Abstract
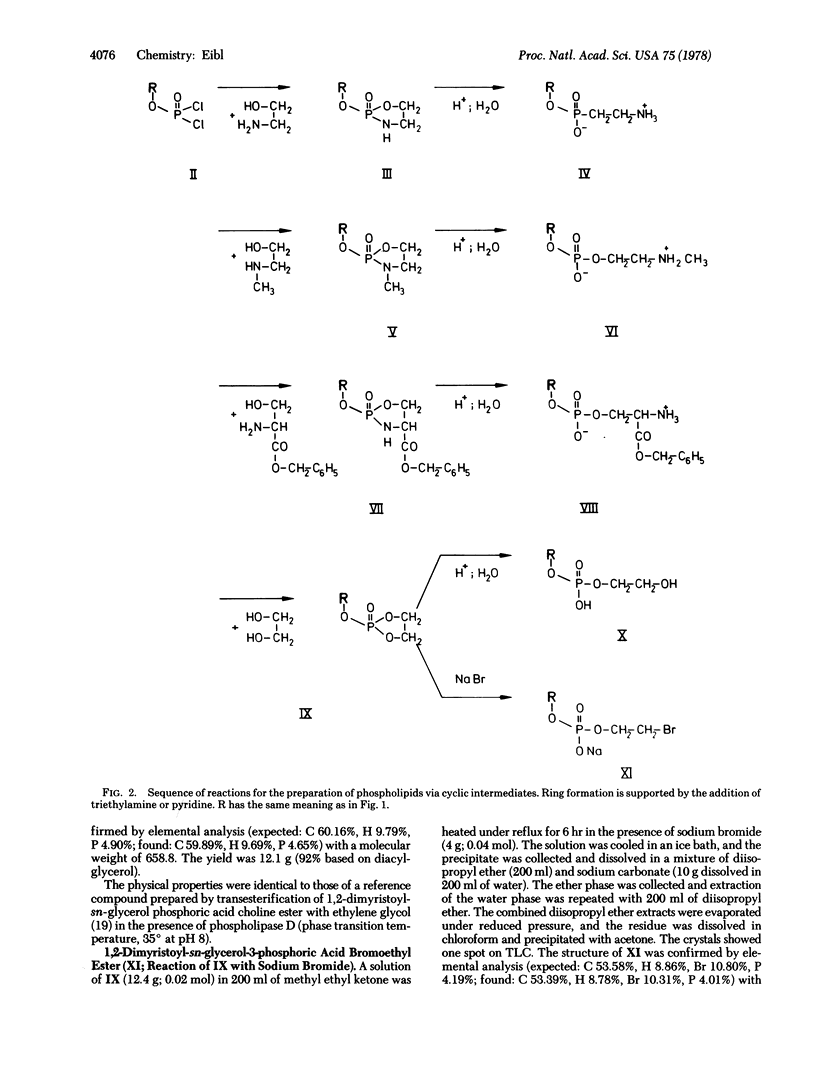
The synthesis of phospholipids described herein allows an almost quantitative conversion of 1,2-diacylglycerols to phospholipids via cyclic intermediates such as oxazaphospholanes or dioxaphospholanes, which are the only products observed when ethanolamine or ethylene glycol is allowed to react with phosphatidic acid dichlorides. The acidic hydrolysis of the cyclic intermediates occurs rapidly without the formation of by-products and results in phospholipids differing in the structure of the polar part depending on which vicinal aminoalcohols or diols are used. For instance, phosphatidylethanolamines, -(N-methyl)ethanolamines, and -serine benzyl esters are directly formed from the corresponding oxazaphospholanes. Phosphatidyl(N,N-dimethyl)ethanolamines and -cholines are prepared by amination of the bromoethyl esters of phosphatidic acids, which can be obtained by treatment of dioxaphospholanes with sodium bromide. A similar sequence of reactions starting from 1-acyl-2-benzylglycerols or monoacylpropane-1,3-diols will result in the respective monoacyl analogues such as lysophospholipids or the so-called desoxylysophospholipids. The mild reaction conditions, good yields (>90% based on diacylglycerol), and high purity of the products make this route an attractive procedure for phospholipid synthesis; in addition, it avoids the need for chromatography and thus can be utilized on a large scale.
Keywords: phosphatidic acid dichlorides, specific hydrolysis
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnold D., Weltzien H. U., Westphal O. Uber die Synthese von Lysolecithinen und ihren Atheranaloga. Justus Liebigs Ann Chem. 1967;709:234–239. doi: 10.1002/jlac.19677090126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cubero Robles E., van den Berg D. Synthesis of lecithins by acylation of O-(sn-glycero-3-phosphoryl) choline with fatty acid anhydrides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Dec 17;187(4):520–526. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(69)90049-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eibl H., Arnold D., Weltzien H. U., Westphal O. Zur Synthese von alpha- und beta-Lecithinen und ihren Atheranaloga. Justus Liebigs Ann Chem. 1967;709:226–230. doi: 10.1002/jlac.19677090124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eibl H., Westphal O. Palmitoyl-propandiol-(1.3)-phosphorylcholin (2-Desoxy-lysolecithin) und omega.omega'-Alkandiol-Analoga. Justus Liebigs Ann Chem. 1967;709:244–245. doi: 10.1002/jlac.19677090128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta C. M., Radhakrishnan R., Khorana H. G. Glycerophospholipid synthesis: improved general method and new analogs containing photoactivable groups. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4315–4319. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRT R., BERCHTOLD R. Zur Synthese der Phosphatide. 2. Eine neue Synthese der Lecithine. Pharm Acta Helv. 1958 Aug-Oct;33(8-10):349–356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Eibl H. The influence of phospholipid polar groups on gramicidin channels. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jan 4;464(1):37–44. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90368-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slotboom A. J., Bonsen P. P. Recent developments in the chemistry of phospholipids. Chem Phys Lipids. 1970 Dec;5(2):301–397. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(70)90001-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Träuble H., Eibl H. Electrostatic effects on lipid phase transitions: membrane structure and ionic environment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jan;71(1):214–219. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.1.214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Träuble H. Phase transitions in lipids. Biomembranes. 1972;3:197–227. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-0961-1_14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyäuble H., Teubner M., Woolley P., Eibl H. Electrostatic interactions at charged lipid membranes. I. Effects of pH and univalent cations on membrane structure. Biophys Chem. 1976 Jul;4(4):319–342. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(76)80013-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weltzien H. U., Westphal O. O-Methylierte und O-acetylierte Lysolecithine. Justus Liebigs Ann Chem. 1967;709:240–243. doi: 10.1002/jlac.19677090127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



