Abstract
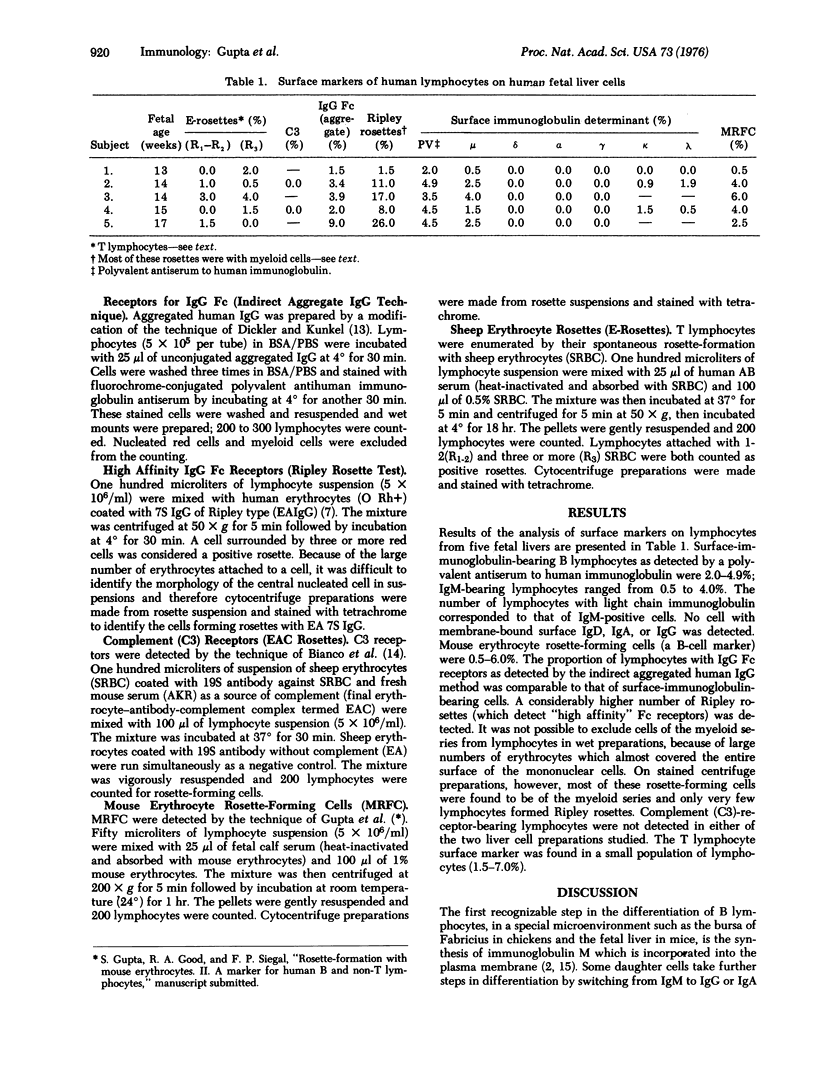
Lymphocytes were isolated from five fetal livers (13-17 weeks) and examined for different surface markers. Immunoglobulin M was found on 0.5-4.0% of lymphocytes. No membrane-bound surface IgD, IgA. or IgG was detected. Mouse erythrocyte rosette-forming lymphocytes ranged from 0.5 to 6.0%. Thymus-processed (T) lymphocytes, which were defined as those forming spontaneous rosettes with sheep erythrocytes, as well as lymphocytes with IgG Fc receptors, were present in a small proportion. No complement-receptor-bearing lymphocytes were found in the two cell populations of fetal liver studied. It is evident that during the ontogeny of bone-marrow-derived (B) lymphocytes IgM is the first surface immunoglobulin to appear. Receptors for the binding of mouse erythrocytes are present at the same time as surface IgM. The slight excess of mouse erythrocyte rosette-forming cells over cells having surface immunoglobulin M could mean that IgM appears later than do the receptors for the binding of mouse erythrocytes.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bianco C., Patrick R., Nussenzweig V. A population of lymphocytes bearing a membrane receptor for antigen-antibody-complement complexes. I. Separation and characterization. J Exp Med. 1970 Oct 1;132(4):702–720. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.4.702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickler H. B., Kunkel H. G. Interaction of aggregated -globulin with B lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1972 Jul 1;136(1):191–196. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.1.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froland S. S., Natvig J. B. Identification of three different human lymphocyte populations by surface markers. Transplant Rev. 1973;16:114–162. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1973.tb00119.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta S., Grieco M. H. Rosette formation with mouse erythrocytes: probable marker for human B lymphocytes. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1975;49(6):734–742. doi: 10.1159/000231457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lay W. H., Mendes N. F., Bianco C., Nussenzweig V. Binding of sheep red blood cells to a large population of human lymphocytes. Nature. 1971 Apr 23;230(5295):531–532. doi: 10.1038/230531a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litman G. W., Fromme D., Chartrand S. L., Finstad J., Good R. A. Significance of heavy chain mass and antigenic relationship in immunoglobulin evolution. Immunochemistry. 1971 Apr;8(4):345–349. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90156-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchalonis J., Edelman G. M. Phylogenetic origins of antibody structure. I. Multichain structure of immunoglobulins in the smooth dogfish (Mustelus canis). J Exp Med. 1965 Sep 1;122(3):601–618. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.3.601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore M. A., Metcalf D. Ontogeny of the haemopoietic system: yolk sac origin of in vivo and in vitro colony forming cells in the developing mouse embryo. Br J Haematol. 1970 Mar;18(3):279–296. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1970.tb01443.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen J. J., Cooper M. D., Raff M. C. In vitro generation of B lymphocytes in mouse foetal liver, a mammalian 'bursa equivalent'. Nature. 1974 May 24;249(455):361–363. doi: 10.1038/249361a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papamichail M., Brown J. C., Holborow E. J. Immunoglobulins on the surface of human lymphocytes. Lancet. 1971 Oct 16;2(7729):850–852. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90224-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabellino E., Colon S., Grey H. M., Unanue E. R. Immunoglobulins on the surface of lymphocytes. I. Distribution and quantitation. J Exp Med. 1971 Jan 1;133(1):156–167. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.1.156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts I. M., Whittingham S., Cowling D. C., Mackay I. R. Antigen-binding cells in human fetal liver. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1975;49(6):743–753. doi: 10.1159/000231458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe D. S., Hug K., Forni L., Pernis B. Immunoglobulin D as a lymphocyte receptor. J Exp Med. 1973 Oct 1;138(4):965–972. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.4.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitetta E. S., Melcher U., McWilliams M., Lamm M. E., Phillips-Quagliata J. M., Uhr J. W. Cell surface immunoglobulin. XI. The appearance of an IgD-like molecule on murine lymphoid cells during ontogeny. J Exp Med. 1975 Jan 1;141(1):206–215. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.1.206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitetta E. S., Uhr J. W. Immunoglobulin-receptors revisited. Science. 1975 Sep 19;189(4207):964–969. doi: 10.1126/science.1083069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



