Abstract
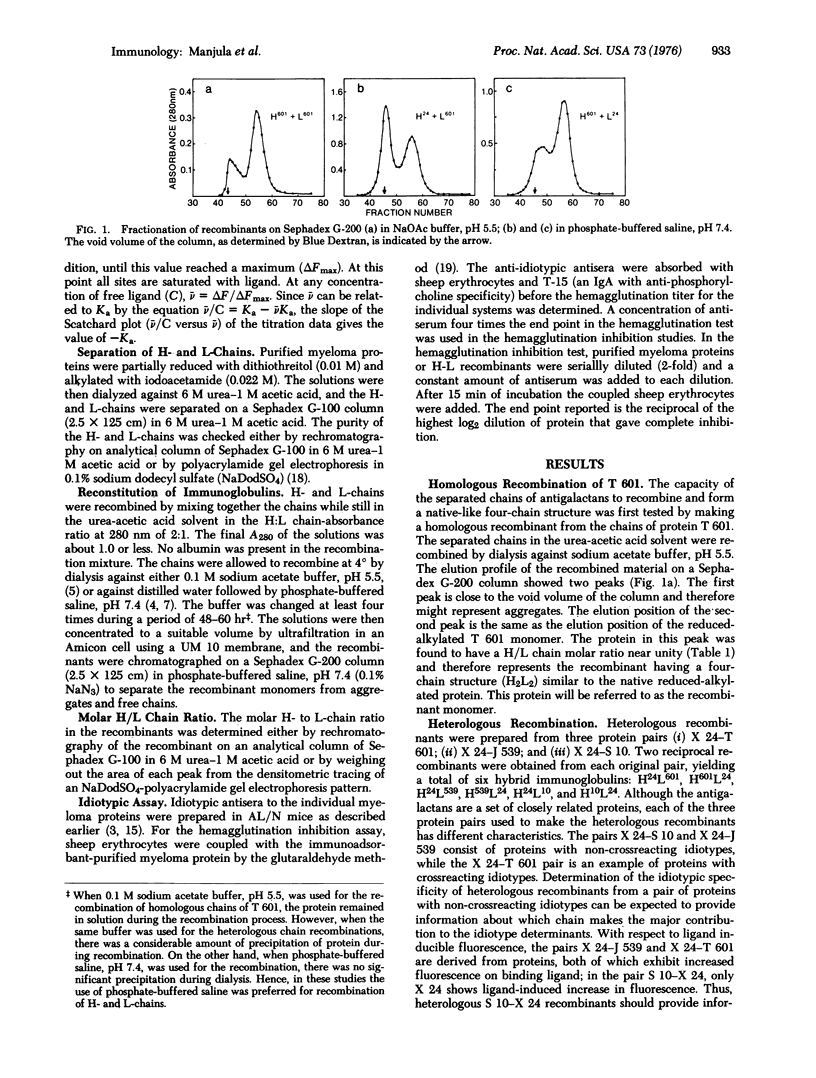
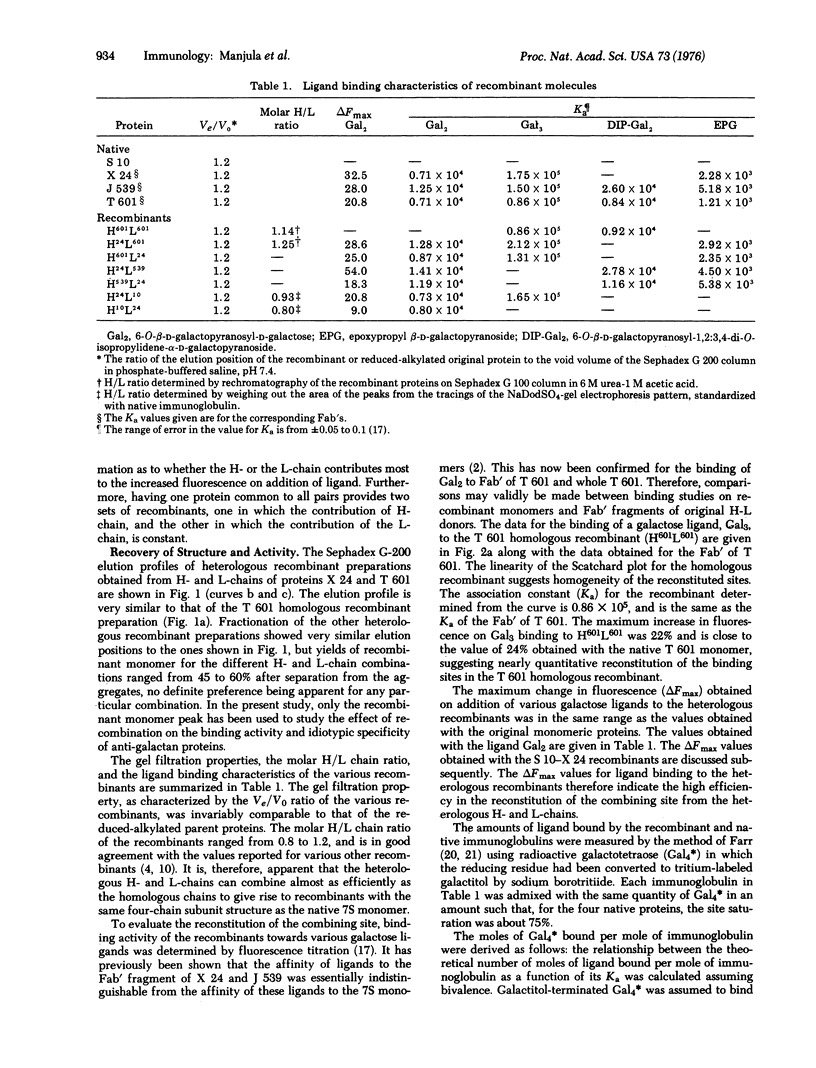
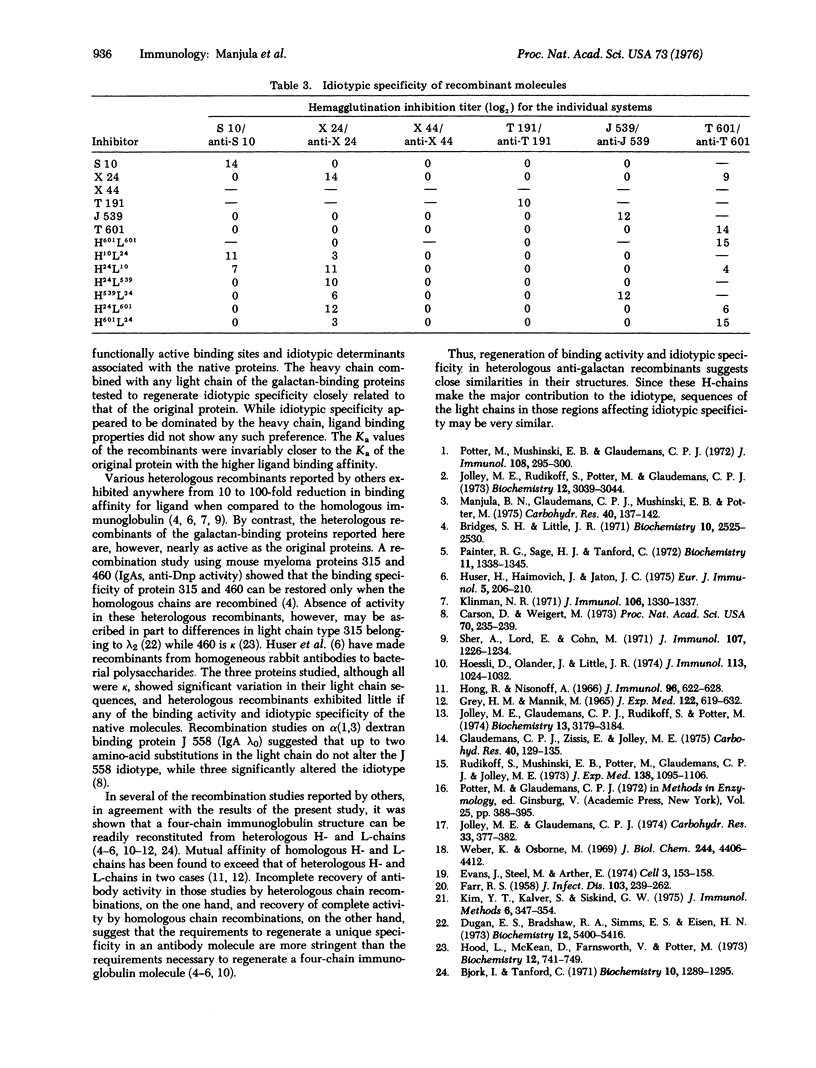
The interactions among the subunits of a unique set of mouse myeloma proteins having specificity for beta-D-(1,6) galactans has been studied by making homologous and heterologous recombinants of heavy and light chains. The recombinations were carried out by mixing together the desired heavy and light chains that had been separated on a Sephadex G-100 column in urea-acetic acid and renaturing the chains at near neutral pH. One homologous and six heterologous recombinants have been prepared. All the recombinants prepared possessed a four-chain native-like structure. The ligand binding activity and idiotypic specificity of the homologous recombinant were essentially indistinguishable from those of the original native protein. All the heterologous heavy-light chain combinations also led to the regeneration of functional binding sites. The affinity of the heterologous recombinants towards various galactose ligands was comparable to those of the native molecules. Furthermore, the ligand binding affinity of the recombinants was almost invariably closer to the Ka of the original protein that had a higher affinity. Idiotypic specificity of the heterologous recombinants paralleled that of the original protein that had contributed the heavy chain.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Björk I., Tanford C. Recovery of native conformation of rabbit immunoglobulin G upon recombination of separately renatured heavy and light chains at near-neutral pH. Biochemistry. 1971 Apr 13;10(8):1289–1295. doi: 10.1021/bi00784a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridges S. H., Little J. R. Recovery of binding activity in reconstituted mouse myeloma proteins. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2525–2530. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson D., Weigert M. Immunochemical analysis of the cross-reacting idiotypes of mouse myeloma proteins with anti-dextran activity and normal anti-dextran antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jan;70(1):235–239. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.1.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dugan E. S., Bradshaw R. A., Simms E. S., Eisen H. N. Amino acid sequence of the light chain of a mouse myeloma protein (MOPC-315). Biochemistry. 