Abstract
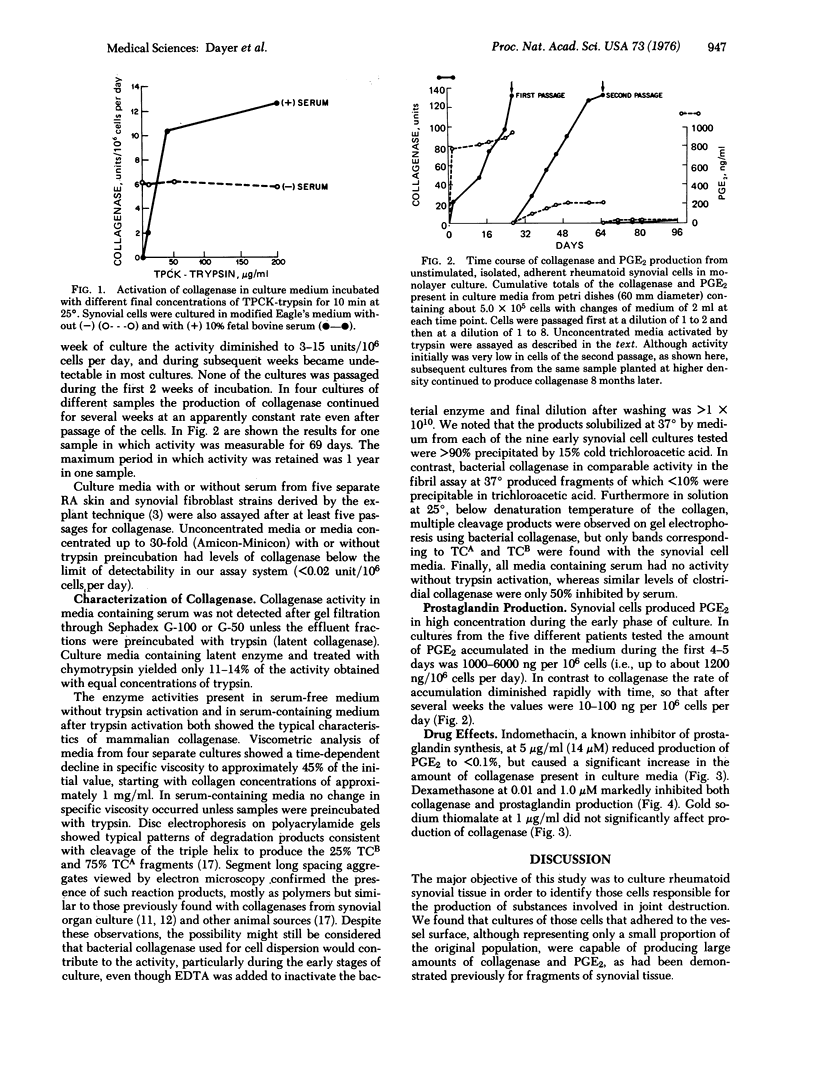
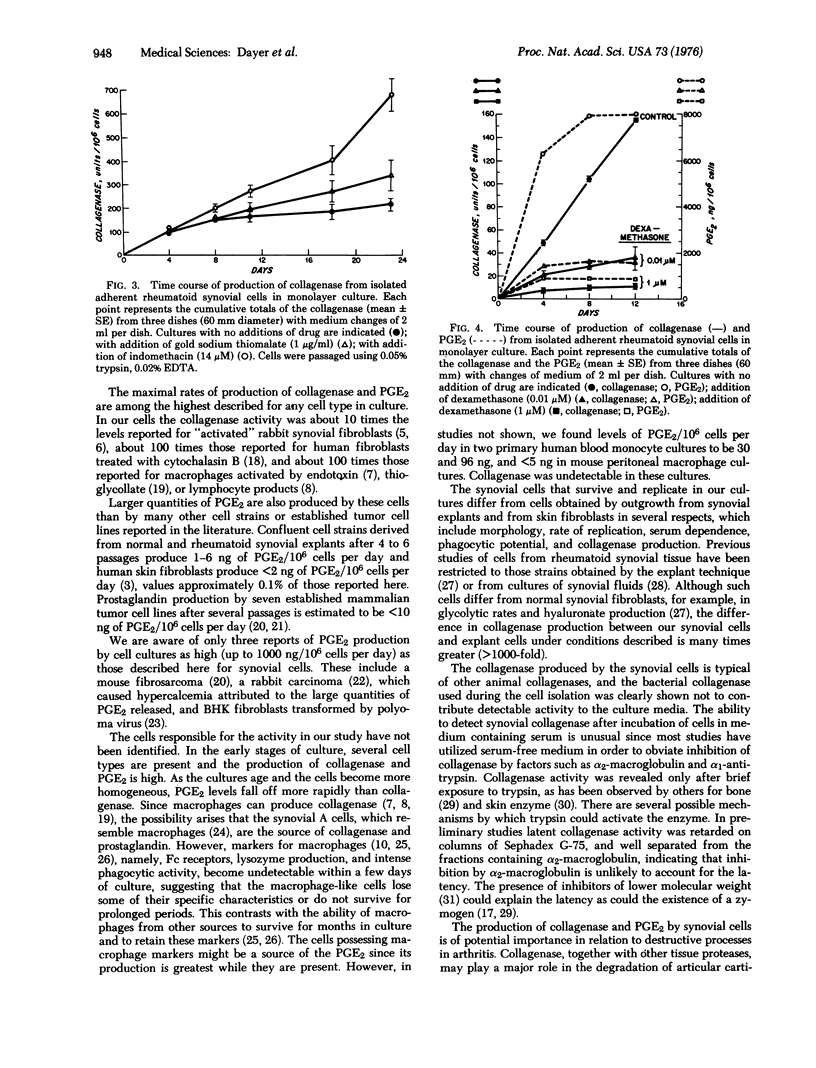
We have studied cells dispersed with proteolytic enzymes from rheumatoid arthritic synovectomy specimens to determine the cell type(s) responsible for joint destruction. Initially 10-50% of these cells adhered to culture dishes within 24 hr and were of two main types: small, round cells and larger, stellate cells. During 1-4 days of culture, 5-25% had Fc receptors and 25-50% showed brisk phagocytosis. Daily producition, per 10(6) cells of collagenase (EC 3.4.24.3) (after trypsin pretreatment) was up to 70 mug of collagen fibrils lysed per min at 37 degrees (70 units), of prostaglandin (PGE2), up to about 1200 ng, and of lysozyme, up to about 100 mug. Under identical conditions of assay, fibroblasts grown from explants of synovium produced no detectable collagenase or lysozyme, and PGE2 was only 2-4 ng. With the dispersed cell preparations, macrophage markers (Fc receptors and lysozyme) were undetectable after 4 days and PGE2 decreased rapidly after about 7 more days. However, collagenase production continued for 3-25 weeks, and in some cultures, after cell passage. At these later stages, large, slow-growing stellate cells were predominant and could phagocytose carbon particles if incubated for greater than 6-8 hr. Indomethacin (14 muM) inhibited PGE2 but stimulated collagenase production whereas dexamethasone (10 nM) inhibited both. Production of PGE2 and collagenase in large amounts in vitro by these cells suggests that they may be involved in joint destruction in vivo. The precise origin of these synovial cells and the mechanisms responsible for the sustained production of collagenase at a high rate remain unidentified.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauer E. A., Stricklin G. P., Jeffrey J. J., Eisen A. Z. Collagenase production by human skin fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 May 5;64(1):232–240. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90243-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castor C. W. Synovial cell activation induced by a polypeptide mediator. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Jun 13;256:304–317. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb36057.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen F., Jaffe B. M. Production of prostaglandins by cells in vitro: radioimmunoassay measurement of the conversion of arachidonic acid to PGE2 and PGF2 alpha. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Dec 10;55(3):724–729. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91204-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evanson J. M., Jeffrey J. J., Krane S. M. Studies on collagenase from rheumatoid synovium in tissue culture. J Clin Invest. 1968 Dec;47(12):2639–2651. doi: 10.1172/JCI105947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flower R. J., Cheung H. S., Cushman D. W. Quantitative determination of prostaglandins and malondialdehyde formed by the arachidonate oxygenase (prostaglandin synthetase) system of bovine seminal vesicle. Prostaglandins. 1973 Sep;4(3):325–341. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(73)90020-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon S., Cohn Z. A. The macrophage. Int Rev Cytol. 1973;36:171–214. