Abstract
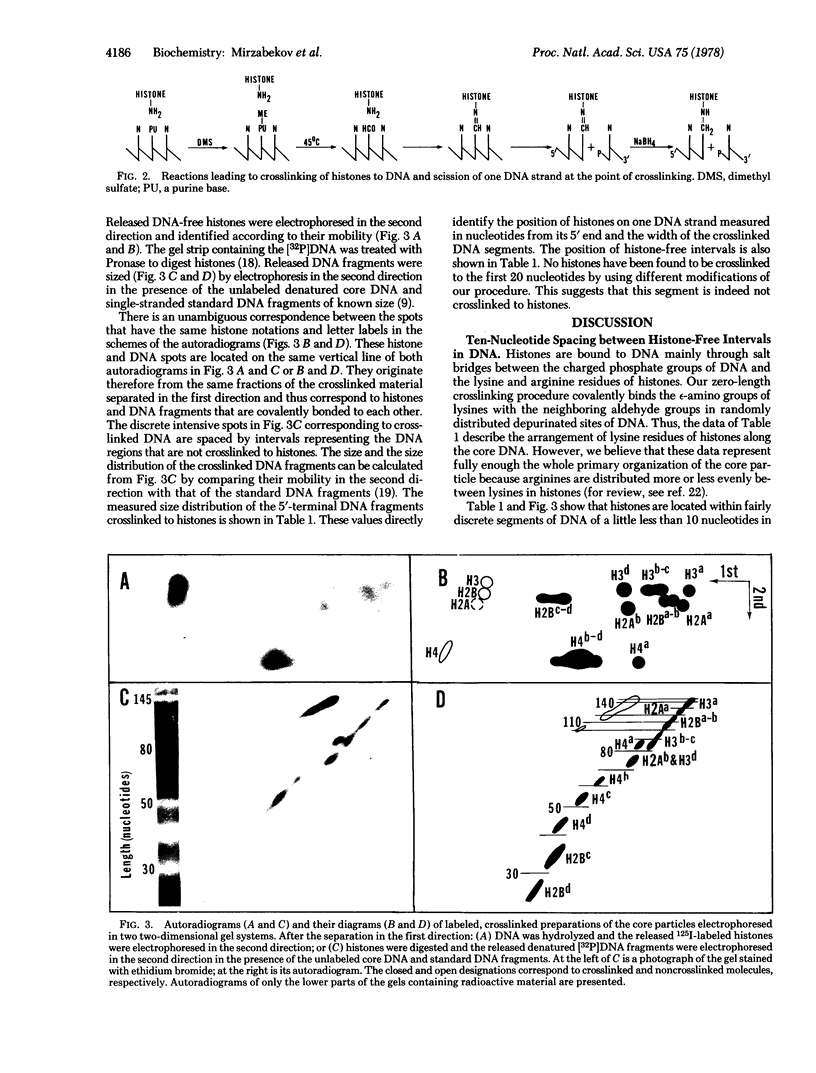
A high-resolution map for the arrangement of histones along DNA in the nucleosome core particle has been determined by a sequencing procedure based on crosslinking histones to the 5'-terminal DNA fragments produced by scission of one DNA strand at the point of crosslinking. The position of histones on DNA has been identified by measuring the length of crosslinked DNA fragments. The results demonstrate that each of the histones is arranged within several adjacent or dispersed DNA segments of a little less than 10 nucleotides in length. Histone-free intervals are located between these segments at the regular distances of about (10)n nucleotides from the 5' end of the DNA and are likely to face one side of the DNA helix. Histones appear to be arranged in a similar manner on both DNA strands and do not form "locks" around DNA. A linearized model of the core particle is proposed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axel R. Cleavage of DNA in nuclei and chromatin with staphylococcal nuclease. Biochemistry. 1975 Jul;14(13):2921–2925. doi: 10.1021/bi00684a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camerini-Otero R. D., Sollner-Webb B., Felsenfeld G. The organization of histones and DNA in chromatin: evidence for an arginine-rich histone kernel. Cell. 1976 Jul;8(3):333–347. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90145-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgin S. C., Weintraub H. Chromosomal proteins and chromatin structure. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:725–774. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.003453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felsenfeld G. Chromatin. Nature. 1978 Jan 12;271(5641):115–122. doi: 10.1038/271115a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch J. T., Lutter L. C., Rhodes D., Brown R. S., Rushton B., Levitt M., Klug A. Structure of nucleosome core particles of chromatin. Nature. 1977 Sep 1;269(5623):29–36. doi: 10.1038/269029a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glover J. S., Salter D. N., Shepherd B. P. A study of some factors that influence the iodination of ox insulin. Biochem J. 1967 Apr;103(1):120–128. doi: 10.1042/bj1030120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg R. D. Chromatin structure: a repeating unit of histones and DNA. Science. 1974 May 24;184(4139):868–871. doi: 10.1126/science.184.4139.868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg R. D. Structure of chromatin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:931–954. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.004435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levina E. S., Mirzabekov A. D. Kovalentnoe sviazyvanie belkov s DNK v sostave khromatina. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR. 1975 Apr 11;(5):1222–1225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malchy B., Kaplan H. Reactive properties of the amino groups of histones in calf thymus chromatin. J Mol Biol. 1974 Feb 5;82(4):537–545. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90247-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Jeffrey A., van deSande H. Chain length determination of small double- and single-stranded DNA molecules by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Biochemistry. 