal hemoglobin molecule. Semin Hematol. 1974 Oct;11(4):441–462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechler M. M., Bruni C. B., Martin R. G., Terry W. An intercistronic region in the histidine operon of Salmonella typhimurium. J Mol Biol. 1972 Aug 28;69(3):427–452. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90256-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rieder R. F. Human hemoglobin stability and instability: molecular mechanisms and some clinical correlations. Semin Hematol. 1974 Oct;11(4):423–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson A. B. Evolution and the distribution of glutaminyl and asparaginyl residues in proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Mar;71(3):885–888. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.3.885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson A. B., Tedro S. Sequence dependent deamidation rates for model peptides of hen egg-white lysozyme. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1973;5(4):275–278. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1973.tb03461.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streisinger G., Okada Y., Emrich J., Newton J., Tsugita A., Terzaghi E., Inouye M. Frameshift mutations and the genetic code. This paper is dedicated to Professor Theodosius Dobzhansky on the occasion of his 66th birthday. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1966;31:77–84. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1966.031.01.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White H. B., 3rd, Laux B. E., Dennis D. Messenger RNA structure: compatibility of hairpin loops with protein sequence. Science. 1972 Mar 17;175(4027):1264–1266. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4027.1264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]