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60218-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon S., Cohn Z. Macrophage-melanocyte heterokaryons. I. Preparation and properties. J Exp Med. 1970 May 1;131(5):981–1003. doi: 10.1084/jem.131.5.981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon S., Todd J., Cohn Z. A. In vitro synthesis and secretion of lysozyme by mononuclear phagocytes. J Exp Med. 1974 May 1;139(5):1228–1248. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.5.1228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross J. Collagen biology: structure, degradation, and disease. Harvey Lect. 1974;68:351–432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamerman D., Rosenberg L. C., Schubert M. Diarthrodial joints revisited. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1970 Jun;52(4):725–774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammarström S., Samuelsson B., Bjursell G. Prostaglandin levels in normal and transformed baby-hamster-kidney fibroblasts. Nat New Biol. 1973 May 9;243(123):50–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. D., Jr, Cohen G. L., Krane S. M. Synovial collagenase: its presence in culture from joint disease of diverse etiology. Arthritis Rheum. 1969 Apr;12(2):92–102. doi: 10.1002/art.1780120206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. D., Jr, DiBona D. R., Krane S. M. Collagenases in human synovial fluid. J Clin Invest. 1969 Nov;48(11):2104–2113. doi: 10.1172/JCI106177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. D., Jr, Krane S. M. Collagenases (third of three parts). N Engl J Med. 1974 Sep 26;291(13):652–661. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197409262911305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. D., Jr, Reynolds J. J., Werb Z. Cytochalasin B increases collagenase production by cells in vitro. Nature. 1975 Sep 18;257(5523):243–244. doi: 10.1038/257243a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hook R. M., Hook C. W., Brown S. I. Fibroblast collagenase partial purification and characterization. Invest Ophthalmol. 1973 Oct;12(10):771–776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koob T. J., Jeffrey J. J., Eisen A. Z. Regulation of human skin collagenase activity by hydrocortisone and dexamethasone in organ culture. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Dec 11;61(3):1083–1088. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90266-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krane S. M. Collagenase production by human synovial tissues. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Jun 13;256:289–303. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb36056.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine L., Gjtierrez Cernosek R. M., Van Vunakis H. Specificities of prostaglandins B 1 , F 1 , and F 2 antigen-antibody reactions. J Biol Chem. 1971 Nov 25;246(22):6782–6785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay J. M., Panayi G., Neill W. A., Robinson A., Smith W., Marmion B. P., Duthie J. J. Cytology of rheumatoid synovial cells in culture. I. Composition and sequence of cell populations in cultures of rheumatoid synovial fluid. Ann Rheum Dis. 1974 May;33(3):225–233. doi: 10.1136/ard.33.3.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osserman E. F., Lawlor D. P. Serum and urinary lysozyme (muramidase) in monocytic and monomyelocytic leukemia. J Exp Med. 1966 Nov 1;124(5):921–952. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.5.921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson D. R., McGuire M. B., Levine L. Prostaglandins in the rheumatic diseases. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Jun 13;256:318–329. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb36058.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson D. R., Smith H., McGuire M. B., Levine L. Prostaglandin synthesis by rheumatoid synovium and its stimulation by colchicine. Prostaglandins. 1975 Jul;10(1):67–85. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(75)90094-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson D. R., Tashjian A. H., Jr, Levine L. Prostaglandin-stimulated bone resorption by rheumatoid synovia. A possible mechanism for bone destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest. 1975 Nov;56(5):1181–1188. doi: 10.1172/JCI108195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tashjian A. H., Jr, Voelkel E. F., Levine L., Goldhaber P. Evidence that the bone resorption-stimulating factor produced by mouse fibrosarcoma cells is prostaglandin E 2 . A new model for the hypercalcemia of cancer. J Exp Med. 1972 Dec 1;136(6):1329–1343. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.6.1329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaes G. The release of collagenase as an inactive proenzyme by bone explants in culture. Biochem J. 1972 Jan;126(2):275–289. doi: 10.1042/bj1260275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voelkel E. F., Tashjian A. H., Jr, Franklin R., Wasserman E., Levine L. Hypercalcemia and tumor-prostaglandins: the VX2 carcinoma model in the rabbit. Metabolism. 1975 Aug;24(8):973–986. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(75)90089-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl L. M., Wahl S. M., Mergenhagen S. E., Martin G. R. Collagenase production by endotoxin-activated macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3598–3601. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl L. M., Wahl S. M., Mergenhagen S. E., Martin G. R. Collagenase production by lymphokine-activated macrophages. Science. 1975 Jan 24;187(4173):261–263. doi: 10.1126/science.163038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werb Z., Burleigh M. C. A specific collagenase from rabbit fibroblasts in monolayer culture. Biochem J. 1974 Feb;137(2):373–385. doi: 10.1042/bj1370373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werb Z., Gordon S. Secretion of a specific collagenase by stimulated macrophages. J Exp Med. 1975 Aug 1;142(2):346–360. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.2.346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werb Z., Reynolds J. J. Stimulation by endocytosis of the secretion of collagenase and neutral proteinase from rabbit synovial fibroblasts. J Exp Med. 1974 Dec 1;140(6):1482–1497. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.6.1482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolley D. E., Roberts D. R., Evanson J. M. Inhibition of human collagenase activity by a small molecular weight serum protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Sep 16;66(2):747–754. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90573-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