1975 Aug 26;14(17):3787–3794. doi: 10.1021/bi00688a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirzabekov A. D., San'ko D. F., Kolchinsky A. M., Melnikova A. F. Protein arrangement in the DNA grooves in chromatin and nucleoprotamine in vitro and in vivo revealed by methylation. Eur J Biochem. 1977 May 16;75(2):379–389. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11539.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirzabekov A. D., Shick V. V., Belyavsky A. V., Karpov V. L., Bavykin S. G. The structure of nucleosomes: the arrangement of histones in the DNA grooves and along the DNA chain. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 1):149–155. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naktinis V. I., Maleeva N. E., San'ko D. F., Mirzabekov A. D. Dva prostykh metoda vydeleniia DNK iz razlichnykh istochnikov s primeneniem tsetavlona. Biokhimiia. 1977 Oct;42(10):1783–1790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noll M. DNA folding in the nucleosome. J Mol Biol. 1977 Oct 15;116(1):49–71. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90118-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noll M. Internal structure of the chromatin subunit. Nucleic Acids Res. 1974 Nov;1(11):1573–1578. doi: 10.1093/nar/1.11.1573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oudet P., Spadafora C., Chambon P. Nucleosome structure II: structure of the SV40 minichromosome and electron microscopic evidence for reversible transitions of the nucleosome structure. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 1):301–312. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Air G. M., Barrell B. G., Brown N. L., Coulson A. R., Fiddes C. A., Hutchison C. A., Slocombe P. M., Smith M. Nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage phi X174 DNA. Nature. 1977 Feb 24;265(5596):687–695. doi: 10.1038/265687a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. T., Whitlock J. P. Mapping DNAase l-susceptible sites in nucleosomes labeled at the 5' ends. Cell. 1976 Oct;9(2):347–353. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90124-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Felsenfeld G. A comparison of the digestion of nuclei and chromatin by staphylococcal nuclease. Biochemistry. 1975 Jul;14(13):2915–2920. doi: 10.1021/bi00684a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein A., Bina-Stein M., Simpson R. T. Crosslinked histone octamer as a model of the nucleosome core. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2780–2784. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshavsky A. J., Bakayev V. V., Georgiev G. P. Heterogeneity of chromatin subunits in vitro and location of histone H1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Feb;3(2):477–492. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.2.477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshavsky A. J., Bakayev V. V., Ilyin Y. V., Bayev A. A., Jr, Georgiev G. P. Studies on chromatin. Free DNA in sheared chromatin. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Jul 1;66(2):211–223. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10510.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Palter K., Van Lente F. Histones H2a, H2b, H3, and H4 form a tetrameric complex in solutions of high salt. Cell. 1975 Sep;6(1):85–110. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90077-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]