Abstract
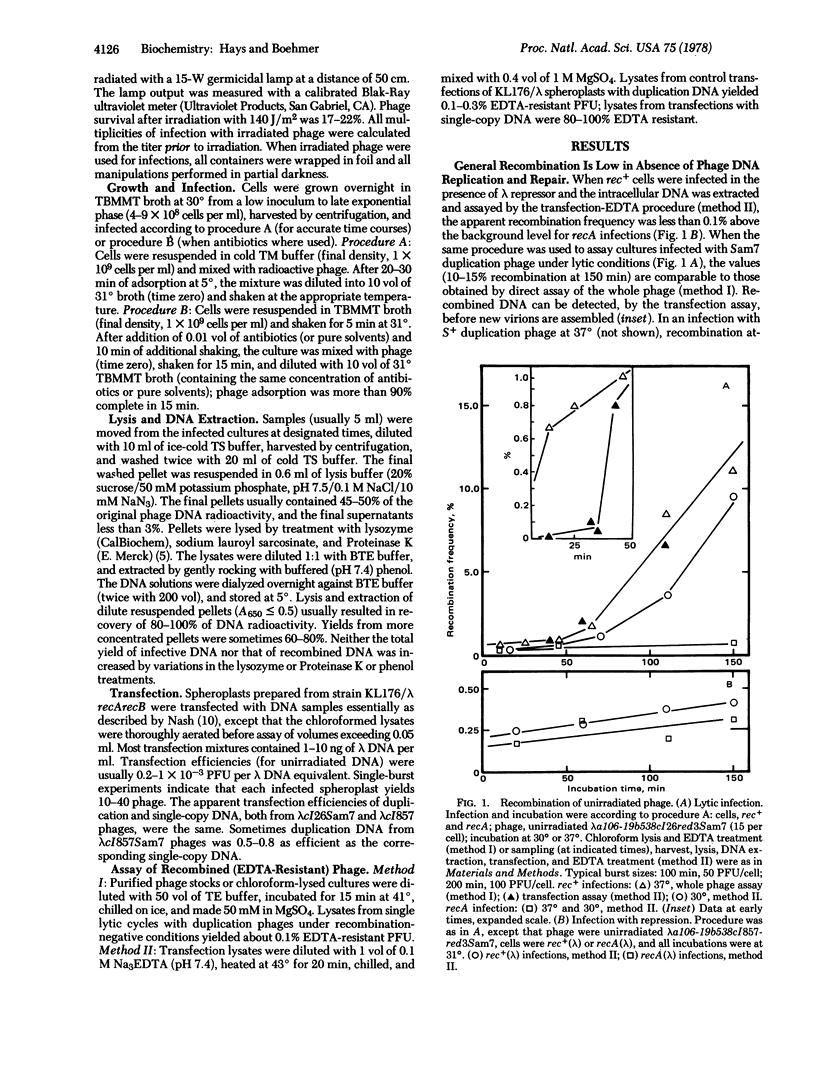
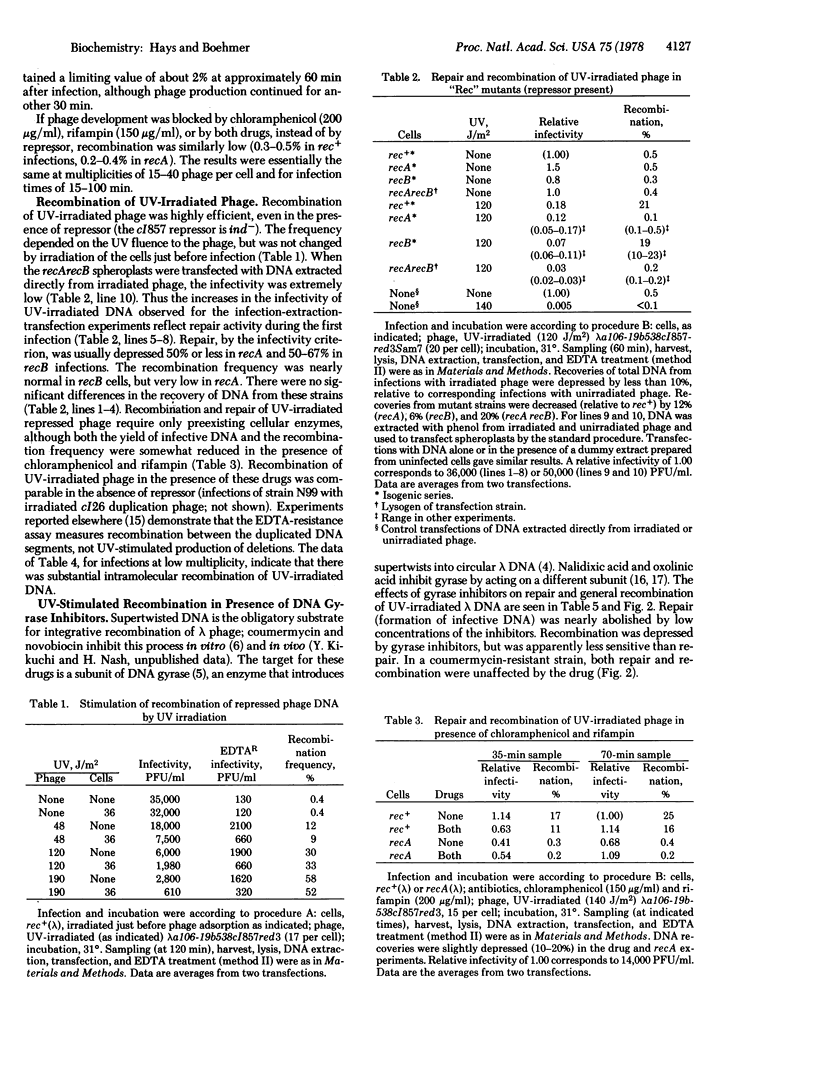
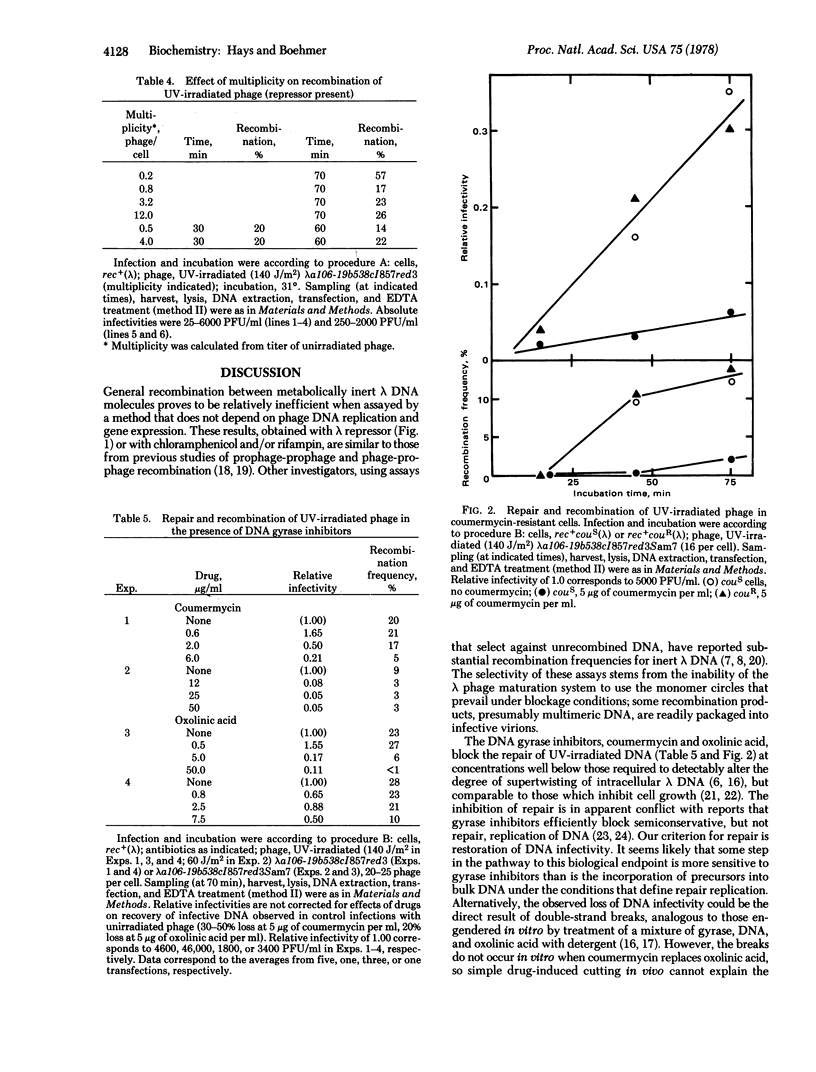
Intracellular lambda DNA (from EDTA-sensitive tandem duplication phages) was extracted from infected rec+ bacteria and scored for infectivity and recombination (loss of duplication) by transfection of recA recB spheroplasts and subsequent assay for EDTA resistance. When phage development was blocked by repressor or by antibiotics (chloramphenicol and/or rifampin), the apparent recombination frequency was about 0.1% above the background value for recA infections. Prior irradiation of the phage greatly stimulated recombination; the frequency was 20% when UV fluence was 140 J/m2. Repair (recovery of infectivity) and recombination of irradiated phage DNA proceeded readily in the presence of chloramphenicol and rifampin. Inhibitors of DNA gyrase (coumermycin and oxolinic acid) blocked repair and reduced recombination. UV-stimulated recombination was very low in recA but nearly normal in recB cells: repair was reduced in both mutant strains. The recombination remained high as phage/cell ratios less than unity.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CLARK A. J., MARGULIES A. D. ISOLATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF RECOMBINATION-DEFICIENT MUTANTS OF ESCHERICHIA COLI K12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Feb;53:451–459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.2.451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark A. J. Progress toward a metabolic interpretation of genetic recombination of Escherichia coli and bacteriophage lambda. Genetics. 1974 Sep;78(1):259–271. doi: 10.1093/genetics/78.1.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmons S. W., Thomas J. O. Tandem genetic duplications in phage lambda. IV. The locations of spontaneously arising tandem duplications. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jan 15;91(2):147–152. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90155-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M., Mizuuchi K., O'Dea M. H., Itoh T., Tomizawa J. I. Nalidixic acid resistance: a second genetic character involved in DNA gyrase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4772–4776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M., Mizuuchi K., O'Dea M. H., Nash H. A. DNA gyrase: an enzyme that introduces superhelical turns into DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):3872–3876. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.3872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M., O'Dea M. H., Itoh T., Tomizawa J. Novobiocin and coumermycin inhibit DNA supercoiling catalyzed by DNA gyrase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4474–4478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman S., Gottesman M. Excision of prophage lambda in a cell-free system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2188–2192. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman L., Braun A., Feldberg R., Mahler I. Enzymatic repair of DNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:19–43. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.000315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamberg M., Svensson J., Samuelsson B. Thromboxanes: a new group of biologically active compounds derived from prostaglandin endoperoxides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):2994–2998. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.2994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard-Flanders P., Theriot L. Mutants of Escherichia coli K-12 defective in DNA repair and in genetic recombination. Genetics. 1966 Jun;53(6):1137–1150. doi: 10.1093/genetics/53.6.1137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda H., Kobayashi I. Involvement of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase in a recA-independent pathway of genetic recombination in Escheria coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3932–3936. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh T., Tomizawa J. I. Involvement of DNA gyrase in bacteriophage T7 DNA replication. Nature. 1977 Nov 3;270(5632):78–80. doi: 10.1038/270078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi I., Ikeda H. Formation of recombinant DNA of bacteriophage lambda by recA function of Escherichia coli without duplication, transcription, translation, and maturation. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Jun 24;153(3):237–245. doi: 10.1007/BF00431589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin P. F., Howard-Flanders P. Genetic exchanges caused by ultraviolet photoproducts in phage lambda DNA molecules: the role of DNA replication. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Jul 23;146(2):107–115. doi: 10.1007/BF00268079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meselson M. Reciprocal recombination in prophage lambda. J Cell Physiol. 1967 Oct;70(2 Suppl):113–118. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040700409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuuchi K., Gellert M., Nash H. A. Involement of supertwisted DNA in integrative recombination of bacteriophage lambda. J Mol Biol. 1978 May 25;121(3):375–392. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90370-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash H. A. Integrative recombination in bacteriophage lambda: analysis of recombinant DNA. J Mol Biol. 1975 Feb 5;91(4):501–514. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90276-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash H. A. LambdaattB-attP, a lambda derivative containing both sites involved in integrative recombination. Virology. 1974 Jan;57(1):207–216. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90121-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan M. J. Coumermycin A1: A preferential inhibitor of replicative DNA synthesis in Escherichia coli. I. In vivo characterization. Biochemistry. 1976 Aug 24;15(17):3769–3777. doi: 10.1021/bi00662a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan M. J., Wells R. D. Coumerimycin A1: A preferential inhibitor of replicative DNA synthesis in Escherichia coli. II. In vivo characterization. Biochemistry. 1976 Aug 24;15(17):3778–3782. doi: 10.1021/bi00662a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl F. W., McMilin K. D., Stahl M. M., Malone R. E., Nozu Y., Russo V. E. A role for recombination in the production of "free-loader" lambda bacteriophage particles. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jul 14;68(1):57–67. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90262-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staudenbauer W. L. Letters to the editor: Novobiocin-a specific inhibitor of semiconservative DNA replication in permeabilized Escherichia coli cells. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jul 25;96(1):201–205. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90191-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staudenbauer W. L. Replication of Escherichia coli DNA in vitro: inhibition by oxolinic acid. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Mar 1;62(3):491–497. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10183.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugino A., Peebles C. L., Kreuzer K. N., Cozzarelli N. R. Mechanism of action of nalidixic acid: purification of Escherichia coli nalA gene product and its relationship to DNA gyrase and a novel nicking-closing enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi S. Joint molecules of lambda DNA as an intermediate of genetic recombination. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Jan 7;150(1):43–52. doi: 10.1007/BF02425324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkins A. S., Mistry J. Phage lambda's generalized recombination system. Study of the intracellular DNA pool during lytic infection. Mol Gen Genet. 1974 Apr 3;129(4):275–293. doi: 10.1007/BF00265693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