1973 Dec 18;12(26):5400–5416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans J., Steel M., Arthur E. A hemagglutination inhibition technique for detection of immunoglobulins in supernatants of human lymphoblastoid cell lines. Cell. 1974 Oct;3(2):153–158. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(74)90120-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARR R. S. A quantitative immunochemical measure of the primary interaction between I BSA and antibody. J Infect Dis. 1958 Nov-Dec;103(3):239–262. doi: 10.1093/infdis/103.3.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaudemans C. P., Zissis E., Jolley M. E. Binding studies on a mouse-myeloma immunoglobulin A having specificity for beta-D-(1 yields 6)-linked D-galactopyranosyl residues. Carbohydr Res. 1975 Mar;40(1):129–135. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)82675-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grey H. M., Mannik M. Specificity of recombination of H and L chains from human gamma-G-myeloma proteins. J Exp Med. 1965 Sep 1;122(3):619–632. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.3.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoessli D., Olander J., Little J. R. Heterologous recombination between mouse myeloma 315 heavy chains and rabbit antibody light chains: structural and functional properties of the hybrid molecules. J Immunol. 1974 Sep;113(3):1024–1032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong R., Nisonoff A. Heterogeneity in the complementation of polypeptide subunits of a purified antibody isolated from an individual rabbit. J Immunol. 1966 Apr;96(4):622–628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hood L., McKean D., Farnsworth V., Potter M. Mouse immunoglobulin chains. A survey of the amino-terminal sequences of kappa chains. Biochemistry. 1973 Feb;12(4):741–749. doi: 10.1021/bi00728a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huser H., Haimovich J., Jaton J. C. Antigen binding and idiotypic properties of reconstituted immunoglobulins G derived from homogeneous rabbit anti-pneumococcal antibodies. Eur J Immunol. 1975 Mar;5(3):206–210. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830050311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolley M. E., Glaudemans C. P., Rudikoff S., Potter M. Structural requirements for the binding of derivatives of D-galactose to two homogeneous murine immunoglobulins. Biochemistry. 1974 Jul 16;13(15):3179–3184. doi: 10.1021/bi00712a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolley M. E., Glaudemans C. P. The determination of binding constants for binding between carbohydrate ligands and certain proteins. Carbohydr Res. 1974 Apr;33(2):377–382. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)82819-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolley M. E., Rudikoff S., Potter M., Glaudemans C. P. Spectral changes on binding of oligosaccharides to murine immunoglobulin A myeloma proteins. Biochemistry. 1973 Jul 31;12(16):3039–3044. doi: 10.1021/bi00740a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y. T., Kalver S., Siskind G. W. A comparison of the Farr technique with equilibrium dialysis for measurement of antibody concentration and affinity. J Immunol Methods. 1975 Feb;6(4):347–354. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(75)90005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klinman N. R. Regain of homogeneous binding activity after recombination of chains of "mono- focal" antibody. J Immunol. 1971 May;106(5):1330–1337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manjula B. N., Glaudemans C. P., Mushinski E., Potter M. A new, mouse-myeloma immunoglobulin A having specificity for beta-D-(1 yields 6)-linked D-galactopyranosyl residues. Carbohydr Res. 1975 Mar;40(1):137–142. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)82676-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Painter R. G., Sage H. J., Tanford C. Contributions of heavy and light chains of rabbit immunoglobulin G to antibody activity. II. Binding activities of reconstituted immunoglobulins. Biochemistry. 1972 Apr 11;11(8):1338–1345. doi: 10.1021/bi00758a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter M., Mushinski E. B., Glaudemans C. P. Antigen-binding IgA myeloma proteins in mice: specificities to antigens containing -D 1 leads to 6 linked galactose side chains and a protein antigen in wheat. J Immunol. 1972 Feb;108(2):295–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudikoff S., Mushinski E. B., Potter M., Glaudemans C. P., Jolley M. E. Six BALB-c IgA myeloma proteins that bind beta-(1-6)-D-galactan. Partial amino acid sequences and idiotypes. J Exp Med. 1973 Nov 1;138(5):1095–1105. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.5.1095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sher A., Lord E., Cohn M. Reconstitution from subunits of the hapten binding sites and idiotypic determinants of mouse anti-phosphorylcholine myeloma proteins. J Immunol. 1971 Nov;107(5):1226–1234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



