Abstract
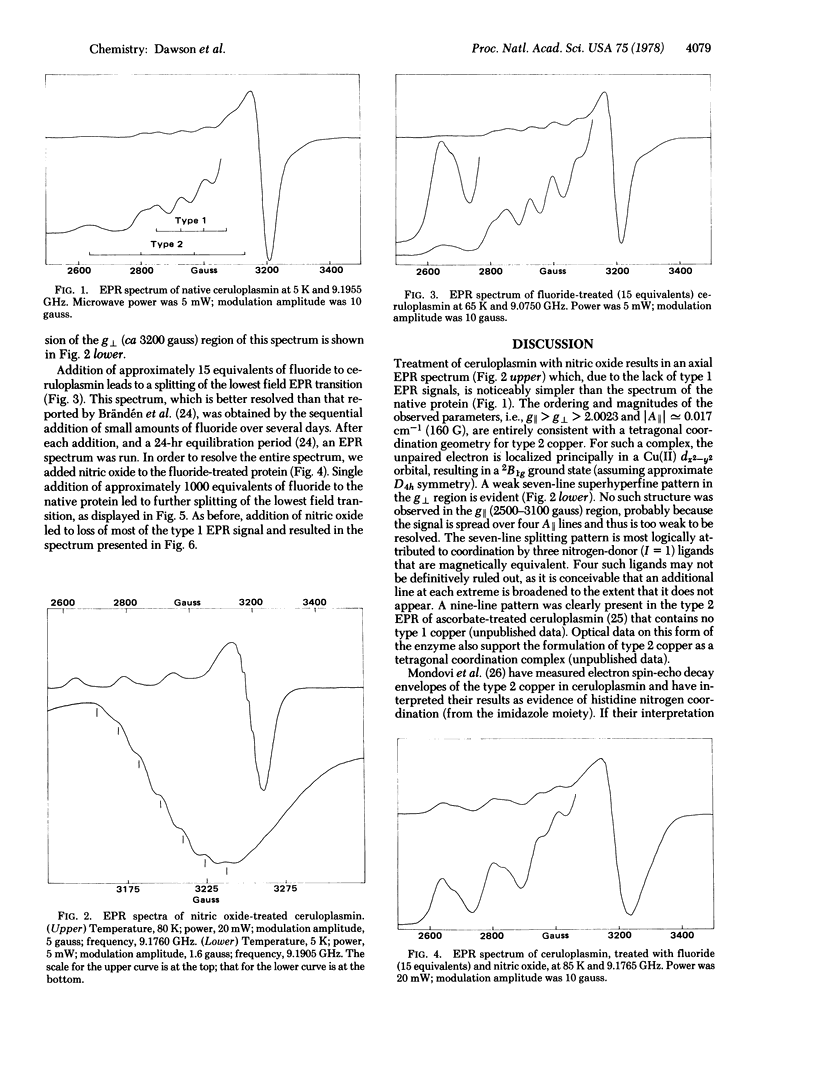
The electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spectra of the blue copper oxidase ceruloplasmin [ferroxidase, iron (II):oxygen oxidoreductase, EC 1.16.3.1] and of a derivative having the type I (blue) copper centers reversibly bleached are reported. The EPR spectrum of bleached ceruloplasmin has a seven-line superhyperfine structure in the g : formula: (see text) region that is attributed to the presence of three nitrogen-donor type 2 copper ligands. The EPR data suggest further that the type 2 copper in ceruloplasmin possesses a tetragonal coordination gometry. In the presence of varying amounts of fluoride, superhyperfine splitting patterns in the g : formula: (see text) region of both ceruloplasmin derivatives indicate that a maximum of two fluorides may be bound to the type 2 copper.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andréasson L. E., Vänngård T. Evidence of a specific copper(II) in human ceruloplasmin as a binding site for inhibitory anions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Feb 17;200(2):247–257. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(70)90168-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bereman R. D., Kosman D. J. Stereoelectronic properties of metalloenzymes. 5. Identification and assignment of ligand hyperfine splittings in the electron spin resonance spectrum of galactose oxidase. J Am Chem Soc. 1977 Oct 26;99(22):7322–7325. doi: 10.1021/ja00464a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brändén R., Malmström B. G., Vänngård T. The effect of fluoride on the spectral and catalytic properties of the three copper-containing oxidases. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jul 2;36(1):195–200. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02901.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers W., Curzon G., Garbett K., Speyer B. E., Young S. N., Williams R. J. Anion-binding and the state of copper in caeruloplasmin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 May 17;310(1):38–50. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(73)90006-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson C. R., Strothkamp K. G., Krul K. G. Ascorbate oxidase and related copper proteins. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Sep 30;258:209–220. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb29281.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deinum J., Vänngård T. The stoichiometry of the paramagnetic copper and the oxidation-reduction potentials of type I copper in human ceruloplasmin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jun 15;310(2):321–330. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(73)90112-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk K. E., Reinhammar B. Visible and near-infrared circular dichroism of some blue copper proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Nov 28;285(1):84–90. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90182-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frieden E., Hsieh H. S. The biological role of ceruloplasmin and its oxidase activity. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1976;74:505–529. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3270-1_43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herve M., Garnier A., Tosi L., Steinbuch M. Ceruloplasmin-anion interaction. A circular dichroism spectroscopic study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Aug 9;439(2):432–441. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(76)90080-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasper C. B. Ceruloplasmin-anion interactions. Induced spectral transitions in the visible range. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jun 25;243(12):3218–3222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malkin R., Malmström B. G. The state and function of copper in biological systems. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1970;33:177–244. doi: 10.1002/9780470122785.ch4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malkin R., Malmström R. G., Vänngård T. The requirement of the "non-blue" copper (II) for the activity of fungal laccase. FEBS Lett. 1968 Jul;1(1):50–54. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(68)80016-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markley J. L., Ulrich E. L., Berg S. P., Krogmann D. W. Nuclear magnetic resonance studies of the copper binding sites of blue copper proteins: oxidized, reduced, and apoplastocyanin. Biochemistry. 1975 Oct 7;14(20):4428–4433. doi: 10.1021/bi00691a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKee D. J., Frieden E. Binding of transition metal ions by ceruloplasmin (ferroxidase). Biochemistry. 1971 Oct 12;10(21):3880–3883. doi: 10.1021/bi00797a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMillin D. R., Holwerda R. A., Gray H. B. Preparation and spectroscopic studies of cobalt(II)-stellacyanin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1339–1341. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMillin D. R., Rosenberg R. C., Gray H. B. Preparation and spectroscopic studies of cobalt(II) derivatives of blue copper proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4760–4762. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mondoví B., Graziani M. T., Mims W. B., Oltzik R., Peisach J. Pulsed electron paramagnetic resonance studies of types I and II coper of Rhus vernicifera laccase and porcine ceruloplasmin. Biochemistry. 1977 Sep 20;16(19):4198–4202. doi: 10.1021/bi00638a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mondoví B., Morpurgo L., Rotilio G., Finazzi-Agró A. Recent studies on copper containing oxidases. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1976;74:424–437. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3270-1_36. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rydén L., Björk I. Reinvestigation of some physicochemical and chemical properties of human ceruloplasmin (ferroxidase). Biochemistry. 1976 Aug 10;15(16):3411–3417. doi: 10.1021/bi00661a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon E. I., Clendening P. J., Gray H. B., Grunthaner F. J. Letter: Direct observation of sulfur coordination in bean plastocyanin by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. J Am Chem Soc. 1975 Jun 25;97(13):3878–3879. doi: 10.1021/ja00846a087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon E. I., Hare J. W., Gray H. B. Spectroscopic studies and a structural model for blue copper centers in proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1389–1393. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon E. I., Rawlings J., McMillin D. R., Stephens P. J., Gray H. B. Infrared and visible circular dichroism and magnetic circular dichroism studies on cobalt (II)-substituted blue copper proteins. J Am Chem Soc. 1976 Dec 8;98(25):8046–8048. doi: 10.1021/ja00441a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosi L., Garnier A., Herve M., Steinbuch M. Ceruloplasmin-anicn interaction. A resonance Raman spectroscopic study. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Jul 8;65(1):100–106. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80066-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tullius T. D., Frank P., Hodgson K. O. Characterization of the blue copper site in oxidized azurin by extended x-ray absorption fine structure: Determination of a short Cu-S distance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4069–4073. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wever R., van Leeuwen F. X., van Gelder B. F. The reaction of nitric oxide with ceruloplasmin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Apr 12;302(2):236–239. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(73)90152-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



